
Battle of Varna
Encyclopedia
The Battle of Varna took place on November 10, 1444 near Varna
in eastern Bulgaria
. In this battle the Ottoman Empire
under Sultan
Murad II
defeated the Polish
and Hungarian
armies under Władysław III of Poland and János Hunyadi
. It was the final battle of the Crusade of Varna
.
and Transylvania
, and the defeats of the "long campaign" of Janos Hunyadi in 1442–3, the Ottoman sultan Murad II signed a ten-year truce
with Hungary. After he had made peace with the Karaman Emirate in Anatolia
in August 1444, he resigned the throne to his twelve year-old son Mehmed II
.
Anticipating a new Islamic invasion, Hungary co-operated with Venice
and the pope
, Eugene IV
, to organize a new crusader army. On this news Murad was recalled to the throne by his son to reclaim the throne and lead the army into battle.
, Papal knights, Teutonic Knights
, Bosnians
, Croatians
, Bulgarians
, Lithuanians
, Serbs
and Ruthenians
(Ukrainians
)
Papal, Venetian and Genoese ships had blockaded the Dardanelles
as the Hungarian army was to advance on Varna, where it would meet the Papal fleet and sail down the coast to Constantinople, pushing the Ottomans out of Europe. The Hungarian advance was rapid, Ottoman fortresses were bypassed, while local Bulgarians from Vidin
, Oryahovo
, and Nicopolis
joined the army (Fruzhin
, son of Ivan Shishman, also participated in the campaign with his own guard). On October 10 near Nicopolis, some 4,000 Wallachian cavalrymen under Mircea II, one of Vlad Dracul's sons, also joined.
Refugee Armenians
in Hungary also took part in the wars of their new country against the Ottomans
as early as the battle of Varna in 1444, when some Armenians
were seen amongst the Christian forces.
of around 50,000 men approached Varna from the west. At a supreme military council called by Hunyadi during the night, the Papal legate
, cardinal
Julian Cesarini, insisted on a quick withdrawal. However, the Christians were caught between the Black Sea
, Lake Varna
, the steep wooded slopes of the Franga plateau (356 m high), and the enemy. Cesarini then proposed a defense using the Wagenburg of the Hussite
s until the arrival of the Christian fleet. The Hungarian magnates and the Croatian and Czech commanders backed him, but the young (20-year-old) Władysław and Hunyadi rejected the defensive tactics. Hunyadi declared: "To escape is impossible, to surrender is unthinkable. Let us fight with bravery and honor our arms." Władysław accepted this position and gave him the command. Andreas del Palatio states that Hunyadi commanded the "Wallachian army" indicating a large Romanian component in Hunyadi's personal army.
In the morning of November 10, Hunyadi deployed the army of some 20,000 crusaders
as an arc between Lake Varna and the Franga plateau; the line was about 3.5 km long. Two banners with a total of 3,500 men from the king's Polish and Hungarian bodyguards, Hungarian royal mercenaries, and banners of Hungarian nobles held the center. The Wallachian cavalry was left in reserve behind the center.
The right flank that lined up the hill towards the village of Kamenar numbered 6,500 men in 5 banners. Bishop Jan Dominek of Varadin with his personal banner led the force; Cesarini commanded a banner of German mercenaries and a Bosnian one. The Bishop of Eger led his own banner, and the military governor of Slavonia
, ban Franco Talotsi, commanded one Croatian banner.
The left flank, a total of 5,000 men in 5 banners, was led by Michael Szilágyi, Hunyadi's brother in law, and was made up of Hunyadi's Transylvanians, Bulgarians, German mercenaries and banners of Hungarian magnates. Behind the Hungarians, closer to the Black Sea and the lake, was the Wagenburg, defended by 300 or 600 Czech and Ruthenian
mercenaries under hetman Ceyka, along with Poles, Lithuanians and Wallachians. Every wagon was manned by 7 to 10 soldiers and the Wagenburg was equipped with bombards
.
The Ottoman center included the Janissaries and levies from Rumelia
deployed around two Thracian
burial mounds. Murad observed and directed the battle from one of them. The Janissaries dug in behind ditches and two palisades. The right wing consisted of Kapikulus and Sipahis from Rumelia
, and the left wing was made up by Akıncı
s, Sipahis from Anatolia
, and other forces. Janissary archers and Akıncı light cavalry were deployed on the Franga plateau.
 The light Ottoman cavalry assaulted the Croats of ban Talotsi. Christians from the left riposted with bombards and firearms and stopped the attack. Christian soldiers chased the Ottomans in a disorderly pursuit. The Anatolian cavalry ambushed them from the flank. The Christian right wing attempted to flee to the small fortress of Galata on the other side of Varna Bay, but most of them were slain in the marshland around Varna Lake and the river Devnya, where Cesarini also met his end. Only ban Talotsi's troops managed to withdraw behind the Wagenburg.
The light Ottoman cavalry assaulted the Croats of ban Talotsi. Christians from the left riposted with bombards and firearms and stopped the attack. Christian soldiers chased the Ottomans in a disorderly pursuit. The Anatolian cavalry ambushed them from the flank. The Christian right wing attempted to flee to the small fortress of Galata on the other side of Varna Bay, but most of them were slain in the marshland around Varna Lake and the river Devnya, where Cesarini also met his end. Only ban Talotsi's troops managed to withdraw behind the Wagenburg.
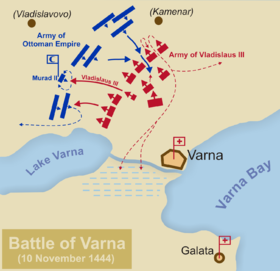 The other Ottoman flank assaulted the Hungarians and Bulgarians of Michael Szilagyi. Their push was stopped and turned back; then Sipahis attacked again. Hunyadi decided to help and advised Władysław to wait until he returned; then advanced with two cavalry companies. The young king, ignoring Hunyadi's advice, rushed 500 of his Polish knights against the Ottoman center. They attempted to overrun the Janissary infantry and take Murad prisoner, and almost succeeded. But Władysław had fallen in a pitfall in front of Murad's tent and slain by the Janissary
The other Ottoman flank assaulted the Hungarians and Bulgarians of Michael Szilagyi. Their push was stopped and turned back; then Sipahis attacked again. Hunyadi decided to help and advised Władysław to wait until he returned; then advanced with two cavalry companies. The young king, ignoring Hunyadi's advice, rushed 500 of his Polish knights against the Ottoman center. They attempted to overrun the Janissary infantry and take Murad prisoner, and almost succeeded. But Władysław had fallen in a pitfall in front of Murad's tent and slain by the Janissary
bodyguards, his head was cut off and later taken to the Ottoman court. The remaining Polish cavalry was smashed by the Ottomans.
On his return, Hunyadi tried frantically to salvage the king's body but all he could accomplish was to organize the retreat of the remains of his army. It suffered thousands of casualties, and was virtually annihilated. Many European prisoners were slaughtered or sold as slaves; the minnesinger
Michael Beheim wrote a song based on the story of one Hans Mergest who spent 16 years in Ottoman captivity after the battle.
. The defeat also set the stage for the fall of Constantinople
in 1453.
 In the aftermath the Ottomans had removed a significant opposition to their expansion into central and eastern Europe, subsequent battles allowed a huge number of European people to become Ottoman subjects.
In the aftermath the Ottomans had removed a significant opposition to their expansion into central and eastern Europe, subsequent battles allowed a huge number of European people to become Ottoman subjects.
Varna
Varna is the largest city and seaside resort on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast and third-largest in Bulgaria after Sofia and Plovdiv, with a population of 334,870 inhabitants according to Census 2011...
in eastern Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
. In this battle the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
under Sultan
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
Murad II
Murad II
Murad II Kodja was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1421 to 1451 ....
defeated the Polish
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
and Hungarian
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
armies under Władysław III of Poland and János Hunyadi
John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi John Hunyadi (Hungarian: Hunyadi János , Medieval Latin: Ioannes Corvinus or Ioannes de Hunyad, Romanian: Iancu (Ioan) de Hunedoara, Croatian: Janko Hunjadi, Serbian: Сибињанин Јанко / Sibinjanin Janko, Slovak: Ján Huňady) John Hunyadi (Hungarian: Hunyadi János , Medieval Latin: ...
. It was the final battle of the Crusade of Varna
Crusade of Varna
The Crusade of Varna was a string of events in 1443–44 between the Kingdom of Hungary, the Serbian Despotate, the Principality of Wallachia and the Ottoman Empire...
.
Background
After failed expeditions in 1440–2 against BelgradeBelgrade
Belgrade is the capital and largest city of Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers, where the Pannonian Plain meets the Balkans. According to official results of Census 2011, the city has a population of 1,639,121. It is one of the 15 largest cities in Europe...
and Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
, and the defeats of the "long campaign" of Janos Hunyadi in 1442–3, the Ottoman sultan Murad II signed a ten-year truce
Peace of Szeged
The Treaty of Edirne and the Peace of Szeged were two halves of a peace treaty between Sultan Murad II of the Ottoman Empire and King Vladislaus of the Kingdom of Hungary. Despot Đurađ Branković of the Serbian Despotate also had a large role in the proceedings...
with Hungary. After he had made peace with the Karaman Emirate in Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
in August 1444, he resigned the throne to his twelve year-old son Mehmed II
Mehmed II
Mehmed II , was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire for a short time from 1444 to September 1446, and later from...
.
Anticipating a new Islamic invasion, Hungary co-operated with Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
and the pope
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
, Eugene IV
Pope Eugene IV
Pope Eugene IV , born Gabriele Condulmer, was pope from March 3, 1431, to his death.-Biography:He was born in Venice to a rich merchant family, a Correr on his mother's side. Condulmer entered the Order of Saint Augustine at the monastery of St. George in his native city...
, to organize a new crusader army. On this news Murad was recalled to the throne by his son to reclaim the throne and lead the army into battle.
Preparations
A mixed Papal army consisting mainly of Hungarian, Polish (whose combined armies numbered 15,000) and Wallchian (4,000) forces, with smaller detachments of CzechsCzech people
Czechs, or Czech people are a western Slavic people of Central Europe, living predominantly in the Czech Republic. Small populations of Czechs also live in Slovakia, Austria, the United States, the United Kingdom, Chile, Argentina, Canada, Germany, Russia and other countries...
, Papal knights, Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem , commonly the Teutonic Order , is a German medieval military order, in modern times a purely religious Catholic order...
, Bosnians
Bosnians
Bosnians are people who reside in, or come from, Bosnia and Herzegovina. By the modern state definition a Bosnian can be anyone who holds citizenship of the state. This includes, but is not limited to, members of the constituent ethnic groups of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Bosniaks, Bosnian Serbs and...
, Croatians
Croats
Croats are a South Slavic ethnic group mostly living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and nearby countries. There are around 4 million Croats living inside Croatia and up to 4.5 million throughout the rest of the world. Responding to political, social and economic pressure, many Croats have...
, Bulgarians
Bulgarians
The Bulgarians are a South Slavic nation and ethnic group native to Bulgaria and neighbouring regions. Emigration has resulted in immigrant communities in a number of other countries.-History and ethnogenesis:...
, Lithuanians
Lithuanians
Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language...
, Serbs
Serbs
The Serbs are a South Slavic ethnic group of the Balkans and southern Central Europe. Serbs are located mainly in Serbia, Montenegro and Bosnia and Herzegovina, and form a sizable minority in Croatia, the Republic of Macedonia and Slovenia. Likewise, Serbs are an officially recognized minority in...
and Ruthenians
Ruthenians
The name Ruthenian |Rus']]) is a culturally loaded term and has different meanings according to the context in which it is used. Initially, it was the ethnonym used for the East Slavic peoples who lived in Rus'. Later it was used predominantly for Ukrainians...
(Ukrainians
Ukrainians
Ukrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens...
)
Papal, Venetian and Genoese ships had blockaded the Dardanelles
Dardanelles
The Dardanelles , formerly known as the Hellespont, is a narrow strait in northwestern Turkey connecting the Aegean Sea to the Sea of Marmara. It is one of the Turkish Straits, along with its counterpart the Bosphorus. It is located at approximately...
as the Hungarian army was to advance on Varna, where it would meet the Papal fleet and sail down the coast to Constantinople, pushing the Ottomans out of Europe. The Hungarian advance was rapid, Ottoman fortresses were bypassed, while local Bulgarians from Vidin
Vidin
Vidin is a port town on the southern bank of the Danube in northwestern Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Serbia and Romania, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as of the Metropolitan of Vidin...
, Oryahovo
Oryahovo
Oryahovo is a port city in northwestern Bulgaria, part of Vratsa Province. It is located in a hilly country on the right bank of the Danube, just east of the mouth of the river Ogosta, a few more kilometres downstream from where the Jiu flows into the Danube on Romanian territory. The town is...
, and Nicopolis
Nikopol, Bulgaria
Nikopol is a town in northern Bulgaria, the administrative center of Nikopol municipality, part of Pleven Province, on the right bank of the Danube river, 4 km downstream from the mouth of the Osam river. It spreads at the foot of steep chalk cliffs along the Danube and up a narrow valley...
joined the army (Fruzhin
Fruzhin
Fruzhin was a 15th-century Bulgarian noble who fought actively against the Ottoman conquest of the Second Bulgarian Empire. A son of one of the last Bulgarian tsars, Ivan Shishman of the Tarnovo Tsardom, Fruzhin co-organized the so-called Uprising of Konstantin and Fruzhin along with Constantine...
, son of Ivan Shishman, also participated in the campaign with his own guard). On October 10 near Nicopolis, some 4,000 Wallachian cavalrymen under Mircea II, one of Vlad Dracul's sons, also joined.
Refugee Armenians
Armenians
Armenian people or Armenians are a nation and ethnic group native to the Armenian Highland.The largest concentration is in Armenia having a nearly-homogeneous population with 97.9% or 3,145,354 being ethnic Armenian....
in Hungary also took part in the wars of their new country against the Ottomans
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
as early as the battle of Varna in 1444, when some Armenians
Armenians
Armenian people or Armenians are a nation and ethnic group native to the Armenian Highland.The largest concentration is in Armenia having a nearly-homogeneous population with 97.9% or 3,145,354 being ethnic Armenian....
were seen amongst the Christian forces.
Deployment
Late on November 9, a large Ottoman armyMilitary of the Ottoman Empire
The history of military of the Ottoman Empire can be divided in five main periods. The foundation era covers the years between 1300 and 1453 , the classical period covers the years between 1451 and 1606 , the reformation period covers the years between 1606 and 1826 ,...
of around 50,000 men approached Varna from the west. At a supreme military council called by Hunyadi during the night, the Papal legate
Papal legate
A papal legate – from the Latin, authentic Roman title Legatus – is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic Church. He is empowered on matters of Catholic Faith and for the settlement of ecclesiastical matters....
, cardinal
Cardinal (Catholicism)
A cardinal is a senior ecclesiastical official, usually an ordained bishop, and ecclesiastical prince of the Catholic Church. They are collectively known as the College of Cardinals, which as a body elects a new pope. The duties of the cardinals include attending the meetings of the College and...
Julian Cesarini, insisted on a quick withdrawal. However, the Christians were caught between the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
, Lake Varna
Lake Varna
Lake Varna is the largest by volume and deepest liman or lake along the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, divided from the sea by a 2 km-wide strip of sand and having an area of 17 km², maximal depth 19 m, and a volume of 166 million m³....
, the steep wooded slopes of the Franga plateau (356 m high), and the enemy. Cesarini then proposed a defense using the Wagenburg of the Hussite
Hussite
The Hussites were a Christian movement following the teachings of Czech reformer Jan Hus , who became one of the forerunners of the Protestant Reformation...
s until the arrival of the Christian fleet. The Hungarian magnates and the Croatian and Czech commanders backed him, but the young (20-year-old) Władysław and Hunyadi rejected the defensive tactics. Hunyadi declared: "To escape is impossible, to surrender is unthinkable. Let us fight with bravery and honor our arms." Władysław accepted this position and gave him the command. Andreas del Palatio states that Hunyadi commanded the "Wallachian army" indicating a large Romanian component in Hunyadi's personal army.
In the morning of November 10, Hunyadi deployed the army of some 20,000 crusaders
Crusaders
The Crusaders are a New Zealand professional rugby union team based in Christchurch that competes in the Super Rugby competition. They are the most successful team in Super Rugby history with seven titles...
as an arc between Lake Varna and the Franga plateau; the line was about 3.5 km long. Two banners with a total of 3,500 men from the king's Polish and Hungarian bodyguards, Hungarian royal mercenaries, and banners of Hungarian nobles held the center. The Wallachian cavalry was left in reserve behind the center.
The right flank that lined up the hill towards the village of Kamenar numbered 6,500 men in 5 banners. Bishop Jan Dominek of Varadin with his personal banner led the force; Cesarini commanded a banner of German mercenaries and a Bosnian one. The Bishop of Eger led his own banner, and the military governor of Slavonia
Slavonia
Slavonia is a geographical and historical region in eastern Croatia...
, ban Franco Talotsi, commanded one Croatian banner.
The left flank, a total of 5,000 men in 5 banners, was led by Michael Szilágyi, Hunyadi's brother in law, and was made up of Hunyadi's Transylvanians, Bulgarians, German mercenaries and banners of Hungarian magnates. Behind the Hungarians, closer to the Black Sea and the lake, was the Wagenburg, defended by 300 or 600 Czech and Ruthenian
Ruthenians
The name Ruthenian |Rus']]) is a culturally loaded term and has different meanings according to the context in which it is used. Initially, it was the ethnonym used for the East Slavic peoples who lived in Rus'. Later it was used predominantly for Ukrainians...
mercenaries under hetman Ceyka, along with Poles, Lithuanians and Wallachians. Every wagon was manned by 7 to 10 soldiers and the Wagenburg was equipped with bombards
Bombard (weapon)
A bombard is a large-caliber, muzzle-loading medieval cannon or mortar, used chiefly in sieges for throwing heavy stone balls. The name bombarde was first noted and sketched in a French historical text around 1380. The modern term bombardment derives from this.Bombards were usually used during...
.
The Ottoman center included the Janissaries and levies from Rumelia
Rumelia
Rumelia was an historical region comprising the territories of the Ottoman Empire in Europe...
deployed around two Thracian
Thracians
The ancient Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting areas including Thrace in Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Thracian language – a scarcely attested branch of the Indo-European language family...
burial mounds. Murad observed and directed the battle from one of them. The Janissaries dug in behind ditches and two palisades. The right wing consisted of Kapikulus and Sipahis from Rumelia
Rumelia
Rumelia was an historical region comprising the territories of the Ottoman Empire in Europe...
, and the left wing was made up by Akıncı
Akinci
Akıncı were irregular light cavalry,scout divisions and advance troops of the Ottoman Empire's military. When the pre-existing Turkish ghazis were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire's military they became known as "akıncı." They were one of the first divisions to face the opposing military and...
s, Sipahis from Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
, and other forces. Janissary archers and Akıncı light cavalry were deployed on the Franga plateau.
The battle


Janissary
The Janissaries were infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops and bodyguards...
bodyguards, his head was cut off and later taken to the Ottoman court. The remaining Polish cavalry was smashed by the Ottomans.
On his return, Hunyadi tried frantically to salvage the king's body but all he could accomplish was to organize the retreat of the remains of his army. It suffered thousands of casualties, and was virtually annihilated. Many European prisoners were slaughtered or sold as slaves; the minnesinger
Minnesang
Minnesang was the tradition of lyric and song writing in Germany which flourished in the 12th century and continued into the 14th century. People who wrote and performed Minnesang are known as Minnesingers . The name derives from the word minne, Middle High German for love which was their main...
Michael Beheim wrote a song based on the story of one Hans Mergest who spent 16 years in Ottoman captivity after the battle.
Aftermath
The death of Władysław left Hungary in the hands of the four-year-old Ladislaus Posthumous of Bohemia and HungaryLadislas the Posthumous
Ladislaus the Posthumous was Duke of Austria from 1440, King of Hungary from 1444 and King of Bohemia from 1453.- Biography :...
. The defeat also set the stage for the fall of Constantinople
Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire, which occurred after a siege by the Ottoman Empire, under the command of Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II, against the defending army commanded by Byzantine Emperor Constantine XI...
in 1453.
Legacy

External links
- Battle map (Hungarian)
- Ervin Liptai (1984), Magyarország hadtörténete I. Zrínyi Katonai Kiadó, Budapest. ISBN 963-326-320-4
- Battle of Varna animated battle map by Jonathan Webb

