Slot-waveguide
Encyclopedia
A slot-waveguide is an optical waveguide that guides strongly confined light
in a subwavelength
-scale low refractive index
region by total internal reflection
.
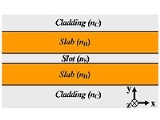
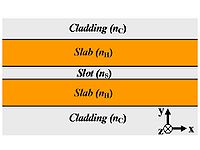
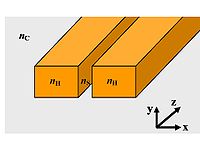
A slot-waveguide consists of two strips or slabs of high-refractive-index (nH) materials separated by a subwavelength-scale low-refractive-index (nS) slot region and surrounded by low-refractive-index (nC) cladding materials.
(E-field) at high-refractive-index-contrast interfaces. Maxwell’s equations state that, to satisfy the continuity of the normal component of the electric displacement field D at an interface, the corresponding E-field must undergo a discontinuity with higher amplitude in the low-refractive-index side. That is, at an interface between two regions of dielectric constant
s εS and εH, respectively:
where the superscript N indicates the normal components of D and E vector fields. Thus, if nS<H, then ESN>>EHN.
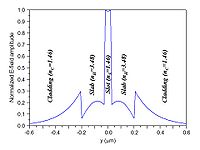
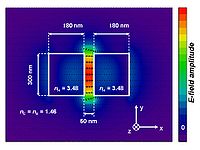 Given that the slot critical dimension (distance between the high-index slabs or strips) is comparable to the exponential decay length of the fundamental eigenmode of the guided-wave structure, the resulting E-field normal to the high-index-contrast interfaces is enhanced in the slot and remains high across it. The power density in the slot is much higher than that in the high-index regions. Since wave propagation is due to total internal reflection, there is no interference effect involved and the slot-structure exhibits very low wavelength sensitivity .
Given that the slot critical dimension (distance between the high-index slabs or strips) is comparable to the exponential decay length of the fundamental eigenmode of the guided-wave structure, the resulting E-field normal to the high-index-contrast interfaces is enhanced in the slot and remains high across it. The power density in the slot is much higher than that in the high-index regions. Since wave propagation is due to total internal reflection, there is no interference effect involved and the slot-structure exhibits very low wavelength sensitivity .
-oxide
-semiconductor
(MOS) electro-optic modulation
in high-confinement silicon photonic waveguides by Vilson Rosa de Almeida and Carlos Angulo Barrios, then a Ph.D. student and a Postdoctoral Associate, respectively, at Cornell University
. Theoretical analysis and experimental demonstration of the first slot-waveguide implemented in the Si/SiO2 material system at 1.55 μm operation wavelength were reported by Cornell researchers in 2004.
Since these pioneering works, several guided-wave configurations based on the slot-waveguide concept have been proposed and demonstrated. Relevant examples are the following:
In 2005, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
proposed to use multiple slot regions in the same guided-wave structure (multi-slot waveguide) in order to increase the optical field in the low-refractive-index regions . The experimental demonstration of such multiple slot waveguide in a horizontal configuration was first published in 2007 .
In 2006, the slot-waveguide approach was extended to the terahertz frequency band by researchers at RWTH Aachen University . Researchers at the California Institute of Technology
also demonstrated that a slot waveguide, in combination with nonlinear electrooptic polymers, could be used to build ring modulators with exceptionally high tunability. Later this same principle enabled Baehr-Jones et al. to demonstrate a mach-zehnder modulator with an exceptionally low drive voltage of 0.25 V
In 2007, a non-planar implementation of the slot-waveguide principle of operation was demonstrated by researchers at the University of Bath
. They showed concentration of optical energy within a subwavelength-scale air hole running down the length of a photonic-crystal fiber
.
, photolithography
, chemical vapour deposition [usually low-pressure chemical vapour deposition (LPCVD) or plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD)], thermal oxidation
, reactive-ion etching and focused ion beam
.
In vertical slot-waveguides, the slot and strips widths are defined by electron- or photo-lithography and dry etching techniques whereas in horizontal slot-waveguides the slot and strips thicknesses are defined by a thin-film deposition technique or thermal oxidation. Thin film deposition or oxidation provides better control of the layers dimensions and smoother interfaces between the high-index-contrast materials than lithography and dry etching techniques. This makes horizontal slot-waveguides less sensitive to scattering optical losses due to interface roughness than vertical configurations.
Fabrication of a non-planar (fiber-based) slot-waveguide configuration has also been demonstrated by means of conventional microstructured optical fiber
technology .
, and optical intensity in low-index materials at levels that cannot be achieved with conventional waveguides. This property allows highly efficient interaction between fields and active materials, which may lead to all-optical switching, optical amplification and optical detection on integrated photonics. Strong E-field confinement can be localized in a nanometer-scale low-index region. As firstly pointed out in , the slot waveguide can be used to greatly increase the sensitivity of compact optical sensing devices or to enhance the efficiency of near-field optics
probes.
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
in a subwavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
-scale low refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
region by total internal reflection
Total internal reflection
Total internal reflection is an optical phenomenon that happens when a ray of light strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is...
.
A slot-waveguide consists of two strips or slabs of high-refractive-index (nH) materials separated by a subwavelength-scale low-refractive-index (nS) slot region and surrounded by low-refractive-index (nC) cladding materials.


Principle of operation
The principle of operation of a slot-waveguide is based on the discontinuity of the electric fieldElectric field
In physics, an electric field surrounds electrically charged particles and time-varying magnetic fields. The electric field depicts the force exerted on other electrically charged objects by the electrically charged particle the field is surrounding...
(E-field) at high-refractive-index-contrast interfaces. Maxwell’s equations state that, to satisfy the continuity of the normal component of the electric displacement field D at an interface, the corresponding E-field must undergo a discontinuity with higher amplitude in the low-refractive-index side. That is, at an interface between two regions of dielectric constant
Dielectric constant
The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum...
s εS and εH, respectively:
- DSN=DHN
- εSESN=εHEHN
- nS2ESN=nH2EHN
where the superscript N indicates the normal components of D and E vector fields. Thus, if nS<


Invention
The slot-waveguide was born in 2003 as an unexpected outcome of theoretical studies on metalMetal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
-oxide
Oxide
An oxide is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom in its chemical formula. Metal oxides typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of −2....
-semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
(MOS) electro-optic modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
in high-confinement silicon photonic waveguides by Vilson Rosa de Almeida and Carlos Angulo Barrios, then a Ph.D. student and a Postdoctoral Associate, respectively, at Cornell University
Cornell University
Cornell University is an Ivy League university located in Ithaca, New York, United States. It is a private land-grant university, receiving annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions...
. Theoretical analysis and experimental demonstration of the first slot-waveguide implemented in the Si/SiO2 material system at 1.55 μm operation wavelength were reported by Cornell researchers in 2004.
Since these pioneering works, several guided-wave configurations based on the slot-waveguide concept have been proposed and demonstrated. Relevant examples are the following:
In 2005, researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. MIT has five schools and one college, containing a total of 32 academic departments, with a strong emphasis on scientific and technological education and research.Founded in 1861 in...
proposed to use multiple slot regions in the same guided-wave structure (multi-slot waveguide) in order to increase the optical field in the low-refractive-index regions . The experimental demonstration of such multiple slot waveguide in a horizontal configuration was first published in 2007 .
In 2006, the slot-waveguide approach was extended to the terahertz frequency band by researchers at RWTH Aachen University . Researchers at the California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Pasadena, California, United States. Caltech has six academic divisions with strong emphases on science and engineering...
also demonstrated that a slot waveguide, in combination with nonlinear electrooptic polymers, could be used to build ring modulators with exceptionally high tunability. Later this same principle enabled Baehr-Jones et al. to demonstrate a mach-zehnder modulator with an exceptionally low drive voltage of 0.25 V
In 2007, a non-planar implementation of the slot-waveguide principle of operation was demonstrated by researchers at the University of Bath
University of Bath
The University of Bath is a campus university located in Bath, United Kingdom. It received its Royal Charter in 1966....
. They showed concentration of optical energy within a subwavelength-scale air hole running down the length of a photonic-crystal fiber
Photonic-crystal fiber
Photonic-crystal fiber is a new class of optical fiber based on the properties of photonic crystals. Because of its ability to confine light in hollow cores or with confinement characteristics not possible in conventional optical fiber, PCF is now finding applications in fiber-optic...
.
Fabrication
Planar slot-waveguides have been fabricated in different material systems such as Si/SiO2 and Si3N4/SiO2 . Both, vertical (slot plane is normal to the substrate plane) and horizontal (slot plane is parallel to the substrate plane) configurations have been implemented by using conventional micro- and nano-fabrication techniques. These processing tools include electron beam lithographyElectron beam lithography
Electron beam lithography is the practice of emitting a beam of electrons in a patterned fashion across a surface covered with a film , and of selectively removing either exposed or non-exposed regions of the resist...
, photolithography
Photolithography
Photolithography is a process used in microfabrication to selectively remove parts of a thin film or the bulk of a substrate. It uses light to transfer a geometric pattern from a photomask to a light-sensitive chemical "photoresist", or simply "resist," on the substrate...
, chemical vapour deposition [usually low-pressure chemical vapour deposition (LPCVD) or plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD)], thermal oxidation
Thermal oxidation
In microfabrication, thermal oxidation is a way to produce a thin layer of oxide on the surface of a wafer. The technique forces an oxidizing agent to diffuse into the wafer at high temperature and react with it. The rate of oxide growth is often predicted by the Deal-Grove model...
, reactive-ion etching and focused ion beam
Focused ion beam
Focused ion beam, also known as FIB, is a technique used particularly in the semiconductor industry, materials science and increasingly in the biological field for site-specific analysis, deposition, and ablation of materials. An FIB setup is a scientific instrument that resembles a scanning...
.
In vertical slot-waveguides, the slot and strips widths are defined by electron- or photo-lithography and dry etching techniques whereas in horizontal slot-waveguides the slot and strips thicknesses are defined by a thin-film deposition technique or thermal oxidation. Thin film deposition or oxidation provides better control of the layers dimensions and smoother interfaces between the high-index-contrast materials than lithography and dry etching techniques. This makes horizontal slot-waveguides less sensitive to scattering optical losses due to interface roughness than vertical configurations.
Fabrication of a non-planar (fiber-based) slot-waveguide configuration has also been demonstrated by means of conventional microstructured optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
technology .
Applications
A slot-waveguide produces high E-field amplitude, optical powerOptical power
Optical power is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length of the device. The dioptre is the most common unit of measurement of optical power...
, and optical intensity in low-index materials at levels that cannot be achieved with conventional waveguides. This property allows highly efficient interaction between fields and active materials, which may lead to all-optical switching, optical amplification and optical detection on integrated photonics. Strong E-field confinement can be localized in a nanometer-scale low-index region. As firstly pointed out in , the slot waveguide can be used to greatly increase the sensitivity of compact optical sensing devices or to enhance the efficiency of near-field optics
Near-field optics
Near-field optics is that branch of optics that considers configurations that depend on the passage of light to, from, through, or near an element with subwavelength features and the coupling of that light to a second element located a subwavelength distance from the first. The barrier of spatial...
probes.

