
Dougong
Encyclopedia
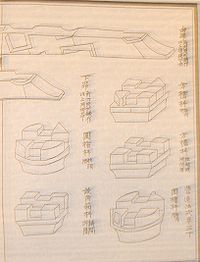

Bracket (architecture)
A bracket is an architectural member made of wood, stone, or metal that overhangs a wall to support or carry weight. It may also support a statue, the spring of an arch, a beam, or a shelf. Brackets are often in the form of scrolls, and can be carved, cast, or molded. They can be entirely...
, one of the most important elements in traditional Chinese
Chinese architecture
Chinese architecture refers to a style of architecture that has taken shape in East Asia over many centuries. The structural principles of Chinese architecture have remained largely unchanged, the main changes being only the decorative details...
architecture.
The use of dougong first appeared in buildings of the late centuries BC and evolved into a structural network that joined pillars and columns to the frame of the roof. Dougong was widely used in the ancient Chinese during the Spring and Autumn Period (770–476 BC) and developed into a complex set of interlocking parts by its peak in the Tang
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
and Song
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
periods. The pieces are fit together by joinery
Woodworking joints
Joinery is a part of woodworking that involves joining together pieces of wood, to create furniture, structures, toys, and other items. Some wood joints employ fasteners, bindings, or adhesives, while others use only wood elements. The characteristics of wooden joints - strength, flexibility,...
alone without glue
Adhesive
An adhesive, or glue, is a mixture in a liquid or semi-liquid state that adheres or bonds items together. Adhesives may come from either natural or synthetic sources. The types of materials that can be bonded are vast but they are especially useful for bonding thin materials...
or fastener
Fastener
A fastener is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together.Fasteners can also be used to close a container such as a bag, a box, or an envelope; or they may involve keeping together the sides of an opening of flexible material, attaching a lid to a container,...
s, due to the precision and quality of the carpentry.
After the Song Dynasty, brackets and bracket sets became more ornamental than structural when used in palatial structures and important religious buildings, no longer the traditional dougong.
Function
Dougong is part of the network of wooden supports essential to the timber frame structure of traditional Chinese building because the walls in these structures are not load-bearing (curtain wallCurtain wall
A curtain wall is an outer covering of a building in which the outer walls are non-structural, but merely keep out the weather. As the curtain wall is non-structural it can be made of a lightweight material reducing construction costs. When glass is used as the curtain wall, a great advantage is...
s), sometimes made of latticework
Latticework
Latticework is a framework consisting of a criss-crossed pattern of strips of building material, typically wood or metal. The design is created by crossing the strips to form a network...
, mud
Mud
Mud is a mixture of water and some combination of soil, silt, and clay. Ancient mud deposits harden over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone . When geological deposits of mud are formed in estuaries the resultant layers are termed bay muds...
or other delicate material. Walls functioned to delineate spaces in the structure rather than to support weight.
Multiple interlocking bracket sets are formed by placing a large wooden block (dou) on a column to provide a solid base for the bow-shaped brackets (gong) that support the beam or another gong above it. The function of dougong is to provide increased support for the weight of the horizontal beams that span the vertical columns or pillars by transferring the weight on horizontal beams over a larger area to the vertical columns. This process can be repeated many times, and rise many stories. Adding multiple sets of interlocking brackets or dougong reduces the amount of strain on the horizontal beams when transferring their weight to a column. Multiple dougong also allows structures to be elastic and to withstand damage from earthquakes.
During the Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
an innovation occurred through the invention of new wooden components that aided dougong in supporting the roof. This allowed dougong to add a decorative element to buildings in the traditional Chinese integration of artistry and function, and bracket sets became smaller and more numerous. Brackets could be hung under eaves, giving the appearance of graceful baskets of flowers while also supporting the roof.
The Bao'en Temple
Bao'en Temple
Bao'en Temple is a well-preserved fifteenth century Buddhist monastery complex located in northwestern Sichuan province, China...
in Sichuan
Sichuan
' , known formerly in the West by its postal map spellings of Szechwan or Szechuan is a province in Southwest China with its capital in Chengdu...
is a good example of the Ming style. It has forty-eight types and 2,200 sets of dougong to support and ornament it. It is a well-preserved fifteenth century monastery complex located in northwestern Sichuan province
Sichuan
' , known formerly in the West by its postal map spellings of Szechwan or Szechuan is a province in Southwest China with its capital in Chengdu...
, China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. It was built by Wang Xi, a local chieftain, between 1440 and 1446 during Emperor Yingzong
Zhengtong Emperor
Zhu Qizhen was an emperor of the Ming Dynasty. He ruled as the Zhengtong Emperor from 1435 to 1449, and as the Tianshun Emperor from 1457 to 1464....
's reign (1427–64) in the Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
(1368–1644).

