
Units of energy
Encyclopedia
Because energy
is defined via work
, the SI
unit for energy is the same as the unit of work – the joule
(J), named in honour of James Prescott Joule
and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat
. In slightly more fundamental terms, 1 joule is equal to 1 newton-metre
and, in terms of SI base unit
s:

An energy unit that is used in atomic physics
, particle physics
and high energy physics is the electronvolt
(eV). One eV is equivalent to 1.60217653×10−19 J. In spectroscopy
the unit cm−1 = 0.000123986 eV is used to represent energy since energy is inversely proportional to wavelength from the equation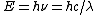 .
.
In discussions of energy production and consumption, the units barrel of oil equivalent
and ton of oil equivalent
are often used.
source IEA
/Unit Converter
When discussing amounts of energy released in explosion
s or bolide impact event
s, the TNT equivalent
unit is often used. 1 ton of TNT equivalent is equal to 4.2 × 109 joules. Therefore, 1 kt TNT is 4.2 × 1012 joules, and 1 Mt TNT is 4.2 × 1015 joules.
Note that torque
, the "rotational force" or "angular force" which causes a change in rotational motion is typically expressed in newton-metres. This is not a simple coincidence: a torque of 1 newton-metre applied on 1 radian
requires exactly 1 newton-metre = 1 joule of energy.
is 1 g
cm
2 s
−2, equal to 1.0×10−7 J.
for both energy and work include the foot-pound force
(1.3558 J), the British thermal unit
(Btu) which has various values in the region of 1055 J, and the horsepower
-hour (2.6845 MJ).
, particularly for utility bills, is the kilowatt-hour (kWh), and one kWh is equivalent to 3.6×106 J (3600 kJ or 3.6 MJ). Electricity usage is often given in units of kilowatt-hours per year (kWh/yr). This is actually a measurement of average power
consumption, i.e., the average rate at which energy is transferred.
equals the amount of thermal energy
necessary to raise the temperature
of one gram
of water
by 1 Celsius
degree, at a pressure
of 1 atm
. For thermochemistry a calorie of 4.184 J is used, but other calories have also been defined, such as the International Steam Table calorie of 4.1868 J. Food energy
is measured in large calories or kilocalories, often simply written capitalized as "Calories" (= 103 calories).
s (eV). The Hartree (the atomic unit of energy) is commonly used in calculations. Historically Rydberg
units have been used.
and related fields it is common to measure energy levels in units of reciprocal centimetres
. These units (cm−1) are strictly speaking not energy units but units proportional to energies, with hc being the proportionality constant.
s upon explosion. To define the tonne of TNT, this was arbitrarily standardized by letting 1000 thermochemical calories = 1 gram TNT = 4184 J
(exactly).
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
is defined via work
Mechanical work
In physics, work is a scalar quantity that can be described as the product of a force times the distance through which it acts, and it is called the work of the force. Only the component of a force in the direction of the movement of its point of application does work...
, the SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
unit for energy is the same as the unit of work – the joule
Joule
The joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
(J), named in honour of James Prescott Joule
James Prescott Joule
James Prescott Joule FRS was an English physicist and brewer, born in Salford, Lancashire. Joule studied the nature of heat, and discovered its relationship to mechanical work . This led to the theory of conservation of energy, which led to the development of the first law of thermodynamics. The...
and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat
Mechanical equivalent of heat
In the history of science, the mechanical equivalent of heat was a concept that had an important part in the development and acceptance of the conservation of energy and the establishment of the science of thermodynamics in the 19th century....
. In slightly more fundamental terms, 1 joule is equal to 1 newton-metre
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
and, in terms of SI base unit
SI base unit
The International System of Units defines seven units of measure as a basic set from which all other SI units are derived. These SI base units and their physical quantities are:* metre for length...
s:

An energy unit that is used in atomic physics
Atomic physics
Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. It is primarily concerned with the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus and...
, particle physics
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
and high energy physics is the electronvolt
Electronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
(eV). One eV is equivalent to 1.60217653×10−19 J. In spectroscopy
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
the unit cm−1 = 0.000123986 eV is used to represent energy since energy is inversely proportional to wavelength from the equation
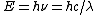 .
.In discussions of energy production and consumption, the units barrel of oil equivalent
Barrel of oil equivalent
The barrel of oil equivalent is a unit of energy based on the approximate energy released by burning one barrel of crude oil. The US Internal Revenue Service defines it as equal to 5.8 × 106 BTU...
and ton of oil equivalent
Ton of oil equivalent
The tonne of oil equivalent is a unit of energy: the amount of energy released by burning one tonne of crude oil, approximately 42 GJ .The toe is sometimes used for large...
are often used.
| Gcal (109) | MBtu (106) | GJ (109) | MWh (106) | toe | tce |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 39.6832 | 41.8680 | 11.6300 | 1 | 1.4286 |
| 0.2520 | 1 | 1.0551 | 0.2931 | 0.0252 | 0.0360 |
| 0.2388 | 0.9478 | 1 | 0.2778 | 0.0239 | 0.0341 |
source IEA
International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis...
/Unit Converter
When discussing amounts of energy released in explosion
Explosion
An explosion is a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner, usually with the generation of high temperatures and the release of gases. An explosion creates a shock wave. If the shock wave is a supersonic detonation, then the source of the blast is called a "high explosive"...
s or bolide impact event
Impact event
An impact event is the collision of a large meteorite, asteroid, comet, or other celestial object with the Earth or another planet. Throughout recorded history, hundreds of minor impact events have been reported, with some occurrences causing deaths, injuries, property damage or other significant...
s, the TNT equivalent
TNT equivalent
TNT equivalent is a method of quantifying the energy released in explosions. The ton of TNT is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 gigajoules, which is approximately the amount of energy released in the detonation of one ton of TNT...
unit is often used. 1 ton of TNT equivalent is equal to 4.2 × 109 joules. Therefore, 1 kt TNT is 4.2 × 1012 joules, and 1 Mt TNT is 4.2 × 1015 joules.
Note that torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
, the "rotational force" or "angular force" which causes a change in rotational motion is typically expressed in newton-metres. This is not a simple coincidence: a torque of 1 newton-metre applied on 1 radian
Radian
Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
requires exactly 1 newton-metre = 1 joule of energy.
Other units of energy
In cgs units, one ergErg
An erg is the unit of energy and mechanical work in the centimetre-gram-second system of units, symbol "erg". Its name is derived from the Greek ergon, meaning "work"....
is 1 g
Gram
The gram is a metric system unit of mass....
cm
Centimetre
A centimetre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one hundredth of a metre, which is the SI base unit of length. Centi is the SI prefix for a factor of . Hence a centimetre can be written as or — meaning or respectively...
2 s
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
−2, equal to 1.0×10−7 J.
US units
The imperial/U.S. unitsUnited States customary units
United States customary units are a system of measurements commonly used in the United States. Many U.S. units are virtually identical to their imperial counterparts, but the U.S. customary system developed from English units used in the British Empire before the system of imperial units was...
for both energy and work include the foot-pound force
Foot-pound force
The foot-pound force, or simply foot-pound is a unit of work or energy in the Engineering and Gravitational Systems in United States customary and Imperial units of measure. It is the energy transferred on applying a force of 1 pound-force through a displacement of 1 foot...
(1.3558 J), the British thermal unit
British thermal unit
The British thermal unit is a traditional unit of energy equal to about 1055 joules. It is approximately the amount of energy needed to heat of water, which is exactly one tenth of a UK gallon or about 0.1198 US gallons, from 39°F to 40°F...
(Btu) which has various values in the region of 1055 J, and the horsepower
Horsepower
Horsepower is the name of several units of measurement of power. The most common definitions equal between 735.5 and 750 watts.Horsepower was originally defined to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses in continuous operation. The unit was widely adopted to measure the...
-hour (2.6845 MJ).
Electricity
The energy unit used for everyday electricityElectricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
, particularly for utility bills, is the kilowatt-hour (kWh), and one kWh is equivalent to 3.6×106 J (3600 kJ or 3.6 MJ). Electricity usage is often given in units of kilowatt-hours per year (kWh/yr). This is actually a measurement of average power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
consumption, i.e., the average rate at which energy is transferred.
Food industry
The calorieCalorie
The calorie is a pre-SI metric unit of energy. It was first defined by Nicolas Clément in 1824 as a unit of heat, entering French and English dictionaries between 1841 and 1867. In most fields its use is archaic, having been replaced by the SI unit of energy, the joule...
equals the amount of thermal energy
Thermal energy
Thermal energy is the part of the total internal energy of a thermodynamic system or sample of matter that results in the system's temperature....
necessary to raise the temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
of one gram
Gram
The gram is a metric system unit of mass....
of water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
by 1 Celsius
Celsius
Celsius is a scale and unit of measurement for temperature. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius , who developed a similar temperature scale two years before his death...
degree, at a pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
of 1 atm
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
. For thermochemistry a calorie of 4.184 J is used, but other calories have also been defined, such as the International Steam Table calorie of 4.1868 J. Food energy
Food energy
Food energy is the amount of energy obtained from food that is available through cellular respiration.Food energy is expressed in food calories or kilojoules...
is measured in large calories or kilocalories, often simply written capitalized as "Calories" (= 103 calories).
Atom physics and chemistry
In physics and chemistry, it is still common to measure energy on the atomic scale in the non-SI, but convenient, units electronvoltElectronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
s (eV). The Hartree (the atomic unit of energy) is commonly used in calculations. Historically Rydberg
Rydberg
Rydberg can refer to:* Rydberg , a crater on the moon*In physics,** Rydberg constant**Rydberg formula**Rydberg atom **Rydberg molecule...
units have been used.
Spectroscopy
In spectroscopySpectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
and related fields it is common to measure energy levels in units of reciprocal centimetres
Wavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber is a property of a wave, its spatial frequency, that is proportional to the reciprocal of the wavelength. It is also the magnitude of the wave vector...
. These units (cm−1) are strictly speaking not energy units but units proportional to energies, with hc being the proportionality constant.
Explosions
A gram of TNT releases 980–1100 calorieCalorie
The calorie is a pre-SI metric unit of energy. It was first defined by Nicolas Clément in 1824 as a unit of heat, entering French and English dictionaries between 1841 and 1867. In most fields its use is archaic, having been replaced by the SI unit of energy, the joule...
s upon explosion. To define the tonne of TNT, this was arbitrarily standardized by letting 1000 thermochemical calories = 1 gram TNT = 4184 J
Joule
The joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
(exactly).
See also
- Conversion of units of energyConversion of units of energyThe SI unit for energy is the joule.The kilowatt hour, or kilowatt-hour, is equal to 3.6 megajoules....

