
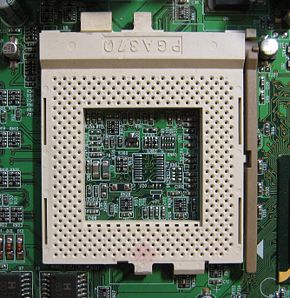
CPU socket
Encyclopedia

Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
and a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
(PCB). This allows the CPU to be replaced without soldering.
Common sockets have retention clips that apply a constant force, which must be overcome when a device is inserted. For chips with a large number of pins, either zero-insertion force (ZIF) sockets or land grid array (LGA) sockets are used instead. These designs apply a compression force once either a handle (for ZIF type) or a surface plate (LGA type) is put into place. This provides superior mechanical retention while avoiding the risk of bending pins when inserting the chip into the socket.
CPU sockets are used in desktop
Desktop computer
A desktop computer is a personal computer in a form intended for regular use at a single location, as opposed to a mobile laptop or portable computer. Early desktop computers are designed to lay flat on the desk, while modern towers stand upright...
and server computers. As they allow easy swapping of components, they are also used for prototyping new circuits.Laptop
Laptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
s typically use surface mount CPUs, which need less space than a socketed part.
Function
A CPU socket is made of plasticPlastic
A plastic material is any of a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic organic solids used in the manufacture of industrial products. Plastics are typically polymers of high molecular mass, and may contain other substances to improve performance and/or reduce production costs...
, a metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
lever or latch, and metal contacts for each of the pins or lands on the CPU. Many packages are keyed to ensure the proper insertion of the CPU. CPUs with a PGA package are inserted into the socket and the latch is closed.
List of sockets and slots
| Socket name |
Year of introduction | Year of End Of Life | CPU families | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch | Bus speed | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIP Dual in-line package In microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is... |
1970s | Still available | Intel 8086 Intel 8088 |
DIP | 40 | 2.54mm | 5/10 MHz | |
| PLCC Plastic leaded chip carrier A plastic leaded chip carrier is a chip carrier with a equiangular plastic housing. It is a reduced cost evolution of the ceramic leadless chip carrier .... |
? | Still available | Intel 80186 Intel 80286 Intel 80386 |
PLCC | 68, 132 | 1.27mm | 6–40 MHz | |
| Socket 1 Socket 1 Socket 1 was the second of a series of standard CPU sockets created by Intel into which various x86 microprocessors were inserted. It was an upgrade to Intel's first standard pin grid array socket and the first with an official designation... |
1989 | ? | Intel 80486 | PGA | 169 | ? | 16–50 MHz | |
| Socket 2 Socket 2 Socket 2 was one of the series of CPU sockets into which various x86 microprocessors were inserted. It was an updated Socket 1 with added support for Pentium OverDrive processors.... |
? | ? | Intel 80486 | PGA | 238 | ? | 16–50 MHz | |
| Socket 3 Socket 3 Socket 3 was one of the series of CPU Sockets into which various x86 microprocessors were inserted. It was sometimes found alongside a secondary socket designed for a math coprocessor chip, in this case the 487. Socket 3 resulted from Intel's creation of lower voltage microprocessors... |
1991 | ? | Intel 80486 | PGA | 237 | ? | 16–50 MHz | |
| Socket 4 Socket 4 Socket 4, presented in 1993, was the first CPU socket designed for the early P5 Pentium microprocessors. Socket 4 was the only 5-volt socket for the Pentium. After Socket 4, Intel switched to the 3.3-volt-powered Socket 5. Socket 4 does support a special Pentium OverDrive, which allows running at... |
? | ? | Intel Pentium | PGA | 273 | ? | 60–66 MHz | |
| Socket 5 Socket 5 Socket 5 was created for the second generation of Intel P5 Pentium processors operating at speeds from 75 to 120 MHz as well as certain Pentium OverDrive and Pentium MMX processors with core voltage 3.3 V. Consisting of 320 pins, this was the first socket to use a staggered pin grid array, or... |
? | ? | Intel Pentium AMD Advanced Micro Devices Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. or AMD is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Sunnyvale, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for commercial and consumer markets... K5 AMD K5 The K5 was AMD's first x86 processor to be developed entirely in-house. Introduced in March 1996, its primary competition was Intel's Pentium microprocessor. The K5 was an ambitious design, closer to a Pentium Pro than a Pentium regarding technical solutions and internal architecture... IDT Integrated Device Technology Integrated Device Technology, Inc. is a publicly traded corporation headquartered in San Jose, California, that designs, manufactures, and markets low-power, high-performance mixed-signal semiconductor solutions for the advanced communications, computing, and consumer industries. The company... WinChip WinChip The WinChip series was a low-power Socket 7-based x86 processor designed by Centaur Technology and marketed by its parent company IDT.-Design:The design of the WinChip was quite different from other processors of the time... C6 IDT WinChip 2 |
PGA | 320 | ? | 50–66 MHz | |
| Socket 6 Socket 6 Socket 6 was a 486-generation CPU socket, a slightly modified version of the more common Socket 3.Intel designed this new standard near the end of the 80486's market life, so few motherboards were produced that used it, especially as the Socket 3 standard was already sufficient.... |
? | ? | Intel 80486 | PGA | 235 | ? | ? | |
| Socket 7 Socket 7 Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others.Socket 7 was... |
1994 | ? | Intel Pentium Intel Pentium MMX AMD Advanced Micro Devices Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. or AMD is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Sunnyvale, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for commercial and consumer markets... K6 AMD K6 The K6 microprocessor was launched by AMD in 1997. The main advantage of this particular microprocessor is that it was designed to fit into existing desktop designs for Pentium branded CPUs. It was marketed as a product which could perform as well as its Intel Pentium II equivalent but at a... |
PGA | 321 | ? | 50–66 MHz | |
| Super Socket 7 Super Socket 7 The Super Socket 7, also referred to as Super 7, is an extension of the Socket 7 ZIF socket specification. It features a 100 MHz front-side bus, support for AGP, and a SPGA package. Super Socket was used by AMD K6-2 and K6-III processors, and some of the final Cyrix M-II processors... |
1998 | ? | AMD K6-2 AMD K6-2 The K6-2 was an x86 microprocessor introduced by AMD on May 28, 1998, and available in speeds ranging from 266 to 550 MHz. An enhancement of the original K6, the K6-2 introduced AMD's 3D-Now! SIMD instruction set, featured a larger 64 KiB Level 1 cache , and an upgraded system-bus interface... AMD AMD K6-III AMD K6-III The K6-III, code-named "Sharptooth", was an x86 microprocessor manufactured by AMD, released on 22 February 1999, with 400 and 450 MHz models. It was the last Socket 7 desktop processor. For an extremely short time after its release, the fastest available desktop processor from Intel was the... Rise Rise Technology Rise Technology, was a short lived microprocessor manufacturer that produced the Intel x86 MMX compatible mP6 processor.The Santa Clara, California based company was started by David Lin in 1993 with funding from 15 Taiwanese investors, including UMC, ACER and VIA Technologies... mP6 MP6 This article is about the mP6 microprocessor. The Rise mP6 was a superpipelined and superscalar microprocessor designed by Rise Technology to compete with the Intel Pentium line.-History:... Cyrix MII Cyrix 6x86 The Cyrix 6x86 is a sixth-generation, 32-bit 80x86-compatible microprocessor designed by Cyrix and manufactured by IBM and SGS-Thomson. It was originally released in 1996.-Architecture:... |
PGA | 321 | ? | 66–100 MHz | |
| Socket 8 Socket 8 The Socket 8 CPU socket was used exclusively with the Intel Pentium Pro and Pentium II Overdrive computer processors. Intel discontinued Socket 8 in favor of Slot 1 with the introduction of the Pentium II.-Technical specifications:... |
1995 | ? | Intel Pentium Pro Pentium Pro The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel introduced in November 1, 1995 . It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications... |
PGA | 387 | ? | 60–66 MHz | |
| Slot 1 Slot 1 Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III... |
1997 | ? | Intel Pentium II Pentium II The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million... Intel Pentium III Pentium III The Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile microprocessors based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 26, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded microprocessors... |
Slot | 242 | ? | 66–133 MHz | Celeron (Covington, Mendocino) Pentium II (Klamath) Pentium III (Katmai)- all versions Pentium III (coppermine) |
| Slot 2 Slot 2 Slot 2 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the 330-lead Single Edge Contact Cartridge used by some of Intel's Pentium II Xeon and certain models of the Pentium III Xeon.... |
1998 | ? | Intel Pentium II Xeon | Slot | 330 | ? | 100–133 MHz | |
| Socket 463/ Socket NexGen |
? | ? | NexGen NexGen NexGen was a private semiconductor company that designed x86 microprocessors until it was purchased by AMD in 1996.Like competitor Cyrix, NexGen was a fabless design house that designed its chips but relied on other companies for production... Nx586 |
PGA | 463 | ? | ? | |
| Socket 499 | ? | ? | Alpha 21164A | Slot | 587 | ? | ? | |
| Slot A Slot A Slot A refers to the physical and electrical specification for a 242-lead single-edge-connector used by early versions of AMD's Athlon processor.The Slot A connector allows for a higher bus rate than Socket 7 or Super Socket 7... |
1999 | ? | AMD Athlon Athlon Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices . The original Athlon was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and, in a first, retained the initial performance lead it had over Intel's competing processors... |
Slot | 242 | ? | 100 MHz | |
| Slot B | ? | ? | Alpha 21264 Alpha 21264 The Alpha 21264 was a Digital Equipment Corporation RISC microprocessor introduced in October, 1996. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture .- Description :... |
Slot | 587 | ? | ? | |
| Socket 370 Socket 370 Socket 370 is a common format of CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number of pin holes in the socket for CPU pins... |
1999 | ? | Intel Pentium III Pentium III The Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile microprocessors based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 26, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded microprocessors... Intel Celeron Celeron Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers.... VIA VIA Technologies VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets... Cyrix III Cyrix III Cyrix III is an x86-compatible Socket 370 CPU. VIA Technologies launched the processor in February 2000. VIA had recently purchased both Centaur Technology and Cyrix. Cyrix III was to be based upon a core from one of the two companies.- Joshua :... VIA VIA Technologies VIA Technologies is a Taiwanese manufacturer of integrated circuits, mainly motherboard chipsets, CPUs, and memory, and is part of the Formosa Plastics Group. It is the world's largest independent manufacturer of motherboard chipsets... C3 VIA C3 The VIA C3 is a family of x86 central processing units for personal computers designed by Centaur Technology and sold by VIA Technologies. The different CPU cores are built following the design methodology of Centaur Technology.-Samuel 2 and Ezra cores:... |
PGA | 370 | 1.27mm | 66–133 MHz | |
| Socket 462/ Socket A Socket A Socket A is the CPU socket used for AMD processors ranging from the Athlon Thunderbird to the Athlon XP/MP 3200+, and AMD budget processors including the Duron and Sempron. Socket A also supports AMD Geode NX embedded processors... |
2000 | ? | AMD Athlon AMD Duron AMD Athlon XP AMD Athlon XP-M AMD Athlon MP AMD Sempron |
PGA | 462 | ? | 100–200 MHz This is a double data rate bus having a 400 MT/s (megatransfers/second) fsb in the later models |
|
| Socket 423 Socket 423 Socket 423 is a 423 pin CPU socket used for the first generation of Pentium 4 processors, based on the Willamette core.-Technical specifications:This socket houses any processor designed in the Socket 423 package.... |
2000 | ? | Intel Pentium 4 Pentium 4 Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the... |
PGA | 423 | 1mm | 400 MT/s (100 MHz) | Willamette core only |
| Socket 478 Socket 478 Socket 478 is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs.Socket 478 was launched with the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based... / Socket N |
2000 | ? | Intel Pentium 4 Pentium 4 Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the... Intel Celeron Celeron Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers.... Intel Pentium 4 EE Intel Pentium 4 M |
PGA | 478 | 1.27mm | 400–800 MT/s (100–200 MHz) | |
| Socket 495 Socket 495 Socket 495 is the CPU socket for the Intel Celeron mobile processors.-Technical specifications:This socket is a 495 pin CPU socket designed to house any processor in the Socket 495 package... |
2000 | ? | Intel Celeron Celeron Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers.... |
PGA | 495 | 1.27mm | ? | |
| PAC418 PAC418 Socket PAC418 is a 418 pin microprocessor socket designed to interface an Intel Itanium processor to the rest of the computer . It provides both an electrical interface as well as physical support. This socket is designed to support a microprocessor module.-Technical specifications:Socket PAC418... |
2001 | ? | Intel Itanium Itanium Itanium is a family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors that implement the Intel Itanium architecture . Intel markets the processors for enterprise servers and high-performance computing systems... |
PGA | 418 | ? | 133 MHz | |
| Socket 603 Socket 603 Socket 603 is a motherboard socket for Intel's Xeon processor.-Technical specifications:Socket 603 was designed by Intel as a zero insertion force socket intended for workstations and server platforms. It contains 603 contacts arrayed in a grid about the center of the socket, each contact has a... |
2001 | ? | Intel Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... |
PGA | 603 | 1.27mm | 400–533 MT/s (100–133 MHz) | |
| PAC611 PAC611 Socket PAC611 is a 611 pin microprocessor socket designed to interface an Intel Itanium 2 processor to the rest of the computer . It provides both an electrical interface as well as physical support... |
2002 | ? | Intel Itanium 2 HP PA-8800, PA-8900 |
PGA | 611 | ? | ? | |
| Socket 604 Socket 604 Socket 604 is a 604 pin microprocessor socket designed to interface an Intel's Xeon processor to the rest of the computer. It provides both an electrical interface as well as physical support. This socket is designed to support a heatsink.... |
2002 | ? | Intel Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... |
PGA | 604 | 1.27mm | 400–1066 MT/s (100–266 MHz) | |
| Socket 754 Socket 754 Socket 754 is a CPU socket originally developed by AMD to succeed its Athlon XP platform . Socket 754 was the first socket developed by AMD to support their new consumer version of the 64 bit microprocessor family known as AMD64.-Technical specifications:Socket 754 was the original socket for... |
2003 | ? | AMD Athlon 64 Athlon 64 The Athlon 64 is an eighth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP... AMD Sempron Sempron Sempron has been the marketing name used by AMD for several different budget desktop CPUs, using several different technologies and CPU socket formats. The Sempron replaced the AMD Duron processor and competes against Intel's Celeron series of processors... AMD Turion 64 |
PGA | 754 | 1.27mm | 200–800 MHz | |
| Socket 940 Socket 940 Socket 940 is a 940-pin socket for 64-bit AMD server processors. This socket is entirely square in shape and pins are arranged in a grid with the exception of four key pins used to align the processor and the corners... |
2003 | ? | AMD Opteron Opteron Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same... Athlon 64 FX |
PGA Pin grid array A pin grid array, often abbreviated PGA, is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or roughly square, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package... |
940 | 1.27mm | 200–1000 MHz | |
| Socket 479 Socket 479 Socket 479 is the CPU socket for the Intel Pentium M and Celeron M, mobile processors. Normally used in laptops, but has also been used with Tualatin-M Pentium III processors. The official naming by Intel is µFCPGA and µPGA479M... |
2003 | ? | Intel Pentium M Pentium M The Pentium M brand refers to a family of mobile single-core x86 microprocessors introduced in March 2003 , and forming a part of the Intel Carmel notebook platform under the then new Centrino brand... Intel Celeron M |
PGA | 479 | ? | 400–533 MT/s (100–133 MHz) | |
| Socket 939 Socket 939 Socket 939 is a CPU socket released by AMD in June 2004 to supersede the previous Socket 754 for Athlon 64 processors. Socket 939 was succeeded by Socket AM2 in May 2006. It is the second socket designed for AMD's AMD64 range of processors.-Availability:... |
2004 | 11/2008 | AMD Athlon 64 Athlon 64 The Athlon 64 is an eighth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP... AMD Athlon 64 FX AMD Athlon 64 X2 Athlon 64 X2 The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-core desktop CPU designed by AMD. It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and... AMD Opteron Opteron Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same... |
PGA | 939 | 1.27mm | 200–1000 MHz | Support of Athlon 64 FX to 1 GHz Support of Opteron Opteron Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same... limited to 100-series only |
| LGA 775/ Socket T Socket T LGA 775, also known as Socket T, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. LGA stands for land grid array. Unlike earlier common CPU sockets, such as its predecessor Socket 478, the LGA 775 has no socket holes; instead, it has 775 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor... |
2004 | ? | Intel Pentium 4 Pentium 4 Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the... Intel Pentium D Pentium D The Pentium D brand refers to two series of desktop dual-core 64-bit x86-64 microprocessors with the NetBurst microarchitecture manufactured by Intel. Each CPU comprised two dies, each containing a single core, residing next to each other on a multi-chip module package. The brand's first processor,... Intel Celeron Celeron Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers.... Intel Celeron D Intel Pentium XE Intel Core 2 Duo Intel Core 2 Quad Intel Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... |
LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
775 | 1.09mm x 1.17mm | 1600 MHz | |
| Socket 563 Socket 563 Socket 563 is a microPGA CPU socket used exclusively for low-power Athlon XP-M processors .This socket can usually be found in laptops and requires a low-power mobile part in a special 563-pin µPGA package which is different from the Socket A package used for other Athlon processors.There are... |
? | ? | AMD Athlon Athlon Athlon is the brand name applied to a series of x86-compatible microprocessors designed and manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices . The original Athlon was the first seventh-generation x86 processor and, in a first, retained the initial performance lead it had over Intel's competing processors... XP-M |
PGA | 563 | ? | ? | |
| Socket M Socket M Socket M is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006 for the Intel Core line of mobile processors.-Technical specifications:Socket M is used in all Intel Core products, as well as the Core-derived Dual-Core Xeon codenamed Sossaman... |
2006 | ? | Intel Core Solo Intel Core Duo Intel Dual-Core Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... Intel Core 2 Duo |
PGA | 478 | ? | 533–667 MT/s (133–166 MHz) | For notebook platform Replaces Socket 479 Socket 479 Socket 479 is the CPU socket for the Intel Pentium M and Celeron M, mobile processors. Normally used in laptops, but has also been used with Tualatin-M Pentium III processors. The official naming by Intel is µFCPGA and µPGA479M... |
| LGA 771 LGA 771 LGA 771, also known as Socket J, is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006. It is used in Intel Core microarchitecture based DP-capable server processors, the Dual-Core Xeon is codenamed Dempsey, Woodcrest, and Wolfdale and the Quad-Core processors Clovertown, Harpertown... / Socket J |
2006 | ? | Intel Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... |
LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
771 | 1.09mm x 1.17mm | 1600 MHz | |
| Socket S1 Socket S1 Socket S1 is the CPU socket type used by AMD for their Turion 64, Athlon 64 Mobile and later Sempron processors, which debuted with the dual core Turion 64 X2 CPUs on May 17, 2006.-Technical specifications:... |
2006 | ? | AMD Turion 64 X2 | PGA | 638 | 1.27mm | 200–800 MHz | |
| Socket AM2 Socket AM2 The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments... |
2006 | ? | AMD Athlon 64 Athlon 64 The Athlon 64 is an eighth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP... AMD Athlon 64 X2 Athlon 64 X2 The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-core desktop CPU designed by AMD. It was designed from scratch as native dual-core by using an already multi-CPU enabled Athlon 64, joining it with another functional core on one die, and connecting both via a shared dual-channel memory controller/north bridge and... |
PGA Pin grid array A pin grid array, often abbreviated PGA, is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or roughly square, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package... |
940 | 1.27mm | 200–1000 MHz | Replaces Socket 754 and Socket 939 |
| Socket F Socket F Socket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:... |
2006 | ? | AMD Athlon 64 FX AMD Opteron Opteron Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same... |
LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
1207 | 1.1mm | ? | Replaces Socket 940 Socket 940 Socket 940 is a 940-pin socket for 64-bit AMD server processors. This socket is entirely square in shape and pins are arranged in a grid with the exception of four key pins used to align the processor and the corners... |
| Socket AM2+ Socket AM2+ Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together... |
2007 | ? | AMD Athlon 64 Athlon 64 The Athlon 64 is an eighth-generation, AMD64-architecture microprocessor produced by AMD, released on September 23, 2003. It is the third processor to bear the name Athlon, and the immediate successor to the Athlon XP... AMD Athlon X2 AMD Phenom AMD Phenom II Phenom II Phenom II is a family of AMD's multi-core 45 nm processors using the AMD K10 microarchitecture, succeeding the original Phenom. Advanced Micro Devices released the Socket AM2+ version of Phenom II in December 2008, while Socket AM3 versions with DDR3 support, along with an initial batch of... |
PGA Pin grid array A pin grid array, often abbreviated PGA, is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or roughly square, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package... |
940 | 1.27mm | 200–2600 MHz | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2 Socket AM2 The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 , is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments... AM2+ Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2 AM2 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2+ |
| Socket P Socket P The Intel Socket P is the mobile processor socket replacement for Core microarchitecture chips such as Core 2 Duo. It launched on May 9, 2007, as part of the Santa Rosa platform with the Merom and Penryn processors.-Technical specifications:... |
2007 | ? | Intel Core 2 | PGA | 478 | 533–1066 MT/s (133–266 MHz) | For notebook platform Replaces Socket M Socket M Socket M is a CPU interface introduced by Intel in 2006 for the Intel Core line of mobile processors.-Technical specifications:Socket M is used in all Intel Core products, as well as the Core-derived Dual-Core Xeon codenamed Sossaman... |
|
| Socket 441 Socket 441 Socket 441 is the CPU socket for the Intel Atom low-power processors, normally used in ultra-Mobile PCs, smartphones and other portable and low-power applications.-See also:* List of Intel microprocessors... |
2008 | ? | Intel Atom Intel Atom Intel Atom is the brand name for a line of ultra-low-voltage x86 and x86-64 CPUs from Intel, designed in 45 nm CMOS and used mainly in netbooks, nettops, embedded application ranging from health care to advanced robotics and Mobile Internet devices... |
PGA | 441 | ? | 400–667 MHz | |
| LGA 1366/ Socket B Socket B LGA 1366, also known as Socket B, is an Intel CPU socket. This socket supersedes Intel's LGA 775 in the high-end and performance desktop segments. It also replaces the server-oriented LGA 771 in the entry level and is superseded itself by LGA 2011. LGA stands for land grid array... |
2008 | ? | Intel Core i7 (900 series) Intel Xeon (35xx, 36xx, 55xx, 56xx series) |
LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
1366 | 4.8-6.4 GT/s | Replaces server-oriented Socket J (LGA 771) in the entry level. | |
| Socket AM3 Socket AM3 Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it... |
2009 | ? | AMD Phenom II Phenom II Phenom II is a family of AMD's multi-core 45 nm processors using the AMD K10 microarchitecture, succeeding the original Phenom. Advanced Micro Devices released the Socket AM2+ version of Phenom II in December 2008, while Socket AM3 versions with DDR3 support, along with an initial batch of... AMD Athlon II Athlon II Athlon II is a family of AMD multi-core 45 nm central processing units, which is aimed at the midrange to budget market and is a complementary product lineup to the Phenom II.-Features:... AMD Sempron Sempron Sempron has been the marketing name used by AMD for several different budget desktop CPUs, using several different technologies and CPU socket formats. The Sempron replaced the AMD Duron processor and competes against Intel's Celeron series of processors... |
PGA | 941 | 1.27mm | 200–3200 MHz | Separated power planes Replaces Socket AM2+ Socket AM2+ Socket AM2+ is a CPU socket, which is the immediate successor to Socket AM2 that is used by several AMD processors such as Athlon 64 X2. Socket AM2+ is a mid-migration from Socket AM2 to Socket AM3 and both AM2+ and AM2 socket CPUs and motherboards have the potential to operate together... AM3 Pkg. CPUs can work in Socket AM2/AM2+ Sempron 140 Only |
| LGA 1156 LGA 1156 LGA 1156, also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. LGA stands for land grid array. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155.... / Socket H |
2009 | ? | Intel Core i7 (800 series) Intel Core i5 (700, 600 series) Intel Core i3 (500 series) Intel Xeon Xeon The Xeon is a brand of multiprocessing- or multi-socket-capable x86 microprocessors from Intel Corporation targeted at the non-consumer server, workstation and embedded system markets.-Overview:... (X3400, L3400 series) Intel Pentium (G6000 series) Intel Celeron Celeron Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers.... (G1000 series) |
LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
1156 | ? | 2.5 GT/s | DMI Direct Media Interface The Direct Media Interface is the link between an Intel northbridge and an Intel southbridge on a computer motherboard. It was first used between the 9xx chipsets and the ICH6, released in 2004. Previous chipsets had used the Hub Interface to perform the same function. Server chipsets use a... bus is a (perhaps modified) PCI-E PCI Express PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards... x4 v1.1 interface |
| Socket G34 Socket G34 Socket G34 is a CPU socket designed by AMD to support AMD's multi-chip module Opteron 6000-series server processors. G34 was launched on March 29, 2010, alongside the initial grouping of Opteron 6100 processors designed for it. Socket G34 supports four DDR3 SDRAM channels, two for each die in the... |
2010 | ? | AMD Opteron Opteron Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same... (6000 series) |
LGA | 1974 | ? | 200–3200 MHz | Replaces Socket F Socket F Socket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:... |
| Socket C32 Socket C32 The AMD Socket C32 is the server processor socket for AMD's current single-CPU and dual-CPU Opteron 4000 series CPUs. It is the successor to Socket AM3 for single-CPU servers and the successor for Socket F for lower-end dual-CPU servers... |
2010 | ? | AMD Opteron Opteron Opteron is AMD's x86 server and workstation processor line, and was the first processor which supported the AMD64 instruction set architecture . It was released on April 22, 2003 with the SledgeHammer core and was intended to compete in the server and workstation markets, particularly in the same... (4000 series) |
LGA | 1207 | ? | 200–3200 MHz | Replaces Socket F Socket F Socket F is a CPU socket designed by AMD for its Opteron line of CPUs released on August 15, 2006. In 2010 Socket F was replaced by Socket C32 for entry-level servers and Socket G34 for high-end servers.-Technical specifications:... , Socket AM3 Socket AM3 Socket AM3 is a CPU socket for AMD processors. AM3 was launched as the successor to Socket AM2+ on February 9, 2009, alongside the initial grouping of Phenom II processors designed for it... |
| LGA 1248 LGA 1248 LGA 1248 is an Intel CPU Socket for Itanium 9300-series processors. It replaces PAC611 used by Itanium 9100-series processors and adds Intel QuickPath Interconnect functionalities.-See also:* List of Intel microprocessors... |
2010 | ? | Intel Intel Itanium 9300-series | LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
1248 | ? | 4.8 GT/s | |
| LGA 1567 LGA 1567 LGA 1567 is a CPU socket used for the high-end server segment. LGA 1567 has 1567 protruding pins to make contact with the pads on the processor.It supports Intel Nehalem, codenamed Beckton, Xeon 7500 and Xeon 6500 series processors first released in March 2010... |
2010 | ? | Intel Intel Xeon 6500/7500-series | LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
1567 | ? | 4.8-6.4 GT/s | |
| LGA 1155 LGA 1155 LGA 1155, also called Socket H2, is an Intel microprocessor compatible socket which supports Intel Sandy Bridge and the up-coming Ivy Bridge microprocessors.... / Socket H2 |
2011/Q1 | ? | Intel Sandy Bridge-DT | LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
1155 | ? | 5 GT/s | Supports 20 PCI-E PCI Express PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards... 2.0 lanes. |
| LGA 2011 LGA 2011 LGA 2011, also called Socket R, is a CPU socket by Intel. It replaces Intel's LGA 1366 and LGA 1567 in the performance and high-end desktop and server platforms. The socket has 2,011 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor.Socket R uses QPI to connect the CPU... / Socket R |
2011/Q3 | ? | Intel Sandy Bridge B2 | LGA Land grid array The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit... |
2011 | ? | 4.8-6.4 GT/s | Supports 40 PCI-E PCI Express PCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards... 3.0 lanes. |
| Socket FM1 Socket FM1 Socket FM1 is a CPU socket used by AMD's A-series mainstream Fusion processors released in July 2011.- References :* http://www.tomshardware.com/news/amd-llano-socket-fm1-sample,12549.html... |
2011 | ? | AMD Llano Processor | PGA | 905 | 1.27mm | ||
| Socket name |
Year of introduction | Year of EOL | CPU families | Package | Pin count | Pin pitch | Bus speed | Notes |
Slotkets
SlotketSlotket
In computer hardware terminology, slotkets, also known as slockets, are adapters that allow socket-based microprocessors to be used on slot-based motherboards....
s are special adapters for using socket processors in bus-compatible slot motherboards.
See also
External links
- Socket ID Guide
- CPU Sockets Chart - A fairly detailed table listing x86 Sockets and associated attributes.
- techPowerUp! CPU Database
- Processor sockets

