
Phosphagen
Encyclopedia
The phosphagens are energy storage compounds, also known as high-energy phosphate compounds, are chiefly found in muscular
tissue in animal
s. They allow a high-energy phosphate pool to be maintained in a concentration range, which, if it all were ATP
, would create problems due to the ATP
consuming reactions in these tissues. As muscle tissues can have sudden demands for lots of energy; these compounds can maintain a reserve of high-energy phosphates that can be used as needed, to provide the energy that could not be immediately supplied by glycolysis
or oxidative phosphorylation
. Phosphagens supply immediate but limited energy.
The actual biomolecule
used as a phosphagen is dependent on the organism. The majority of animals use arginine/phosphoarginine as phosphagens; however, the phylum Chordata (i.e., animals with spinal cords) use creatine
. Creatine phosphate, or phosphocreatine, is made from ATP by the enzyme creatine kinase
in a reversible reaction:
However, annelids (segmented worms) use a set of unique phosphagens; for example, earthworms use the compound lombricine
.
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
tissue in animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s. They allow a high-energy phosphate pool to be maintained in a concentration range, which, if it all were ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
, would create problems due to the ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
consuming reactions in these tissues. As muscle tissues can have sudden demands for lots of energy; these compounds can maintain a reserve of high-energy phosphates that can be used as needed, to provide the energy that could not be immediately supplied by glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+...
or oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
. Phosphagens supply immediate but limited energy.
The actual biomolecule
Biomolecule
A biomolecule is any molecule that is produced by a living organism, including large polymeric molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites, and natural products...
used as a phosphagen is dependent on the organism. The majority of animals use arginine/phosphoarginine as phosphagens; however, the phylum Chordata (i.e., animals with spinal cords) use creatine
Creatine
Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid that occurs naturally in vertebrates and helps to supply energy to all cells in the body, primarily muscle. This is achieved by increasing the formation of Adenosine triphosphate...
. Creatine phosphate, or phosphocreatine, is made from ATP by the enzyme creatine kinase
Creatine kinase
Creatine kinase , also known as creatine phosphokinase or phospho-creatine kinase , is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and consumes adenosine triphosphate to create phosphocreatine and adenosine diphosphate...
in a reversible reaction:
- Creatine + ATP
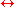 creatine phosphate + ADP (this reaction is Mg++-dependent)
creatine phosphate + ADP (this reaction is Mg++-dependent)
However, annelids (segmented worms) use a set of unique phosphagens; for example, earthworms use the compound lombricine
Lombricine
Lombricine is a phosphagen that is unique to earthworms. Structurally, it is a phosphodiester of the guanidine, 2-guanidinoethanol , and D-serine , which is then further phosphorylated by lombricine kinase to phospholombricine....
.

