
Slot 1
Encyclopedia
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel
's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro
, Celeron
, Pentium II
and the Pentium III
. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented.
, Intel had combined processor and cache dies in the same Socket 8
package. These were connected by a full-speed bus, resulting in significant performance benefits. Unfortunately, this method required that the two components be bonded together early in the production process, before testing was possible. As a result, a single, tiny flaw in either die made it necessary to discard the entire assembly, causing low production yield and high cost.
Intel subsequently designed a circuit board where the CPU and cache remained closely integrated, but were mounted on a printed circuit board
, called a Single-Edged Contact Cartridge (SECC). The CPU and cache could be tested separately, before final assembly into a package, reducing cost and making the CPU more attractive to markets other than that of high-end servers. These cards could also be easily plugged into a Slot 1, thereby eliminating the chance for pins of a typical CPU to be bent or broken when installing in a socket.
The form factor used for Slot 1 was a 5-inch-long, 242-contact edge connector
named SC242. To prevent the cartridge from being inserted the wrong way, the slot was keyed to allow installation in only one direction. The SC232 was later used for AMD's Slot A
as well, and while the two slots were identical mechanically, they were electrically incompatible. To discourage Slot A users from trying to install a Slot 1 CPU, the connector was rotated 180 degrees on Slot A motherboards.
With the new Slot 1, Intel added support for symmetric multiprocessing
(SMP). A maximum of two Pentium II or Pentium III CPUs can be used in a dual slot motherboard. The Celeron does not have official SMP support.
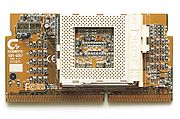
There are also converter cards, known as Slotket
s, which hold a Socket 8
so that a Pentium Pro
CPU can be used with Slot 1 motherboards. These specific converters, however, are rare. Another kind of slotket allows using a Socket 370 CPU in a Slot 1. Many of these latter devices are equipped with own voltage regulator modules, in order to supply the new CPU with a lower core voltage, which the motherboard would not otherwise allow.


 The Single Edge Contact Cartridge, or "SECC", was used at the beginning of the Slot 1-era for Pentium II CPUs. Inside the cartridge, the CPU itself is enclosed in a hybrid plastic and metal case. The back of the housing is plastic and has several markings on it: the name, "Pentium II"; the Intel logo; a hologram; and the model number. The front consists of a black anodized aluminum plate, which is used to hold the CPU cooler. The SECC form is very solid, because the CPU itself is resting safely inside the case. As compared to socket-based CPUs, there are no pins that can be bent, and the CPU is less likely to be damaged by improper installation of a cooler.
The Single Edge Contact Cartridge, or "SECC", was used at the beginning of the Slot 1-era for Pentium II CPUs. Inside the cartridge, the CPU itself is enclosed in a hybrid plastic and metal case. The back of the housing is plastic and has several markings on it: the name, "Pentium II"; the Intel logo; a hologram; and the model number. The front consists of a black anodized aluminum plate, which is used to hold the CPU cooler. The SECC form is very solid, because the CPU itself is resting safely inside the case. As compared to socket-based CPUs, there are no pins that can be bent, and the CPU is less likely to be damaged by improper installation of a cooler.
Following SECC, the SEPP-form (Single Edge Processor Package) appeared on the market. It was designed for lower-priced Celeron CPUs. This form lacks a case entirely, consisting solely of the printed-circuit board holding the components.
The Pentium III processors also use a protective case, renamed SECC2. The only item to be carried forward from the old SECC form is the backplate. The CPU lies free and, as with Celerons, the heatsink lies directly on the core.
-CPUs: Socket 8, Slot 1 and Socket 370.
Slot 1 is a successor to Socket 8
. While the Socket 8 CPUs (Pentium Pro) directly had the L2-cache embedded into the CPU, it is located (outside of the core) on a circuit board shared with the core itself. The exception is later Slot 1 CPUs with the Coppermine core which have the L2-Cache embedded into the die.
In the beginning of 2000, while the Pentium-III-CPUs with FC-PGA
-housing appeared, Slot 1 was slowly succeeded by Socket 370
, after Intel had already offered Socket 370 and Slot 1 at the same time since the beginning of 1999. Socket 370 was initially made for the low-cost Celeron processors, while Slot 1 was thought of as a platform for the expensive Pentium II and early Pentium III models. Cache and core were both embedded into the die.
Slot 1 also obsoleted the old Socket 7
, at least regarding Intel, as the standard platform for the home-user. After abandoning the Intel P5
Pentium MMX CPU, Intel completely left the Socket 7 market to the manufacturers AMD, Cyrix and IDT.

Intel Corporation
Intel Corporation is an American multinational semiconductor chip maker corporation headquartered in Santa Clara, California, United States and the world's largest semiconductor chip maker, based on revenue. It is the inventor of the x86 series of microprocessors, the processors found in most...
's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro
Pentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel introduced in November 1, 1995 . It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications...
, Celeron
Celeron
Celeron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers....
, Pentium II
Pentium II
The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million...
and the Pentium III
Pentium III
The Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile microprocessors based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 26, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded microprocessors...
. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented.
General
With the introduction of the Pentium II CPU, the need for greater access for testing had made the transition from socket to slot necessary. Previously with the Pentium ProPentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel introduced in November 1, 1995 . It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications...
, Intel had combined processor and cache dies in the same Socket 8
Socket 8
The Socket 8 CPU socket was used exclusively with the Intel Pentium Pro and Pentium II Overdrive computer processors. Intel discontinued Socket 8 in favor of Slot 1 with the introduction of the Pentium II.-Technical specifications:...
package. These were connected by a full-speed bus, resulting in significant performance benefits. Unfortunately, this method required that the two components be bonded together early in the production process, before testing was possible. As a result, a single, tiny flaw in either die made it necessary to discard the entire assembly, causing low production yield and high cost.
Intel subsequently designed a circuit board where the CPU and cache remained closely integrated, but were mounted on a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
, called a Single-Edged Contact Cartridge (SECC). The CPU and cache could be tested separately, before final assembly into a package, reducing cost and making the CPU more attractive to markets other than that of high-end servers. These cards could also be easily plugged into a Slot 1, thereby eliminating the chance for pins of a typical CPU to be bent or broken when installing in a socket.
The form factor used for Slot 1 was a 5-inch-long, 242-contact edge connector
Edge connector
An edge connector is the portion of a printed circuit board consisting of traces leading to the edge of the board that are intended to plug into a matching socket. The edge connector is a money-saving device because it only requires a single discrete female connector , and they also tend to be...
named SC242. To prevent the cartridge from being inserted the wrong way, the slot was keyed to allow installation in only one direction. The SC232 was later used for AMD's Slot A
Slot A
Slot A refers to the physical and electrical specification for a 242-lead single-edge-connector used by early versions of AMD's Athlon processor.The Slot A connector allows for a higher bus rate than Socket 7 or Super Socket 7...
as well, and while the two slots were identical mechanically, they were electrically incompatible. To discourage Slot A users from trying to install a Slot 1 CPU, the connector was rotated 180 degrees on Slot A motherboards.
With the new Slot 1, Intel added support for symmetric multiprocessing
Symmetric multiprocessing
In computing, symmetric multiprocessing involves a multiprocessor computer hardware architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single shared main memory and are controlled by a single OS instance. Most common multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture...
(SMP). A maximum of two Pentium II or Pentium III CPUs can be used in a dual slot motherboard. The Celeron does not have official SMP support.
There are also converter cards, known as Slotket
Slotket
In computer hardware terminology, slotkets, also known as slockets, are adapters that allow socket-based microprocessors to be used on slot-based motherboards....
s, which hold a Socket 8
Socket 8
The Socket 8 CPU socket was used exclusively with the Intel Pentium Pro and Pentium II Overdrive computer processors. Intel discontinued Socket 8 in favor of Slot 1 with the introduction of the Pentium II.-Technical specifications:...
so that a Pentium Pro
Pentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel introduced in November 1, 1995 . It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications...
CPU can be used with Slot 1 motherboards. These specific converters, however, are rare. Another kind of slotket allows using a Socket 370 CPU in a Slot 1. Many of these latter devices are equipped with own voltage regulator modules, in order to supply the new CPU with a lower core voltage, which the motherboard would not otherwise allow.
Form Factors



Following SECC, the SEPP-form (Single Edge Processor Package) appeared on the market. It was designed for lower-priced Celeron CPUs. This form lacks a case entirely, consisting solely of the printed-circuit board holding the components.
The Pentium III processors also use a protective case, renamed SECC2. The only item to be carried forward from the old SECC form is the backplate. The CPU lies free and, as with Celerons, the heatsink lies directly on the core.
History
Historically, there are three platforms for the Intel P6P6 (microarchitecture)
The P6 microarchitecture is the sixth generation Intel x86 microarchitecture, implemented by the Pentium Pro microprocessor that was introduced in November 1995. It is sometimes referred to as i686. It was succeeded by the NetBurst microarchitecture in 2000, but eventually revived in the Pentium M...
-CPUs: Socket 8, Slot 1 and Socket 370.
Slot 1 is a successor to Socket 8
Socket 8
The Socket 8 CPU socket was used exclusively with the Intel Pentium Pro and Pentium II Overdrive computer processors. Intel discontinued Socket 8 in favor of Slot 1 with the introduction of the Pentium II.-Technical specifications:...
. While the Socket 8 CPUs (Pentium Pro) directly had the L2-cache embedded into the CPU, it is located (outside of the core) on a circuit board shared with the core itself. The exception is later Slot 1 CPUs with the Coppermine core which have the L2-Cache embedded into the die.
In the beginning of 2000, while the Pentium-III-CPUs with FC-PGA
Flip-chip pin grid array
Flip-chip pin grid array is a form of pin grid array integrated circuit packaging in which the die faces downwards on the top of the substrate with the back of the die exposed...
-housing appeared, Slot 1 was slowly succeeded by Socket 370
Socket 370
Socket 370 is a common format of CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number of pin holes in the socket for CPU pins...
, after Intel had already offered Socket 370 and Slot 1 at the same time since the beginning of 1999. Socket 370 was initially made for the low-cost Celeron processors, while Slot 1 was thought of as a platform for the expensive Pentium II and early Pentium III models. Cache and core were both embedded into the die.
Slot 1 also obsoleted the old Socket 7
Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by Intel, as well as compatibles made by Cyrix/IBM, AMD, IDT and others.Socket 7 was...
, at least regarding Intel, as the standard platform for the home-user. After abandoning the Intel P5
P5 (microarchitecture)
The original Pentium microprocessor was introduced on March 22, 1993. Its microarchitecture, deemed P5, was Intel's fifth-generation and first superscalar x86 microarchitecture. As a direct extension of the 80486 architecture, it included dual integer pipelines, a faster FPU, wider data bus,...
Pentium MMX CPU, Intel completely left the Socket 7 market to the manufacturers AMD, Cyrix and IDT.
Chipsets and officially supported CPUs


Intel 440FX
- Introduced in: May 6, 1996
- FSBFront side busA front-side bus is a computer communication interface often used in computers during the 1990s and 2000s.It typically carries data between the central processing unit and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge....
: 66 MHz - PIOProgrammed input/outputProgrammed input/output is a method of transferring data between the CPU and a peripheral such as a network adapter or an ATA storage device....
/WDMAWDMA (computer)The Word DMA interface was the fastest method used to transfer data between the computer and an ATA device until UDMA.... - Supported RAM type: EDO-DRAM
- Supported CPUs:
- Pentium ProPentium ProThe Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel introduced in November 1, 1995 . It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications...
- Pentium IIPentium IIThe Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million...
with 66 MHz FSB - CeleronCeleronCeleron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers....
(Covington, Mendocino)
- Pentium Pro
- Used in both Socket 8 (Pentium Pro) and Slot 1 (Pentium II, early Celerons)
- Does not support AGPAccelerated Graphics PortThe Accelerated Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Since 2004 AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express...
or SDRAMSDRAMSynchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs... - Allowed up to two CPUs for SMPSMP-In technology:* Shape memory polymers, in the field of chemical engineering.* Simulation Model Portability: A standard developed by ESA and ECSS for space mission simulators....
Intel 440LX
- Introduced in: August 27, 1997
- FSB: 66 MHz
- Supported RAM type: SDRAMSDRAMSynchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs...
- Supported CPUs: Pentium II, Celeron
- AGP 1x Mode
- UDMA/33
- Pentium IIPentium IIThe Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million...
with 66 MHz FSB - CeleronCeleronCeleron is a brand name given by Intel Corp. to a number of different x86 computer microprocessor models targeted at budget personal computers....
(Covington, Mendocino)
- Pentium II
- Introduced support for AGPAccelerated Graphics PortThe Accelerated Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Since 2004 AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express...
and SDRAMSDRAMSynchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs... - Allowed up to two CPUs for SMPSMP-In technology:* Shape memory polymers, in the field of chemical engineering.* Simulation Model Portability: A standard developed by ESA and ECSS for space mission simulators....
Intel 440BX
- Introduced in: April 1998
- FSB: 66 and 100 MHz (some motherboards supported overclocking to 133 MHz, allowing usage of Socket 370 CPUs using a SlocketSlotketIn computer hardware terminology, slotkets, also known as slockets, are adapters that allow socket-based microprocessors to be used on slot-based motherboards....
) - AGP 2x Mode
- UDMA/33
- Supported RAM types: SDRAMSDRAMSynchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs...
(PC66PC66PC66 refers to internal removable computer memory standard defined by the JEDEC. PC66 is Synchronous DRAM operating at a clock frequency of 66.66 MHz, on a 64-bit bus, at a voltage of 3.3 V. PC66 is available in 168 pin DIMM and 144 pin SO-DIMM form factors. The theoretical bandwidth is...
and PC100PC100PC100 is a standard for internal removable computer random access memory, defined by the JEDEC. PC100 refers to Synchronous DRAM operating at a clock frequency of 100 MHz, on a 64-bit-wide bus, at a voltage of 3.3 V. PC100 is available in 168-pin DIMM and 144-pin SO-DIMM form factors...
, PC133PC133PC133 is a computer memory standard defined by the JEDEC. PC133 refers to Synchronous DRAM operating at a clock frequency of 133 MHz, on a 64-bit-wide bus, at a voltage of 3.3 V. PC133 is available in 168 pin DIMM and 144 pin SO-DIMM form factors...
with overclocking) - Supported CPUs:
- Pentium IIPentium IIThe Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB - Pentium IIIPentium IIIThe Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile microprocessors based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 26, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded microprocessors...
with 100 MHz FSB (133 with overclocking) - Celeron (Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
- Pentium II
- Allowed up to two CPUs for SMPSMP-In technology:* Shape memory polymers, in the field of chemical engineering.* Simulation Model Portability: A standard developed by ESA and ECSS for space mission simulators....
Intel 440ZX
- Introduced in: November 1998
- FSB: 66 and 100 MHz (some motherboards supported overclocking to 133 MHz, allowing usage of Socket 370 CPUs using a SlocketSlotketIn computer hardware terminology, slotkets, also known as slockets, are adapters that allow socket-based microprocessors to be used on slot-based motherboards....
) - AGP 2x Mode
- UDMA/33
- Supported RAM types: SDRAMSDRAMSynchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs...
(PC66PC66PC66 refers to internal removable computer memory standard defined by the JEDEC. PC66 is Synchronous DRAM operating at a clock frequency of 66.66 MHz, on a 64-bit bus, at a voltage of 3.3 V. PC66 is available in 168 pin DIMM and 144 pin SO-DIMM form factors. The theoretical bandwidth is...
and PC100PC100PC100 is a standard for internal removable computer random access memory, defined by the JEDEC. PC100 refers to Synchronous DRAM operating at a clock frequency of 100 MHz, on a 64-bit-wide bus, at a voltage of 3.3 V. PC100 is available in 168-pin DIMM and 144-pin SO-DIMM form factors...
, PC133PC133PC133 is a computer memory standard defined by the JEDEC. PC133 refers to Synchronous DRAM operating at a clock frequency of 133 MHz, on a 64-bit-wide bus, at a voltage of 3.3 V. PC133 is available in 168 pin DIMM and 144 pin SO-DIMM form factors...
with overclocking) - Supported CPUs:
- Pentium IIPentium IIThe Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB - Pentium IIIPentium IIIThe Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile microprocessors based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 26, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded microprocessors...
with 100 MHz FSB (133 with overclocking) - Celeron (Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
- Pentium II
Intel 820/820E (Camino)
- Introduced in: November 1999
- FSB: 66, 100, and 133 MHz
- AGP 4x Mode
- UDMA/66 (i820), UDMA/100 (i820E)
- Supported RAM types: RDRAMRDRAMDirect Rambus DRAM or DRDRAM is a type of synchronous dynamic RAM. RDRAM was developed by Rambus inc., in the mid-1990s as a replacement for then-prevalent DIMM SDRAM memory architecture....
, SDRAMSDRAMSynchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs...
(PC133) - Supported CPUs: All Slot 1 CPUs
- Allowed up to two CPUs for SMPSMP-In technology:* Shape memory polymers, in the field of chemical engineering.* Simulation Model Portability: A standard developed by ESA and ECSS for space mission simulators....
Via Apollo Pro / Pro+
- Introduced in: 1998?
- FSB: 66, 100 MHz (some motherboards supported overclocking to 133 MHz, allowing usage of Socket 370 CPUs using a SlocketSlotketIn computer hardware terminology, slotkets, also known as slockets, are adapters that allow socket-based microprocessors to be used on slot-based motherboards....
) - AGP 2x Mode
- UDMA/33 (VT82C586B/VT82C596A), UDMA/66 (VT82C596B)
- Supported CPUs:
- Pentium ProPentium ProThe Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel introduced in November 1, 1995 . It introduced the P6 microarchitecture and was originally intended to replace the original Pentium in a full range of applications...
with 66 MHz FSB - Pentium IIPentium IIThe Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors, the Pentium II featured an improved version of the first P6-generation core of the Pentium Pro, which contained 5.5 million...
with 66 and 100 MHz FSB - Pentium IIIPentium IIIThe Pentium III brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile microprocessors based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 26, 1999. The brand's initial processors were very similar to the earlier Pentium II-branded microprocessors...
with 100 MHz FSB (133 with overclocking) - Celeron (Covington, Mendocino, Coppermine)
- Pentium Pro
Via Apollo Pro 133
- Introduced in: July 1999
- FSB: 66, 100, and 133 MHz
- AGP 2x Mode
- UDMA/33 (VT82C596A), UDMA/66 (VT82C596B/VT82C686A), UDMA/100 (VT82C686B)
- Supported CPUs: All Slot 1 CPUs
Via Apollo Pro 133A
- Introduced in: Oct 1999
- FSB: 66, 100, and 133 MHz
- AGP 4x Mode
- UDMA/66 (VT82C596B/VT82C686A), UDMA/100 (VT82C686B)
- Supported CPUs: All Slot 1 CPUs
- Allowed up to two CPUs for SMPSMP-In technology:* Shape memory polymers, in the field of chemical engineering.* Simulation Model Portability: A standard developed by ESA and ECSS for space mission simulators....
Pentium III B and EB models
A special series of Pentium III for Slot 1 had an addition to its name (Pentium III EB). The "E" indicates a Coppermine core, and the "B" a 133 MHz FSB. Ironically, no consumer-oriented Intel chipset (except select few i820-based motherboards) officially supports a FSB of 133 MHz. To use this CPU, one must either use the VIA Apollo Pro 133A chipset, an Intel 800-series chipset (which was relatively expensive and often required RDRAM, limiting it to high-end workstations or servers), or the Intel 440BX outside of its specifications (which, on some motherboards, is indeed possibly stable).External links
- Picture of a Socket 8 to Slot 1 Slocket adapter
- [ftp://download.intel.com/design/PentiumII/applnots/24339702.PDF Intel's specifications for the SC242 connectors]
- Intel's detailed Slot 1 CPU (Coppermine) information, including Slot 1 pinout
- An image of a motherboard with Slot 1 connector
- An image of a Pentium II processor

