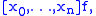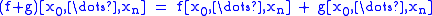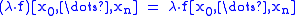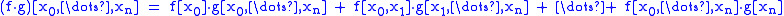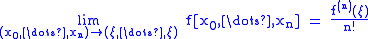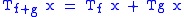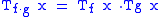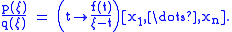Divided differences
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
divided differences is a recursive
division
process.
The method can be used to calculate the coefficients in the interpolation polynomial
in the Newton form.
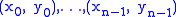
The forward divided differences are defined as:
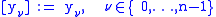

The backward divided differences are defined as:
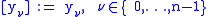
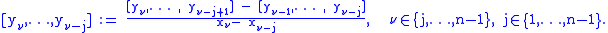
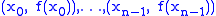
one sometimes writes


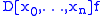
Several notations for the divided difference of the function ƒ on the nodes x0, ..., xn are used:
etc.
 , this yields
, this yields
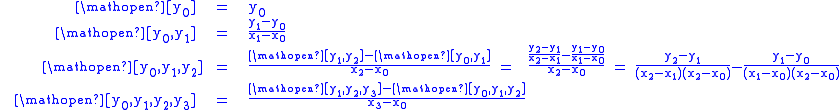
To make the recursive process more clear the divided differences can be put in a tabular form
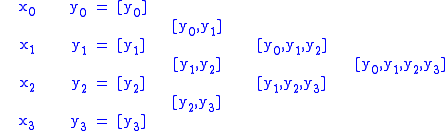
.
Let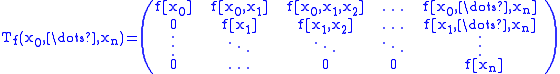 .
.
Then it holds
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
divided differences is a recursive
Recursion
Recursion is the process of repeating items in a self-similar way. For instance, when the surfaces of two mirrors are exactly parallel with each other the nested images that occur are a form of infinite recursion. The term has a variety of meanings specific to a variety of disciplines ranging from...
division
Division (mathematics)
right|thumb|200px|20 \div 4=5In mathematics, especially in elementary arithmetic, division is an arithmetic operation.Specifically, if c times b equals a, written:c \times b = a\,...
process.
The method can be used to calculate the coefficients in the interpolation polynomial
Polynomial interpolation
In numerical analysis, polynomial interpolation is the interpolation of a given data set by a polynomial: given some points, find a polynomial which goes exactly through these points.- Applications :...
in the Newton form.
Definition
Given n data points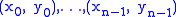
The forward divided differences are defined as:
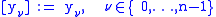

The backward divided differences are defined as:
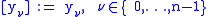
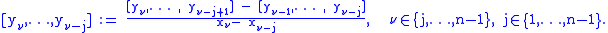
Notation
If the data points are given as a function ƒ,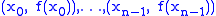
one sometimes writes


Several notations for the divided difference of the function ƒ on the nodes x0, ..., xn are used:
etc.
Example
For the first few values of , this yields
, this yields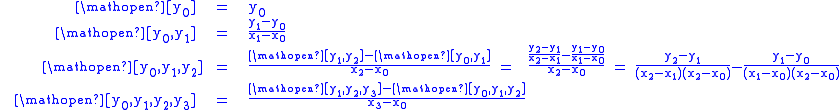
To make the recursive process more clear the divided differences can be put in a tabular form
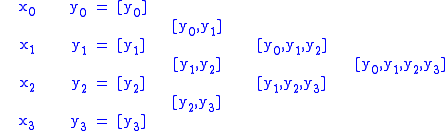
Properties
- LinearityLinear functionalIn linear algebra, a linear functional or linear form is a linear map from a vector space to its field of scalars. In Rn, if vectors are represented as column vectors, then linear functionals are represented as row vectors, and their action on vectors is given by the dot product, or the...
- Leibniz ruleLeibniz rule (generalized product rule)In calculus, the general Leibniz rule, named after Gottfried Leibniz, generalizes the product rule. It states that if f and g are n-times differentiable functions, then the nth derivative of the product fg is given by...
- From the mean value theorem for divided differences it follows that
Matrix form
The divided difference scheme can be put into an upper triangular matrixTriangular matrix
In the mathematical discipline of linear algebra, a triangular matrix is a special kind of square matrix where either all the entries below or all the entries above the main diagonal are zero...
.
Let
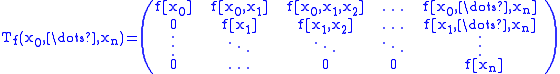 .
.Then it holds
-
- This follows from the Leibniz rule. It means that multiplication of such matrices is commutativeCommutativityIn mathematics an operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the end result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it...
. Summarised, the matrices of divided difference schemes with respect to the same set of nodes form a commutative ringCommutative ringIn ring theory, a branch of abstract algebra, a commutative ring is a ring in which the multiplication operation is commutative. The study of commutative rings is called commutative algebra....
.- Since
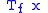 is a triangular matrix, its eigenvalues are obviously
is a triangular matrix, its eigenvalues are obviously 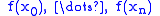 .
. - Let
 be a Kronecker delta-like function, that is
be a Kronecker delta-like function, that is
- Since
-
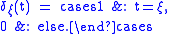
- This follows from the Leibniz rule. It means that multiplication of such matrices is commutative
- Obviously
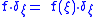 , thus
, thus 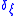 is an eigenfunctionEigenfunctionIn mathematics, an eigenfunction of a linear operator, A, defined on some function space is any non-zero function f in that space that returns from the operator exactly as is, except for a multiplicative scaling factor. More precisely, one has...
is an eigenfunctionEigenfunctionIn mathematics, an eigenfunction of a linear operator, A, defined on some function space is any non-zero function f in that space that returns from the operator exactly as is, except for a multiplicative scaling factor. More precisely, one has...
of the pointwise function multiplication. That is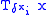 is somehow an "eigenmatrix" of
is somehow an "eigenmatrix" of 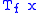 :
: 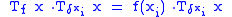 . However, all columns of
. However, all columns of 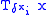 are multiples of each other, the matrix rank of
are multiples of each other, the matrix rank of  is 1. So you can compose the matrix of all eigenvectors from the
is 1. So you can compose the matrix of all eigenvectors from the 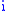 -th column of each
-th column of each 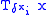 . Denote the matrix of eigenvectors with
. Denote the matrix of eigenvectors with 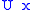 . Example
. Example
-

- The diagonalizationDiagonalizable matrixIn linear algebra, a square matrix A is called diagonalizable if it is similar to a diagonal matrix, i.e., if there exists an invertible matrix P such that P −1AP is a diagonal matrix...
of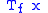 can be written as
can be written as
-
 .
.
-
Expanded form
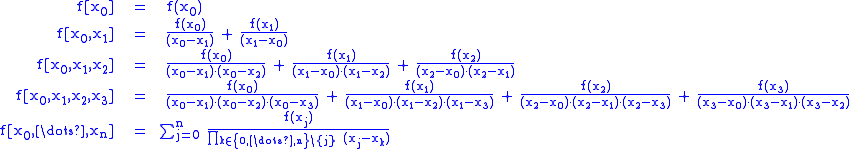
With help of a polynomial function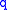 with
with 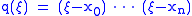
this can be written as
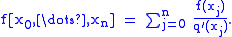
Partial fractions
You can represent partial fractionPartial fractionIn algebra, the partial fraction decomposition or partial fraction expansion is a procedure used to reduce the degree of either the numerator or the denominator of a rational function ....
s using the expanded form of divided differences.
(This does not simplify computation, but is interesting in itself.)
If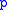 and
and  are polynomial functions,
are polynomial functions,
where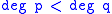
and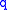 is given in terms of linear factors by
is given in terms of linear factors by 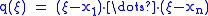 ,
,
then it follows from partial fraction decomposition that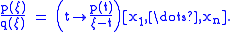
If limitsLimit of a functionIn mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input....
of the divided differences are accepted,
then this connection does also hold, if some of the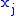 coincide.
coincide.
If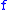 is a polynomial function with arbitrary degree
is a polynomial function with arbitrary degree
and it is decomposed by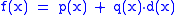 using polynomial division of
using polynomial division of 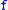 by
by 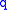 ,
,
then
Peano form
The divided differences can be expressed as
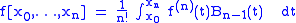
where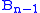 is a B-splineB-splineIn the mathematical subfield of numerical analysis, a B-spline is a spline function that has minimal support with respect to a given degree, smoothness, and domain partition. B-splines were investigated as early as the nineteenth century by Nikolai Lobachevsky...
is a B-splineB-splineIn the mathematical subfield of numerical analysis, a B-spline is a spline function that has minimal support with respect to a given degree, smoothness, and domain partition. B-splines were investigated as early as the nineteenth century by Nikolai Lobachevsky...
of degree for the data points
for the data points 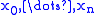 and
and 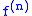 is the
is the  -th derivativeDerivativeIn calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
-th derivativeDerivativeIn calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
of the function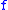 .
.
This is called the Peano form of the divided differences and is called the Peano kernel for the divided differences, both named after Giuseppe PeanoGiuseppe PeanoGiuseppe Peano was an Italian mathematician, whose work was of philosophical value. The author of over 200 books and papers, he was a founder of mathematical logic and set theory, to which he contributed much notation. The standard axiomatization of the natural numbers is named the Peano axioms in...
is called the Peano kernel for the divided differences, both named after Giuseppe PeanoGiuseppe PeanoGiuseppe Peano was an Italian mathematician, whose work was of philosophical value. The author of over 200 books and papers, he was a founder of mathematical logic and set theory, to which he contributed much notation. The standard axiomatization of the natural numbers is named the Peano axioms in...
.
First order
If nodes are cumulated, then the numerical computation of the divided differences is inaccurate, because you divide almost two zeros, each of which with a high relative error due to differences of similar valuesLoss of significanceLoss of significance is an undesirable effect in calculations using floating-point arithmetic. It occurs when an operation on two numbers increases relative error substantially more than it increases absolute error, for example in subtracting two large and nearly equal numbers. The effect is that...
.
However we know, that difference quotientDifference quotientThe primary vehicle of calculus and other higher mathematics is the function. Its "input value" is its argument, usually a point expressible on a graph...
s approximate the derivativeDerivativeIn calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
and vice versa: for
for 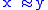
This approximation can be turned into an identity whenever Taylor's theoremTaylor's theoremIn calculus, Taylor's theorem gives an approximation of a k times differentiable function around a given point by a k-th order Taylor-polynomial. For analytic functions the Taylor polynomials at a given point are finite order truncations of its Taylor's series, which completely determines the...
applies.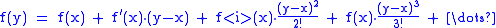
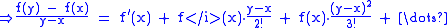
You can eliminate the odd powers of by expanding the Taylor seriesTaylor seriesIn mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
by expanding the Taylor seriesTaylor seriesIn mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
at the center between and
and 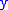 :
: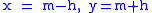 , that is
, that is 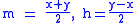
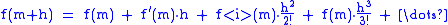

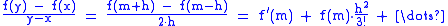
Higher order
The Taylor series or any other representation with function seriesFunction seriesIn calculus, a function series is a series, where the summands are not just real or complex numbers but functions.Examples of function series include power series, Laurent series, Fourier series, etc....
can in principle be used to approximate divided differences.
Taylor series are infinite sums of power functionMonomialIn mathematics, in the context of polynomials, the word monomial can have one of two different meanings:*The first is a product of powers of variables, or formally any value obtained by finitely many multiplications of a variable. If only a single variable x is considered, this means that any...
s.
The mapping from a function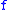 to a divided difference
to a divided difference 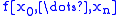 is a linear functionalLinear functionalIn linear algebra, a linear functional or linear form is a linear map from a vector space to its field of scalars. In Rn, if vectors are represented as column vectors, then linear functionals are represented as row vectors, and their action on vectors is given by the dot product, or the...
is a linear functionalLinear functionalIn linear algebra, a linear functional or linear form is a linear map from a vector space to its field of scalars. In Rn, if vectors are represented as column vectors, then linear functionals are represented as row vectors, and their action on vectors is given by the dot product, or the...
.
We can as well apply this functional to the function summands.
Express power notation with an ordinary function:
Regular Taylor series is a weighted sum of power functions: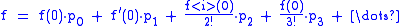
Taylor series for divided differences: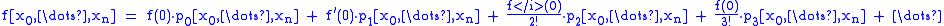
We know that the first terms vanish,
terms vanish,
because we have a higher difference order than polynomial order,
and in the following term the divided difference is one: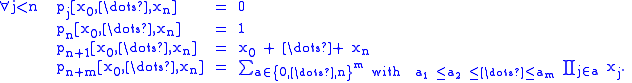
It follows that the Taylor series for the divided difference essentially starts with
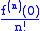
which is also a simple approximation of the divided difference,
according to the mean value theorem for divided differences.
If we would have to compute the divided differences for the power functions
in the usual way, we would encounter the same numerical problems
that we had when computing the divided difference of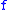 .
.
The nice thing is, that there is a simpler way.
It holds
Consequently we can compute the divided differences of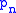
by a division of formal power seriesFormal power seriesIn mathematics, formal power series are a generalization of polynomials as formal objects, where the number of terms is allowed to be infinite; this implies giving up the possibility to substitute arbitrary values for indeterminates...
.
See how this reduces to the successive computation of powers
when we compute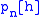 for several
for several  .
.
Cf. an implementation in HaskellHaskell (programming language)Haskell is a standardized, general-purpose purely functional programming language, with non-strict semantics and strong static typing. It is named after logician Haskell Curry. In Haskell, "a function is a first-class citizen" of the programming language. As a functional programming language, the...
.
If you need to compute a whole divided difference scheme with respect to a Taylor series,
see the section about divided differences of power series.
Polynomials and power series
Divided differences of polynomials are particularly interesting, because they can benefit from the Leibniz rule.
The matrix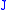 with
with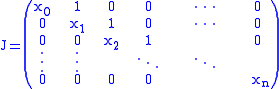
contains the divided difference scheme for the identity functionIdentity functionIn mathematics, an identity function, also called identity map or identity transformation, is a function that always returns the same value that was used as its argument...
with respect to the nodes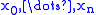 ,
,
thus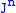 contains the divided differences for the power functionMonomialIn mathematics, in the context of polynomials, the word monomial can have one of two different meanings:*The first is a product of powers of variables, or formally any value obtained by finitely many multiplications of a variable. If only a single variable x is considered, this means that any...
contains the divided differences for the power functionMonomialIn mathematics, in the context of polynomials, the word monomial can have one of two different meanings:*The first is a product of powers of variables, or formally any value obtained by finitely many multiplications of a variable. If only a single variable x is considered, this means that any...
with exponent .
.
Consequently you can obtain the divided differences for a polynomial function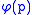
with respect to the polynomialPolynomialIn mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
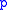
by applying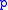 (more precisely: its corresponding matrix polynomial function
(more precisely: its corresponding matrix polynomial function 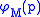 ) to the matrix
) to the matrix 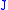 .
.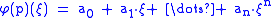

-

This is known as Opitz' formula.
Now consider increasing the degree of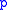 to infinity,
to infinity,
i.e. turn the Taylor polynomial to a Taylor seriesTaylor seriesIn mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
.
Let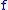 be a function which corresponds to a power series.
be a function which corresponds to a power series.
You can compute a divided difference scheme by computing the according matrix series applied to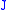 .
.
If the nodes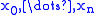 are all equal,
are all equal,
then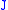 is a Jordan block and
is a Jordan block and
computation boils down to generalizing a scalar function to a matrix functionMatrix functionIn mathematics, a matrix function is a function which maps a matrix to another matrix.- Extending scalar functions to matrix functions :There are several techniques for lifting a real function to a square matrix function such that interesting properties are maintained...
using Jordan decompositionJordan decompositionIn mathematics, Jordan decomposition may refer to* Hahn decomposition theorem, and the Jordan decomposition of a measure* Jordan normal form of a matrix* Jordan–Chevalley decomposition of a matrix...
.
Forward differences
When the data points are equidistantly distributed we get the special case called forward differences. They are easier to calculate than the more general divided differences.
Definition
Given n data points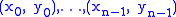
with
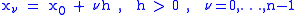
the divided differences can be calculated via forward differences defined as
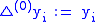

Example
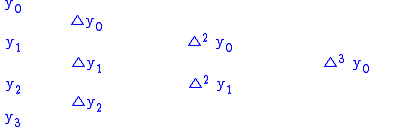
Computer Program
- The diagonalization
-