
Sidereal and tropical astrology
Encyclopedia
Sidereal
and tropical
are astronomical terms used to describe two different definitions of a "year". They are also used as terms for two systems of ecliptic coordinates
used in astrology
.
Both divide the ecliptic
into a number of "signs" named after constellation
s, but while the sidereal system defines the signs based on the fixed star
s, the tropical system defines it based on the position of vernal equinox (i.e. the intersection of the ecliptic with the celestial equator
). Because of the precession of the equinoxes
, the two systems do not remain fixed relative to each other but drift apart by about 1.4 arc degrees per century.
The tropical system was adopted during the Hellenistic period and remains prevalent in western astrology
. A sidereal system is used in Hindu astrology, and in some 20th-century systems of western astrology
.
While classical tropical astrology is based on the orientation of the Earth relative to the Sun and planets of the solar system
, sidereal astrology deals with the position of the Earth relative to both of these as well as the stars of the celestial sphere
. The actual positions of certain fixed stars as well as their constellations is an additional consideration in the horoscope.
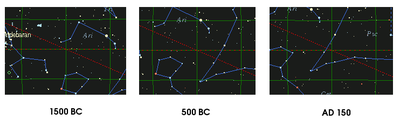 The classical zodiac
The classical zodiac
was introduced in the neo-Babylonian period (ca. 7th to 6th century BC). At the time, the precession of the equinoxes
had not been discovered. Classical Hellenistic astrology
consequently developed without consideration of the effects of precession.
The discovery of the precession of the equinoxes is attributed to Hipparchus
, a Greek astronomer active in the later Hellenistic period (ca. 130 BCE).
Ptolemy
writing some 250 years after Hipparchus was thus aware of the effects of precession. He opted for a definition of the zodiac based on the point of vernal equinox, i.e. the tropical system.
While Ptolemy noted that Ophiuchus is in contact with the ecliptic, he was aware that the twelve signs were just conventional names for 30 degrees segments (especially since the Aries sign had ceased to be in contact with the Aries constellation already in his time).
At the same time, Hindu astrology had been introduced based on the Hellenistic system via Indo-Greek cultural contact. The Hindu system opted for defining the zodiac based on the fixed stars, i.e. directly tied to the eponymous zodiacal constellations.
. The difference between the Vedic and the Western zodiacs is currently around 24 degrees. This corresponds to a separation of c. 1700 years, when the vernal equinox was approximately at the center of the constellation Pisces and the tropical zodiac coincided with the sidereal one (around 290 AD, or at 23.86° as of 2000 according to N. C. Lahiri, renowned author of Lahiri's Ephemeris published from kolkata, India. The separation is believed to have taken place in the centuries following Ptolemy
(2nd century AD), apparently going back to Indo-Greek transmission of the system. But earlier Greek astronomers like Eudoxus spoke of vernal equinox at 15° in Aries, while later Greeks spoke of vernal equinox at 8° and then 0° in Aries (cf. p. 16, S. Jim Tester in ref.), which suggests use of sidereal zodiac in Greece before Ptolemy and Hipparchus.
Cyril Fagan
assumes the origin of the zodiac in 786 BC, when the vernal equinox lay somewhere in mid-Aries, based on a major conjunction that occurred that year, corresponding to a difference of some 39 degrees or days.
Most sidereal astrologers simply divide the ecliptic into 12 equal signs of 30 degrees but approximately aligned to the 12 zodiac constellations. Assuming an origin of the system in 786 BCE, this results in an identical system as that of the classical tropical zodiac, shifted by 25.5 days, i.e., if in tropical astrology, Aries is taken to begin at March 21, sidereal Aries will begin on April 15.
But a small number of sidereal astrologers do not take the astrological signs as an equal division of the ecliptic, but define their signs based on the actual width of the individual constellations.
Stephen Schmidt in 1970 introduced Astrology 14, a system with additional signs based on the constellations of Ophiuchus
and Cetus
.
In 1995, Walter Berg
introduced his 13-sign zodiac, which has the additional sign of Ophiuchus
. Berg's system has been well-received in Japan
after his book was translated by radio host Mizui Kumi (水井久美) in 1996.
in 1930 are used. For example, the Sun enters the IAU boundary of Aries on April 19 at the lower right corner, a position that is still rather closer to the "body" of Pisces than of Aries. Needless to say, the IAU defined the constellation boundaries without consideration of astrological purposes.
The dates the Sun passes through the 13 astronomical constellations of the ecliptic
are listed below, accurate to the year 2002. The dates will increment by one day every 70½ years, and already several have changed. The corresponding tropical and sidereal dates are given as well.
Sidereal time
Sidereal time is a time-keeping system astronomers use to keep track of the direction to point their telescopes to view a given star in the night sky...
and tropical
Tropical year
A tropical year , for general purposes, is the length of time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the cycle of seasons, as seen from Earth; for example, the time from vernal equinox to vernal equinox, or from summer solstice to summer solstice...
are astronomical terms used to describe two different definitions of a "year". They are also used as terms for two systems of ecliptic coordinates
Ecliptic coordinate system
The ecliptic coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the ecliptic for its fundamental plane. The ecliptic is the path that the sun appears to follow across the celestial sphere over the course of a year. It is also the intersection of the Earth's orbital plane and the celestial...
used in astrology
Astrology
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
.
Both divide the ecliptic
Ecliptic
The ecliptic is the plane of the earth's orbit around the sun. In more accurate terms, it is the intersection of the celestial sphere with the ecliptic plane, which is the geometric plane containing the mean orbit of the Earth around the Sun...
into a number of "signs" named after constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
s, but while the sidereal system defines the signs based on the fixed star
Fixed star
The fixed stars are celestial objects that do not seem to move in relation to the other stars of the night sky. Hence, a fixed star is any star except for the Sun. A nebula or other starlike object may also be called a fixed star. People in many cultures have imagined that the stars form pictures...
s, the tropical system defines it based on the position of vernal equinox (i.e. the intersection of the ecliptic with the celestial equator
Celestial equator
The celestial equator is a great circle on the imaginary celestial sphere, in the same plane as the Earth's equator. In other words, it is a projection of the terrestrial equator out into space...
). Because of the precession of the equinoxes
Precession of the equinoxes
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In particular, it refers to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation, which, like a wobbling top, traces out a pair of cones joined...
, the two systems do not remain fixed relative to each other but drift apart by about 1.4 arc degrees per century.
The tropical system was adopted during the Hellenistic period and remains prevalent in western astrology
Western astrology
Western astrology is the system of astrology most popular in Western countries. Western astrology is historically based on Ptolemy's Tetrabiblos , which in turn was a continuation of Hellenistic and ultimately Babylonian traditions....
. A sidereal system is used in Hindu astrology, and in some 20th-century systems of western astrology
Western astrology
Western astrology is the system of astrology most popular in Western countries. Western astrology is historically based on Ptolemy's Tetrabiblos , which in turn was a continuation of Hellenistic and ultimately Babylonian traditions....
.
While classical tropical astrology is based on the orientation of the Earth relative to the Sun and planets of the solar system
Solar System
The Solar System consists of the Sun and the astronomical objects gravitationally bound in orbit around it, all of which formed from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud approximately 4.6 billion years ago. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun...
, sidereal astrology deals with the position of the Earth relative to both of these as well as the stars of the celestial sphere
Celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with the Earth and rotating upon the same axis. All objects in the sky can be thought of as projected upon the celestial sphere. Projected upward from Earth's equator and poles are the...
. The actual positions of certain fixed stars as well as their constellations is an additional consideration in the horoscope.
History

Zodiac
In astronomy, the zodiac is a circle of twelve 30° divisions of celestial longitude which are centred upon the ecliptic: the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year...
was introduced in the neo-Babylonian period (ca. 7th to 6th century BC). At the time, the precession of the equinoxes
Precession of the equinoxes
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In particular, it refers to the gradual shift in the orientation of Earth's axis of rotation, which, like a wobbling top, traces out a pair of cones joined...
had not been discovered. Classical Hellenistic astrology
Hellenistic astrology
Hellenistic astrology is a tradition of horoscopic astrology that was developed and practiced in Hellenistic Egypt and the Mediterranean, whose texts were written in Greek , mainly around the late 2nd or early 1st century B.C.E...
consequently developed without consideration of the effects of precession.
The discovery of the precession of the equinoxes is attributed to Hipparchus
Hipparchus
Hipparchus, the common Latinization of the Greek Hipparkhos, can mean:* Hipparchus, the ancient Greek astronomer** Hipparchic cycle, an astronomical cycle he created** Hipparchus , a lunar crater named in his honour...
, a Greek astronomer active in the later Hellenistic period (ca. 130 BCE).
Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
writing some 250 years after Hipparchus was thus aware of the effects of precession. He opted for a definition of the zodiac based on the point of vernal equinox, i.e. the tropical system.
While Ptolemy noted that Ophiuchus is in contact with the ecliptic, he was aware that the twelve signs were just conventional names for 30 degrees segments (especially since the Aries sign had ceased to be in contact with the Aries constellation already in his time).
At the same time, Hindu astrology had been introduced based on the Hellenistic system via Indo-Greek cultural contact. The Hindu system opted for defining the zodiac based on the fixed stars, i.e. directly tied to the eponymous zodiacal constellations.
Hindu astrology
Traditional Hindu astrology is based on the sidereal or visible zodiac, accounting for the shift of the equinoxes by a correction called ayanamsaAyanamsa
Ayanamsa , also ayanabhāga , is the Sanskrit term in Indian astronomy for the amount of precession...
. The difference between the Vedic and the Western zodiacs is currently around 24 degrees. This corresponds to a separation of c. 1700 years, when the vernal equinox was approximately at the center of the constellation Pisces and the tropical zodiac coincided with the sidereal one (around 290 AD, or at 23.86° as of 2000 according to N. C. Lahiri, renowned author of Lahiri's Ephemeris published from kolkata, India. The separation is believed to have taken place in the centuries following Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
(2nd century AD), apparently going back to Indo-Greek transmission of the system. But earlier Greek astronomers like Eudoxus spoke of vernal equinox at 15° in Aries, while later Greeks spoke of vernal equinox at 8° and then 0° in Aries (cf. p. 16, S. Jim Tester in ref.), which suggests use of sidereal zodiac in Greece before Ptolemy and Hipparchus.
Sideral western astrology
Some western astrologists have shown interest in the sidereal system during the 20th century.Cyril Fagan
Cyril Fagan
Cyril Fagan was an astrologer, who claimed historical use of sidereal astrology in the west and established it as a separate field from tropical astrology....
assumes the origin of the zodiac in 786 BC, when the vernal equinox lay somewhere in mid-Aries, based on a major conjunction that occurred that year, corresponding to a difference of some 39 degrees or days.
Most sidereal astrologers simply divide the ecliptic into 12 equal signs of 30 degrees but approximately aligned to the 12 zodiac constellations. Assuming an origin of the system in 786 BCE, this results in an identical system as that of the classical tropical zodiac, shifted by 25.5 days, i.e., if in tropical astrology, Aries is taken to begin at March 21, sidereal Aries will begin on April 15.
But a small number of sidereal astrologers do not take the astrological signs as an equal division of the ecliptic, but define their signs based on the actual width of the individual constellations.
Stephen Schmidt in 1970 introduced Astrology 14, a system with additional signs based on the constellations of Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century...
and Cetus
Cetus
Cetus is a constellation. Its name refers to Cetus, a sea monster in Greek mythology, although it is often called 'the whale' today. Cetus is located in the region of the sky that contains other water-related constellations such as Aquarius, Pisces, and Eridanus.-Ecliptic:Although Cetus is not...
.
In 1995, Walter Berg
Walter Berg
Walter Berg is a British astrologer, known for his system of a 13-sign sidereal astrology , "a sidereal system that uses the actual star constellations of the true zodiac"....
introduced his 13-sign zodiac, which has the additional sign of Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus (astrology)
Ophiuchus has sometimes been used in sidereal astrology as a thirteenth sign in addition to the twelve signs of the tropical Zodiac, because the eponymous constellation Ophiuchus as defined by the 1930 IAU constellation boundaries is situated behind the sun between November 29 and December 18.The...
. Berg's system has been well-received in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
after his book was translated by radio host Mizui Kumi (水井久美) in 1996.
Modern constellations along the ecliptic
For the purpose of determining the constellations in contact with the ecliptic, the constellation boundaries as defined by the International Astronomical UnionInternational Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
in 1930 are used. For example, the Sun enters the IAU boundary of Aries on April 19 at the lower right corner, a position that is still rather closer to the "body" of Pisces than of Aries. Needless to say, the IAU defined the constellation boundaries without consideration of astrological purposes.
The dates the Sun passes through the 13 astronomical constellations of the ecliptic
Ecliptic
The ecliptic is the plane of the earth's orbit around the sun. In more accurate terms, it is the intersection of the celestial sphere with the ecliptic plane, which is the geometric plane containing the mean orbit of the Earth around the Sun...
are listed below, accurate to the year 2002. The dates will increment by one day every 70½ years, and already several have changed. The corresponding tropical and sidereal dates are given as well.
| Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Sidereal Date Cyril Fagan Cyril Fagan Cyril Fagan was an astrologer, who claimed historical use of sidereal astrology in the west and established it as a separate field from tropical astrology.... |
Tropical date | IAU Definition Walter Berg Walter Berg Walter Berg is a British astrologer, known for his system of a 13-sign sidereal astrology , "a sidereal system that uses the actual star constellations of the true zodiac".... |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
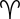 |
Aries Aries (astrology) Aries is the first astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the zero degree and the 29th degree of celestial longitude. The Sun enters Aries when it reaches the northern vernal equinox, which is usually on March 21 each year, and remains in this sign until around April 20... |
April 15 - May 15 | March 21 - April 20 | April 19 - May 13 May 17 - May 18 |
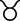 |
Taurus Taurus (astrology) Taurus is the second astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the 30th and 59th degree of celestial longitude. Generally, the Sun transits this area of the zodiac between April 21 to May 21 each year... |
May 16 - June 15 | April 21 - May 20 | May 14 - May 16 May 19 - June 19 |
 |
Gemini Gemini (astrology) Gemini is the third astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the Zodiac between the 60th and 89th degree of celestial longitude. Generally, the Sun transits this area of the zodiac between May 21 to June 20 each year... |
June 16 - July 15 | May 21 - June 20 | June 20 - July 20 |
 |
Cancer Cancer (astrology) Cancer is the fourth astrological sign in the Zodiac. It is considered a water sign and one of four cardinal signs. Cancer is ruled by the Moon. Individuals born when the Sun is in this sign are considered Cancerian individuals... |
July 16 - August 15 | June 21 - July 21 | July 21 - August 9 |
 |
Leo Leo (astrology) Leo is the fifth astrological sign of the Zodiac, originating from the constellation of Leo. In astrology, Leo is considered to be a "masculine", positive sign. It is also considered a fire sign and is one of four fixed signs ruled by the Sun.Individuals born when the Sun is in this sign are... |
August 16 - September 15 | July 22 - August 22 | August 11 - September 15 |
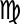 |
Virgo Virgo (astrology) Virgo is the sixth astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the 150th and 179th degree of celestial longitude. Generally, the Sun transits this area of the zodiac between August 23 to September 22 each year... |
September 16 - October 15 | August 23 - September 22 | September 16 - October 30 |
 |
Libra Libra (astrology) Libra is the seventh astrological sign in the Zodiac, originating from the constellation of Libra. In astrology, Libra is considered a "masculine", positive sign. It is also considered an air sign and is one of four cardinal signs... |
October 16 - November 15 | September 23 - October 22 | October 31 - November 22 |
 |
Scorpius Scorpio (astrology) |Infobox align="right" style="border:3px solid white;"||style="text-align: center;"|Scorpio is the eighth astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the 210th and 239th degree of celestial longitude. Generally, the Sun transits this area of the zodiac between 24 October and... |
November 16 - December 15 | October 23 - November 21 | November 23 - November 28 |
 / / |
Ophiuchus Ophiuchus (astrology) Ophiuchus has sometimes been used in sidereal astrology as a thirteenth sign in addition to the twelve signs of the tropical Zodiac, because the eponymous constellation Ophiuchus as defined by the 1930 IAU constellation boundaries is situated behind the sun between November 29 and December 18.The... |
N/A | November 29 - December 17 | |
 |
Sagittarius Sagittarius (astrology) Sagittarius is the ninth astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the 240th and 269th degree of celestial longitude... |
December 16 - January 14 | November 22 - December 21 | December 18 - January 17 |
 |
Capricorn | January 15 - February 14 | December 22 - January 20 | January 18 - February 15 |
 |
Aquarius | February 15 - March 14 | January 21 - February 19 | February 16 - March 11 |
 |
Pisces | March 15 - April 14 | February 20 - March 20 | March 12 - April 18 |

