Oxidative folding
Encyclopedia
Oxidative protein folding
is a process that is responsible for the formation of disulfide bonds between cysteine
residues in protein
s. The driving force behind this process is a redox reaction, in which electrons are passed between several proteins and finally to a terminal electron acceptor.
s, the mechanism of oxidative folding is best studied in Gram-negative bacteria. The formation of disulfide bonds in a protein is made possible by two related pathways: an oxidative pathway, which is responsible for the formation of the disulfides, and an isomerization pathway which shuffles incorrectly formed disulfides.
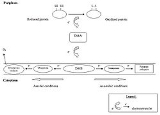
.jpg) The oxidative pathway relies, just like the isomerization pathway, on a protein relay. The first member of this protein relay is a small periplasmic protein (21 kDa) called DsbA
The oxidative pathway relies, just like the isomerization pathway, on a protein relay. The first member of this protein relay is a small periplasmic protein (21 kDa) called DsbA
, which has two cysteine residues that have to be oxidized in order for it to be active. When in its oxidized state, the protein is able to form disulfide bonds between cysteine residues in newly synthesized, and yet unfolded proteins by the transfer of its own disulfide bond onto the folding protein. After the transfer of this disulfide bond, DsbA is in a reduced state and in order for it to act catalytically again, it has to be reoxidized. This is made possible by a 21 kDa inner membrane
protein, called DsbB, which has two pairs of cysteine residues. A mixed disulfide is formed between a cysteine residue of DsbB and one of DsbA. Eventually, this cross-link between the two proteins is broken by a nucleophilic attack of the second cystein residue in the DsbA active site
. On his turn, DsbB is reoxidized by transferring electron
s to oxidized ubiquinone, which passes them to cytochrome
oxidases, which finally reduce oxygen
; this is in aerobic conditions. As molecular oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic conditions, oxidative folding is conveniently coupled to it through the respiratory chain. In anaerobic conditions however, DsbB passes its electrons to menaquinone, followed by a transfer of electrons to fumarate reductase
or nitrate reductase
.
.jpg) Especially for proteins that contain more than one disulfide bond, it is important that incorrect disulfide bonds become rearranged. This is carried out in the isomerization pathway by the protein DsbC, that acts as a disulfide isomerase
Especially for proteins that contain more than one disulfide bond, it is important that incorrect disulfide bonds become rearranged. This is carried out in the isomerization pathway by the protein DsbC, that acts as a disulfide isomerase
. DsbC is a dimer
, consisting of two identical 23 kDa subunits
and has four cysteine residues in each subunit. One of these cysteines (Cys-98) attacks an incorrect disulfide in a misfolded protein and a mixed disulfide is formed between DsbC and this protein. Next, the attack of a second cysteine residue results in the forming of a more stable disulfide in the refolded protein. This may be a cysteine residue either from the earlier misfolded protein or one from DsbC. In the last case, DsbC becomes oxidized and has to be reduced in order to play another catalytic role. There is also a second isomerase that can reorganize incorrect disulfide bonds. This protein is called DsbG and it is also a dimer that serves as a chaperone. In order to fulfil their role as isomerases, DsbC and DsbG need to be kept in a reduced state. This is carried out by DsbD, which has to be reduced itself to be functional. Thioredoxin, which itself is reduced by thioredoxin reductase
and NADPH, ensures the reduction of the DsbD protein.
Because these two pathways coexist next to each other in the same periplasmic compartment, there must be a mechanism to prevent oxidation of DsbC by DsbB. This mechanism indeed exists as DsbB can distinguish between DsbA and DsbC because this latter has the ability to dimerize.
.jpg) A very similar pathway is followed in eukaryotes, in which the protein relay consists of proteins with very analogous properties as those of the protein relay in Gram-negative bacteria. However, a major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is found in the fact that the process of oxidative protein folding occurs in the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER) in eukaryotes. A second difference is that in eukaryotes, the use of molecular oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor is not linked to the process of oxidative folding through the respiratory chain as is the case in bacteria. In fact, one of the proteins involved in the oxidative folding process uses a flavin-dependent reaction to pass electrons directly to molecular oxygen.
A very similar pathway is followed in eukaryotes, in which the protein relay consists of proteins with very analogous properties as those of the protein relay in Gram-negative bacteria. However, a major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is found in the fact that the process of oxidative protein folding occurs in the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER) in eukaryotes. A second difference is that in eukaryotes, the use of molecular oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor is not linked to the process of oxidative folding through the respiratory chain as is the case in bacteria. In fact, one of the proteins involved in the oxidative folding process uses a flavin-dependent reaction to pass electrons directly to molecular oxygen.
A homolog
of DsbA, called protein disulfide isomerase
(PDI), is responsible for the formation of the disulfide bonds in unfolded eukaryotic proteins. This protein has two thioredoxine-like active sites, which both contain two cysteine residues. By transferring the disulfide bond between these two cysteine residues onto the folding protein it is responsible for the latter’s oxidation. In contrast to bacteria, where the oxidative and isomerization pathways are carried out by different proteins, PDI is also responsible for the reduction and isomerization of the disulfide bonds. In order for PDI to catalyse the formation of disulfide bonds in unfolded proteins, it has to be reoxidized. This is carried out by an ER membrane-associated protein, Ero1p, which is no homolog of DsbB. This Ero1p protein forms a mixed disulfide with PDI, which is resolved by a nucleophilic attack of the second cystein residue in one of the active sites of PDI. As result, oxidized PDI is obtained. Ero1p itself is oxidized by transferring electrons to molecular oxygen. As it is an FAD
-binding protein, this transfer of electrons is strongly favoured when Ero1p is bound to FAD. Also a transport system that imports FAD into the ER lumen has been described in eukaryotes. Furthermore, it has been shown that the ability to reduce or rearrange incorrect disulfide bonds in missfolded proteins is provided by the oxidation of reduced glutathione
(GSH) to oxidized glutathione (GSSG).
(ROS). In bacteria, this problem is solved by coupling oxidative folding to the respiratory chain. There, the reduction of molecular oxygen to water
is carried out by a complex series of proteins, which catalyse this reaction very efficiently. In eukaryotes, the respiratory chain is separated from oxidative folding since cellular respiration
takes place in the mitochondria and the formation of disulfide bonds occurs in the ER. Because of this, there is much more risk that ROS are produced in eukaryotic cells during oxidative folding. As is known these ROS may cause many diseases such as atherosclerosis
and some neurodegenerative diseases.
(RNaseA). These two proteins have multiple disulfide bonds and so they are very useful to follow and understand the process of oxidative folding. Another example is alkaline phosphatase
, which contains two essential disulfides. It was used as an indicator protein to screen the effect of mutations in DsbA.
Protein folding
Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil....
is a process that is responsible for the formation of disulfide bonds between cysteine
Cysteine
Cysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
residues in protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. The driving force behind this process is a redox reaction, in which electrons are passed between several proteins and finally to a terminal electron acceptor.
In prokaryotes
In prokaryoteProkaryote
The prokaryotes are a group of organisms that lack a cell nucleus , or any other membrane-bound organelles. The organisms that have a cell nucleus are called eukaryotes. Most prokaryotes are unicellular, but a few such as myxobacteria have multicellular stages in their life cycles...
s, the mechanism of oxidative folding is best studied in Gram-negative bacteria. The formation of disulfide bonds in a protein is made possible by two related pathways: an oxidative pathway, which is responsible for the formation of the disulfides, and an isomerization pathway which shuffles incorrectly formed disulfides.
Oxidative pathway
.jpg)
DsbA
DSBA oxidoreductase is sub-family of the Thioredoxin family. The efficient and correct folding of bacterial disulfide bonded proteins in vivo is dependent upon a class of periplasmic oxidoreductase proteins called DsbA, after the Escherichia coli enzyme. The bacterial protein-folding factor DsbA is...
, which has two cysteine residues that have to be oxidized in order for it to be active. When in its oxidized state, the protein is able to form disulfide bonds between cysteine residues in newly synthesized, and yet unfolded proteins by the transfer of its own disulfide bond onto the folding protein. After the transfer of this disulfide bond, DsbA is in a reduced state and in order for it to act catalytically again, it has to be reoxidized. This is made possible by a 21 kDa inner membrane
Inner membrane
The inner membrane is the biological membrane of an organelle or Gram-negative bacteria that is within an outer membrane....
protein, called DsbB, which has two pairs of cysteine residues. A mixed disulfide is formed between a cysteine residue of DsbB and one of DsbA. Eventually, this cross-link between the two proteins is broken by a nucleophilic attack of the second cystein residue in the DsbA active site
Active site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
. On his turn, DsbB is reoxidized by transferring electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s to oxidized ubiquinone, which passes them to cytochrome
Cytochrome
Cytochromes are, in general, membrane-bound hemoproteins that contain heme groups and carry out electron transport.They are found either as monomeric proteins or as subunits of bigger enzymatic complexes that catalyze redox reactions....
oxidases, which finally reduce oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
; this is in aerobic conditions. As molecular oxygen serves as the terminal electron acceptor in aerobic conditions, oxidative folding is conveniently coupled to it through the respiratory chain. In anaerobic conditions however, DsbB passes its electrons to menaquinone, followed by a transfer of electrons to fumarate reductase
Fumarate reductase
Fumarate reductase is the enzyme that converts fumarate to succinate, and is important in microbial metabolism as a part of anaerobic respiration.Succinate + acceptor fumarate + reduced acceptor...
or nitrate reductase
Nitrate reductase
Nitrate reductases are molybdoenzymes that reduce nitrate to nitrite .* Eukaryotic nitrate reductases are part of the sulfite oxidase family of molybdoenzymes....
.
Isomerization pathway
.jpg)
Isomerase
In biochemistry, an isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the structural rearrangement of isomers. Isomerases thus catalyze reactions of the formwhere B is an isomer of A.-Nomenclature:...
. DsbC is a dimer
Protein dimer
In biochemistry, a dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two, usually non-covalently bound, macromolecules like proteins or nucleic acids...
, consisting of two identical 23 kDa subunits
Protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit or subunit protein is a single protein molecule that assembles with other protein molecules to form a protein complex: a multimeric or oligomeric protein. Many naturally occurring proteins and enzymes are multimeric...
and has four cysteine residues in each subunit. One of these cysteines (Cys-98) attacks an incorrect disulfide in a misfolded protein and a mixed disulfide is formed between DsbC and this protein. Next, the attack of a second cysteine residue results in the forming of a more stable disulfide in the refolded protein. This may be a cysteine residue either from the earlier misfolded protein or one from DsbC. In the last case, DsbC becomes oxidized and has to be reduced in order to play another catalytic role. There is also a second isomerase that can reorganize incorrect disulfide bonds. This protein is called DsbG and it is also a dimer that serves as a chaperone. In order to fulfil their role as isomerases, DsbC and DsbG need to be kept in a reduced state. This is carried out by DsbD, which has to be reduced itself to be functional. Thioredoxin, which itself is reduced by thioredoxin reductase
Thioredoxin reductase
Thioredoxin Reductases are the only known enzymes to reduce thioredoxin . Two classes of thioredoxin reductase have been identified: one class in bacteria and some eukaryotes and one in animals. Both classes are flavoproteins which function as homodimers...
and NADPH, ensures the reduction of the DsbD protein.
Because these two pathways coexist next to each other in the same periplasmic compartment, there must be a mechanism to prevent oxidation of DsbC by DsbB. This mechanism indeed exists as DsbB can distinguish between DsbA and DsbC because this latter has the ability to dimerize.
In eukaryotes
.jpg)
A homolog
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
of DsbA, called protein disulfide isomerase
Protein disulfide isomerase
Protein disulfide isomerase or PDI is an enzyme in the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotes that catalyzes the formation and breakage of disulfide bonds between cysteine residues within proteins as they fold...
(PDI), is responsible for the formation of the disulfide bonds in unfolded eukaryotic proteins. This protein has two thioredoxine-like active sites, which both contain two cysteine residues. By transferring the disulfide bond between these two cysteine residues onto the folding protein it is responsible for the latter’s oxidation. In contrast to bacteria, where the oxidative and isomerization pathways are carried out by different proteins, PDI is also responsible for the reduction and isomerization of the disulfide bonds. In order for PDI to catalyse the formation of disulfide bonds in unfolded proteins, it has to be reoxidized. This is carried out by an ER membrane-associated protein, Ero1p, which is no homolog of DsbB. This Ero1p protein forms a mixed disulfide with PDI, which is resolved by a nucleophilic attack of the second cystein residue in one of the active sites of PDI. As result, oxidized PDI is obtained. Ero1p itself is oxidized by transferring electrons to molecular oxygen. As it is an FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
-binding protein, this transfer of electrons is strongly favoured when Ero1p is bound to FAD. Also a transport system that imports FAD into the ER lumen has been described in eukaryotes. Furthermore, it has been shown that the ability to reduce or rearrange incorrect disulfide bonds in missfolded proteins is provided by the oxidation of reduced glutathione
Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide that contains an unusual peptide linkage between the amine group of cysteine and the carboxyl group of the glutamate side-chain...
(GSH) to oxidized glutathione (GSSG).
ROS and diseases
Because of the property of Ero1p to transfer electrons directly to molecular oxygen via a flavin-dependent reaction, its activity may produce reactive oxygen speciesReactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen. Examples include oxygen ions and peroxides. Reactive oxygen species are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired valence shell electrons....
(ROS). In bacteria, this problem is solved by coupling oxidative folding to the respiratory chain. There, the reduction of molecular oxygen to water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
is carried out by a complex series of proteins, which catalyse this reaction very efficiently. In eukaryotes, the respiratory chain is separated from oxidative folding since cellular respiration
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate , and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions that involve...
takes place in the mitochondria and the formation of disulfide bonds occurs in the ER. Because of this, there is much more risk that ROS are produced in eukaryotic cells during oxidative folding. As is known these ROS may cause many diseases such as atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition in which an artery wall thickens as a result of the accumulation of fatty materials such as cholesterol...
and some neurodegenerative diseases.
Examples
Classical examples of proteins from which the process of oxidative folding is well studied are bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) and ribonuclease ARibonuclease A
Ribonuclease A is a pancreatic ribonuclease that cleaves single-stranded RNA. Bovine pancreatic RNase A is one of the classic model systems of protein science.-History:...
(RNaseA). These two proteins have multiple disulfide bonds and so they are very useful to follow and understand the process of oxidative folding. Another example is alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase is a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. The process of removing the phosphate group is called dephosphorylation...
, which contains two essential disulfides. It was used as an indicator protein to screen the effect of mutations in DsbA.

