States Reorganisation Act
Encyclopedia
The States Reorganisation Act of 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries and governance of India
's states and territories
. The act reorganised the boundaries of India's states along linguistic lines, and amended the Indian Constitution to replace the three types of states, known as Parts A, B, and C states, with a single type of state.
Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have been made since 1956, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 remains the single most extensive change in state boundaries since the independence of India in 1947.
 The British Indian Empire
The British Indian Empire
, which included present-day India, Pakistan
and Bangladesh
, was divided into two types of territories: the Provinces of British India, which were governed directly by British officials responsible to the Governor-General of India
; and princely state
s, under the rule of local hereditary rulers who recognised British suzerainty
in return for local autonomy, in most cases as established by treaty. As a result of the reforms of the early 20th century, most of the British provinces had directly-elected legislatures as well as governors, although some of the smaller provinces were governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the Governor-General. Major reforms put forward by the British in the 1930s also recognised the principle of federalism
, which was carried forward into the governance of independent India.
On 15 August 1947, British India was granted independence as the separate dominion
s of India
and Pakistan
. The British dissolved their treaty relations with more than five hundred princely states, who were encouraged to accede
to either India or Pakistan, while under no compulsion to do so. Most of the states acceded to India, and a few to Pakistan. Bhutan
and Hyderabad
opted for independence, although the armed intervention of India conquered Hyderabad and brought it into the Indian Union.
Between 1947 and about 1950, the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian Union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into new provinces, such as Rajputana
, Himachal Pradesh
, Madhya Bharat
, and Vindhya Pradesh
, made up of multiple princely states; a few, including Mysore
, Hyderabad
, Bhopal, and Bilaspur
, became separate provinces. The Government of India Act 1935
remained the constitutional law of India pending adoption of a new Constitution.
The new Constitution of India
, which came into force on 26 January 1950, made India a sovereign, secular, democratic, republic, and a Union of states (replacing provinces) and territories. The states would have extensive autonomy and complete democracy in the Union, while the Union territories would be administered by the Government of India
. The constitution of 1950 distinguished between three types of states.
, West Bengal
, Bihar
, Bombay
, Madhya Pradesh
(formerly Central Provinces and Berar), Madras
, Orissa
, East Punjab, and Uttar Pradesh
(formerly the United Provinces).
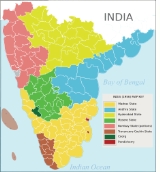
The eight Part B states were former princely states or groups of princely states, governed by a rajpramukh
, who was often a former prince, and an elected legislature. The rajpramukh was appointed by the President of India
. The Part B states were Hyderabad
, Saurashtra, Mysore
, Travancore-Cochin
, Madhya Bharat
, Vindhya Pradesh
, Patiala and East Punjab States Union
(PEPSU), and Rajasthan
.
The ten Part C states included both the former chief commissioners' provinces and some princely states, and each was governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the President of India. The Part C states included Delhi
, Kutch, Himachal Pradesh
, Bilaspur
, Coorg
, Bhopal
, Manipur
, Ajmer-Merwara
, and Tripura
.
Jammu and Kashmir
had a special status until 1957. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands were established as a Union territory ruled by a lieutenant governor appointed by the central government.
-speaking state out of the northern portion of Madras State
gathered strength in the years after independence, and in 1953, the 16 northern, Telugu-speaking districts of Madras State became the new State of Andhra
.
Other small changes were made to state boundaries during the 1950-1956 period. The small state of Bilaspur was merged with Himachal Pradesh on 1 July 1954, and Chandernagore, a former enclave of French India
, was incorporated into West Bengal
in 1955.
appointed the States Reorganisation Commission to prepare for the creation of states on linguistic lines. This was headed by Justice Fazal Ali
and the commission itself was also known as the Fazal Ali Commission. The efforts of this commission were overseen by Govind Ballabh Pant
, who served as Home Minister from December 1954. The commission created a report in 1955 recommending the reorganisation of India's states.
States
Union territories
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
's states and territories
States and territories of India
India is a federal union of states comprising twenty-eight states and seven union territories. The states and territories are further subdivided into districts and so on.-List of states and territories:...
. The act reorganised the boundaries of India's states along linguistic lines, and amended the Indian Constitution to replace the three types of states, known as Parts A, B, and C states, with a single type of state.
Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have been made since 1956, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 remains the single most extensive change in state boundaries since the independence of India in 1947.
Political integration after independence and the Constitution of 1950

British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
, which included present-day India, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
, was divided into two types of territories: the Provinces of British India, which were governed directly by British officials responsible to the Governor-General of India
Governor-General of India
The Governor-General of India was the head of the British administration in India, and later, after Indian independence, the representative of the monarch and de facto head of state. The office was created in 1773, with the title of Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William...
; and princely state
Princely state
A Princely State was a nominally sovereign entitity of British rule in India that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule such as suzerainty or paramountcy.-British relationship with the Princely States:India under the British Raj ...
s, under the rule of local hereditary rulers who recognised British suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
in return for local autonomy, in most cases as established by treaty. As a result of the reforms of the early 20th century, most of the British provinces had directly-elected legislatures as well as governors, although some of the smaller provinces were governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the Governor-General. Major reforms put forward by the British in the 1930s also recognised the principle of federalism
Federalism
Federalism is a political concept in which a group of members are bound together by covenant with a governing representative head. The term "federalism" is also used to describe a system of the government in which sovereignty is constitutionally divided between a central governing authority and...
, which was carried forward into the governance of independent India.
On 15 August 1947, British India was granted independence as the separate dominion
Dominion
A dominion, often Dominion, refers to one of a group of autonomous polities that were nominally under British sovereignty, constituting the British Empire and British Commonwealth, beginning in the latter part of the 19th century. They have included Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Newfoundland,...
s of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. The British dissolved their treaty relations with more than five hundred princely states, who were encouraged to accede
Instrument of Accession
The Instrument of Accession was a legal document created in 1947 to enable each of the rulers of the princely states under British suzerainty to join one of the new dominions of India or Pakistan created by the Partition of British India.-Background:...
to either India or Pakistan, while under no compulsion to do so. Most of the states acceded to India, and a few to Pakistan. Bhutan
Bhutan
Bhutan , officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked state in South Asia, located at the eastern end of the Himalayas and bordered to the south, east and west by the Republic of India and to the north by the People's Republic of China...
and Hyderabad
Hyderabad State
-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
opted for independence, although the armed intervention of India conquered Hyderabad and brought it into the Indian Union.
Between 1947 and about 1950, the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian Union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into new provinces, such as Rajputana
Rajputana
Rājputāna was the pre-1949 name of the present-day Indian state of Rājasthān, the largest state of the Republic of India in terms of area. George Thomas was the first in 1800 A.D., to term this region as Rajputana...
, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over , and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east...
, Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat , also known as Malwa Union was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jivaji Rao Scindia as its Rajpramukh...
, and Vindhya Pradesh
Vindhya Pradesh
Vindhya Pradesh is a former state of India. It occupied an area of 23,603 sq. miles. It was created in 1948, shortly after Indian independence, from the territories of the princely states in the eastern portion of the former Central India Agency. It was named for the Vindhya Range, which runs...
, made up of multiple princely states; a few, including Mysore
Mysore State
The Kingdom of Mysore was one of the three largest princely states within the erstwhile British Empire of India. Upon India gaining its independence in 1947, the Maharaja of Mysore merged his realm with the Union of India...
, Hyderabad
Hyderabad State
-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
, Bhopal, and Bilaspur
Bilaspur, Himachal Pradesh
Bilaspur is a city and a municipal council in Bilaspur district in the state of Himachal Pradesh, India.-Geography:Bilaspur is located at . It has an average elevation of 673 metres . It is hot in summer and cold in winters. It rains mostly in July to august .It lies near the reservoir of...
, became separate provinces. The Government of India Act 1935
Government of India Act 1935
The Government of India Act 1935 was originally passed in August 1935 , and is said to have been the longest Act of Parliament ever enacted by that time. Because of its length, the Act was retroactively split by the Government of India Act 1935 into two separate Acts:# The Government of India...
remained the constitutional law of India pending adoption of a new Constitution.
The new Constitution of India
Constitution of India
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India. It lays down the framework defining fundamental political principles, establishes the structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions, and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens...
, which came into force on 26 January 1950, made India a sovereign, secular, democratic, republic, and a Union of states (replacing provinces) and territories. The states would have extensive autonomy and complete democracy in the Union, while the Union territories would be administered by the Government of India
Government of India
The Government of India, officially known as the Union Government, and also known as the Central Government, was established by the Constitution of India, and is the governing authority of the union of 28 states and seven union territories, collectively called the Republic of India...
. The constitution of 1950 distinguished between three types of states.
Three types of states
Part A states, which were the former governors' provinces of British India, were ruled by an elected governor and state legislature. The nine Part A states were AssamAssam
Assam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
, West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
, Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, Bombay
Bombay State
The Bombay State was a state of India, dissolved with the formation of Maharashtra and Gujarat states on May 1, 1960.-History:During British rule, portions of the western coast of India under direct British rule were part of the Bombay Presidency...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh , often called the Heart of India, is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and Indore is the largest city....
(formerly Central Provinces and Berar), Madras
Madras State
Madras State was the name by which the Indian districts in Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Northern Kerala, Bellary and Dakshina Kannada were collectively known as from 1950 to 1953....
, Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
, East Punjab, and Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
(formerly the United Provinces).
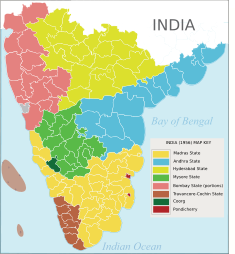
The eight Part B states were former princely states or groups of princely states, governed by a rajpramukh
Rajpramukh
Rajpramukh was an administrative title in India which existed from India's independence in 1947 until 1956. Rajpramukhs were the appointed governors of certain of India's provinces and states....
, who was often a former prince, and an elected legislature. The rajpramukh was appointed by the President of India
President of India
The President of India is the head of state and first citizen of India, as well as the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces. President of India is also the formal head of all the three branches of Indian Democracy - Legislature, Executive and Judiciary...
. The Part B states were Hyderabad
Hyderabad State
-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
, Saurashtra, Mysore
Mysore State
The Kingdom of Mysore was one of the three largest princely states within the erstwhile British Empire of India. Upon India gaining its independence in 1947, the Maharaja of Mysore merged his realm with the Union of India...
, Travancore-Cochin
Travancore-Cochin
Travancore-Cochin or Thiru-Kochi is a former state of India . It was created on 1 July 1949 by the merger of two former princely states, the kingdoms of Travancore and Cochin....
, Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat , also known as Malwa Union was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jivaji Rao Scindia as its Rajpramukh...
, Vindhya Pradesh
Vindhya Pradesh
Vindhya Pradesh is a former state of India. It occupied an area of 23,603 sq. miles. It was created in 1948, shortly after Indian independence, from the territories of the princely states in the eastern portion of the former Central India Agency. It was named for the Vindhya Range, which runs...
, Patiala and East Punjab States Union
Patiala and East Punjab States Union
The Patiala and East Punjab States Union was a state of India from 1948-56. It was created by combining eight princely states: Patiala, Jind, Nabha, Kapurthala, Faridkot, Kalsia, Malerkotla and Nalagarh. The state was inaugurated on July 15, 1948 and formally became a state of India in 1950. The...
(PEPSU), and Rajasthan
Rajasthan
Rājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
.
The ten Part C states included both the former chief commissioners' provinces and some princely states, and each was governed by a chief commissioner appointed by the President of India. The Part C states included Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
, Kutch, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over , and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east...
, Bilaspur
Bilaspur, Himachal Pradesh
Bilaspur is a city and a municipal council in Bilaspur district in the state of Himachal Pradesh, India.-Geography:Bilaspur is located at . It has an average elevation of 673 metres . It is hot in summer and cold in winters. It rains mostly in July to august .It lies near the reservoir of...
, Coorg
Kodagu
Kodagu , also known by its anglicised former name of Coorg, is an administrative district in Karnataka, India. It occupies an area of in the Western Ghats of southwestern Karnataka. As of 2001, the population was 548,561, 13.74% of which resided in the district's urban centres, making it the least...
, Bhopal
Bhopal (state)
Bhopal State was an independent state of 18th century India, a princely salute state in a subsidiary alliance with British India from 1818 to 1947, and an independent country from 1947 to 1949...
, Manipur
Manipur
Manipur is a state in northeastern India, with the city of Imphal as its capital. Manipur is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south and Assam to the west; it also borders Burma to the east. It covers an area of...
, Ajmer-Merwara
Ajmer-Merwara
Ajmer-Merwara is a former province of British India in the historical Ajmer region. The territory of the province was ceded to the British by Daulat Rao Sindhia by a treaty on June 25, 1818....
, and Tripura
Tripura
Tripura is a state in North-East India, with an area of . It is the third smallest state of India, according to area. Tripura is surrounded by Bangladesh on the north, south, and west. The Indian states of Assam and Mizoram lie to the east. The capital is Agartala and the main languages spoken are...
.
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
had a special status until 1957. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands were established as a Union territory ruled by a lieutenant governor appointed by the central government.
The movement for linguistic states
Political movements for the creation of new, linguistic-based states developed around India in the years after independence. The movement to create a TeluguTelugu language
Telugu is a Central Dravidian language primarily spoken in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India, where it is an official language. It is also spoken in the neighbouring states of Chattisgarh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Orissa and Tamil Nadu...
-speaking state out of the northern portion of Madras State
Madras State
Madras State was the name by which the Indian districts in Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Northern Kerala, Bellary and Dakshina Kannada were collectively known as from 1950 to 1953....
gathered strength in the years after independence, and in 1953, the 16 northern, Telugu-speaking districts of Madras State became the new State of Andhra
Andhra State
Andhra State was a state in India created on October 1, 1953 from the Telugu-speaking northern districts of Madras Presidency. On November 1, 1956 it was merged with the Telangana region of Hyderabad State to form the united Telugu-speaking state of Andhra Pradesh.- Madras Manade movement :In 1953,...
.
Other small changes were made to state boundaries during the 1950-1956 period. The small state of Bilaspur was merged with Himachal Pradesh on 1 July 1954, and Chandernagore, a former enclave of French India
French India
French India is a general name for the former French possessions in India These included Pondichéry , Karikal and Yanaon on the Coromandel Coast, Mahé on the Malabar Coast, and Chandannagar in Bengal...
, was incorporated into West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
in 1955.
The States Reorganisation Commission
In December 1953, Prime Minister Jawaharlal NehruJawaharlal Nehru
Jawaharlal Nehru , often referred to with the epithet of Panditji, was an Indian statesman who became the first Prime Minister of independent India and became noted for his “neutralist” policies in foreign affairs. He was also one of the principal leaders of India’s independence movement in the...
appointed the States Reorganisation Commission to prepare for the creation of states on linguistic lines. This was headed by Justice Fazal Ali
Fazal Ali
Sir ‘’’Sayyid Fazl Ali’’, also known as Fazal Ali was governor of Assam and Orissa and a judge . He was knighted by the British government in 1941. He headed the Fazal Ali Commission that made recommendations about the reorganization of India's states . He was governor of Orissa from 1952 to 1956...
and the commission itself was also known as the Fazal Ali Commission. The efforts of this commission were overseen by Govind Ballabh Pant
Govind Ballabh Pant
Bharat Ratna Pandit Govind Ballabh Pant was a statesman of India, an Indian independence activist, and one of the foremost political leaders from Uttarakhand and of the movement to establish Hindi as the official language of India.-Early life:Govind Ballabh Pant was born on September 10, 1887 in...
, who served as Home Minister from December 1954. The commission created a report in 1955 recommending the reorganisation of India's states.
The States Reorganisation Act
The States Reorganisation Act of 1956, which went into effect on 1 November, eliminated the distinction between part A, B, and C states. It also reorganised the state boundaries and created or dissolved states and union territories.Changes to states and union territories
On 1 November 1956, India was divided into the following states and union territories:States
- Andhra PradeshAndhra PradeshAndhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
: Andhra was renamed Andhra PradeshAndhra PradeshAndhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
, and enlarged by the addition of the TelanganaTelanganaTelangana is a region in the present state of Andhra Pradesh, India and formerly was part of Hyderabad state which was ruled by Nizam. It is bordered with the states of Maharashtra on the north and north-west, Karnataka on the west, Chattisgarh on the north-east and Orissa to the east...
region of erstwhile Hyderabad StateHyderabad State-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
. - AssamAssamAssam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
: No change of boundary in 1956. - BiharBiharBihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
: No change of boundary in 1956. - Bombay StateBombay StateThe Bombay State was a state of India, dissolved with the formation of Maharashtra and Gujarat states on May 1, 1960.-History:During British rule, portions of the western coast of India under direct British rule were part of the Bombay Presidency...
: the state was enlarged by the addition of SaurashtraSaurashtraSaurashtra is a region of western India, located on the Arabian Sea coast of Gujarat state. It is a peninsula also called Kathiawar after the Kathi Darbar who ruled part of the region once. The Peninsula is shared with the Kachchh region which occupies the north, Saurashtra or Sorath forming the...
and Kutch, the Marathi-speaking districts of Nagpur DivisionNagpur DivisionNagpur Division is one of six administrative divisions of Maharashtra State in India. Nagpur is the easternmost division in the state, with an administrative headquarters in the city of Nagpur...
of Madhya Pradesh, and the MarathwadaMarathwadaThe name Marathwada identifies one of the five regions in Maharashtra state of India. The region coincides with the Aurangabad Division.-Historical highlights:...
region of Hyderabad. The southernmost districts of Bombay were transferred to Mysore StateMysore StateThe Kingdom of Mysore was one of the three largest princely states within the erstwhile British Empire of India. Upon India gaining its independence in 1947, the Maharaja of Mysore merged his realm with the Union of India...
. (In 1960, the state was split into the modern states of MaharashtraMaharashtraMaharashtra is a state located in India. It is the second most populous after Uttar Pradesh and third largest state by area in India...
and Gujarat.) - Jammu and KashmirJammu and KashmirJammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
: No change of boundary in 1956. - KeralaKeralaor Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
: formed by the merger of Travancore-CochinTravancore-CochinTravancore-Cochin or Thiru-Kochi is a former state of India . It was created on 1 July 1949 by the merger of two former princely states, the kingdoms of Travancore and Cochin....
state with the Malabar DistrictMalabar DistrictMalabar District was an administrative district of Madras Presidency in British India and independent India's Madras State. The British district included the present-day districts of Kannur, Kozhikode, Wayanad, Malappuram, Palakkad , and Chavakad Taluk of Thrissur District in the northern part of...
of Madras StateMadras StateMadras State was the name by which the Indian districts in Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Northern Kerala, Bellary and Dakshina Kannada were collectively known as from 1950 to 1953....
, KasaragodKasaragodKasaragod is a town and a municipality in Kasaragod district in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of Kasaragod district as well as of Kasaragod Taluk...
of South Kanara(Dakshina KannadaDakshina Kannada- Geography :The district geography consists of sea shore in the west and Western Ghats in the east. The major rivers are Netravathi, Kumaradhara, Phalguni, Shambhavi, Nandini or Pavanje and Payaswini which all join Arabian sea. Vast areas of evergreen forests which once covered this district, have...
) and adding southern part of TravancoreTravancoreKingdom of Travancore was a former Hindu feudal kingdom and Indian Princely State with its capital at Padmanabhapuram or Trivandrum ruled by the Travancore Royal Family. The Kingdom of Travancore comprised most of modern day southern Kerala, Kanyakumari district, and the southernmost parts of...
(Kanyakumari) to Madras stateMadras StateMadras State was the name by which the Indian districts in Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Northern Kerala, Bellary and Dakshina Kannada were collectively known as from 1950 to 1953....
. - Madhya PradeshMadhya PradeshMadhya Pradesh , often called the Heart of India, is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and Indore is the largest city....
: Madhya BharatMadhya BharatMadhya Bharat , also known as Malwa Union was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jivaji Rao Scindia as its Rajpramukh...
, Vindhya PradeshVindhya PradeshVindhya Pradesh is a former state of India. It occupied an area of 23,603 sq. miles. It was created in 1948, shortly after Indian independence, from the territories of the princely states in the eastern portion of the former Central India Agency. It was named for the Vindhya Range, which runs...
, and Bhopal were merged into Madhya PradeshMadhya PradeshMadhya Pradesh , often called the Heart of India, is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and Indore is the largest city....
, and the Marathi-speaking districts of Nagpur DivisionNagpur DivisionNagpur Division is one of six administrative divisions of Maharashtra State in India. Nagpur is the easternmost division in the state, with an administrative headquarters in the city of Nagpur...
were transferred to Bombay StateBombay StateThe Bombay State was a state of India, dissolved with the formation of Maharashtra and Gujarat states on May 1, 1960.-History:During British rule, portions of the western coast of India under direct British rule were part of the Bombay Presidency...
. - Madras StateMadras StateMadras State was the name by which the Indian districts in Tamil Nadu, Andhra, Northern Kerala, Bellary and Dakshina Kannada were collectively known as from 1950 to 1953....
: the state was reduced to its present boundaries by the transfer of Malabar DistrictMalabar DistrictMalabar District was an administrative district of Madras Presidency in British India and independent India's Madras State. The British district included the present-day districts of Kannur, Kozhikode, Wayanad, Malappuram, Palakkad , and Chavakad Taluk of Thrissur District in the northern part of...
to the new state of KeralaKeralaor Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
. The southern part of TravancoreTravancoreKingdom of Travancore was a former Hindu feudal kingdom and Indian Princely State with its capital at Padmanabhapuram or Trivandrum ruled by the Travancore Royal Family. The Kingdom of Travancore comprised most of modern day southern Kerala, Kanyakumari district, and the southernmost parts of...
(Kanyakumari districtKanyakumari DistrictKanyakumari District ) is a district of Tamil Nadu state, India and is the southernmost land area of mainland India.The district is the second most urbanised district in Tamilnadu, next only to Chennai and ahead of Coimbatore. It also has the highest literacy and education levels in the...
) was added to the state. (The state was renamed Tamil NaduTamil NaduTamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
in 1969.) - Mysore StateMysore StateThe Kingdom of Mysore was one of the three largest princely states within the erstwhile British Empire of India. Upon India gaining its independence in 1947, the Maharaja of Mysore merged his realm with the Union of India...
: enlarged by the addition of Coorg state and the Kannada speaking districts from southern Bombay state and western Hyderabad stateHyderabad State-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
. (The state was renamed KarnatakaKarnatakaKarnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
in 1973.) - OrissaOrissaOrissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
: No change of boundary in 1956. - PunjabPunjab (India)Punjab ) is a state in the northwest of the Republic of India, forming part of the larger Punjab region. The state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast and Rajasthan to the southwest as well as the Pakistani province of Punjab to the...
: the Patiala and East Punjab States UnionPatiala and East Punjab States UnionThe Patiala and East Punjab States Union was a state of India from 1948-56. It was created by combining eight princely states: Patiala, Jind, Nabha, Kapurthala, Faridkot, Kalsia, Malerkotla and Nalagarh. The state was inaugurated on July 15, 1948 and formally became a state of India in 1950. The...
was merged into Punjab. - RajasthanRajasthanRājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
: enlarged by the addition of Ajmer-MerwaraAjmer-MerwaraAjmer-Merwara is a former province of British India in the historical Ajmer region. The territory of the province was ceded to the British by Daulat Rao Sindhia by a treaty on June 25, 1818....
state. - Uttar PradeshUttar PradeshUttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
: No change of boundary in 1956. - West BengalWest BengalWest Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
: No change of boundary in 1956.
Union territories
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- LakshadweepLakshadweepLakshadweep , formerly known as the Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands, is a group of islands in the Laccadive Sea, 200 to 440 km off the coast of the South West Indian state of Kerala...
- Pondicherry
- DelhiDelhiDelhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
See also
- Swatantra Tripura CommitteeSwatantra Tripura CommitteeThe Swatantra Tripura Committee was a coordination of political forces in Tripura, India, that struggled against the integration of Tripura into the state of Assam. The campaign was active 1955-1956....
- Unification of KarnatakaUnification of KarnatakaThe Unification of Karnataka refers to the formation of the Indian state of Karnataka, then called as Mysore State, in 1956 when several Indian states were created by redrawing borders based on linguistic demographics...
- Mangalorean regionalismMangalorean regionalismMangalorean regionalism centers on increasing Tulu Nadu's influence and political power through the formation of a separate Tulu Nadu state from Karnataka. Tulu Nadu is a region on the south-western coast of India. It consists of the Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka, and the...

