Banert cascade
Encyclopedia
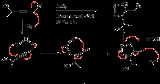
The Banert cascade is an organic reaction
in which an NH-1,2,3-triazole
is prepared from a propargyl
halide
or sulfate
and sodium azide
in a dioxane- water mixture at elevated temperatures. This cascade reaction
is unusual because it consists of two consecutive rearrangement reaction
s.
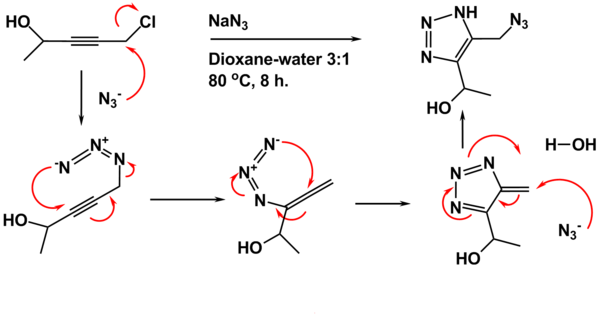 The starting material is prepared from propargyl chloride
The starting material is prepared from propargyl chloride
and an aldehyde
or ketone
such as acetaldehyde
. In the first step an azido compound is formed in situ
in a nucleophilic displacement
of chloride by the azide
ion. A (3,3)Sigmatropic reaction
takes place between the azide
and the alkyne
to the allenyl azide. This allene
rearranges to the triazafulvene in a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
. The exocyclic alkene
in this intermediate is very electrophilic because the triazole group has a dipole moment
of 5 debye
. The reaction sequence concludes with nucleophilic attack
of a second azide ion on this alkene with more double bond rearrangements and proton abstraction from a proton source.
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
in which an NH-1,2,3-triazole
1,2,3-Triazole
1,2,3-Triazole is one of a pair of isomeric chemical compounds with molecular formula C2H3N3, called triazoles, which have a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms...
is prepared from a propargyl
Propargyl
In organic chemistry, propargyl is an alkyl functional group of 2-propynyl with the structure HC≡C−CH2−, derived from the alkyne propyne.The term propargylic refers to a saturated position on a molecular framework next to an alkynyl group...
halide
Halide
A halide is a binary compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, or astatide compound. Many salts are halides...
or sulfate
Sulfate
In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
and sodium azide
Sodium azide
Sodium azide is the inorganic compound with the formula NaN3. This colourless azide salt is the gas-forming component in many car airbag systems. It is used for the preparation of other azide compounds. It is an ionic substance and is highly soluble in water. It is extremely...
in a dioxane- water mixture at elevated temperatures. This cascade reaction
Cascade reaction
A cascade reaction or tandem reaction or domino reaction is a consecutive series of intramolecular organic reactions which often proceed via highly reactive intermediates. It allows the organic synthesis of complex multinuclear molecules from a single acyclic precursor. The substrate contains many...
is unusual because it consists of two consecutive rearrangement reaction
Rearrangement reaction
A rearrangement reaction is a broad class of organic reactions where the carbon skeleton of a molecule is rearranged to give a structural isomer of the original molecule. Often a substituent moves from one atom to another atom in the same molecule...
s.

Propargyl chloride
Propargyl chloride, or 3-chloro-1-propyne, is a highly toxic and flammable clear brown liquid with chemical formula CHCCH2Cl. It is miscible with benzene or ethanol and insoluble in water. Its refractive index is 1.4350...
and an aldehyde
Aldehyde
An aldehyde is an organic compound containing a formyl group. This functional group, with the structure R-CHO, consists of a carbonyl center bonded to hydrogen and an R group....
or ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
such as acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO or MeCHO. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale industrially. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants as part...
. In the first step an azido compound is formed in situ
In situ
In situ is a Latin phrase which translated literally as 'In position'. It is used in many different contexts.-Aerospace:In the aerospace industry, equipment on board aircraft must be tested in situ, or in place, to confirm everything functions properly as a system. Individually, each piece may...
in a nucleophilic displacement
Nucleophilic substitution
In organic and inorganic chemistry, nucleophilic substitution is a fundamental class of reactions in which an electron nucleophile selectively bonds with or attacks the positive or partially positive charge of an atom or a group of atoms called the leaving group; the positive or partially positive...
of chloride by the azide
Azide
Azide is the anion with the formula N3−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid. N3− is a linear anion that is isoelectronic with CO2 and N2O. Per valence bond theory, azide can be described by several resonance structures, an important one being N−=N+=N−...
ion. A (3,3)Sigmatropic reaction
Sigmatropic reaction
A sigmatropic reaction in organic chemistry is a pericyclic reaction wherein the net result is one σ-bond is changed to another σ-bond in an uncatalyzed intramolecular process. The name sigmatropic is the result of a compounding of the long-established sigma designation from single carbon-carbon...
takes place between the azide
Azide
Azide is the anion with the formula N3−. It is the conjugate base of hydrazoic acid. N3− is a linear anion that is isoelectronic with CO2 and N2O. Per valence bond theory, azide can be described by several resonance structures, an important one being N−=N+=N−...
and the alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
to the allenyl azide. This allene
Allene
An allene is a compound in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon centres. Allenes are classified as polyenes with cumulated dienes. The parent compound of allene is propadiene. Compounds with an allene-type structure but with more than three carbon atoms are...
rearranges to the triazafulvene in a 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
1,3-dipolar cycloaddition
The 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition, also known as the Huisgen cycloaddition or Huisgen reaction, is an organic chemical reaction belonging to the larger class of concerted, pericyclic cycloadditions. It is the reaction between a 1,3-dipole and a dipolarophile, most of which are substituted alkenes, to...
. The exocyclic alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
in this intermediate is very electrophilic because the triazole group has a dipole moment
Dipole moment
Dipole moment can be defined as the product of magnitude of charge & distance of separation between the charges.Dipole moment may refer to:*Electric dipole moment, the measure of the electrical polarity of a system of charges...
of 5 debye
Debye
The debye is a CGS unit of electric dipole momentElectric dipole moment is defined as charge times displacement: Historically the debye was defined as the dipole moment resulting from two charges of opposite sign but an equal magnitude of 10-10 statcoulomb10-10 statcoulomb is approximately 0.2083...
. The reaction sequence concludes with nucleophilic attack
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
of a second azide ion on this alkene with more double bond rearrangements and proton abstraction from a proton source.

