
Squirrel cage rotor
Encyclopedia

Alternating current
In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current , the flow of electric charge is only in one direction....
induction motor
Induction motor
An induction or asynchronous motor is a type of AC motor where power is supplied to the rotor by means of electromagnetic induction. These motors are widely used in industrial drives, particularly polyphase induction motors, because they are robust and have no brushes...
. An electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
with a squirrel cage rotor is termed a squirrel cage motor.
Structure
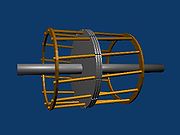
The core of the rotor is built with stacks of electrical steel laminations. Figure 3 shows one of many laminations used.
The rotor has a smaller number of slots than the stator and must be a non-integral multiple of stator slots so as to prevent magnetic interlocking of rotor and stator teeth at the starting instant.
Theory

Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotor system, found in an electric generator, electric motor and biological rotors.Depending on the configuration of a spinning electromotive device the stator may act as the field magnet, interacting with the armature to create motion, or it may act as the...
of an induction motor set up a rotating magnetic field
Rotating magnetic field
A rotating magnetic field is a magnetic field which changes direction at a constant angular rate. This is a key principle in the operation of the alternating-current motor. Nikola Tesla claimed in his autobiography that he identified the concept of the rotating magnetic field in 1882. In 1885,...
around the rotor
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is the non-stationary part of a rotary electric motor, electric generator or alternator, which rotates because the wires and magnetic field of the motor are arranged so that a torque is developed about the rotor's axis. In some designs, the rotor can act to serve as the motor's armature,...
. The relative motion between this field and the rotation of the rotor induces electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
in the conductive bars. In turn these currents lengthwise in the conductors react with the magnetic field of the motor to produce force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
acting at a tangent
Tangent
In geometry, the tangent line to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve at a point on the curve if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope where f...
orthogonal to the rotor, resulting in torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
to turn the shaft. In effect the rotor is carried around with the magnetic field but at a slightly slower rate of rotation. The difference in speed is called slip and increases with load.
The conductors are often skewed slightly along the length of the rotor to reduce noise and smooth out torque fluctuations that might result at some speeds due to interactions with the pole pieces of the stator. The number of bars on the squirrel cage determines to what extent the induced currents are fed back to the stator coils and hence the current through them. The constructions that offer the least feedback employ prime numbers of bars.
The iron core serves to carry the magnetic field across the motor. In structure and material it is designed to minimize losses. The thin laminations, separated by varnish insulation, reduce stray circulating currents that would result in eddy current
Eddy current
Eddy currents are electric currents induced in conductors when a conductor is exposed to a changing magnetic field; due to relative motion of the field source and conductor or due to variations of the field with time. This can cause a circulating flow of electrons, or current, within the body of...
loss. The material is a low carbon but high silicon
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
iron with several times the resistivity of pure iron, further reducing eddy-current loss. The low carbon content makes it a magnetically soft material with low hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of a system not just on its current environment but also on its past. This dependence arises because the system can be in more than one internal state. To predict its future evolution, either its internal state or its history must be known. If a given input alternately...
loss.
The same basic design is used for both single-phase and three-phase motors over a wide range of sizes. Rotors for three-phase will have variations in the depth and shape of bars to suit the design classification.
Practical Demonstration
To demonstrate how the cage rotor works, the stator of a single-phase motor and a copper pipe (as rotor) may be used. If adequate ac power is applied to the stator, an alternating magnetic field revolves around the stator. If the copper pipe is inserted inside the stator, there will be an induced current in the pipe, and this current produces another magnetic field. The interaction of the stator revolving field and motor induced field produce a torque and thus rotation.Use in synchronous motors
Synchronous motorSynchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC motor distinguished by a rotor spinning with coils passing magnets at the same rate as the power supply frequency and resulting rotating magnetic field which drives it....
s must use other types of rotors although they may employ a squirrel cage winding to allow them to reach near-synchronous speed while starting. Once operating at synchronous speed, the magnetic field is rotating at the same speed as the rotor, so no current will be induced into the squirrel cage windings and they will have no further effect on the operation of the synchronous motor in steady state operation.

