
Eyelid
Encyclopedia
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye
. With the exception of the prepuce
and the labia minora
, it has the thinnest skin of the whole body. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle
retracts the eyelid to "open" the eye. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyelid features a row of eyelash
es which serve to heighten the protection of the eye from dust and foreign debris, as well as from perspiration. "Palpebral" (and "blepharo") means relating to the eyelids. Its key function is to regularly spread the tears and other secretions on the eye surface to keep it moist, since the cornea must be continuously moist. They keep the eyes from drying out when asleep. Moreover, the blink reflex protects the eye from foreign bodies.
, subcutaneous tissue, orbicularis oculi
, orbital septum
& tarsal plates, and palpebral conjunctiva
. The meibomian glands lie within the eyelid and secrete the lipid part of the tearfilm
.
and the lacrimal nerve
s from the ophthalmic branch (V1) of the trigeminal nerve
(CN V). The skin of the lower eyelid is supplied by branches of the infratrochlear at the medial angle, the rest is supplied by branches of the infraorbital nerve
of the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve.
As with most of the muscles of the orbit, it is innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (Cranial Nerve III). This is why when one looks upward, the eyelid tends to move up with it. [1] An adjoining smooth muscle, the superior tarsal muscle, is sympathetically innervated and is occasionally considered to be part of the levator palpebrae superioris.
, branching off from the lacrimal artery
and ophthalmic artery
, respectively.
, it is common in many cultures to pull the eyelids of the deceased down to close the eyes. This is a typical part of the last offices
.
Most of the cosmetic eyelid surgeries are aimed to enhance the look of the face and to boost one's self-confidence by restoring a youthful eyelid appearance. They are intended to remove fat and excess skin that may be found on the eyelids after a certain age. Cosmetic eyelid surgeries are mostly used to regain a younger and refreshed look but the costs are quite raised, so not everyone affords them.
Eyelid surgeries are also performed to improve one's peripheral vision or to treat different eyelid related conditions such as chalazion
, eyelid tumors, ptosis
, trichiasis
, and other.
Eyelid surgeries are overall safe procedures but they carry certain risks since the area on which the operation is performed is so close to the eye.
Human eye
The human eye is an organ which reacts to light for several purposes. As a conscious sense organ, the eye allows vision. Rod and cone cells in the retina allow conscious light perception and vision including color differentiation and the perception of depth...
. With the exception of the prepuce
Prepuce
Prepuce may refer to:* The foreskin, which surrounds and protects the head of the penis* The clitoral hood, which surrounds and protects the head of the clitoris...
and the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
, it has the thinnest skin of the whole body. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle
Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
The levator palpebrae superioris is the muscle in the orbit that elevates the superior eyelid.-Structure:...
retracts the eyelid to "open" the eye. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eyelid features a row of eyelash
Eyelash
An eyelash or simply lash is one of the hairs that grow at the edge of the eyelid. Eyelashes protect the eye from debris and perform some of the same function as whiskers do on a cat or a mouse in the sense that they are sensitive to being touched, thus providing a warning that an object is near...
es which serve to heighten the protection of the eye from dust and foreign debris, as well as from perspiration. "Palpebral" (and "blepharo") means relating to the eyelids. Its key function is to regularly spread the tears and other secretions on the eye surface to keep it moist, since the cornea must be continuously moist. They keep the eyes from drying out when asleep. Moreover, the blink reflex protects the eye from foreign bodies.
Layers
The eyelid is made up of several layers; from superficial to deep, these are: skinSkin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
, subcutaneous tissue, orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oculi muscle
The orbicularis oculi is a muscle in the face that closes the eyelids. It arises from the nasal part of the frontal bone, from the frontal process of the maxilla in front of the lacrimal groove, and from the anterior surface and borders of a short fibrous band, the medial palpebral ligament.From...
, orbital septum
Orbital septum
The orbital septum is a membranous sheet that acts as the anterior boundary of the orbit. It extends from the orbital rims to the eyelids...
& tarsal plates, and palpebral conjunctiva
Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva covers the sclera and lines the inside of the eyelids. It is composed of rare stratified columnar epithelium.-Function:...
. The meibomian glands lie within the eyelid and secrete the lipid part of the tearfilm
Tears
Tears are secretions that clean and lubricate the eyes. Lacrimation or lachrymation is the production or shedding of tears....
.
Skin
The skin is similar to areas elsewhere, but has more pigment cells. In diseased persons these may wander and cause a discoloration of the lids. It contains sweat glands and hairs, the latter becoming eyelashes as the border of the eyelid is met.Innervation
In humans, the sensory nerve supply to the upper eyelids is from the infratrochlear, supratrochlear, supraorbitalSupraorbital
Supraorbital refers to the region immediately above the eye sockets, where in humans the eyebrows are located. It denotes several anatomical features, such as:*Supraorbital artery*Supraorbital foramen*Supraorbital gland*Supraorbital nerve...
and the lacrimal nerve
Lacrimal nerve
The lacrimal nerve is the smallest of the three branches of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve.It sometimes receives a filament from the trochlear nerve, but this is possibly derived from the branch that goes from the ophthalmic to the trochlear nerve.It passes forward in a separate...
s from the ophthalmic branch (V1) of the trigeminal nerve
Trigeminal nerve
The trigeminal nerve contains both sensory and motor fibres. It is responsible for sensation in the face and certain motor functions such as biting, chewing, and swallowing. Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system...
(CN V). The skin of the lower eyelid is supplied by branches of the infratrochlear at the medial angle, the rest is supplied by branches of the infraorbital nerve
Infraorbital nerve
After the maxillary nerve enters the infraorbital canal, the nerve is frequently called the infraorbital nerve. This nerve innervates the lower eyelid, upper lip, and part of the nasal vestibule and exits the infraorbital foramen of the maxilla.-See also:...
of the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve.
As with most of the muscles of the orbit, it is innervated by the superior division of the oculomotor nerve (Cranial Nerve III). This is why when one looks upward, the eyelid tends to move up with it. [1] An adjoining smooth muscle, the superior tarsal muscle, is sympathetically innervated and is occasionally considered to be part of the levator palpebrae superioris.
Blood supply
In humans, the eyelids are supplied with blood by two arches on each upper and lower lid. The arches are formed by anastamoses of the lateral palpebral arteries and medial palpebral arteriesMedial palpebral arteries
The medial palpebral arteries are arteries of the head. They are two in number, superior and inferior, arise from the ophthalmic, opposite the pulley of the Obliquus superior.-Course:...
, branching off from the lacrimal artery
Lacrimal artery
The lacrimal artery arises close to the optic foramen, and is one of the largest branches derived from the ophthalmic artery: not infrequently it is given off before the artery enters the orbit....
and ophthalmic artery
Ophthalmic artery
The ophthalmic artery is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the OA supply all the structures in the orbit as well as some structures in the nose, face and meninges...
, respectively.
Death
After deathDeath
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
, it is common in many cultures to pull the eyelids of the deceased down to close the eyes. This is a typical part of the last offices
Last offices
The last offices are the procedures performed, usually by a nurse in the developed world, to a dead person shortly after death has been confirmed. They can vary from hospital to hospital, and culture to culture.-Name:...
.
Eyelid disorders
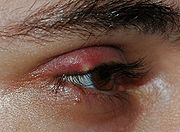
Any condition that affects the eyelid is called eyelid disorder. The most common eyelid disorders, their causes, symptoms and treatments are the following:- Hordeolum (styeStyeAn external stye or sty , also hordeolum , is an infection of the sebaceous glands of Zeis at the base of the eyelashes, or an infection of the apocrine sweat glands of Moll. External styes form on the outside of the lids and can be seen as small red bumps. Internal styes are infections of the...
) is an infection of the sebaceous glandSebaceous glandThe sebaceous glands are microscopic glands in the skin that secrete an oily/waxy matter, called sebum, to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair of mammals...
s of ZeissZeissCarl Zeiss AG is a German manufacturer of optical systems, industrial measurements and medical devices, founded in Jena, Germany in 1846 by Carl Zeiss, Ernst Abbe, and Otto Schott...
usually caused by Staphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus is a facultative anaerobic Gram-positive coccal bacterium. It is frequently found as part of the normal skin flora on the skin and nasal passages. It is estimated that 20% of the human population are long-term carriers of S. aureus. S. aureus is the most common species of...
bacteriaBacteriaBacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. It is characterized by an acute onset of symptoms and it looks like a red bump placed underneath the eyelid. The main symptoms of styes include pain, redness of the eyelid and sometimes swollen eyelids. Styes usually disappear within a week without treatment. Otherwise, antibioticAntibioticAn antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
s may be prescribed and home remedies such as warm water compresses may be used to promote faster healing. Styes are normally harmless and do not cause long lasting damage.
- ChalazionChalazionA chalazion , also known as a meibomian gland lipogranuloma, is a cyst in the eyelid that is caused by inflammation of a blocked meibomian gland, usually on the upper eyelid. Chalazia differ from styes in that they are subacute and usually painless nodules...
is caused by the obstruction of the oil glands and can occur in both upper and lower eyelids. Chalazia may be mistaken as styes due to the similar symptoms. This condition is however less painful and it tends to be chronic. Chalazia heals within few months if treatment is administered and otherwise it can resorb within two years. Chalazia that do not respond to topical medication is usually treated with surgery as a last resort.
- BlepharitisBlepharitisBlepharitis is an ocular condition characterized by chronic inflammation of the eyelid, the severity and time course of which can vary. Onset can be acute, resolving without treatment within 2–4 weeks , but more generally is a long standing inflammation varying in severity...
is a common condition that causes inflammation of the eyelids and which is quite difficult to manage because it tends to recur. This condition is mainly caused by staphylococcus infection and scalp dandruffDandruffDandruff is the shedding of dead skin cells from the scalp . Dandruff is sometimes caused by frequent exposure to extreme heat and cold. As it is normal for skin cells to die and flake off, a small amount of flaking is normal and common; about 487,000 cells/cm2 get released normally after...
. Blepharitis symptoms include burning sensation, the feeling that there is something in the eye, excessive tearing, blurred vision, redness of the eye, light sensitivity, red and swollen eyelids, dry eye and sometimes crusting of the eyelashes on awakening. Treatment normally consists in maintaining a good hygiene of the eye and holding warm compresses on the affected eyelid to remove the crusts. Gently scrubbing the eyelid with the warm compress is recommended as it eases the healing process. In more serious cases, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- EntropionEntropionEntropion is a medical condition in which the eyelid folds inward. It is very uncomfortable, as the eyelashes constantly rub against the cornea. Entropion is usually caused by genetic factors and may be congenital...
usually results from aging, but sometimes can be due to a congenital defect, a spastic eyelid muscle, or a scar on the inside of the lid that could be from surgery, injury, or disease. It is an asymptomaticAsymptomaticIn medicine, a disease is considered asymptomatic if a patient is a carrier for a disease or infection but experiences no symptoms. A condition might be asymptomatic if it fails to show the noticeable symptoms with which it is usually associated. Asymptomatic infections are also called subclinical...
condition that can rarely lead to trichiasisTrichiasisTrichiasis is a medical term for abnormally positioned eyelashes that grow back toward the eye, touching the cornea or conjunctiva. This can be caused by infection, inflammation, autoimmune conditions, congenital defects, eyelid agenesis and trauma such as burns or eyelid injury.Standard treatment...
which requires surgery. It mostly affects the lower lid and it is characterized by the turning inward of the lid, toward globe.
- EctropionEctropionEctropion is a medical condition in which the lower eyelid turns outwards. It is one of the notable aspects of newborns exhibiting congenital Harlequin type ichthyosis, but ectropion can occur due to any weakening of tissue of the lower eyelid. The condition can be repaired surgically...
is another aging-related eyelid condition that causes chronic eye irritation and scarring. It may also be the result of allergiesAllergyAn Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
and its main symptoms are excessive tearing and hardening of the eyelid conjunctiva.
- Eyelid edemaEdemaEdema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
is a condition in which the eyelids are swollen and contain excessive fluid. It may be serious when it increases the intraocular pressure. Eyelid edema is caused by an allergic reaction that one has to food, drugs, plan allergens, trichinosis or infections. The main symptoms are swollen red eyelids, pain, and itching. Treatment may vary depending on what is causing the condition. Whereas infections are fought against with antibiotics, allergic edemas treatments consists in staying away from the allergenAllergenAn allergen is any substance that can cause an allergy. In technical terms, an allergen is a non-parasitic antigen capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivity reaction in atopic individuals....
. Chronic bouts of eyelid edema can lead to blepharochalasisBlepharochalasisBlepharochalasis is an inflammation of the eyelid that is characterized by exacerbations and remissions of eyelid edema, which results in a stretching and subsequent atrophy of the eyelid tissue resulting in redundant folds over the lid margins...
.
- Eyelid tumorTumorA tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
s may also occur. Basal cell carcinomas are the most frequently encountered kind of cancer affecting the eyelid, making up 85% to 95% of all malignant eyelid tumors. The tumors may be benign or malignant. Usually benign tumors are localized and removed before becoming a cancerous threat and before they become large enough to impair one's vision. Malignant tumors on the other hand tend to spread to surrounding areas and tissuesTissue (biology)Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
.
- BlepharospasmBlepharospasmA blepharospasm , is any abnormal contraction or twitch of the eyelid....
(eyelid twitching) is an involuntary spasm of the eyelid muscle. The most common factors that make the muscle in the eyelid twitch are fatigue, stress, and caffeine. Eyelid twitching is not considered a harmful condition and therefore there is no treatment available. Patients are however advised to get more sleep and drink less caffeine.
- Eyelid dermatitisDermatitis-Etymology:Dermatitis derives from Greek derma "skin" + -itis "inflammation" and genetic disorder.-Terminology:There are several different types of dermatitis. The different kinds usually have in common an allergic reaction to specific allergens. The term may describe eczema, which is also called...
is the inflammation of the eyelid skin. It is mostly a result of allergies or it is triggered by contact dermatitis of the eyelid. Symptoms that one may experience are dry and flaky skin on the eyelids and swollen eyelids. The affected eyelid may itch. Treatment consists in proper eye hygiene and avoiding the allergens that trigger the condition. In rare cases, topical creams may be used but only under a doctor's supervision.
- PtosisPtosisPtosis refers to droopiness of a body part. Specifically, it can refer to:* Ptosis * Ptosis * Enteroptosis * Gastroptosis...
(drooping eyelid) is when the upper eyelid droops or sags due to weakness or paralysis of the levator muscle (responsible for raising the eyelid), or due to damage to nerves controlling the muscle. It can be a manifestation of the normal aging process, a congenital condition or due to an injury or disease. Risk factors related to ptosis include diabetes, stroke, Horner syndrome, myasthenia gravis, brain tumor or other cancers that can affect nerve or muscle function.
- Ablepharia (Ablepharon) Congenital absence of or reduction in the size of the eyelids.
Eyelid surgeries
The eyelid surgeries are called blepharoplasties and are performed either out of medical reasons or to improve one's facial appearance.Most of the cosmetic eyelid surgeries are aimed to enhance the look of the face and to boost one's self-confidence by restoring a youthful eyelid appearance. They are intended to remove fat and excess skin that may be found on the eyelids after a certain age. Cosmetic eyelid surgeries are mostly used to regain a younger and refreshed look but the costs are quite raised, so not everyone affords them.
Eyelid surgeries are also performed to improve one's peripheral vision or to treat different eyelid related conditions such as chalazion
Chalazion
A chalazion , also known as a meibomian gland lipogranuloma, is a cyst in the eyelid that is caused by inflammation of a blocked meibomian gland, usually on the upper eyelid. Chalazia differ from styes in that they are subacute and usually painless nodules...
, eyelid tumors, ptosis
Ptosis (eyelid)
Ptosis is a drooping of the upper or lower eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer, when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to amblyopia...
, trichiasis
Trichiasis
Trichiasis is a medical term for abnormally positioned eyelashes that grow back toward the eye, touching the cornea or conjunctiva. This can be caused by infection, inflammation, autoimmune conditions, congenital defects, eyelid agenesis and trauma such as burns or eyelid injury.Standard treatment...
, and other.
Eyelid surgeries are overall safe procedures but they carry certain risks since the area on which the operation is performed is so close to the eye.
See also

- BlepharospasmBlepharospasmA blepharospasm , is any abnormal contraction or twitch of the eyelid....
- CellulitisCellulitisCellulitis is a diffuse inflammation of connective tissue with severe inflammation of dermal and subcutaneous layers of the skin. Cellulitis can be caused by normal skin flora or by exogenous bacteria, and often occurs where the skin has previously been broken: cracks in the skin, cuts, blisters,...
- ChalazionChalazionA chalazion , also known as a meibomian gland lipogranuloma, is a cyst in the eyelid that is caused by inflammation of a blocked meibomian gland, usually on the upper eyelid. Chalazia differ from styes in that they are subacute and usually painless nodules...
- DermatochalasisDermatochalasisDermatochalasis is a medical condition. It is defined as an excess of skin in the upper or lower eyelid. It may be either an acquired or a congenital condition. It is generally treated with blepharoplasty....
- EctropionEctropionEctropion is a medical condition in which the lower eyelid turns outwards. It is one of the notable aspects of newborns exhibiting congenital Harlequin type ichthyosis, but ectropion can occur due to any weakening of tissue of the lower eyelid. The condition can be repaired surgically...
- EntropionEntropionEntropion is a medical condition in which the eyelid folds inward. It is very uncomfortable, as the eyelashes constantly rub against the cornea. Entropion is usually caused by genetic factors and may be congenital...
- Hay-Wells syndromeHay-Wells syndromeHay–Wells syndrome is one of at least 150 known types of ectodermal dysplasia.These disorders affect tissues that arise from the ectodermal germ layer, such as skin, hair, and nails.-Genetics:...
- PtosisPtosis (eyelid)Ptosis is a drooping of the upper or lower eyelid. The drooping may be worse after being awake longer, when the individual's muscles are tired. This condition is sometimes called "lazy eye", but that term normally refers to amblyopia...
- Stye (Hordeolum)StyeAn external stye or sty , also hordeolum , is an infection of the sebaceous glands of Zeis at the base of the eyelashes, or an infection of the apocrine sweat glands of Moll. External styes form on the outside of the lids and can be seen as small red bumps. Internal styes are infections of the...
Sources
- "eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVDEncyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference SuiteEncyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite is an encyclopædia published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc., available on DVD.-Contents:...
2009.

