80th parallel north
Encyclopedia
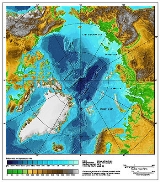
The 80th parallel north is a circle of latitude
that is 80 degrees
north
of the Earth's
equatorial plane
, in the Arctic
. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean
, Europe
, Asia
, the Arctic Ocean
and North America
.
Starting at the Prime Meridian
and heading eastwards, the parallel 80° north passes through:
Circle of latitude
A circle of latitude, on the Earth, is an imaginary east-west circle connecting all locations that share a given latitude...
that is 80 degrees
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
north
True north
True north is the direction along the earth's surface towards the geographic North Pole.True geodetic north usually differs from magnetic north , and from grid north...
of the Earth's
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
equatorial plane
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
, in the Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, the Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
and North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
.
Starting at the Prime Meridian
Prime Meridian
The Prime Meridian is the meridian at which the longitude is defined to be 0°.The Prime Meridian and its opposite the 180th meridian , which the International Date Line generally follows, form a great circle that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.An international...
and heading eastwards, the parallel 80° north passes through:
| Co-ordinates | Country, territory or sea | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 80°0′N 0°0′E | Atlantic Ocean Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area... |
Greenland Sea Greenland Sea The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the... |
| 80°0′N 15°58′E | Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... - island of Spitsbergen Spitsbergen Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. Constituting the western-most bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea... |
|
| 80°0′N 16°33′E | Atlantic Ocean Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area... |
Greenland Sea Greenland Sea The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the... |
| 80°0′N 18°38′E | Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... - island of Nordaustlandet Nordaustlandet Nordaustlandet is the second-largest island in the archipelago of Svalbard, Norway, with an area of . It lies north east of Spitsbergen, separated by Hinlopenstretet. Much of Nordaustlandet lies under large ice caps, mainly Austfonna and Vestfonna, the remaining parts of the north being tundra... |
|
| 80°0′N 27°10′E | Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... |
Passing just south of the islands of Storøya and Kvitøya Kvitøya Kvitøya is an island in the Svalbard archipelago in the Arctic Ocean, with an area of . It is located at , making it the easternmost part of the Kingdom of Norway... , Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... , > Passing just south of Victoria Island Victoria Island (Russian Arctic) Victoria Island is a small Arctic island situated at 80°9'N 36°46'E, halfway between the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard and the Russian archipelago of Franz Josef Land. This westernmost of all Russian Arctic islands is about 14 km² and almost completely covered with ice... , |
| 80°0′N 50°34′E | Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... - Northbrook Island Northbrook Island Northbrook Island is an island located at in the southern edge of the Franz Josef Archipelago, Russia. Its highest point is 344 m.Northbrook Island is one of the most accessible locations in the island group... |
|
| 80°0′N 51°12′E | Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... |
|
| 80°0′N 58°47′E | Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... - Salm Island Salm Island Salm Island is a roughly round-shaped island in Franz Josef Land, Russia.Salm Island is almost completely glaciarized except for a cape in its southern shore. Its maximum length is 17 km and its area is 344 km²... |
|
| 80°0′N 60°0′E | Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... |
|
| 80°0′N 66°13′E | Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... |
|
| 80°0′N 91°18′E | Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... - Pioneer Island and October Revolution Island October Revolution Island October Revolution Island is the largest island of the Severnaya Zemlya group in the Russian Arctic.... |
|
| 80°0′N 99°20′E | Laptev Sea Laptev Sea The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy... |
|
| 80°0′N 105°40′E | Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... |
|
| 80°0′N 100°9′W | Nunavut Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... - Meighen Island Meighen Island Meighen Island is an uninhabited member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, part of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. Located at 79°55'N 99°30'W, it measures in size and is topped with an ice cap. The island is continuously icebound, and its northwestern... |
|
| 80°0′N 98°45′W | Sverdrup Channel Sverdrup Channel The Sverdrup Channel is an area of sea in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago within the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut. To the north-west of the channel is Meighen Island, to the east is Axel Heiberg Island, and to the south is Amund Ringnes Island. The Fay Islands are located in the channel.... |
|
| 80°0′N 96°37′W | Nunavut Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... - Axel Heiberg Island Axel Heiberg Island Axel Heiberg Island is an island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located in the Arctic Ocean, it is the 31st largest island in the world and Canada's seventh largest island. According to Statistics Canada, it has an area of .... |
|
| 80°0′N 87°9′W | Eureka Sound Eureka Sound Eureka Sound is a high Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk, Nunavut, Canada. It separates Axel Heiberg Island from Ellesmere Island. Stor Island is located within the sound. Eureka Sound is long, and wide. Fort Eureka is nearby.... |
|
| 80°0′N 86°12′W | Nunavut Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... - Fosheim Peninsula Fosheim Peninsula The Fosheim Peninsula is located in western Ellesmere Island, a part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Eureka, a permanent research community, is located on the north side of Slidre Fiord, a few kilometers east of Eureka Sound... , Ellesmere Island Ellesmere Island Ellesmere Island is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Lying within the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, it is considered part of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, with Cape Columbia being the most northerly point of land in Canada... |
|
| 80°0′N 82°44′W | Cañon Fiord Cañon Fiord Cañon Fiord is a natural inlet in the west of Ellesmere Island, Nunavut in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. To the north, it opens into Greely Fiord.... |
|
| 80°0′N 82°1′W | Nunavut Nunavut Nunavut is the largest and newest federal territory of Canada; it was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, though the actual boundaries had been established in 1993... - Ellesmere Island Ellesmere Island Ellesmere Island is part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Lying within the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, it is considered part of the Queen Elizabeth Islands, with Cape Columbia being the most northerly point of land in Canada... |
|
| 80°0′N 70°40′W | Nares Strait Nares Strait Nares Strait is a waterway between Ellesmere Island and Greenland that is the northern part of Baffin Bay where it meets the Lincoln Sea. From south to north, the strait includes Smith Sound, Kane Basin, Kennedy Channel, Hall Basin and Robeson Channel... |
|
| 80°0′N 65°3′W | ||
| 80°0′N 17°9′W | Atlantic Ocean Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area... |
Greenland Sea Greenland Sea The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the... |
See also
- 79th parallel north79th parallel northThe 79th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 79 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane, in the Arctic. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia, the Arctic Ocean and North America....
- 81st parallel north81st parallel northThe 81st parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 81 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane, in the Arctic. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia, the Arctic Ocean and North America....

