
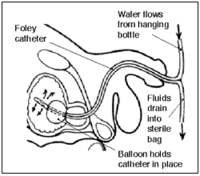
Foley catheter
Encyclopedia
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter is a tube that can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel. Catheters thereby allow drainage, administration of fluids or gases, or access by surgical instruments. The process of inserting a catheter is catheterization...
is a flexible tube that is often passed through the urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
and into the bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
. The tube has two separated channels, or lumen
Lumen
Lumen can mean:* Lumen , the SI unit of luminous flux* Lumen , the cavity or channel within a tubular structure* Thylakoid lumen, the inner membrane space of the chloroplast* Phenobarbital...
s, running down its length. One lumen is open at both ends, and allows urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
to drain out into a collection bag. The other lumen has a valve on the outside end and connects to a balloon
Balloon
A balloon is an inflatable flexible bag filled with a gas, such as helium, hydrogen, nitrous oxide, oxygen, or air. Modern balloons can be made from materials such as rubber, latex, polychloroprene, or a nylon fabric, while some early balloons were made of dried animal bladders, such as the pig...
at the tip; the balloon is inflated with sterile water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
when it lies inside the bladder, in order to stop it from slipping out. Foley catheters are commonly made from silicone rubber
Silicone rubber
Silicone rubber is an elastomer composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations...
or natural rubber.
The name comes from the designer, Frederic Foley
Frederic Foley
Dr. Frederic Eugene Basil Foley, MD was an American urologist who is remembered for designing the Foley catheter.-Biography:Frederic Foley was born in St. Cloud, Minnesota in 1891...
, a surgeon working in Boston, Massachusetts in the 1930s. His original design was adopted by C. R. Bard, Inc.
C. R. Bard, Inc.
C. R. Bard, Inc. , now branded simply as Bard, is a manufacturer of medical equipment headquartered in Murray Hill, New Jersey and active worldwide. An S&P 500 company with approximately 11,000 employees as of 2009, Bard specializes in the manufacture of vascular, urology, oncology, and surgical...
of Murray Hill, New Jersey
Murray Hill, New Jersey
Murray Hill is an unincorporated area within portions of both Berkeley Heights and New Providence, located in Union County in northern New Jersey, United States....
, who manufactured the first prototypes and named them in honor of the surgeon.
The relative size of a Foley catheter is described using French units
French catheter scale
The French scale or French gauge system is commonly used to measure the size of a catheter. It is most often abbreviated as Fr, but can often abbreviated as FR or F. It may also be abbreviated as CH or Ch in French speaking countries...
(F). The most common sizes are 10 F to 28 F. 1 F is equivalent to 0.33 mm = .013" = 1/77" of diameter. Thus the size in French units is roughly equal to the circumference of the catheter in millimetres.

"Coudé" (French for elbowed) catheters have a 45° bend at the tip to allow easier passage through an enlarged prostate
Prostate
The prostate is a compound tubuloalveolar exocrine gland of the male reproductive system in most mammals....
.
"Council tip" catheters have a small hole at the tip which allows them to be passed over a wire.
"Three way" or "triple lumen" catheters have a third channel, which is used to infuse sterile saline or another irrigating solution. These are used primarily after surgery on the bladder or prostate
Prostate
The prostate is a compound tubuloalveolar exocrine gland of the male reproductive system in most mammals....
, to wash away blood and blood clots.
A Foley catheter can also be used to "ripen" the cervix
Cervix
The cervix is the lower, narrow portion of the uterus where it joins with the top end of the vagina. It is cylindrical or conical in shape and protrudes through the upper anterior vaginal wall...
, to allow the induction
Induction (birth)
Labor induction is a method of artificially or prematurely stimulating childbirth in a woman.-Indications:Common suggested reasons for induction include:* Postterm pregnancy, i.e. if the pregnancy has gone past the 42 week mark....
of labour
Childbirth
Childbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
. The balloon is inserted behind the cervical wall and inflated. The remaining length of the catheter is pulled slightly taut, and taped to the inside of the woman's leg. The inflated balloon applies pressure to the cervix, as the baby's head would prior to labour, causing it to dilate. As the cervix dilates over time, the catheter is readjusted to again be slightly taut, and re-taped to maintain pressure on the cervix. When the cervix has dilated sufficiently, the catheter simply drops out.
A major problem with Foley catheters is that they have a tendency to contribute to urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli...
s (UTI). This occurs because bacteria can travel up the catheters to the bladder where the urine can become infected. To combat this, the industry is moving to antiseptic coated catheters. This has been helpful, but it has not completely solved this major problem. An additional problem is that Foley catheters tend to become coated over time with a biofilm
Biofilm
A biofilm is an aggregate of microorganisms in which cells adhere to each other on a surface. These adherent cells are frequently embedded within a self-produced matrix of extracellular polymeric substance...
that can obstruct the drainage. This increases the amount of stagnant urine left in the bladder, which further contributes to the problem of urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary tract. Symptoms include frequent feeling and/or need to urinate, pain during urination, and cloudy urine. The main causal agent is Escherichia coli...
s. When a Foley catheter becomes clogged, it must be flushed or replaced.
When Foley catheters are used
Foley catheters are used during the following situations:- On patients who are anesthesizedAnesthesiaAnesthesia, or anaesthesia , traditionally meant the condition of having sensation blocked or temporarily taken away...
or sedatedSedationSedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure...
for surgery or other medical care - On comaComaIn medicine, a coma is a state of unconsciousness, lasting more than 6 hours in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light or sound, lacks a normal sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. A person in a state of coma is described as...
tose patients - On some incontinentUrinary incontinenceUrinary incontinence is any involuntary leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a profound impact on quality of life. Urinary incontinence almost always results from an underlying treatable medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners...
patients - On patients whose prostate is enlarged to the point that urine flow from the bladder is cut off. The catheter is kept in until the problem is resolved.
- On patients with acute urinary retention.
- On patients who are unable due to paralysis or physical injury to use either standard toilet facilities or urinals.
- Following urethral surgeries
- Following ureterUreterIn human anatomy, the ureters are muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually long and ~3-4 mm in diameter....
ectomy - To ripen the cervixCervixThe cervix is the lower, narrow portion of the uterus where it joins with the top end of the vagina. It is cylindrical or conical in shape and protrudes through the upper anterior vaginal wall...
during induction of labor - On patients with kidney disease whose urine output must be constantly and accurately measured
They are also used in cases of severe epistaxis, in order to block blood from freely flowing down the nasal passage into the mouth.
Risks
There are several risks when using a Foley catheter (or catheters generally), including:- The balloon can break while the catheter is being inserted. In this case, the healthcare provider will remove all the balloon fragments.
- The balloon might not inflate after it is in place. In some institutions, the healthcare provider will check the balloon inflation before inserting the catheter into the urethra. If the balloon still does not inflate after its placement into the bladder, it will be discarded and replaced with a new catheter.
- Urine stops flowing into the bag. The healthcare provider will check for correct positioning of the catheter and bag or for obstruction of urine flow within the catheter tube.
- Urine flow is blocked. The Foley catheter will be discarded and replaced with a new catheter.
- The urethra begins to bleed. The healthcare provider will monitor the bleeding.
- Introduction of an infection into the bladder. The risk of infection in the bladder or urinary tract increases with the number of days the catheter is in place.
- If the balloon is opened before the Foley catheter is completely inserted into the bladder, bleeding, damage and even rupture of the urethra can occur.In some individuals, long-term permanent scarring and strictures of the urethra could occur.
- Defective catheters may be supplied, which break in situ. The most common fractures occur near the distal end or at the balloon.
Alternative treatments
- For obstructed prostates due to BPH: The Spanner Prostatic stentProstatic stentA prostatic stent is a stent used to keep open the male urethra and allow the passing of urine in cases of prostatic obstruction and lower urinary tract symptoms . Prostatic obstruction is a common condition with a variety of etiologies...
- Intermittent self catheterization

