
Sturmgeschütz III
Encyclopedia
The Sturmgeschütz III assault gun
was Germany's
most produced armoured fighting vehicle
during World War II
. It was built on the chassis
of the proven Panzer III
tank. Initially intended as a mobile, armoured light gun for infantry support, the StuG was continually modified and was widely employed as a tank destroyer
.
when it was discovered that during the offensives on the western front the infantry lacked the means to effectively engage fortifications. The artillery of the time was heavy and not mobile enough to keep up with the advancing infantry to destroy bunkers, pillboxes, and other minor obstacles with direct-fire. Although the problem was well-known in the German army, it was General Erich von Manstein
who is considered the father of the Sturmartillerie. This is because the initial proposal was from (then) Colonel Erich von Manstein and submitted to General Ludwig Beck
in 1935, suggesting that Sturmartillerie ("assault artillery") units should be used in a direct-fire support role for infantry divisions. On June 15, 1936, Daimler-Benz
AG received an order to develop an armoured infantry support vehicle capable of mounting a 75 mm (2.95 in) artillery piece. The gun mount's fixed, fully integrated casemate
superstructure was to allow a limited traverse of a minimum of 25° and provided overhead protection for the crew. The height of the vehicle was not to exceed that of the average man.
Daimler-Benz AG used the chassis and running gear of its recently designed Pz.Kpfw. III medium tank as a basis for the new vehicle. Prototype manufacture was passed over to Alkett, which produced five examples in 1937 of the experimental 0-series StuG based upon the Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. B. These prototypes featured a mild steel
superstructure and Krupp
’s short-barreled 75 mm StuK 37 L/24 cannon. This model was known as the Sturmgeschütz Ausführung A.
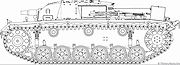 While the StuG III was considered self-propelled artillery it was not initially clear which arm of the Wehrmacht
While the StuG III was considered self-propelled artillery it was not initially clear which arm of the Wehrmacht
would handle the new weapon. The Panzer arm, the natural user of tracked fighting vehicles, had no resources to spare for the formation of StuG units, and neither did the infantry branch. It was agreed, after a discussion, it would best be employed as part of the artillery arm.
The StuGs were organised into battalions (later renamed "brigades" for disinformation purposes) and followed their own specific doctrine. Infantry support using direct-fire was its intended role. Later there was also a strong emphasis on destroying enemy armour whenever encountered.
 As the StuG III was designed to fill an infantry close support combat role, early models were fitted with a low-velocity 75 mm StuK 37 L/24 gun to destroy soft-skin targets and fortifications. After the Germans encountered the Soviet
As the StuG III was designed to fill an infantry close support combat role, early models were fitted with a low-velocity 75 mm StuK 37 L/24 gun to destroy soft-skin targets and fortifications. After the Germans encountered the Soviet
KV-1
and T-34
tanks, the StuG III was equipped with a high-velocity 75 mm StuK 40 L/43 main gun (Spring 1942) and later – the 75 mm StuK 40 L/48 (Autumn 1942) anti-tank gun. These versions were known as the Sturmgeschütz 40 Ausführung F, Ausf. F/8 and Ausf. G.
When the StuG IV
entered production in late 1943 and early 1944, the "III" was added to the name to separate it from the Panzer IV
-based assault guns. All previous and following models were thereafter known as Sturmgeschütz III.
Beginning with the StuG III Ausf. G, a 7.92 mm
MG34 could be mounted on a shield on top of the superstructure for added anti-infantry protection from December 1942. Some of the F/8 models were retrofitted with a shield as well. Many of the later StuG III Ausf. G models were equipped with an additional coaxial 7.92 mm MG34.
The vehicles of the Sturmgeschütz series were cheaper and faster to build than contemporary German tank
s; at 82,500 RM
, a StuG III Ausf G was cheaper than a Panzer III
Ausf. M, which cost 103,163 RM. This was due to the omission of the turret, which greatly simplified manufacture and allowed the chassis to carry a larger gun than it could otherwise. By the end of the war, 10,619 StuG IIIs and StuH 42s had been built.
and Panthers
have earned a greater notoriety, assault guns collectively destroyed more tanks. Because of their low silhouette, StuG IIIs were easy to camouflage and a difficult target. Sturmgeschütz crews were considered to be the elite of the artillery units. Sturmgeschütz units held a very impressive record of tank kills—some 20,000 enemy tanks by the spring of 1944. As of April 10, 1945, there were 1,053 StuG IIIs and 277 StuH 42s in service. Approximately 9,500 StuG IIIs of various types were produced until March 1945 by Alkett and a small number by MIAG.
The StuG assault guns were extremely cost-effective to build compared to the heavier German tanks, though in the anti-tank role it was best used defensively, as the lack of a traversable turret would be a severe disadvantage in the assault role. As the German military situation deteriorated later in the war, more and more StuG guns were constructed in comparison to tanks, in an effort to replace losses and bolster defences against the encroaching Allied forces.
In 1943 and 1944, the Finnish Army
received a total of 59 StuG III Ausf. Gs from Germany and used them against the Soviet Union
. 30 of the vehicles were received in 1943 and 29 in 1944. The 1943 batch destroyed at least 87 enemy tanks for a loss of only 8 StuGs (some of these were destroyed by their crews to avoid capture) while the 1944 didn't see any real action. After the war, the StuGs were the main combat vehicles of the Finnish Army
until the early 1960s. These StuGs gained the nickname "Sturmi" which can be found in some plastic kit models.
100 StuG III Ausf. G were delivered to Romania
in the autumn of 1943. They were officially known as TAs (or TAs T3 to avoid confusion with TAs T4) in the army inventory. By February 1945, 13 units were still in use with the 2nd Armoured Regiment. None of this initial batch survived the end of the war. 31 TAs were on the army inventory in November 1947. Most of them were probably StuG III Ausf. G and a small number of Panzer IV/70 (V), known as TAs T4. These TAs were supplied by the Red Army or were damaged units repaired by the Romanian Army. All German equipment was scrapped in 1954 due to the Army's decision to use Soviet armour.
StuG IIIs were also exported to other nations such as Bulgaria, Hungary, Italy, and Spain.
Many German Sturmgeschütz IIIs were stranded in Yugoslavia after the war. These were used by the Yugoslav Peoples Army until the 1950s.
After the Second World War the Soviet Union
donated some of their captured German vehicles to Syria
, which continued to use them along with other war surplus AFVs (like long-barreled Panzer IV
s and T-34/85s) during the 1950s and up until the The War over Water
against Israel in the mid-1960s. By the time of the Six Days War all of them had been either destroyed, stripped for spare parts, or interred on the Golan Heights as static pillboxes.
 Examples have been kept in running condition.
Examples have been kept in running condition.
A rotating cupola with periscopes was added for the commander for Ausf G. However, from September 1943, lack of ball bearings (resulting from bombing of Schweinfurt–Regensburg mission) forced cupolas to be welded on. Ball bearings were once again installed from August 1944. Shot deflectors for cupolas were first installed from October 1943 from one factory, to be installed on all StuGs from February 1944. Some vehicles without shot deflectors carried several track pieces wired around the cupola for added protection.
From December 1942, a square machine gun shield for loader was installed, allowing an MG 34 to be factory installed on a StuG for the first time. F/8 models had machine gun shields retro-fitted from early 1943. Machine gun shield for the loader was later replaced by rotating machine gun mount that could be operated by loader inside the vehicle by a periscope. On April 1944, 27 of them were being field tested on the Eastern front. Favorable report lead to installation of these "remote" machine gun mounts from summer of 1944.
Later G versions from November 1943, were fitted with the Topfblende (pot mantlet) (often called Saukopf (Pig's head)) gun mantlet without coaxial mount. This cast mantlet with organic shape was more effective at deflecting shots than the original boxy mantlet armor of varying thickness between 45mm and 50mm. Lack of large castings meant that boxy mantlet was also produced until the very end. Coaxial machine gun was added first to boxy mantlets from June 1944, and then to cast Topfblende from October 1944, in the middle of "Topfblende" mantlet production. With an addition of coaxial, all StuGs carried two MG 34 machine guns from fall of 1944. Some previously completed StuGs with boxy mantlet had a coaxial machine gun hole drilled to retrofit a coaxial machine gun, while Topfblende produced from Nov. 1943 - Oct. 1944 without machine gun opening could not be tampered. Also from Nov.1943, all metal return rollers of a few different types were used due to lack of rubber supply. Zimmerit
anti-magnetic coating to protect vehicles from magnetic mines were used from September 1943-September 1944 only.
 In 1942, a variant of the StuG III Ausf. F was designed with a 105 mm (4.1 in) howitzer
In 1942, a variant of the StuG III Ausf. F was designed with a 105 mm (4.1 in) howitzer
instead of the 7.5 cm StuK 40 L/43 cannon. These new vehicles, designated StuH 42 (Sturmhaubitze 42, Sd.Kfz 142/2), were designed to provide infantry support with the increased number of StuG III Ausf. F/8 and Ausf. Gs being used in the anti-tank role. The StuH 42 mounted a variant of the 10.5 cm leFH 18
howitzer, modified to be electrically fired and fitted with a muzzle brake
. Later models were built from StuG III Ausf. G chassis as well as StuG III Ausf. F and Ausf. F/8 chassis. The muzzle brake was often omitted due to the scarcity of resources later in the war. 1,211 StuH 42 were produced from October 1942 to 1945.
In 1943, 10 StuG IIIs were converted to StuG III (Flamm) configuration by replacing the main gun with a Schwade flamethrower
. These chassis were all refurbished at the depot level and were a variety of pre-Ausf. F models. There are no reports to indicate any of these were used in combat and all were returned to Ausf. G standard at depot level by 1944.
In late 1941 the StuG III chassis was selected to carry the 15 cm sIG 33 heavy infantry gun. These vehicles were known as Sturm-Infanteriegeschütz 33B
. Twenty-four were built of which twelve vehicles saw combat in the Battle of Stalingrad
where they were destroyed or captured. The remaining 12 vehicles were assigned to 23rd Panzer Division.
Some StuG III were also made from a Panzer III chassis but fitted the bogie suspension system of the Panzer IV tank. Only about 20 were manufactured. The intention was to simplify field repairs but this did not work out as planned and the model was canceled. Due to dwindling supply of rubber, rubber saving road wheels were tested during 8-14 November 1942, but did not see production.
Bombing raids on Alkett factory resulted in significant drops in StuG III production in November 1943. To make up for the loss of production, Krupp
displayed a substitution StuG on Panzer IV chassis to Hitler on 16–17 December 1943. From January 1944, the StuG IV, based on the Panzer IV
chassis and with a slightly modified StuG III superstructure entered production.
Field modifications were made to increase the vehicle's survivability, resulting in diversity to already numerous variants: cement plastered on front superstructure, older Ausf.C/D retrofitted with a Kwk40 L48 gun, Ausf.G mounting Panzer IV cupola, a coaxial MG34 through a hole drilled on a boxy mantlet.
The Soviet SU-76i self-propelled gun was based on captured StuG III and Panzer III
vehicles In total, Factory #37 in Sverdlovsk
manufactured 181 SU-76i plus 20 commander SU-76i for Red Army
service by adding an enclosed superstructure and the 76.2 mm S-1 tank gun.
Assault gun
An assault gun is a gun or howitzer mounted on a motor vehicle or armored chassis, designed for use in the direct fire role in support of infantry when attacking other infantry or fortified positions....
was Germany's
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
most produced armoured fighting vehicle
Armoured fighting vehicle
An armoured fighting vehicle is a combat vehicle, protected by strong armour and armed with weapons. AFVs can be wheeled or tracked....
during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. It was built on the chassis
Chassis
A chassis consists of an internal framework that supports a man-made object. It is analogous to an animal's skeleton. An example of a chassis is the underpart of a motor vehicle, consisting of the frame with the wheels and machinery.- Vehicles :In the case of vehicles, the term chassis means the...
of the proven Panzer III
Panzer III
Panzer III was the common name of a medium tank that was developed in the 1930s by Germany and was used extensively in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen III translating as "armoured battle vehicle". It was intended to fight other armoured fighting vehicles and...
tank. Initially intended as a mobile, armoured light gun for infantry support, the StuG was continually modified and was widely employed as a tank destroyer
Tank destroyer
A tank destroyer is a type of armored fighting vehicle armed with a gun or missile launcher, and is designed specifically to engage enemy armored vehicles...
.
Development
The Sturmgeschütz III originated from German experiences in World War IWorld War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
when it was discovered that during the offensives on the western front the infantry lacked the means to effectively engage fortifications. The artillery of the time was heavy and not mobile enough to keep up with the advancing infantry to destroy bunkers, pillboxes, and other minor obstacles with direct-fire. Although the problem was well-known in the German army, it was General Erich von Manstein
Erich von Manstein
Erich von Manstein was a field marshal in World War II. He became one of the most prominent commanders of Germany's World War II armed forces...
who is considered the father of the Sturmartillerie. This is because the initial proposal was from (then) Colonel Erich von Manstein and submitted to General Ludwig Beck
Ludwig Beck
Generaloberst Ludwig August Theodor Beck was a German general and Chief of the German General Staff during the early years of the Nazi regime in Germany before World War II....
in 1935, suggesting that Sturmartillerie ("assault artillery") units should be used in a direct-fire support role for infantry divisions. On June 15, 1936, Daimler-Benz
Daimler-Benz
Daimler-Benz AG was a German manufacturer of automobiles, motor vehicles, and internal combustion engines; founded in 1926. An Agreement of Mutual Interest - which was valid until year 2000 - was signed on 1 May 1924 between Karl Benz's Benz & Cie., and Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft, which had...
AG received an order to develop an armoured infantry support vehicle capable of mounting a 75 mm (2.95 in) artillery piece. The gun mount's fixed, fully integrated casemate
Casemate
A casemate, sometimes rendered casement, is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired. originally a vaulted chamber in a fortress.-Origin of the term:...
superstructure was to allow a limited traverse of a minimum of 25° and provided overhead protection for the crew. The height of the vehicle was not to exceed that of the average man.
Daimler-Benz AG used the chassis and running gear of its recently designed Pz.Kpfw. III medium tank as a basis for the new vehicle. Prototype manufacture was passed over to Alkett, which produced five examples in 1937 of the experimental 0-series StuG based upon the Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. B. These prototypes featured a mild steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
superstructure and Krupp
Krupp
The Krupp family , a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, have become famous for their steel production and for their manufacture of ammunition and armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th...
’s short-barreled 75 mm StuK 37 L/24 cannon. This model was known as the Sturmgeschütz Ausführung A.

Wehrmacht
The Wehrmacht – from , to defend and , the might/power) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the Heer , the Kriegsmarine and the Luftwaffe .-Origin and use of the term:...
would handle the new weapon. The Panzer arm, the natural user of tracked fighting vehicles, had no resources to spare for the formation of StuG units, and neither did the infantry branch. It was agreed, after a discussion, it would best be employed as part of the artillery arm.
The StuGs were organised into battalions (later renamed "brigades" for disinformation purposes) and followed their own specific doctrine. Infantry support using direct-fire was its intended role. Later there was also a strong emphasis on destroying enemy armour whenever encountered.

Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
KV-1
Kliment Voroshilov tank
The Kliment Voroshilov tanks were a series of Soviet heavy tanks, named after the Soviet defense commissar and politician Kliment Voroshilov. The KV series were known for their extremely heavy armour protection during the early war, especially during the first year of the invasion of the Soviet...
and T-34
T-34
The T-34 was a Soviet medium tank produced from 1940 to 1958. Although its armour and armament were surpassed by later tanks of the era, it has been often credited as the most effective, efficient and influential design of World War II...
tanks, the StuG III was equipped with a high-velocity 75 mm StuK 40 L/43 main gun (Spring 1942) and later – the 75 mm StuK 40 L/48 (Autumn 1942) anti-tank gun. These versions were known as the Sturmgeschütz 40 Ausführung F, Ausf. F/8 and Ausf. G.
When the StuG IV
Sturmgeschütz IV
The Sturmgeschütz IV , was a German assault gun of the Second World War.-Development:The Sturmgeschütz IV resulted from Krupp's effort to supply an assault gun...
entered production in late 1943 and early 1944, the "III" was added to the name to separate it from the Panzer IV
Panzer IV
The Panzerkampfwagen IV , commonly known as the Panzer IV, was a medium tank developed in Nazi Germany in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz...
-based assault guns. All previous and following models were thereafter known as Sturmgeschütz III.
Beginning with the StuG III Ausf. G, a 7.92 mm
7.92x57mm Mauser
The 8×57mm IS is a rimless bottlenecked rifle cartridge. The 8×57mm IS was adopted by the German Empire in 1905, and was the German service cartridge in both World Wars...
MG34 could be mounted on a shield on top of the superstructure for added anti-infantry protection from December 1942. Some of the F/8 models were retrofitted with a shield as well. Many of the later StuG III Ausf. G models were equipped with an additional coaxial 7.92 mm MG34.
The vehicles of the Sturmgeschütz series were cheaper and faster to build than contemporary German tank
Tank
A tank is a tracked, armoured fighting vehicle designed for front-line combat which combines operational mobility, tactical offensive, and defensive capabilities...
s; at 82,500 RM
German reichsmark
The Reichsmark was the currency in Germany from 1924 until June 20, 1948. The Reichsmark was subdivided into 100 Reichspfennig.-History:...
, a StuG III Ausf G was cheaper than a Panzer III
Panzer III
Panzer III was the common name of a medium tank that was developed in the 1930s by Germany and was used extensively in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen III translating as "armoured battle vehicle". It was intended to fight other armoured fighting vehicles and...
Ausf. M, which cost 103,163 RM. This was due to the omission of the turret, which greatly simplified manufacture and allowed the chassis to carry a larger gun than it could otherwise. By the end of the war, 10,619 StuG IIIs and StuH 42s had been built.
Operational history
Overall, Sturmgeschütz series assault guns proved very successful and served on all fronts as assault guns and tank destroyers. Although TigersTiger I
Tiger I is the common name of a German heavy tank developed in 1942 and used in World War II. The final official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen Tiger Ausf. E, often shortened to Tiger. It was an answer to the unexpectedly formidable Soviet armour encountered in the initial months of...
and Panthers
Panther tank
Panther is the common name of a medium tank fielded by Nazi Germany in World War II that served from mid-1943 to the end of the European war in 1945. It was intended as a counter to the T-34, and to replace the Panzer III and Panzer IV; while never replacing the latter, it served alongside it as...
have earned a greater notoriety, assault guns collectively destroyed more tanks. Because of their low silhouette, StuG IIIs were easy to camouflage and a difficult target. Sturmgeschütz crews were considered to be the elite of the artillery units. Sturmgeschütz units held a very impressive record of tank kills—some 20,000 enemy tanks by the spring of 1944. As of April 10, 1945, there were 1,053 StuG IIIs and 277 StuH 42s in service. Approximately 9,500 StuG IIIs of various types were produced until March 1945 by Alkett and a small number by MIAG.
The StuG assault guns were extremely cost-effective to build compared to the heavier German tanks, though in the anti-tank role it was best used defensively, as the lack of a traversable turret would be a severe disadvantage in the assault role. As the German military situation deteriorated later in the war, more and more StuG guns were constructed in comparison to tanks, in an effort to replace losses and bolster defences against the encroaching Allied forces.
In 1943 and 1944, the Finnish Army
Finnish Army
The Finnish Army is the land forces branch of the Finnish Defence Forces.Today's Army is divided into six branches: the infantry , field artillery, anti-aircraft artillery, engineers, signals, and materiel troops.-History of the Finnish Army:Between 1809 and 1917 Finland was an autonomous part of...
received a total of 59 StuG III Ausf. Gs from Germany and used them against the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. 30 of the vehicles were received in 1943 and 29 in 1944. The 1943 batch destroyed at least 87 enemy tanks for a loss of only 8 StuGs (some of these were destroyed by their crews to avoid capture) while the 1944 didn't see any real action. After the war, the StuGs were the main combat vehicles of the Finnish Army
Finnish Army
The Finnish Army is the land forces branch of the Finnish Defence Forces.Today's Army is divided into six branches: the infantry , field artillery, anti-aircraft artillery, engineers, signals, and materiel troops.-History of the Finnish Army:Between 1809 and 1917 Finland was an autonomous part of...
until the early 1960s. These StuGs gained the nickname "Sturmi" which can be found in some plastic kit models.
100 StuG III Ausf. G were delivered to Romania
Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania was the Romanian state based on a form of parliamentary monarchy between 13 March 1881 and 30 December 1947, specified by the first three Constitutions of Romania...
in the autumn of 1943. They were officially known as TAs (or TAs T3 to avoid confusion with TAs T4) in the army inventory. By February 1945, 13 units were still in use with the 2nd Armoured Regiment. None of this initial batch survived the end of the war. 31 TAs were on the army inventory in November 1947. Most of them were probably StuG III Ausf. G and a small number of Panzer IV/70 (V), known as TAs T4. These TAs were supplied by the Red Army or were damaged units repaired by the Romanian Army. All German equipment was scrapped in 1954 due to the Army's decision to use Soviet armour.
StuG IIIs were also exported to other nations such as Bulgaria, Hungary, Italy, and Spain.
Many German Sturmgeschütz IIIs were stranded in Yugoslavia after the war. These were used by the Yugoslav Peoples Army until the 1950s.
After the Second World War the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
donated some of their captured German vehicles to Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, which continued to use them along with other war surplus AFVs (like long-barreled Panzer IV
Panzer IV
The Panzerkampfwagen IV , commonly known as the Panzer IV, was a medium tank developed in Nazi Germany in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz...
s and T-34/85s) during the 1950s and up until the The War over Water
The War over Water
The "War over Water" , also the Battle over Water , refers to a series of confrontations between Israel and its Arab neighbors from November 1964 to May 1967 over control of available water sources in the Jordan River drainage basin.-History:The 1949 Armistice Agreements which followed the 1948...
against Israel in the mid-1960s. By the time of the Six Days War all of them had been either destroyed, stripped for spare parts, or interred on the Golan Heights as static pillboxes.

Variants
- StuG III Ausf. 0 (Experimental; 1937, 5 produced): By December 1937 two vehicles were in service with Panzer Regiment 1 in Erfurt. 0 series had 8 road wheels per side with narrow 360mm tracks. These pre-production vehicles had only 14.5mm thick soft steel superstructure and the 7.5 cm StuK 37 L/247.5 cm KwK 37The 7.5 cm KwK 37 L/24 was a German 75 mm tank gun used during World War II, primarily as the chief weapon of the Panzer IV tank....
gun. These never saw combat as they were built with soft-steel superstructure. However, they were used for training purposes as late as 1941. - StuG III Ausf. A (Sd.Kfz. 142; January 1940-May 1940, 30+20 produced): First used in the Battle of FranceBattle of FranceIn the Second World War, the Battle of France was the German invasion of France and the Low Countries, beginning on 10 May 1940, which ended the Phoney War. The battle consisted of two main operations. In the first, Fall Gelb , German armoured units pushed through the Ardennes, to cut off and...
, the StuG III Ausf. A used the chassis of the Panzer III Ausf. F. Front armor increased to 50mm. Daimler-BenzDaimler-BenzDaimler-Benz AG was a German manufacturer of automobiles, motor vehicles, and internal combustion engines; founded in 1926. An Agreement of Mutual Interest - which was valid until year 2000 - was signed on 1 May 1924 between Karl Benz's Benz & Cie., and Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft, which had...
produced first 30. Additional 20 were built by Alkett along with Ausf.B. These 20 are often added to the production numbers of Ausf.B. However these 20 are unique in that they were produced with Ausf.B, but mechanically more similar to Ausf.A. They are converted from Panzer III chassis with 30mm armor. 20mm armor was added to meet the spec of 50mm. They also have Panzer III's escape hatches on either side, which are not present in other models. These Alkette 20 had same 10 speed transmission as Ausf.A, narrow 360mm tracks of Ausf.A, also return roller position was same as Ausf.A. - StuG III Ausf. B: (Sd.Kfz 142; June 1940-May 1941, 300 produced) Widened tracks (38 cm). Two Rubber tires on each roadwheel were accordingly widened from 520x79mm to 520x95mm each. Both types of roadwheels were interchangeable. Troublesome 10 speed transmission was changed to 6 speed. Front most return rollers were re-positioned forward. This reduced vertical movements of tracks before they were fed to drive wheel, hence lessening the chance of tracks being thrown. In the middle of production of Ausf. B. original drive wheel with 8 round holes were changed to a new cast drive wheel with 6 slots. This new drive wheel could take either 380mm tracks or 400mm tracks. 380mm tracks were not exclusive to new drive wheels. Vehicle# 90111 shows older drive wheel with wider 380mm tracks. Additional 20 were converted from Panzer III chassis, which are added to Ausf.A in this article.
- StuG III Ausf. C: (Sd.Kfz 142; April 1941, 50 produced) Gunner's forward view port above driver's visor was a shot trap and thus eliminated; instead, superstructure top was given an opening for gunner's periscope. Idler wheel was redesigned.
- StuG III Ausf. D: (Sd.Kfz 142; May-September 1941, 150 produced) Simply a contract extension on Ausf. C. On-board intercom installed, otherwise identical to Ausf. C.
- StuG III Ausf. E: (Sd.Kfz 142; September 1941-February 1942, 284 produced) Superstructure sides added extended rectangular armored boxes for radio equipments. Increased space allowed room for 6 additional ammunition (maximum raised to 50) plus a machine gun. One MG 34MG 34The Maschinengewehr 34, or MG 34, is a German air-cooled machine gun that was first produced and accepted into service in 1934, and first issued to units in 1935. It accepts the 8x57mm IS cartridge....
and 7 drum-type magazines were carried in the right rear side of the fighting compartment to protect the vehicle from enemy infantry. Vehicle commanders were officially provided with SF14Z stereoscopic scissor periscopes. Stereoscopic scissor type periscopes for artillery spotters may have been used by vehicle commanders from the start.
- StuG III Ausf. F: (Sd.Kfz 142/1; March-September 1942, 366 produced) The first real upgunning of the StuG, this version uses the longer 7.5 cm StuK 40 L/437.5 cm KwK 40The 7.5 cm KwK 40 was a German 7.5 cm Second World War era vehicle mounted gun, used as the primary anti-tank weapon of the German medium tank the SdKfz.161 Panzerkampfwagen IV and the SdKfz.142 Sturmgeschütz III assault guns ...
gun. Firing armor-piercing Panzergranat-Patrone 39, Stuk 40 L/43 could penetrate 91mm of armor inclined 30 degrees from vertical at 500m, 82mm at 1000m, 72mm at 1500m, 63mm at 2000m, allowing Ausf. F to engage most Soviet armors at normal combat ranges. This change marked the StuG as being more of a tank destroyer than an infantry support vehicle. Exhaust fan was added to the rooftop to excavate fumes from spent shells, to enable firing of continuous shots. Additional 30mm armor plates were welded to the 50mm frontal armor from June 1942, making frontal armors 80mm thick. From June 1942, Ausf. F were mounted with approximately 13 inch (334mm to be exact) longer 7.5 cm StuK 40 L/487.5 cm KwK 40The 7.5 cm KwK 40 was a German 7.5 cm Second World War era vehicle mounted gun, used as the primary anti-tank weapon of the German medium tank the SdKfz.161 Panzerkampfwagen IV and the SdKfz.142 Sturmgeschütz III assault guns ...
gun. Firing above mentioned ammunition, longer L48 could penetrate 96mm, 85mm, 74mm, 64mm respectively (30 degrees from vertical).
- StuG III Ausf. F/8: (Sd.Kfz 142/1; September-December 1942, 250 produced) Introduction of an improved hull design similar to that used for the Panzer III Ausf. J / L with increased rear armor. This was 8th version of Panzer III hulls, thus the designation "F/8." This hull has towing hook holes extending from side walls. From October 1942, 30mm additional armors were bolted on to speed up the production line. From F/8, 7.5 cm StuK 40 L/487.5 cm KwK 40The 7.5 cm KwK 40 was a German 7.5 cm Second World War era vehicle mounted gun, used as the primary anti-tank weapon of the German medium tank the SdKfz.161 Panzerkampfwagen IV and the SdKfz.142 Sturmgeschütz III assault guns ...
gun becomes standard until the very last of the Ausf. G. Due to lack of double baffle muzzle brakes, few L48 guns mounted on F/8 were fitted with single baffle ball type muzzle brake found in Panzer IV Ausf. F2.
- StuG III Ausf. G (Sd.Kfz. 142/1; December 1942– April 1945, 7,720 produced, 173 converted from Pz.Kpfw. III chassis): The final and by far the most common of the StuG series. The Ausf. G used the hull of the Pz.Kpfw. III Ausf. M. Upper superstructure was widened: welded boxes on either sides were abandoned. This new superstructure design increased its height to 2160mm. Backside wall of the fighting compartment got straightened, and ventilation fan on top of the superstructure was relocated to the back of fighting compartment. From March 1943, driver's periscope was abandoned. From May 1943, side hull skirts (schurzen) were fitted to G models for added armor protection particularly against anti-tank rifles. Side skirts were retro-fitted to some Ausf. F/8 models, as they were be fitted to all front line StuGs and other tanks by June 1943 in preparation for the battle of KurskBattle of KurskThe Battle of Kursk took place when German and Soviet forces confronted each other on the Eastern Front during World War II in the vicinity of the city of Kursk, in the Soviet Union in July and August 1943. It remains both the largest series of armored clashes, including the Battle of Prokhorovka,...
. Mountings for side skirts proved inadequate, many were lost in the field. From March 1944, improved mounting was introduced, as a result side skirts are seen more often with late model Ausf G. From May 1943, 80mm thick plates were used for frontal armor instead of two plates of 50mm+30mm. However, backlog of completed 50mm armors exited. For those, 30mm additional armors still had to be welded or bolted on, until October 1943.
A rotating cupola with periscopes was added for the commander for Ausf G. However, from September 1943, lack of ball bearings (resulting from bombing of Schweinfurt–Regensburg mission) forced cupolas to be welded on. Ball bearings were once again installed from August 1944. Shot deflectors for cupolas were first installed from October 1943 from one factory, to be installed on all StuGs from February 1944. Some vehicles without shot deflectors carried several track pieces wired around the cupola for added protection.
From December 1942, a square machine gun shield for loader was installed, allowing an MG 34 to be factory installed on a StuG for the first time. F/8 models had machine gun shields retro-fitted from early 1943. Machine gun shield for the loader was later replaced by rotating machine gun mount that could be operated by loader inside the vehicle by a periscope. On April 1944, 27 of them were being field tested on the Eastern front. Favorable report lead to installation of these "remote" machine gun mounts from summer of 1944.
Later G versions from November 1943, were fitted with the Topfblende (pot mantlet) (often called Saukopf (Pig's head)) gun mantlet without coaxial mount. This cast mantlet with organic shape was more effective at deflecting shots than the original boxy mantlet armor of varying thickness between 45mm and 50mm. Lack of large castings meant that boxy mantlet was also produced until the very end. Coaxial machine gun was added first to boxy mantlets from June 1944, and then to cast Topfblende from October 1944, in the middle of "Topfblende" mantlet production. With an addition of coaxial, all StuGs carried two MG 34 machine guns from fall of 1944. Some previously completed StuGs with boxy mantlet had a coaxial machine gun hole drilled to retrofit a coaxial machine gun, while Topfblende produced from Nov. 1943 - Oct. 1944 without machine gun opening could not be tampered. Also from Nov.1943, all metal return rollers of a few different types were used due to lack of rubber supply. Zimmerit
Zimmerit
Zimmerit was a coating produced for German armored fighting vehicles during World War II for the purpose of combating magnetically attached anti-tank mines, although Germany was the only country to use magnetic mines against tanks in large scale numbers...
anti-magnetic coating to protect vehicles from magnetic mines were used from September 1943-September 1944 only.
- Further Variants

Howitzer
A howitzer is a type of artillery piece characterized by a relatively short barrel and the use of comparatively small propellant charges to propel projectiles at relatively high trajectories, with a steep angle of descent...
instead of the 7.5 cm StuK 40 L/43 cannon. These new vehicles, designated StuH 42 (Sturmhaubitze 42, Sd.Kfz 142/2), were designed to provide infantry support with the increased number of StuG III Ausf. F/8 and Ausf. Gs being used in the anti-tank role. The StuH 42 mounted a variant of the 10.5 cm leFH 18
10.5 cm leFH 18
-History:The 10.5 cm leFH 18 was the standard divisional field howitzer used by the Wehrmacht during the Second World War. It was designed and developed by Rheinmetall in 1929-30 and entered service with the Wehrmacht in 1935. Generally it did not equip independent artillery battalions until...
howitzer, modified to be electrically fired and fitted with a muzzle brake
Muzzle brake
Muzzle brakes and recoil compensators are devices that are fitted to the muzzle of a firearm or cannon to redirect propellant gases with the effect of countering both recoil of the gun and unwanted rising of the barrel during rapid fire...
. Later models were built from StuG III Ausf. G chassis as well as StuG III Ausf. F and Ausf. F/8 chassis. The muzzle brake was often omitted due to the scarcity of resources later in the war. 1,211 StuH 42 were produced from October 1942 to 1945.
In 1943, 10 StuG IIIs were converted to StuG III (Flamm) configuration by replacing the main gun with a Schwade flamethrower
Flamethrower
A flamethrower is a mechanical device designed to project a long controllable stream of fire.Some flamethrowers project a stream of ignited flammable liquid; some project a long gas flame. Most military flamethrowers use liquids, but commercial flamethrowers tend to use high-pressure propane and...
. These chassis were all refurbished at the depot level and were a variety of pre-Ausf. F models. There are no reports to indicate any of these were used in combat and all were returned to Ausf. G standard at depot level by 1944.
In late 1941 the StuG III chassis was selected to carry the 15 cm sIG 33 heavy infantry gun. These vehicles were known as Sturm-Infanteriegeschütz 33B
Sturm-Infanteriegeschütz 33B
The Sturm-Infanteriegeschütz 33B was a German self-propelled heavy infantry gun used during World War II. A new, fully enclosed, and heavily armored superstructure was built on the chassis of the Sturmgeschütz III. It mounted the improved sIG 33/1 infantry gun, offset to the right side, for which...
. Twenty-four were built of which twelve vehicles saw combat in the Battle of Stalingrad
Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad was a major battle of World War II in which Nazi Germany and its allies fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad in southwestern Russia. The battle took place between 23 August 1942 and 2 February 1943...
where they were destroyed or captured. The remaining 12 vehicles were assigned to 23rd Panzer Division.
Some StuG III were also made from a Panzer III chassis but fitted the bogie suspension system of the Panzer IV tank. Only about 20 were manufactured. The intention was to simplify field repairs but this did not work out as planned and the model was canceled. Due to dwindling supply of rubber, rubber saving road wheels were tested during 8-14 November 1942, but did not see production.
Bombing raids on Alkett factory resulted in significant drops in StuG III production in November 1943. To make up for the loss of production, Krupp
Krupp
The Krupp family , a prominent 400-year-old German dynasty from Essen, have become famous for their steel production and for their manufacture of ammunition and armaments. The family business, known as Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th...
displayed a substitution StuG on Panzer IV chassis to Hitler on 16–17 December 1943. From January 1944, the StuG IV, based on the Panzer IV
Panzer IV
The Panzerkampfwagen IV , commonly known as the Panzer IV, was a medium tank developed in Nazi Germany in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz...
chassis and with a slightly modified StuG III superstructure entered production.
Field modifications were made to increase the vehicle's survivability, resulting in diversity to already numerous variants: cement plastered on front superstructure, older Ausf.C/D retrofitted with a Kwk40 L48 gun, Ausf.G mounting Panzer IV cupola, a coaxial MG34 through a hole drilled on a boxy mantlet.
The Soviet SU-76i self-propelled gun was based on captured StuG III and Panzer III
Panzer III
Panzer III was the common name of a medium tank that was developed in the 1930s by Germany and was used extensively in World War II. The official German designation was Panzerkampfwagen III translating as "armoured battle vehicle". It was intended to fight other armoured fighting vehicles and...
vehicles In total, Factory #37 in Sverdlovsk
Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg is a major city in the central part of Russia, the administrative center of Sverdlovsk Oblast. Situated on the eastern side of the Ural mountain range, it is the main industrial and cultural center of the Urals Federal District with a population of 1,350,136 , making it Russia's...
manufactured 181 SU-76i plus 20 commander SU-76i for Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
service by adding an enclosed superstructure and the 76.2 mm S-1 tank gun.
Operators
Kingdom of Italy (In 1943, received 10 units and used until 1954) (for testing and modifications)External links
- Information about the Sturmgeschütz III at Panzerworld
- Sturmgeschütz III / IV at Achtung Panzer!
- Sturmgeschutz III Photos of the Sturmgeschutz III at the Canada War Museum in Ottawa, Canada
- AFV Database
- LemaireSoft
- OnWar model specifications: A B D E F G
- Sturmgeschutz - WWII Vehicles
- WarGamer
- Surviving Sturmgeschütz III and Sturmhaubitze 42 tanks - A PDF file presenting the Sturmgeschütz III and Sturmhaubitze 42 tanks still existing in the world
- Sturmgeschütze vor! Info on Sturmgeschütz and Panzerjaeger

