
Donald A. Quarles
Encyclopedia
Donald Aubrey Quarles was a communications engineer, senior level executive with Bell Telephone Laboratories and Western Electric
, and a top official in the United States Department of Defense
during the Eisenhower Administration. He served as both Secretary of the Air Force and Deputy Secretary of Defense.
.
Quarles graduated from Van Buren High School in 1910 at age of 15. He taught mathematics
in Van Buren High School, and attended summer school at University of Missouri
until he was accepted into Yale University
in 1912. He graduated from Yale with a bachelor of arts degree in 1916.
In May 1917, Quarles enlisted in the United States Army
for service during World War I. He was a member of the 42nd Infantry Division (better known as the "Rainbow Division") serving in France and Germany for two years. As an artillery officer, Quarles attained the rank captain before being discharged in August 1917.
. During this time, he also studied theoretical physics
at Columbia University
on a part-time basis. In 1925, he joined Bell Telephone Labs
in Murray Hill, New Jersey
. Through the 1930s and early 1940s, Quarles continued to advance within the Bell Labs organization.
In 1940, he was selected as director of the Transmission Development Department which concentrated on military electronic systems, particularly radar
development. He became director of Bell’s Apparatus Development in 1946. He was elected Mayor of Englewood, New Jersey
in 1946 to 1948. He then was vice president of Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1948. During this time, he was appointed to the new Committee on Electronics within the Department of Defense’s Joint Research and Development Board, becoming chairman of the Committee on Electronics in 1949. In March 1952, Quarles became vice president of Western Electric and president of Sandia Corporation. Sandia was a subsidiary company of Western Electric responsible for operating the Atomic Energy Commission
’s Sandia National Laboratory in Albuquerque
, New Mexico.
Quarles was president of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers
from 1952 to 1953.
appointed Quarles Assistant Secretary of Defense for research and development. Subsequently, he was jointly selected by both the Secretary of Defense
and the Secretary of Commerce
to be the chairman of the Air Navigation Development Board. In March 1954, President Eisenhower appointed Quarles to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
.
On August 11, 1955, President Eisenhower
appointed Quarles as interim Secretary of the Air Force
, and he was sworn into office August 15, 1955. The United States Senate
confirmed his appointment on February 16, 1956. As Secretary, Quarles stressed the need to use cutting edge technology to maintain military superiority over the Soviet Union
. He supported expanded funding for research and development programs, and pressed for rapid fielding of B-52 Stratofortress
, F-102 Delta Dagger
, and F-104 Starfighter
aircraft.
He resigned as Secretary of the Air Force on April 30, 1957 to accept a new Presidential appointment as Deputy Secretary of Defense. He remained in that position until his sudden death from a heart attack in Washington, D.C., on May 8, 1959.
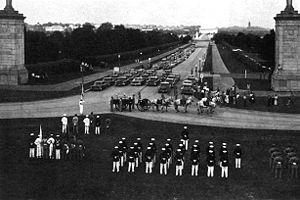 Quarles was given a special military funeral
Quarles was given a special military funeral
arranged by Military District of Washington. Beginning at noon on May 11, 1959, his casket lay in the Bethlehem Chapel at the Washington National Cathedral
for twenty-four hours. The funeral service was held in the nave of the cathedral the next day. Following the service, a hearse carried his casket to the Memorial Gate at Arlington National Cemetery
where the casket was transferred to a caisson
. A military escort, consisting of one platoon each from the Army, Navy
, Marine Corps
, Air Force
, and Coast Guard
lead the funeral procession to the grave site. Vice President Richard M. Nixon led the official party at public funeral service and Arlington procession, and President Eisenhower attended the graveside rites.
Among the many honors Quarles received during his career as an engineer and public official were honorary doctorate degrees in engineering from the University of Arkansas
in 1953 and New York University
in 1955. He received the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
from Italy and the La Cruz Peruana al Merito Aeonautico from Peru
in 1956. In 1957, be received the Order of Aeronautical Merit
from Brazil
and the Major General C.C. Williams Gold Medal from the American Ordnance Association. That year, he was also awarded the United States Air Force Exceptional Service Award.
The Quarles Range
was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names
(US-ACAN) for Quarles at the outset of the International Geophysical Year
and organization of U.S. activity in Antarctica.
Western Electric
Western Electric Company was an American electrical engineering company, the manufacturing arm of AT&T from 1881 to 1995. It was the scene of a number of technological innovations and also some seminal developments in industrial management...
, and a top official in the United States Department of Defense
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
during the Eisenhower Administration. He served as both Secretary of the Air Force and Deputy Secretary of Defense.
Early years
He was born on July 30, 1894 in Van Buren, ArkansasVan Buren, Arkansas
Van Buren is the second largest city in the Fort Smith, Arkansas-Oklahoma Metropolitan Statistical Area and the county seat of Crawford County, Arkansas, United States. The city is located directly northeast of Fort Smith at the Interstate 40 - Interstate 540 junction...
.
Quarles graduated from Van Buren High School in 1910 at age of 15. He taught mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
in Van Buren High School, and attended summer school at University of Missouri
University of Missouri
The University of Missouri System is a state university system providing centralized administration for four universities, a health care system, an extension program, five research and technology parks, and a publishing press. More than 64,000 students are currently enrolled at its four campuses...
until he was accepted into Yale University
Yale University
Yale University is a private, Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States...
in 1912. He graduated from Yale with a bachelor of arts degree in 1916.
In May 1917, Quarles enlisted in the United States Army
United States Army
The United States Army is the main branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is the largest and oldest established branch of the U.S. military, and is one of seven U.S. uniformed services...
for service during World War I. He was a member of the 42nd Infantry Division (better known as the "Rainbow Division") serving in France and Germany for two years. As an artillery officer, Quarles attained the rank captain before being discharged in August 1917.
Laboratory engineer
After the war, Quarles went to work at Western Electric CompanyWestern Electric
Western Electric Company was an American electrical engineering company, the manufacturing arm of AT&T from 1881 to 1995. It was the scene of a number of technological innovations and also some seminal developments in industrial management...
. During this time, he also studied theoretical physics
Theoretical physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics which employs mathematical models and abstractions of physics to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena...
at Columbia University
Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York is a private, Ivy League university in Manhattan, New York City. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the...
on a part-time basis. In 1925, he joined Bell Telephone Labs
Bell Labs
Bell Laboratories is the research and development subsidiary of the French-owned Alcatel-Lucent and previously of the American Telephone & Telegraph Company , half-owned through its Western Electric manufacturing subsidiary.Bell Laboratories operates its...
in Murray Hill, New Jersey
Murray Hill, New Jersey
Murray Hill is an unincorporated area within portions of both Berkeley Heights and New Providence, located in Union County in northern New Jersey, United States....
. Through the 1930s and early 1940s, Quarles continued to advance within the Bell Labs organization.
In 1940, he was selected as director of the Transmission Development Department which concentrated on military electronic systems, particularly radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
development. He became director of Bell’s Apparatus Development in 1946. He was elected Mayor of Englewood, New Jersey
Mayor of Englewood, New Jersey
Mayors of Englewood, New Jersey. The terms begin on January 1 of the new year.*Frank Huttle III 2010 to present.*Michael Wildes 2004 to 2009.*Paul T. Fader 1998 to 2003....
in 1946 to 1948. He then was vice president of Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1948. During this time, he was appointed to the new Committee on Electronics within the Department of Defense’s Joint Research and Development Board, becoming chairman of the Committee on Electronics in 1949. In March 1952, Quarles became vice president of Western Electric and president of Sandia Corporation. Sandia was a subsidiary company of Western Electric responsible for operating the Atomic Energy Commission
United States Atomic Energy Commission
The United States Atomic Energy Commission was an agency of the United States government established after World War II by Congress to foster and control the peace time development of atomic science and technology. President Harry S...
’s Sandia National Laboratory in Albuquerque
Albuquerque, New Mexico
Albuquerque is the largest city in the state of New Mexico, United States. It is the county seat of Bernalillo County and is situated in the central part of the state, straddling the Rio Grande. The city population was 545,852 as of the 2010 Census and ranks as the 32nd-largest city in the U.S. As...
, New Mexico.
Quarles was president of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers
American Institute of Electrical Engineers
The American Institute of Electrical Engineers was a United States based organization of electrical engineers that existed between 1884 and 1963, when it merged with the Institute of Radio Engineers to form the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers .- History :The 1884 founders of the...
from 1952 to 1953.
Public service
In September 1953, President Dwight D. EisenhowerDwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower was the 34th President of the United States, from 1953 until 1961. He was a five-star general in the United States Army...
appointed Quarles Assistant Secretary of Defense for research and development. Subsequently, he was jointly selected by both the Secretary of Defense
United States Secretary of Defense
The Secretary of Defense is the head and chief executive officer of the Department of Defense of the United States of America. This position corresponds to what is generally known as a Defense Minister in other countries...
and the Secretary of Commerce
United States Secretary of Commerce
The United States Secretary of Commerce is the head of the United States Department of Commerce concerned with business and industry; the Department states its mission to be "to foster, promote, and develop the foreign and domestic commerce"...
to be the chairman of the Air Navigation Development Board. In March 1954, President Eisenhower appointed Quarles to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics was a U.S. federal agency founded on March 3, 1915 to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. On October 1, 1958 the agency was dissolved, and its assets and personnel transferred to the newly created National Aeronautics and...
.
On August 11, 1955, President Eisenhower
Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower was the 34th President of the United States, from 1953 until 1961. He was a five-star general in the United States Army...
appointed Quarles as interim Secretary of the Air Force
United States Secretary of the Air Force
The Secretary of the Air Force is the Head of the Department of the Air Force, a component organization within the Department of Defense of the United States of America. The Secretary of the Air Force is appointed from civilian life by the President, by and with the advice and consent of the Senate...
, and he was sworn into office August 15, 1955. The United States Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
confirmed his appointment on February 16, 1956. As Secretary, Quarles stressed the need to use cutting edge technology to maintain military superiority over the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. He supported expanded funding for research and development programs, and pressed for rapid fielding of B-52 Stratofortress
B-52 Stratofortress
The Boeing B-52 Stratofortress is a long-range, subsonic, jet-powered strategic bomber operated by the United States Air Force since the 1950s. The B-52 was designed and built by Boeing, who have continued to provide maintainence and upgrades to the aircraft in service...
, F-102 Delta Dagger
F-102 Delta Dagger
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was a US interceptor aircraft built as part of the backbone of the United States Air Force's air defenses in the late 1950s. Entering service in 1956, its main purpose was to intercept invading Soviet bomber fleets...
, and F-104 Starfighter
F-104 Starfighter
The Lockheed F-104 Starfighter is a single-engine, high-performance, supersonic interceptor aircraft originally developed for the United States Air Force by Lockheed. One of the Century Series of aircraft, it served with the USAF from 1958 until 1969, and continued with Air National Guard units...
aircraft.
He resigned as Secretary of the Air Force on April 30, 1957 to accept a new Presidential appointment as Deputy Secretary of Defense. He remained in that position until his sudden death from a heart attack in Washington, D.C., on May 8, 1959.
Funeral

Military funeral
A military funeral is a specially orchestrated funeral given by a country's military for a soldier, sailor, marine or airman who died in battle, a veteran, or other prominent military figures or heads of state. A military funeral may feature guards of honor, the firing of volley shots as a salute,...
arranged by Military District of Washington. Beginning at noon on May 11, 1959, his casket lay in the Bethlehem Chapel at the Washington National Cathedral
Washington National Cathedral
The Washington National Cathedral, officially named the Cathedral Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul, is a cathedral of the Episcopal Church located in Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States. Of neogothic design, it is the sixth-largest cathedral in the world, the second-largest in...
for twenty-four hours. The funeral service was held in the nave of the cathedral the next day. Following the service, a hearse carried his casket to the Memorial Gate at Arlington National Cemetery
Arlington National Cemetery
Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, is a military cemetery in the United States of America, established during the American Civil War on the grounds of Arlington House, formerly the estate of the family of Confederate general Robert E. Lee's wife Mary Anna Lee, a great...
where the casket was transferred to a caisson
Caisson (military)
A limber is a two-wheeled cart designed to support the trail of an artillery piece, or the stock of a field carriage such as a caisson or traveling forge, allowing it to be towed. A caisson is a two-wheeled cart designed to carry artillery ammunition...
. A military escort, consisting of one platoon each from the Army, Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
, Marine Corps
United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps is a branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for providing power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the United States Navy to deliver combined-arms task forces rapidly. It is one of seven uniformed services of the United States...
, Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
, and Coast Guard
United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard is a branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven U.S. uniformed services. The Coast Guard is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission and a federal regulatory agency...
lead the funeral procession to the grave site. Vice President Richard M. Nixon led the official party at public funeral service and Arlington procession, and President Eisenhower attended the graveside rites.
Among the many honors Quarles received during his career as an engineer and public official were honorary doctorate degrees in engineering from the University of Arkansas
University of Arkansas
The University of Arkansas is a public, co-educational, land-grant, space-grant, research university. It is classified by the Carnegie Foundation as a research university with very high research activity. It is the flagship campus of the University of Arkansas System and is located in...
in 1953 and New York University
New York University
New York University is a private, nonsectarian research university based in New York City. NYU's main campus is situated in the Greenwich Village section of Manhattan...
in 1955. He received the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
The Order of Merit of the Italian Republic was founded as the senior order of knighthood by the second President of the Italian Republic, Luigi Einaudi in 1951...
from Italy and the La Cruz Peruana al Merito Aeonautico from Peru
Peru
Peru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
in 1956. In 1957, be received the Order of Aeronautical Merit
Order of Aeronautical Merit (Brazil)
The Order of Aeronautical Merit is an award of the Brazilian Air Force, established on 1 November 1943 by President Getúlio Vargas. The order is presented in five grades and recognizes distinguished service and exceptional contributions to the Brazilian Air Force....
from Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
and the Major General C.C. Williams Gold Medal from the American Ordnance Association. That year, he was also awarded the United States Air Force Exceptional Service Award.
Legacy
He was posthumously awarded the United States' Medal of Freedom in 1959. In 1966, a mountain range in Antarctica was named after Quarles.The Quarles Range
Quarles Range
Quarles Range is a high and rugged range of the Queen Maud Mountains, extending from the polar plateau between Cooper and Bowman Glaciers and terminating near the edge of Ross Ice Shelf. Peaks in the range were first sighted by Captain Roald Amundsen in 1911, and the range was mapped in detail by...
was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names
Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending names for features in Antarctica...
(US-ACAN) for Quarles at the outset of the International Geophysical Year
International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year was an international scientific project that lasted from July 1, 1957, to December 31, 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific interchange between East and West was seriously interrupted...
and organization of U.S. activity in Antarctica.

