1852 Atlantic hurricane season
Encyclopedia
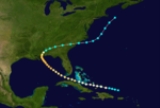
The 1852 Atlantic hurricane season was one of only four Atlantic hurricane seasons in which every known tropical cyclone
attained hurricane status. Five tropical cyclones were reported during the season, which lasted from late August through the middle of October; these dates fall within the range of most Atlantic tropical cyclone activity, and none of the cyclones coexisted with another. Though there were officially five tropical cyclones in the season, hurricane scholar Michael Chenoweth assessed two of the cyclones as being the same storm. There may have been other unconfirmed tropical cyclones during the season, as meteorologist Christopher Landsea
estimated that up to six storms were missed each year from the official database; this estimate was due to small tropical cyclone size, sparse ship reports, and relatively unpopulated coastlines.
Every tropical cyclone in the season was of hurricane status, or with winds at or exceeding 74 mph (119 km/h). In only three other seasons did every cyclone attain hurricane status; those years were 1858
, 1866
, and 1884
. All five cyclones affected land; the strongest was the first storm, which caused severe damage and loss of life when it made landfall
near the border between Mississippi
and Alabama
. The second storm of the season struck Puerto Rico
, where it caused over 100 deaths, primarily from flooding. In the middle of September, the third storm moved across Florida with strong wind gusts and light rainfall, and a week later the fourth storm passed over or north of the Lesser
and Greater Antilles
. The last storm hit the Florida Panhandle, though damage was less than expected.
. It moved on a west-northwest motion before passing through the Bahamas as it attained hurricane status on August 20. After paralleling the northern coast of Cuba
, the storm passed between the Dry Tortugas
and Key West, Florida
on August 22, and two days later it is estimated the hurricane attained peak winds of 115 mph (185 km/h). The storm slowed on August 25 before turning northward, and early on August 26 it made landfall
near Pascagoula, Mississippi
at peak strength, and the hurricane rapidly weakened to tropical storm status as it accelerated east-northeastward. On August 28 it emerged into the Atlantic Ocean from South Carolina
, and after turning to the northeast, it was last observed on August 30 about 130 mi (200 km) southeast of Cape Cod
.
In the Florida Keys
, rough waves forced several ships ashore, leaving some damaged. Strong waves created four new channels in the Chandeleur Islands
, and the storm's passage also destroyed the island lighthouse; the three keepers were found three days later. Two schooners were also washed ashore along Cat Island
. The hurricane produced an estimated storm tide
of 12 feet (3.7 m) in Mobile, Alabama
, where strong winds damaged much of the city, leaving the majority of the houses destroyed. Trees were downed up to 30 miles (50 km) inland, and coastal areas were flooded. Damage along the coastline was estimated at around $1 million (1852 USD, $26 million 2008 USD), and several lives were lost. While crossing the southeastern United States, the storm brought light rainfall but moderately strong winds; in Charleston, South Carolina
, the storm destroyed several bridges and crop fields.
on September 3. Tracking steadily west-northwestward, it quickly moved ashore near Ponce, Puerto Rico
with winds estimated at 80 mph (130 km/h). After crossing southwestern Puerto Rico, the hurricane emerged into the Mona Passage
as a tropical storm. Late on September 5 it made landfall on eastern Dominican Republic
; it quickly weakened over Hispaniola, dissipating on September 6 over the northwestern portion of the island. An assessment by scholar Michael Chenoweth in 2006 indicated this storm was the same as the next hurricane, with it continuing northwestward and ultimately reaching the Gulf of Mexico
. Due to not being considered the same cyclone in the official hurricane database
, this hurricane and the following hurricane are listed separately.
The cyclone is known as the San Lorenzo hurricane, due to its impact in Puerto Rico. There, the passage of the storm caused severe flooding, which destroyed large quantities of crops and damaged several roads. Storm damage was heaviest between Guayanilla
and Mayagüez
. More than 100 people were killed in Puerto Rico, many of which due to flooding.
on September 9, potentially the same hurricane as the previous storm. It tracked generally eastward toward the coast of Florida, with its hurricane intensity estimation based on two ship reports. At about 0000 UTC
on September 12, it moved ashore near Clearwater, Florida
as a minimal hurricane, with an estimated minimum barometric central pressure
of 985 mbar
. Accelerating east-northeastward while crossing the state, the cyclone emerged into the Atlantic Ocean as a weakened tropical storm before regaining hurricane status on September 13. Later that day, it was last observed about 250 mi (400 km) east-southeast of Cape Hatteras
.
A post in Fort Meade, Florida
reported at least 0.55 in (14 mm) of rainfall during the storm's passage. The hurricane was considered "violent", and gusts were estimated to have reached hurricane force. Rough seas and strong easterly winds beached a vessel near St. Augustine
.
. With a steady west-northwest path, the storm moved across the northern Lesser Antilles
on September 23, during which it intensified into a hurricane. It passed a short distance north of Puerto Rico
and the Dominican Republic
as it reached its peak intensity of 90 mph (150 km). Late on September 26 the hurricane turned northwestward, bringing it through the Turks and Caicos Islands
and eastern Bahamas. Recurving north-northeastward, the cyclone moved into open waters, and was last classified as a tropical cyclone on September 30 about 390 mi (630 km) east of Cape Hatteras
. However, one hurricane researcher assessed the hurricane as lasting until October 3, with the cyclone turning eastward and dissipating near the Azores
.
. Passing a short distance south of the island, the hurricane tracked northwestward and brushed the Yucatán Peninsula
before turning north-northeastward into the Gulf of Mexico
. Late on October 9, it made landfall a short distance east of Apalachicola, Florida
at peak winds with an estimated pressure of 969 mbar. Rapidly weakening to tropical storm status, the cyclone continued northeastward and emerged into the Atlantic Ocean from North Carolina on October 11. Later that day, it was last observed about 250 mi (400 km) southeast of Cape Cod.
Heavy damage was reported in Jamaica. Upon making landfall in Florida, the hurricane produced a 7 ft (2 m) storm tide
, and in Georgia
, hurricane force winds extended into the southwestern portion of the state, while tropical storm force winds occurred along the coastline. In the state, moderate winds damaged trees and roofs, though the destruction was less than anticipated.
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
attained hurricane status. Five tropical cyclones were reported during the season, which lasted from late August through the middle of October; these dates fall within the range of most Atlantic tropical cyclone activity, and none of the cyclones coexisted with another. Though there were officially five tropical cyclones in the season, hurricane scholar Michael Chenoweth assessed two of the cyclones as being the same storm. There may have been other unconfirmed tropical cyclones during the season, as meteorologist Christopher Landsea
Christopher Landsea
Christopher W. Landsea is an American meteorologist, formerly a research meteorologist with Hurricane Research Division of Atlantic Oceanographic & Meteorological Laboratory at NOAA, and now the Science and Operations Officer at the National Hurricane Center...
estimated that up to six storms were missed each year from the official database; this estimate was due to small tropical cyclone size, sparse ship reports, and relatively unpopulated coastlines.
Every tropical cyclone in the season was of hurricane status, or with winds at or exceeding 74 mph (119 km/h). In only three other seasons did every cyclone attain hurricane status; those years were 1858
1850-1859 Atlantic hurricane seasons
1830s 1840s 1850s 1860s 1870s-1850 Atlantic hurricane season:The first of three hurricanes to affect the upper Eastern Seaboard moved into North Carolina on July 18. As it moved north, Chesapeake Bay and Delaware Bay took a beating as high waves and tides flooded the coast...
, 1866
1860-1869 Atlantic hurricane seasons
1840s 1850s 1860s 1870s 1880-84-Tropical Storm Four:While there were 6 storms this season, only one affected any landmass as a tropical system; a tropical storm hitting the Lesser Antilles.-Hurricane Three:...
, and 1884
1884 Atlantic hurricane season
The 1884 Atlantic hurricane season ran through the summer and the first half of fall in 1884. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. Due to inactivity of the season, there was no storms in June, July, early to mid-August...
. All five cyclones affected land; the strongest was the first storm, which caused severe damage and loss of life when it made landfall
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
near the border between Mississippi
Mississippi
Mississippi is a U.S. state located in the Southern United States. Jackson is the state capital and largest city. The name of the state derives from the Mississippi River, which flows along its western boundary, whose name comes from the Ojibwe word misi-ziibi...
and Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
. The second storm of the season struck Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
, where it caused over 100 deaths, primarily from flooding. In the middle of September, the third storm moved across Florida with strong wind gusts and light rainfall, and a week later the fourth storm passed over or north of the Lesser
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
and Greater Antilles
Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles are one of three island groups in the Caribbean. Comprising Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola , and Puerto Rico, the Greater Antilles constitute almost 90% of the land mass of the entire West Indies.-Greater Antilles in context :The islands of the Caribbean Sea, collectively known as...
. The last storm hit the Florida Panhandle, though damage was less than expected.
Hurricane One
The first tropical cyclone of the year, also known as the Great Mobile Hurricane of 1852, was first observed on August 19 about 140 mi (230 km) north of Puerto RicoPuerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
. It moved on a west-northwest motion before passing through the Bahamas as it attained hurricane status on August 20. After paralleling the northern coast of Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
, the storm passed between the Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas
The Dry Tortugas are a small group of islands, located at the end of the Florida Keys, USA, about west of Key West, and west of the Marquesas Keys, the closest islands. Still further west is the Tortugas Bank, which is completely submerged. The first Europeans to discover the islands were the...
and Key West, Florida
Key West, Florida
Key West is a city in Monroe County, Florida, United States. The city encompasses the island of Key West, the part of Stock Island north of U.S. 1 , Sigsbee Park , Fleming Key , and Sunset Key...
on August 22, and two days later it is estimated the hurricane attained peak winds of 115 mph (185 km/h). The storm slowed on August 25 before turning northward, and early on August 26 it made landfall
Landfall (meteorology)
Landfall is the event of a tropical cyclone or a waterspout coming onto land after being over water. When a waterspout makes landfall it is reclassified as a tornado, which can then cause damage inland...
near Pascagoula, Mississippi
Pascagoula, Mississippi
Pascagoula is a city in Jackson County, Mississippi, United States. It is the principal city of the Pascagoula, Mississippi Metropolitan Statistical Area, as a part of the Gulfport–Biloxi–Pascagoula, Mississippi Combined Statistical Area. The population was 26,200 at the 2000 census...
at peak strength, and the hurricane rapidly weakened to tropical storm status as it accelerated east-northeastward. On August 28 it emerged into the Atlantic Ocean from South Carolina
South Carolina
South Carolina is a state in the Deep South of the United States that borders Georgia to the south, North Carolina to the north, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Originally part of the Province of Carolina, the Province of South Carolina was one of the 13 colonies that declared independence...
, and after turning to the northeast, it was last observed on August 30 about 130 mi (200 km) southeast of Cape Cod
Cape Cod
Cape Cod, often referred to locally as simply the Cape, is a cape in the easternmost portion of the state of Massachusetts, in the Northeastern United States...
.
In the Florida Keys
Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral archipelago in southeast United States. They begin at the southeastern tip of the Florida peninsula, about south of Miami, and extend in a gentle arc south-southwest and then westward to Key West, the westernmost of the inhabited islands, and on to the uninhabited Dry...
, rough waves forced several ships ashore, leaving some damaged. Strong waves created four new channels in the Chandeleur Islands
Chandeleur Islands
The Chandeleur Islands are a chain of uninhabited barrier islands approximately long, located in the Gulf of Mexico. They form the easternmost point of the state of Louisiana, USA and are a part of the Breton National Wildlife Refuge...
, and the storm's passage also destroyed the island lighthouse; the three keepers were found three days later. Two schooners were also washed ashore along Cat Island
Cat Island (Mississippi)
Cat Island is a barrier island off the Gulf Coast of the United States. The island is named for raccoons which Spanish explorers mistook for cats. It is unknown who discovered Cat Island. It was called Isle-aux-Chats and Isola de Gati in French and Italian, respectively. It is within the...
. The hurricane produced an estimated storm tide
Storm tide
A storm tide is a tide with a high flood period caused by a storm. Storm tides can be a severe danger to the coast and the people living along the coast. The water level can rise to more than 5 meters above the normal tide....
of 12 feet (3.7 m) in Mobile, Alabama
Mobile, Alabama
Mobile is the third most populous city in the Southern US state of Alabama and is the county seat of Mobile County. It is located on the Mobile River and the central Gulf Coast of the United States. The population within the city limits was 195,111 during the 2010 census. It is the largest...
, where strong winds damaged much of the city, leaving the majority of the houses destroyed. Trees were downed up to 30 miles (50 km) inland, and coastal areas were flooded. Damage along the coastline was estimated at around $1 million (1852 USD, $26 million 2008 USD), and several lives were lost. While crossing the southeastern United States, the storm brought light rainfall but moderately strong winds; in Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the second largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. It was made the county seat of Charleston County in 1901 when Charleston County was founded. The city's original name was Charles Towne in 1670, and it moved to its present location from a location on the west bank of the...
, the storm destroyed several bridges and crop fields.
Hurricane Two
Early on September 5, a hurricane was first observed about 65 mi (110 km) southeast of Christiansted, United States Virgin Islands. One meteorologist assessed the hurricane as being located near AntiguaAntigua
Antigua , also known as Waladli, is an island in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean region, the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua means "ancient" in Spanish and was named by Christopher Columbus after an icon in Seville Cathedral, Santa Maria de la...
on September 3. Tracking steadily west-northwestward, it quickly moved ashore near Ponce, Puerto Rico
Ponce, Puerto Rico
Ponce is both a city and a municipality in the southern part of Puerto Rico. The city is the seat of the municipal government.The city of Ponce, the fourth most populated in Puerto Rico, and the most populated outside of the San Juan metropolitan area, is named for Juan Ponce de León y Loayza, the...
with winds estimated at 80 mph (130 km/h). After crossing southwestern Puerto Rico, the hurricane emerged into the Mona Passage
Mona Passage
The Mona Passage is a strait that separates the islands of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico. The Mona Passage connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean Sea, and is an important shipping route between the Atlantic and the Panama Canal....
as a tropical storm. Late on September 5 it made landfall on eastern Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
; it quickly weakened over Hispaniola, dissipating on September 6 over the northwestern portion of the island. An assessment by scholar Michael Chenoweth in 2006 indicated this storm was the same as the next hurricane, with it continuing northwestward and ultimately reaching the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
. Due to not being considered the same cyclone in the official hurricane database
Atlantic hurricane reanalysis
Atlantic hurricane reanalysis is an ongoing project within the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration which seeks to correct and add new information about past Atlantic tropical cyclones...
, this hurricane and the following hurricane are listed separately.
The cyclone is known as the San Lorenzo hurricane, due to its impact in Puerto Rico. There, the passage of the storm caused severe flooding, which destroyed large quantities of crops and damaged several roads. Storm damage was heaviest between Guayanilla
Guayanilla, Puerto Rico
Guayanilla is a municipality of Puerto Rico located in southern coast of the island, bordering the Caribbean Sea, south of Adjuntas, east of Yauco; and west of Peñuelas and about 12 miles west of Ponce. Guayanilla is spread over 16 wards and Guayanilla Pueblo...
and Mayagüez
Mayagüez, Puerto Rico
Mayagüez is the eighth-largest municipality of Puerto Rico. Originally founded as "Nuestra Señora de la Candelaria" it is also known as "La Sultana del Oeste" , "Ciudad de las Aguas Puras" , or "Ciudad del Mangó"...
. More than 100 people were killed in Puerto Rico, many of which due to flooding.
Hurricane Three
A hurricane was located in the central Gulf of MexicoGulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
on September 9, potentially the same hurricane as the previous storm. It tracked generally eastward toward the coast of Florida, with its hurricane intensity estimation based on two ship reports. At about 0000 UTC
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose...
on September 12, it moved ashore near Clearwater, Florida
Clearwater, Florida
Clearwater is a city located in Pinellas County, Florida, US, nearly due west of Tampa and northwest of St. Petersburg. In the west of Clearwater lies the Gulf of Mexico and in the east lies Tampa Bay. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 108,787. It is the county seat of...
as a minimal hurricane, with an estimated minimum barometric central pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
of 985 mbar
Bar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
. Accelerating east-northeastward while crossing the state, the cyclone emerged into the Atlantic Ocean as a weakened tropical storm before regaining hurricane status on September 13. Later that day, it was last observed about 250 mi (400 km) east-southeast of Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras is a cape on the coast of North Carolina. It is the point that protrudes the farthest to the southeast along the northeast-to-southwest line of the Atlantic coast of North America...
.
A post in Fort Meade, Florida
Fort Meade, Florida
Fort Meade is a city in Polk County, Florida, United States. The population was 5,691 at the 2000 census. As of 2004, the population recorded by the U.S. Census Bureau is 5,761...
reported at least 0.55 in (14 mm) of rainfall during the storm's passage. The hurricane was considered "violent", and gusts were estimated to have reached hurricane force. Rough seas and strong easterly winds beached a vessel near St. Augustine
St. Augustine, Florida
St. Augustine is a city in the northeast section of Florida and the county seat of St. Johns County, Florida, United States. Founded in 1565 by Spanish explorer and admiral Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, it is the oldest continuously occupied European-established city and port in the continental United...
.
Hurricane Four
On September 22, a tropical storm was located about 200 mi (330 km) east of GuadeloupeGuadeloupe
Guadeloupe is an archipelago located in the Leeward Islands, in the Lesser Antilles, with a land area of 1,628 square kilometres and a population of 400,000. It is the first overseas region of France, consisting of a single overseas department. As with the other overseas departments, Guadeloupe...
. With a steady west-northwest path, the storm moved across the northern Lesser Antilles
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
on September 23, during which it intensified into a hurricane. It passed a short distance north of Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
and the Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
as it reached its peak intensity of 90 mph (150 km). Late on September 26 the hurricane turned northwestward, bringing it through the Turks and Caicos Islands
Turks and Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union consisting of two groups of tropical islands in the Caribbean, the larger Caicos Islands and the smaller Turks Islands, known for tourism and as an offshore financial centre.The Turks and...
and eastern Bahamas. Recurving north-northeastward, the cyclone moved into open waters, and was last classified as a tropical cyclone on September 30 about 390 mi (630 km) east of Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras is a cape on the coast of North Carolina. It is the point that protrudes the farthest to the southeast along the northeast-to-southwest line of the Atlantic coast of North America...
. However, one hurricane researcher assessed the hurricane as lasting until October 3, with the cyclone turning eastward and dissipating near the Azores
Azores
The Archipelago of the Azores is composed of nine volcanic islands situated in the middle of the North Atlantic Ocean, and is located about west from Lisbon and about east from the east coast of North America. The islands, and their economic exclusion zone, form the Autonomous Region of the...
.
Hurricane Five
A moderately strong hurricane with winds of 105 mph (165 km/h) was first spotted on October 6 east of JamaicaJamaica
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, in length, up to in width and 10,990 square kilometres in area. It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about south of Cuba, and west of Hispaniola, the island harbouring the nation-states Haiti and the Dominican Republic...
. Passing a short distance south of the island, the hurricane tracked northwestward and brushed the Yucatán Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
before turning north-northeastward into the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
. Late on October 9, it made landfall a short distance east of Apalachicola, Florida
Apalachicola, Florida
Apalachicola is a city in Franklin County, Florida, on US 98 about southwest of Tallahassee. The population was 2,334 at the 2000 census. The 2005 census estimated the city's population at 2,340...
at peak winds with an estimated pressure of 969 mbar. Rapidly weakening to tropical storm status, the cyclone continued northeastward and emerged into the Atlantic Ocean from North Carolina on October 11. Later that day, it was last observed about 250 mi (400 km) southeast of Cape Cod.
Heavy damage was reported in Jamaica. Upon making landfall in Florida, the hurricane produced a 7 ft (2 m) storm tide
Storm tide
A storm tide is a tide with a high flood period caused by a storm. Storm tides can be a severe danger to the coast and the people living along the coast. The water level can rise to more than 5 meters above the normal tide....
, and in Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
, hurricane force winds extended into the southwestern portion of the state, while tropical storm force winds occurred along the coastline. In the state, moderate winds damaged trees and roofs, though the destruction was less than anticipated.
See also
- List of Atlantic hurricane seasons
- List of Atlantic hurricanes

