
AMD K6
Encyclopedia
The K6 microprocessor was launched by AMD in 1997. The main advantage of this particular microprocessor is that it was designed to fit into existing desktop designs for Pentium branded CPUs. It was marketed as a product which could perform as well as its Intel Pentium II equivalent but at a significantly lower price. The K6 had a considerable impact on the PC market and presented Intel with serious competition.
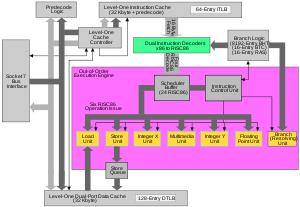 The AMD K6 is a superscalar
The AMD K6 is a superscalar
P5
Pentium-class microprocessor
, manufactured by AMD, which superseded the K5
.
The AMD K6 is based on the Nx686 microprocessor that NexGen
was designing when it was acquired by AMD. Despite the name implying a design evolving from the K5
, it is in fact a totally different design that was created by the NexGen team, including chief processor architect Greg Favor, and adapted after the AMD purchase. The K6 processor included a feedback dynamic instruction reordering mechanism, MMX instructions, and a floating-point unit (FPU). It was also made pin-compatible
with Intel's Pentium, enabling it to be used in the widely available "Socket 7
"-based motherboards. Like the AMD K5
, Nx586, and Nx686 before it, the K6 translated x86 instructions on the fly into dynamic buffered sequences of micro-operation
s. A later variation of the K6 CPU, K6-2
, added floating point
-based SIMD instructions, called 3DNow!
.
The K6 was originally launched in April 1997, running at speeds of 166 and 200 MHz. It was followed by a 233 MHz version later in 1997. Initially, the AMD K6 processors used a Pentium II-based performance rating (PR2) to designate their speed. The PR2 rating was dropped because the rated frequency of the processor was the same as the real frequency. The release of the 266 MHz version of this chip was not until the second quarter of 1998 when AMD was able to move to the 0.25 micrometre manufacturing process. The lower voltage and higher multiplier of the K6-266 meant that it was not 100% compatible with some Socket 7 motherboards, similar to the later K6-2
processors. The final iteration of the K6 design was released in May 1998 running at 300 MHz.
Many viewed the K6 and the acquisition of NexGen as the moment that AMD was put back into the Intel compatible processor market. The actual K6 AMD had been designing was anemic compared to NexGen's design. With the buyout of NexGen, AMD was able to come back into the game with a processor that could perform competitively with Intel's Pentium II.


Background

Superscalar
A superscalar CPU architecture implements a form of parallelism called instruction level parallelism within a single processor. It therefore allows faster CPU throughput than would otherwise be possible at a given clock rate...
P5
P5 (microarchitecture)
The original Pentium microprocessor was introduced on March 22, 1993. Its microarchitecture, deemed P5, was Intel's fifth-generation and first superscalar x86 microarchitecture. As a direct extension of the 80486 architecture, it included dual integer pipelines, a faster FPU, wider data bus,...
Pentium-class microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
, manufactured by AMD, which superseded the K5
AMD K5
The K5 was AMD's first x86 processor to be developed entirely in-house. Introduced in March 1996, its primary competition was Intel's Pentium microprocessor. The K5 was an ambitious design, closer to a Pentium Pro than a Pentium regarding technical solutions and internal architecture...
.
The AMD K6 is based on the Nx686 microprocessor that NexGen
NexGen
NexGen was a private semiconductor company that designed x86 microprocessors until it was purchased by AMD in 1996.Like competitor Cyrix, NexGen was a fabless design house that designed its chips but relied on other companies for production...
was designing when it was acquired by AMD. Despite the name implying a design evolving from the K5
AMD K5
The K5 was AMD's first x86 processor to be developed entirely in-house. Introduced in March 1996, its primary competition was Intel's Pentium microprocessor. The K5 was an ambitious design, closer to a Pentium Pro than a Pentium regarding technical solutions and internal architecture...
, it is in fact a totally different design that was created by the NexGen team, including chief processor architect Greg Favor, and adapted after the AMD purchase. The K6 processor included a feedback dynamic instruction reordering mechanism, MMX instructions, and a floating-point unit (FPU). It was also made pin-compatible
Pin-compatibility
In electronics, a pin-compatible device, such as a logic integrated circuit , memory module or microprocessor, is one that has the same functions assigned to the same particular pins....
with Intel's Pentium, enabling it to be used in the widely available "Socket 7
Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others.Socket 7 was...
"-based motherboards. Like the AMD K5
AMD K5
The K5 was AMD's first x86 processor to be developed entirely in-house. Introduced in March 1996, its primary competition was Intel's Pentium microprocessor. The K5 was an ambitious design, closer to a Pentium Pro than a Pentium regarding technical solutions and internal architecture...
, Nx586, and Nx686 before it, the K6 translated x86 instructions on the fly into dynamic buffered sequences of micro-operation
Micro-operation
In computer central processing units, micro-operations are detailed low-level instructions used in some designs to implement complex machine instructions .Various forms of μops have long been the basis for traditional microcode routines used to simplify the implementation of a...
s. A later variation of the K6 CPU, K6-2
AMD K6-2
The K6-2 was an x86 microprocessor introduced by AMD on May 28, 1998, and available in speeds ranging from 266 to 550 MHz. An enhancement of the original K6, the K6-2 introduced AMD's 3D-Now! SIMD instruction set, featured a larger 64 KiB Level 1 cache , and an upgraded system-bus interface...
, added floating point
Floating point
In computing, floating point describes a method of representing real numbers in a way that can support a wide range of values. Numbers are, in general, represented approximately to a fixed number of significant digits and scaled using an exponent. The base for the scaling is normally 2, 10 or 16...
-based SIMD instructions, called 3DNow!
3DNow!
3DNow! is an extension to the x86 instruction set developed by Advanced Micro Devices . It adds single instruction multiple data instructions to the base x86 instruction set, enabling it to perform simple vector processing, which improves the performance of many graphic-intensive applications...
.
The K6 was originally launched in April 1997, running at speeds of 166 and 200 MHz. It was followed by a 233 MHz version later in 1997. Initially, the AMD K6 processors used a Pentium II-based performance rating (PR2) to designate their speed. The PR2 rating was dropped because the rated frequency of the processor was the same as the real frequency. The release of the 266 MHz version of this chip was not until the second quarter of 1998 when AMD was able to move to the 0.25 micrometre manufacturing process. The lower voltage and higher multiplier of the K6-266 meant that it was not 100% compatible with some Socket 7 motherboards, similar to the later K6-2
AMD K6-2
The K6-2 was an x86 microprocessor introduced by AMD on May 28, 1998, and available in speeds ranging from 266 to 550 MHz. An enhancement of the original K6, the K6-2 introduced AMD's 3D-Now! SIMD instruction set, featured a larger 64 KiB Level 1 cache , and an upgraded system-bus interface...
processors. The final iteration of the K6 design was released in May 1998 running at 300 MHz.
Many viewed the K6 and the acquisition of NexGen as the moment that AMD was put back into the Intel compatible processor market. The actual K6 AMD had been designing was anemic compared to NexGen's design. With the buyout of NexGen, AMD was able to come back into the game with a processor that could perform competitively with Intel's Pentium II.
Models


K6 (Model 6)
- 8.8 million transistors in 350 nm
- L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KB (Data + Instructions)
- MMX
- Socket 7Socket 7Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others.Socket 7 was...
- Front side busFront side busA front-side bus is a computer communication interface often used in computers during the 1990s and 2000s.It typically carries data between the central processing unit and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge....
: 66 MHz - First release: April 2, 1997
- VCore: 2.9 V (166/200) 3.2/3.3 V (233)
- Clockrate: 166, 200, 233 MHz
K6 "Little Foot" (Model 7)
- CPUIDCPUIDThe CPUID opcode is a processor supplementary instruction for the x86 architecture. It was introduced by Intel in 1993 when it introduced the Pentium and SL-Enhanced 486 processors....
: Family 5, Model 7, Stepping 0 - 8.8 million transistors in 250 nm
- L1-Cache: 32 + 32 KB (Data + Instructions)
- MMX
- Socket 7Socket 7Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others.Socket 7 was...
- Front side busFront side busA front-side bus is a computer communication interface often used in computers during the 1990s and 2000s.It typically carries data between the central processing unit and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge....
: 66 MHz - First release: January 6, 1998
- VCore: 2.2 V
- Clockrate: 200, 233, 266, 300 MHz
Further reading
- Gwennap, Linley (31 March 1997). "K6 Is World's Fastest x86 Chip". Microprocessor Report.
- Slater, Michael (28 October 1998). "K6 to Boost AMD's Position in 1997". Microprocessor Report.

