
Sporogenesis
Encyclopedia


Spore
In biology, a spore is a reproductive structure that is adapted for dispersal and surviving for extended periods of time in unfavorable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many bacteria, plants, algae, fungi and some protozoa. According to scientist Dr...
s in biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
. The term is also used to refer to the process of reproduction via spores. Reproductive spores are formed in many eukaryotic
Eukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
organisms, such as plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
and fungi
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
, during their normal reproductive life cycle
Biological life cycle
A life cycle is a period involving all different generations of a species succeeding each other through means of reproduction, whether through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction...
. Dormant spores are formed, for example by certain fungi and algae, primarily in response to unfavorable growing conditions. Most eukaryotic spores are haploid and form through cell division, though some types are diploid or dikaryon
Dikaryon
Dikaryon is from Greek, di meaning 2 and karyon meaning nut, referring to the cell nucleus.The dikaryon is a nuclear feature which is unique to some fungi, in which after plasmogamy the two compatible nuclei of two cells pair off and cohabit without karyogamy within the cells of the hyphae,...
s and form through cell fusion.
Reproduction via spores
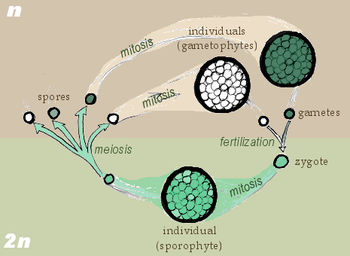
Reproductive spores are generally the result of cell division, most commonly meiosisMeiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
(e.g. in plant sporophyte
Sporophyte
All land plants, and some algae, have life cycles in which a haploid gametophyte generation alternates with a diploid sporophyte, the generation of a plant or algae that has a double set of chromosomes. A multicellular sporophyte generation or phase is present in the life cycle of all land plants...
s). Sporic meiosis is needed to complete the sexual life cycle of the organisms using it.
In some cases, sporogenesis occurs via mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
(e.g. in some fungi and algae). Mitotic sporogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only, it is reproduction which does not involve meiosis, ploidy reduction, or fertilization. A more stringent definition is agamogenesis which is reproduction without...
. Examples are the conidial fungi
Conidium
Conidia, sometimes termed conidiospores, are asexual, non-motile spores of a fungus and are named after the greek word for dust, konia. They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis...
Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. Aspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli...
and Penicillium
Penicillium
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi of major importance in the natural environment as well as food and drug production. Members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria inside the body...
, for which mitospore formation appears to be the primary mode of reproduction. Other fungi, such as ascomycetes, utilize both mitotic and meiotic spores. The red alga Polysiphonia
Polysiphonia
Polysiphonia is a genus of red alga with about 19 species on the coasts of the British Isles and about 200 species world-wide, including Crete in Greece, Antarctica and Greenland. Its members are known by a number of common names.Recorded common names are olann dhearg, craonach, cúnach...
alternates between mitotic and meiotic sporogenesis and both processes are required to complete its complex reproductive life cycle.
In the case of dormant spores in eukaryotes, sporogenesis often occurs as a result of fertilization or karyogamy
Karyogamy
Karyogamy is the fusion of pronuclei of two cells, as part of syngamy, fertilization, or true bacterial conjugation.It is one of the two major modes of reproduction in fungi...
forming a diploid spore equivalent to a zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
. Therefore, zygospores are the result of sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
.
Reproduction via spores involves the spreading of the spores by water or air. Algae and some fungi (chytrids) often use motile zoospore
Zoospore
A zoospore is a motile asexual spore that uses a flagellum for locomotion. Also called a swarm spore, these spores are created by some algae, bacteria and fungi to propagate themselves.-Flagella:...
s that can swim to new locations before developing into sessile organisms. Airborne spores are obvious in fungi, for example when they are released from puffball
Puffball
A puffball is a member of any of several groups of fungus in the division Basidiomycota. The puffballs were previously treated as a taxonomic group called the Gasteromycetes or Gasteromycetidae, but they are now known to be a polyphyletic assemblage. The distinguishing feature of all puffballs is...
s. Other fungi have more active spore dispersal mechanisms. For example, the fungus Pilobolus
Pilobolus
Pilobolus is a genus of fungi that commonly grows on herbivore dung.-Life cycle:The life cycle of Pilobolus begins with a black sporangium that has been discharged onto a plant substrate such as grass. A herbivorous animal such as a horse then eats the substrate, unknowingly consuming the...
can shoot its sporangia towards light. Plant spores designed for dispersal
Biological dispersal
Biological dispersal refers to species movement away from an existing population or away from the parent organism. Through simply moving from one habitat patch to another, the dispersal of an individual has consequences not only for individual fitness, but also for population dynamics, population...
are also referred to as diaspore
Diaspore (botany)
In botany, a diaspore is a plant dispersal unit consisting of a seed or spore plus any additional tissues that assist dispersal. In some seed plants, the diaspore is a seed and fruit together, or a seed and elaiosome. In a few seed plants, the diaspore is most or all of the plant, known as a...
s. Plant spores are most obvious in the reproduction of fern
Fern
A fern is any one of a group of about 12,000 species of plants belonging to the botanical group known as Pteridophyta. Unlike mosses, they have xylem and phloem . They have stems, leaves, and roots like other vascular plants...
s and moss
Moss
Mosses are small, soft plants that are typically 1–10 cm tall, though some species are much larger. They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady locations. They do not have flowers or seeds, and their simple leaves cover the thin wiry stems...
es. However, they also exist in flowering plant
Flowering plant
The flowering plants , also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies...
s where they develop hidden inside the flower. For example, the pollen grains of flowering plants develop out of microspores produced in the anthers.
Reproductive spores grow into multicellular haploid individuals or sporeling
Sporeling
A sporeling is a young plant or fungus produced by a germinated spore, similar to a seedling derived from a germinated seed. They occur in algae, fungi, lichens, bryophytes and seedless vascular plants.- Sporeling development :...
s. In heterosporous organisms, two types of spores exist: microspores give rise to males and megaspores to females. In homosporous organisms, all spores look alike and grow into individuals carrying reproductive parts of both genders.
Formation of reproductive spores
Sporogenesis occurs in reproductive structures termed sporangiaSporangium
A sporangium is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. All plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle...
. The process involves sporogenous cells (sporocytes, also called spore mother cells) undergoing cell division to give rise to spores.
Meiospore formation
In meiotic sporogenesis, a diploid spore mother cell within the sporangium undergoes meiosis, producing a tetrad of haploid spores. In organisms that are heterosporous, two types of spores occur: Microsporangia produce maleMale
Male refers to the biological sex of an organism, or part of an organism, which produces small mobile gametes, called spermatozoa. Each spermatozoon can fuse with a larger female gamete or ovum, in the process of fertilization...
microspores, and megasporangia produce female
Female
Female is the sex of an organism, or a part of an organism, which produces non-mobile ova .- Defining characteristics :The ova are defined as the larger gametes in a heterogamous reproduction system, while the smaller, usually motile gamete, the spermatozoon, is produced by the male...
megaspores. In megasporogenesis, often three of the four spores degenerate after meiosis, whereas in microsporogenesis all four microspores survive.
In gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s, such as conifers, microspores are produced through meiosis from microsporocytes in microstrobili
Strobilus
A strobilus is a structure present on many land plant species consisting of sporangia-bearing structures densely aggregated along a stem. Strobili are often called cones, but many botanists restrict the use of the term cone to the woody seed strobili of conifers...
or male cones. In flowering plant
Flowering plant
The flowering plants , also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by a series of synapomorphies...
s, microspores are produced in the anthers of flowers. Each anther contains four pollen sacs, which contain the microsporocytes. After meiosis, each microspore undergoes mitotic cell division, giving rise to multicellular pollen grains (six nuclei in gymnosperms, three nuclei in flowering plants).
Megasporogenesis occurs in megastrobili
Strobilus
A strobilus is a structure present on many land plant species consisting of sporangia-bearing structures densely aggregated along a stem. Strobili are often called cones, but many botanists restrict the use of the term cone to the woody seed strobili of conifers...
in conifers (for example a pine cone) and inside the ovule
Ovule
Ovule means "small egg". In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: The integument forming its outer layer, the nucellus , and the megaspore-derived female gametophyte in its center...
in the flowers of flowering plants. A megasporocyte inside a megasporangium or ovule undergoes meiosis, producing four megaspores. Only one is a functional megaspore whereas the others stay dysfunctional or degenerate. The megaspore undergoes several mitotic divisions to develop into a female gametophyte
Gametophyte
A gametophyte is the haploid, multicellular phase of plants and algae that undergo alternation of generations, with each of its cells containing only a single set of chromosomes....
(for example the seven-cell/eight-nuclei embryo sac in flowering plants).
Mitospore formation
Some fungi and algae produce mitospores through mitotic cell division within a sporangium. In fungi, such mitospores are referred to as conidia.Formation of dormant spores
Some algae, fungi and bacteria form resting sporeResting spore
A resting spore is a spore created by fungi which is thickly encysted in order to survive through stressful times, such as drought. It protects the spore from biotic , as well as abiotic factors.-Characteristics:Resting spores create the phenomenon known as late potato blight...
s designed to survive unfavorable conditions. Typically, changes in the environment from favorable to unfavorable growing conditions will trigger a switch from asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a mode of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single parent, and inherit the genes of that parent only, it is reproduction which does not involve meiosis, ploidy reduction, or fertilization. A more stringent definition is agamogenesis which is reproduction without...
to sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the creation of a new organism by combining the genetic material of two organisms. There are two main processes during sexual reproduction; they are: meiosis, involving the halving of the number of chromosomes; and fertilization, involving the fusion of two gametes and the...
in these organisms. The resulting spores are protected through the formation of a thick cell wall
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
and can withstand harsh conditions such as drought or extreme temperatures. Examples are chlamydospore
Chlamydospore
A Chlamydospore is the thick-walled big resting spore of several kinds of fungi. It is the life-stage which survives in unfavourable conditions, such as dry or hot seasons....
s, teliospore
Teliospore
Teliospore is the thick-walled resting spore of some fungi , from which the basidium arises.-Development:They develop in telia ....
s, zygospore
Zygospore
A zygospore is a diploid reproductive stage in the life cycle of many fungi and protists. Zygospores are created by the nuclear fusion of haploid cells. In fungi, zygospores are termed chlamydospores and are formed after the fusion of hyphae of different mating types...
s, and myxospores
Myxococcus xanthus
Myxococcus xanthus colonies exist as a self-organized, predatory, saprotrophic, single-species biofilm called a swarm. Myxococcus xanthus, which can be found almost ubiquitously in soil, are thin rod shaped, gram-negative cells that exhibit self-organizing behavior as a response to environmental...
.
Chlamydospore and teliospore formation
ChlamydosporeChlamydospore
A Chlamydospore is the thick-walled big resting spore of several kinds of fungi. It is the life-stage which survives in unfavourable conditions, such as dry or hot seasons....
s are generally multicellular, asexual structures. Teliospore
Teliospore
Teliospore is the thick-walled resting spore of some fungi , from which the basidium arises.-Development:They develop in telia ....
s are a form of chlamydospore produced through the fusion of cells or hyphae where the nuclei
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
of the fused cells stay separate. These nuclei undergo karyogamy
Karyogamy
Karyogamy is the fusion of pronuclei of two cells, as part of syngamy, fertilization, or true bacterial conjugation.It is one of the two major modes of reproduction in fungi...
and meiosis upon germination of the spore.
Zygospore, oospore and auxospore formation
ZygosporeZygospore
A zygospore is a diploid reproductive stage in the life cycle of many fungi and protists. Zygospores are created by the nuclear fusion of haploid cells. In fungi, zygospores are termed chlamydospores and are formed after the fusion of hyphae of different mating types...
s are formed in certain fungi (zygomycota
Zygomycota
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a phylum of fungi. The name comes from zygosporangia, where resistant spherical spores are formed during sexual reproduction. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material...
, for example Rhizopus
Rhizopus
Rhizopus is a genus of common saprobic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found on a wide variety of organic substrates, including "mature fruits and vegetables", faeces, jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts and tobacco. Some Rhizopus species are opportunistic agents...
) and some algae (for example Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae. They are unicellular flagellates. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics...
). The zygospore forms through the isogamic
Isogamy
Isogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves gametes of similar morphology , differing only in allele expression in one or more mating-type regions...
fusion of two cells (motile single cells in Chlamydomonas) or sexual conjugation between two hyphae (in zygomycota). Plasmogamy
Plasmogamy
Plasmogamy is a stage in the sexual reproduction of fungi. In this stage, the cytoplasm of two parent mycelia fuse together without the fusion of nuclei, as occurs in higher terrestrial fungi. After plasmogamy occurs, the secondary mycelium forms. The secondary mycelium consists of dikaryotic...
is followed by karyogamy
Karyogamy
Karyogamy is the fusion of pronuclei of two cells, as part of syngamy, fertilization, or true bacterial conjugation.It is one of the two major modes of reproduction in fungi...
, therefore zygospores are diploid (zygote
Zygote
A zygote , or zygocyte, is the initial cell formed when two gamete cells are joined by means of sexual reproduction. In multicellular organisms, it is the earliest developmental stage of the embryo...
s). They will undergo zygotic meiosis upon germinating.
In oomycetes, the zygote forms through the fertilization of an egg cell with a sperm nucleus and enters a resting stage as a diploid, thick-walled oospore
Oospore
An oospore is a thick-walled sexual spore that develops from a fertilized oosphere in some algae and fungi. Also the result of plasmogamy/karyogamy in oomycetes, which in turn leads to the development of hyphae, then mycelium....
. The germinating oospore undergoes mitosis and gives rise to diploid hyphae which reproduce asexually via mitotic zoospores as long as conditions are favorable.
In diatom
Diatom
Diatoms are a major group of algae, and are one of the most common types of phytoplankton. Most diatoms are unicellular, although they can exist as colonies in the shape of filaments or ribbons , fans , zigzags , or stellate colonies . Diatoms are producers within the food chain...
s, fertilization gives rise to a zygote termed auxospore
Auxospore
In certain species of diatoms, auxospores are specialised cells that are produced at key stages in their cell cycle or life history. Auxospores typically play a role in growth processes, sexual reproduction or dormancy....
. Besides sexual reproduction and as a resting stage, the function of an auxospore is the restoration of the original cell size, as diatoms get progressively smaller during mitotic cell division. Auxospores divide by mitosis.
Endospore formation
The term sporogenesis can also refer to endosporeEndospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and temporarily non-reproductive structure produced by certain bacteria from the Firmicute phylum. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form , but it is not a true spore . It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce...
formation in bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, which allows the cells to survive unfavorable conditions. Endospores are not reproductive structures and their formation does not require cell fusion or division. Instead, they form through the production of an encapsulating spore coat within the spore-forming cell.

