Pierre Desceliers
Encyclopedia
Pierre Desceliers was a French
cartographer
of the Renaissance
and an eminent member of the Dieppe School of Cartography
. He is considered the father of French hydrography
.
Little is known of his life. He was probably born at Arques-la-Bataille
about 1500. However, other sources give his birth date as 1483, although this seems unlikely, given the date of his maps. Desceliers' father was an archer at the Chateau d’Arques and his family possibly originated from the d’Auge area, where the family name survives between Honfleur
and Pont-l’Évêque
.
It is known that Desceliers was ordained and lived near Arques
. He was also an examiner of Maritime Pilots and was authorised to award patents on behalf of the French king, as evidenced by the seal found bearing his initials. He probably also taught hydrography. He made a hydrographic chart of the coast of France
for Francis, Duke of Guise
.
and Dieppois, explorers Giovanni da Verrazano
and the brothers Jean and Raoul Parmentier
. Although it seems unlikely that he took part in any voyages, he was able collect information including portolans, and he incorporated this information into his own maps. A school of cartography formed around him in Dieppe and included Nicolas Desliens among its members.
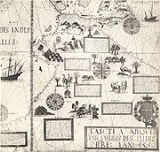
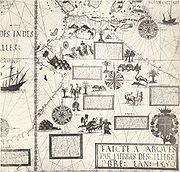
Desceliers made several large portolans:
The Dieppe maps
were produced in a transitional era of mapmaking, between the medieval and modern era. As well as precise knowledge of the coastlines, they also included representations of imaginary places, fantastic people and bizarre animals. In the southern hemisphere section, a landmass entitled Jave la Grande
was shown in the approximate position of Australia
. This has led to speculation that the Dieppe maps
are evidence of European (possibly Portuguese
) exploration of Australia
in the 16th century; one hundred years before its well documented exploration by the Dutch
. The representation of eastern Canada
was well detailed, along with most of the America
north and south, just fifty years after the voyage of Columbus
.
Despite their great value, both artistic and cartographic, the charts quickly fell into disuse after the end of the 16th century, with the arrival of the rigorous maps of Mercator
.
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
cartographer
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
of the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
and an eminent member of the Dieppe School of Cartography
Dieppe maps
The Dieppe maps are a series of world maps produced in Dieppe, France, in the 1540s, 1550s and 1560s. They are large hand-produced maps, commissioned for wealthy and royal patrons, including Henry II of France and Henry VIII of England...
. He is considered the father of French hydrography
Hydrography
Hydrography is the measurement of the depths, the tides and currents of a body of water and establishment of the sea, river or lake bed topography and morphology. Normally and historically for the purpose of charting a body of water for the safe navigation of shipping...
.
Little is known of his life. He was probably born at Arques-la-Bataille
Arques-la-Bataille
Arques-la-Bataille is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Haute-Normandie region in northern France.-Geography:Arques is situated near the confluence of the rivers Eaulne, Varenne and Béthune, with the forest of Arques to the north-east...
about 1500. However, other sources give his birth date as 1483, although this seems unlikely, given the date of his maps. Desceliers' father was an archer at the Chateau d’Arques and his family possibly originated from the d’Auge area, where the family name survives between Honfleur
Honfleur
Honfleur is a commune in the Calvados department in northwestern France. It is located on the southern bank of the estuary of the Seine across from le Havre and very close to the exit of the Pont de Normandie...
and Pont-l’Évêque
Pont-l'Évêque, Calvados
Pont-l'Évêque is a commune in the Calvados department in the Basse-Normandie region in northwestern France. It has given its name to a type of soft cheese .-Population:-Transport:* A13 autoroute* A132 autoroute...
.
It is known that Desceliers was ordained and lived near Arques
Arques-la-Bataille
Arques-la-Bataille is a commune in the Seine-Maritime department in the Haute-Normandie region in northern France.-Geography:Arques is situated near the confluence of the rivers Eaulne, Varenne and Béthune, with the forest of Arques to the north-east...
. He was also an examiner of Maritime Pilots and was authorised to award patents on behalf of the French king, as evidenced by the seal found bearing his initials. He probably also taught hydrography. He made a hydrographic chart of the coast of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
for Francis, Duke of Guise
Francis, Duke of Guise
Francis de Lorraine II, Prince of Joinville, Duke of Guise, Duke of Aumale , called Balafré , was a French soldier and politician.-Early life:...
.

Cartographic work
He was close to Jean AngoJean Ango
Jean Ango was a French ship-owner who provided ships to Francis I for exploration of the globe. A native of Dieppe, Ango took over his father's import-export business, and ventured into the spice trade with Africa and India...
and Dieppois, explorers Giovanni da Verrazano
Giovanni da Verrazano
Giovanni da Verrazzano was an Italian explorer of North America, in the service of the French crown. He is renowned as the first European since the Norse expeditions to North America around AD 1000 to explore the Atlantic coast of North America between the Carolinas and Newfoundland, including New...
and the brothers Jean and Raoul Parmentier
Jean Parmentier
Jean Parmentier , born in Dieppe, France, was a navigator, cartographer, and poet. Jean and his brother Raoul made numerous voyages for the shipowner Jean Ango, and sailed to the coasts of Brazil, North America, West Africa and Sumatra....
. Although it seems unlikely that he took part in any voyages, he was able collect information including portolans, and he incorporated this information into his own maps. A school of cartography formed around him in Dieppe and included Nicolas Desliens among its members.
Desceliers made several large portolans:
- The 1543 portolan mentioned in 1872 in the inventory of the collection of Cardinal Louis d'Este under the title The descriptione carta del Mondo in pecorina scritta a mano, miniata tutta per P. Descheliers. The fate of this map is unknown.
- The 1546 portolan (size: 2560mm x 1260mm), made to order for Francis IFrancis I of FranceFrancis I was King of France from 1515 until his death. During his reign, huge cultural changes took place in France and he has been called France's original Renaissance monarch...
. It later belonged to a certain Jomard, then to the Earl of Crawford and is now stored in EnglandEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
at the John Rylands LibraryJohn Rylands LibraryThe John Rylands Library is a Victorian Gothic building on Deansgate in Manchester, England. The library, which opened to the public in 1900, was founded by Mrs Enriqueta Augustina Rylands in memory of her late husband, John Rylands...
, Manchester (French MS. 1*) - The 1550 portolan, made for Henry IIHenry II of FranceHenry II was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559.-Early years:Henry was born in the royal Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, the son of Francis I and Claude, Duchess of Brittany .His father was captured at the Battle of Pavia in 1525 by his sworn enemy,...
, showing his arms as well as those of Anne de Montmorency (Marshal of France) and Admiral Claude d'Annebaut. This portolan is preserved in LondonLondonLondon is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, at the British LibraryBritish LibraryThe British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom, and is the world's largest library in terms of total number of items. The library is a major research library, holding over 150 million items from every country in the world, in virtually all known languages and in many formats,...
. - The 1553 portolan. This was lost in a fire in DresdenDresdenDresden is the capital city of the Free State of Saxony in Germany. It is situated in a valley on the River Elbe, near the Czech border. The Dresden conurbation is part of the Saxon Triangle metropolitan area....
in 1915. A copy is on display in Dieppe Castle. - Another portolan, dated 1558 whose fate is currently unknown, appeared in the International Exhibition of Geography in ParisParisParis is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
in 1875.
The Dieppe maps
Dieppe maps
The Dieppe maps are a series of world maps produced in Dieppe, France, in the 1540s, 1550s and 1560s. They are large hand-produced maps, commissioned for wealthy and royal patrons, including Henry II of France and Henry VIII of England...
were produced in a transitional era of mapmaking, between the medieval and modern era. As well as precise knowledge of the coastlines, they also included representations of imaginary places, fantastic people and bizarre animals. In the southern hemisphere section, a landmass entitled Jave la Grande
Jave la Grande
La grande isle de Java was, according to Marco Polo, the largest island in the world: his Java Minor was the actual island of Sumatra, which takes its name from the city of Samudera situated on its northern coast....
was shown in the approximate position of Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
. This has led to speculation that the Dieppe maps
Dieppe maps
The Dieppe maps are a series of world maps produced in Dieppe, France, in the 1540s, 1550s and 1560s. They are large hand-produced maps, commissioned for wealthy and royal patrons, including Henry II of France and Henry VIII of England...
are evidence of European (possibly Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
) exploration of Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
in the 16th century; one hundred years before its well documented exploration by the Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
. The representation of eastern Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
was well detailed, along with most of the America
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
north and south, just fifty years after the voyage of Columbus
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
.
Despite their great value, both artistic and cartographic, the charts quickly fell into disuse after the end of the 16th century, with the arrival of the rigorous maps of Mercator
Gerardus Mercator
thumb|right|200px|Gerardus MercatorGerardus Mercator was a cartographer, born in Rupelmonde in the Hapsburg County of Flanders, part of the Holy Roman Empire. He is remembered for the Mercator projection world map, which is named after him...
.

