
Meyer hardness test
Encyclopedia
Projected area
Projected area is two-dimensional area measurement of a three-dimensional object by projecting its shape on to an arbitrary plane. This is often used in mechanical engineering related fields, specifically hardness testing, axial stress and terminal velocity....
of an impression. This is a more fundamental measurement of hardness than other hardness tests which are based on the surface area of an indentation. The principle behind the test is that the mean pressure required to test the material is the measurement of the hardness of the material. The mean pressure is calculated by dividing the load by the projected area of the indentation. The result is called the Meyer hardness, which has units of megapascals (MPa).
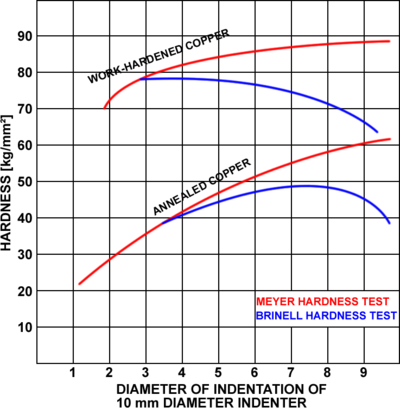
An advantage of the Meyer test is that it is less sensitive to the applied load, especially compared to the Brinell hardness test
Brinell scale
The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science....
. For cold worked materials the Meyer hardness is relatively constant and independent of load, whereas for the Brinell hardness test it decreases with higher loads. For anneal
Annealing (metallurgy)
Annealing, in metallurgy and materials science, is a heat treatment wherein a material is altered, causing changes in its properties such as strength and hardness. It is a process that produces conditions by heating to above the recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature, and...
ed materials the Meyer hardness increases continuously with load due to strain hardening.
Based on Meyer's law
Meyer's law
Meyer's law is an empirical relation between the size of a hardness test indentation and the load required to leave the indentation.- Equation :It take the form:P\,=\,kd^nwhere*P = pressure in megapascals*k = property of the material...
hardness values from this test can be converted into Brinell hardness
Brinell scale
The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science....
values, and vice-versa.
See also
- BrinellingBrinellingBrinelling is a material surface failure caused by contact stress that exceeds the material limit. This failure is caused by just one application of a load great enough to exceed the material limit. The result is a permanent dent or "brinell" mark. It is a common cause of roller bearing failures,...
- Hardness comparisonHardness comparisonThere are a large number of hardness testing methods available . Although it is impossible in many cases to give an exact conversion, it is possible to give an approximate material-specific comparison table e.g...
- Knoop hardness testKnoop hardness testThe Knoop hardness test is a microhardness test - a test for mechanical hardness used particularly for very brittle materials or thin sheets, where only a small indentation may be made for testing purposes...
- Leeb Rebound Hardness TestLeeb rebound hardness testThe Leeb rebound hardness test is one of the four most used method for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces .-History:...
- Rockwell scaleRockwell scaleThe Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on the indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test determines the hardness by measuring the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load compared to the penetration made by a preload. There are different scales, denoted by a single...
- Vickers hardness testVickers hardness testThe Vickers hardness test was developed in 1924 by Smith and Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the...

