
Socket T
Encyclopedia
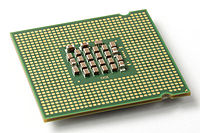
LGA 775, also known as Socket T, is an Intel desktop CPU socket
. LGA stands for land grid array
. Unlike earlier common CPU sockets, such as its predecessor Socket 478
, the LGA 775 has no socket holes; instead, it has 775 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor
(CPU).
cores
, as well as the Smithfield and Presler Pentium D
cores, used the LGA 775 socket. In July 2006, Intel released the desktop version of the Core 2 Duo
(codenamed Conroe), which also uses this socket, as does the subsequent Core 2 Quad. Intel changed from Socket 478
to LGA 775 because the new pin type offers better power distribution to the processor, allowing the front side bus
to be raised to 1600 MT/s
. The 'T' in Socket T was derived from the now cancelled Tejas
core, which was to replace the Prescott core. Another advantage for Intel with this newer architecture is that it is now the motherboard which has the pins, rather than the CPU, transferring the risk of pins being bent from the CPU to the motherboard.
The CPU is pressed into place by a "load plate", rather than human fingers directly. The installing technician lifts the hinged "weld plate", inserts the processor, closes the load plate over the top of the processor, and pushes down a locking lever. The pressure of the locking lever on the load plate clamps the processor's 775 copper contact points firmly down onto the motherboard's 775 pins, ensuring a good connection. The load plate only covers the edges of the top surface of the CPU (processor heatspreader). The center is free to make contact with the cooling device placed on top of the CPU.
An examination of the relevant Intel data sheets shows that LGA 775 which is used for consumer level desktops and LGA 771 used for (Xeon based) workstation and server class computers appear to differ only in the placement of the indexing notches and the swap of two address pins. Many pins devoted to functions such as interfacing multiple CPUs are not clearly defined in the LGA 775 specifications, but from the information available appear to be consistent with those of LGA 771. Considering that LGA 775 predated LGA 771 by nearly a year and a half, it would seem that LGA 771 was adapted from LGA 775 rather than the other way around.
The socket has been superseded by the LGA 1156
(Socket H) and LGA 1366 (Socket B) sockets.
or cold-water block fixed onto the top of the CPU to carry away the heat generated by the CPU. This socket also introduces a new method of connecting the heat dissipation interface to the chip surface and motherboard. With LGA 775, the heat dissipation interface is connected directly to the motherboard on four points, compared with the two connections of the Socket 370 and the "clamshell" four-point connection of the Socket 478
. This was done to avoid the reputed danger of the heat sinks/fans of pre-built computers falling off in transit. LGA 775 was announced to have better heat dissipation properties than the Socket 478 it was designed to replace, but the Prescott core CPUs (in their early incarnations) ran much hotter than the previous Northwood-core Pentium 4
CPUs, and this initially neutralized the benefits of better heat transfer. However, modern Core 2
processors run at lower temperatures than the Prescott CPUs they replace.
 All LGA 775 processors have the following mechanical maximum load limits which should not be exceeded during heat sink assembly, shipping conditions, or standard use. Load above those limits will crack the processor die and make it unusable.
All LGA 775 processors have the following mechanical maximum load limits which should not be exceeded during heat sink assembly, shipping conditions, or standard use. Load above those limits will crack the processor die and make it unusable.
The transition to the LGA packaging has lowered those load limits, which are smaller than the load limits of Socket 478
processors but they are bigger than Socket 370
, Socket 423
and Socket A
processors, which were fragile. They are large enough to ensure that processors will not crack.
CPU socket
A CPU socket or CPU slot is a mechanical component that provides mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board . This allows the CPU to be replaced without soldering....
. LGA stands for land grid array
Land grid array
The land grid array is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits that is notable for having the pins on the socket rather than the integrated circuit...
. Unlike earlier common CPU sockets, such as its predecessor Socket 478
Socket 478
Socket 478 is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs.Socket 478 was launched with the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based...
, the LGA 775 has no socket holes; instead, it has 775 protruding pins which touch contact points on the underside of the processor
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
(CPU).
Technical specifications
The Prescott and Cedar Mill Pentium 4Pentium 4
Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the...
cores
Intel Core
Yonah was the code name for Intel's first generation of 65 nm process mobile microprocessors, based on the Banias/Dothan-core Pentium M microarchitecture. SIMD performance has been improved through the addition of SSE3 instructions and improvements to SSE and SSE2 implementations, while integer...
, as well as the Smithfield and Presler Pentium D
Pentium D
The Pentium D brand refers to two series of desktop dual-core 64-bit x86-64 microprocessors with the NetBurst microarchitecture manufactured by Intel. Each CPU comprised two dies, each containing a single core, residing next to each other on a multi-chip module package. The brand's first processor,...
cores, used the LGA 775 socket. In July 2006, Intel released the desktop version of the Core 2 Duo
Intel Core 2
Core 2 is a brand encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single-die, whereas the quad-core models comprise two dies, each containing two cores, packaged in a...
(codenamed Conroe), which also uses this socket, as does the subsequent Core 2 Quad. Intel changed from Socket 478
Socket 478
Socket 478 is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs.Socket 478 was launched with the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based...
to LGA 775 because the new pin type offers better power distribution to the processor, allowing the front side bus
Front side bus
A front-side bus is a computer communication interface often used in computers during the 1990s and 2000s.It typically carries data between the central processing unit and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge....
to be raised to 1600 MT/s
Megatransfer
In computer technology, transfers per second and its more common derivatives gigatransfers per second and megatransfers per second are informal language that refer to the number of operations transferring data that occur in each second in some given data-transfer channel. It is also known as...
. The 'T' in Socket T was derived from the now cancelled Tejas
Tejas and Jayhawk
Tejas was a code name for Intel's microprocessor which was to be a successor to the latest Pentium 4 with the Prescott core. Jayhawk was a code name for its Xeon counterpart...
core, which was to replace the Prescott core. Another advantage for Intel with this newer architecture is that it is now the motherboard which has the pins, rather than the CPU, transferring the risk of pins being bent from the CPU to the motherboard.
The CPU is pressed into place by a "load plate", rather than human fingers directly. The installing technician lifts the hinged "weld plate", inserts the processor, closes the load plate over the top of the processor, and pushes down a locking lever. The pressure of the locking lever on the load plate clamps the processor's 775 copper contact points firmly down onto the motherboard's 775 pins, ensuring a good connection. The load plate only covers the edges of the top surface of the CPU (processor heatspreader). The center is free to make contact with the cooling device placed on top of the CPU.
An examination of the relevant Intel data sheets shows that LGA 775 which is used for consumer level desktops and LGA 771 used for (Xeon based) workstation and server class computers appear to differ only in the placement of the indexing notches and the swap of two address pins. Many pins devoted to functions such as interfacing multiple CPUs are not clearly defined in the LGA 775 specifications, but from the information available appear to be consistent with those of LGA 771. Considering that LGA 775 predated LGA 771 by nearly a year and a half, it would seem that LGA 771 was adapted from LGA 775 rather than the other way around.
The socket has been superseded by the LGA 1156
LGA 1156
LGA 1156, also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. LGA stands for land grid array. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155....
(Socket H) and LGA 1366 (Socket B) sockets.
Improvements in heat dissipation
The force from the load plate ensures that the processor is completely level, giving the CPU's upper surface optimal contact with the heat sinkHeat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
or cold-water block fixed onto the top of the CPU to carry away the heat generated by the CPU. This socket also introduces a new method of connecting the heat dissipation interface to the chip surface and motherboard. With LGA 775, the heat dissipation interface is connected directly to the motherboard on four points, compared with the two connections of the Socket 370 and the "clamshell" four-point connection of the Socket 478
Socket 478
Socket 478 is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs.Socket 478 was launched with the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based...
. This was done to avoid the reputed danger of the heat sinks/fans of pre-built computers falling off in transit. LGA 775 was announced to have better heat dissipation properties than the Socket 478 it was designed to replace, but the Prescott core CPUs (in their early incarnations) ran much hotter than the previous Northwood-core Pentium 4
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 was a line of single-core desktop and laptop central processing units , introduced by Intel on November 20, 2000 and shipped through August 8, 2008. They had a 7th-generation x86 microarchitecture, called NetBurst, which was the company's first all-new design since the introduction of the...
CPUs, and this initially neutralized the benefits of better heat transfer. However, modern Core 2
Intel Core 2
Core 2 is a brand encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single-die, whereas the quad-core models comprise two dies, each containing two cores, packaged in a...
processors run at lower temperatures than the Prescott CPUs they replace.
LGA 775 mechanical load limits

| Location | Dynamic | Static |
|---|---|---|
| IHS Surface | 756 N (170 lbf Pound-force The pound force is a unit of force in some systems of measurement including English engineering units and British gravitational units.- Definitions :... ) (77 kp Kilogram-force A kilogram-force , or kilopond , is a gravitational metric unit of force. It is equal to the magnitude of the force exerted by one kilogram of mass in a gravitational field... ) |
311 N (70 lbf Pound-force The pound force is a unit of force in some systems of measurement including English engineering units and British gravitational units.- Definitions :... ) (31 kp Kilogram-force A kilogram-force , or kilopond , is a gravitational metric unit of force. It is equal to the magnitude of the force exerted by one kilogram of mass in a gravitational field... ) |
The transition to the LGA packaging has lowered those load limits, which are smaller than the load limits of Socket 478
Socket 478
Socket 478 is a 478-contact CPU socket used for Intel's Pentium 4 and Celeron series CPUs.Socket 478 was launched with the Northwood core to compete with AMD's 462-pin Socket A and their Athlon XP processors. Socket 478 was intended to be the replacement for Socket 423, a Willamette-based...
processors but they are bigger than Socket 370
Socket 370
Socket 370 is a common format of CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number of pin holes in the socket for CPU pins...
, Socket 423
Socket 423
Socket 423 is a 423 pin CPU socket used for the first generation of Pentium 4 processors, based on the Willamette core.-Technical specifications:This socket houses any processor designed in the Socket 423 package....
and Socket A
Socket A
Socket A is the CPU socket used for AMD processors ranging from the Athlon Thunderbird to the Athlon XP/MP 3200+, and AMD budget processors including the Duron and Sempron. Socket A also supports AMD Geode NX embedded processors...
processors, which were fragile. They are large enough to ensure that processors will not crack.

