
Overall pressure ratio
Encyclopedia
In aeronautical engineering, the term overall pressure ratio is defined as the ratio of the stagnation pressure
as measured at the front and rear of the compressor of a gas turbine
engine. Generally speaking, a higher overall pressure ratio implies higher efficiency, but the engine will weigh more, so there is a compromise.
from World War II
had an overall pressure ratio 3.14:1. The immediate post-war SNECMA Atar
improved this marginally to 5.2:1. Improvements in materials, compressor blades, and especially the introduction of multi-spool engines with several different rotational speeds, led to the much higher pressure ratios common today. Modern civilian engines generally operate between 30 and 40:1. The three-spool Rolls-Royce Trent 900
used on the Airbus A380
, for instance, has a pressure ratio of about 39:1.
.
 , is a common figure of merit
, is a common figure of merit
for engine designs. For civilian engines, the pressure ratio can be adjusted as the aircraft climbs, allowing it to offset some of the heat load through the lowered pressure and temperature of the high-altitude air. This is one of the many reasons airliners climb to high altitude as quickly as possible.
Military engines are often forced to work under conditions that maximize the heating load. For instance, the General Dynamics F-111
was required to operate at speeds of Mach 1.1 at sea level
. As a side-effect of these wide operating conditions, and generally older technology in most cases, military engines typically have lower overall pressure ratios. The Pratt & Whitney TF30 used on the F-111 had a pressure ratio of about 20:1, while newer engines like the General Electric F110
and Pratt & Whitney F135
have improved this to about 30:1.
An additional issue is weight: a higher compression ratio implies a heavier engine, which in turn costs fuel to carry around. Thus, for a particular construction technology and set of flight plans an optimal overall pressure ratio can be determined.
The Concorde
's Olympus engines get additional compression from its supersonic inlet, yielding an effective overall pressure ratio of 80:1.
applied to reciprocating engine
s. Compression ratio is a ratio of volumes. In the case of the reciprocating engine, the maximum expansion of the charge is limited by the mechanical movement of the pistons (or rotor), and so the compression can be measured by simply comparing the volume of the cylinder with the piston at the top and bottom of its motion. The same is not true of the "open ended" gas turbine, where operational and structural issues are the limiting factors. Nevertheless the two terms are similar in that they both offer a quick way of determining overall efficiency relative to other engines of the same class.
The broadly equivalent measure of rocket engine
efficiency is chamber pressure/exit pressure, and this ratio can be over 2000 for the Space Shuttle Main Engine
.
The reason for this difference is that compression ratio
is defined via the volume reduction,
Pressure ratio is defined as the pressure
increase
From the combined gas law
we get:
Stagnation pressure
In fluid dynamics, stagnation pressure is the static pressure at a stagnation point in a fluid flow.At a stagnation point the fluid velocity is zero and all kinetic energy has been converted into pressure energy . Stagnation pressure is equal to the sum of the free-stream dynamic pressure and...
as measured at the front and rear of the compressor of a gas turbine
Gas turbine
A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of internal combustion engine. It has an upstream rotating compressor coupled to a downstream turbine, and a combustion chamber in-between....
engine. Generally speaking, a higher overall pressure ratio implies higher efficiency, but the engine will weigh more, so there is a compromise.
History of overall pressure ratios
Early jet engines had limited pressure ratios due to construction innaccuracies of the compressors and various material limits. For instance, the Junkers Jumo 004Junkers Jumo 004
The Jumo 004 was the world's first turbojet engine in production and operational use, and the first successful axial compressor jet engine ever built. Some 8,000 units were manufactured by Junkers in Germany during late World War II and powered the operational Messerschmitt Me 262 jet fighter,...
from World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
had an overall pressure ratio 3.14:1. The immediate post-war SNECMA Atar
SNECMA Atar
The SNECMA Atar is a French axial-flow turbojet engine built by Snecma. It was derived from the German World War II BMW 003 design, but extensively developed though a progression of more powerful models. The name is derived from its original design group, Atelier Technique Aéronautique Rickenbach...
improved this marginally to 5.2:1. Improvements in materials, compressor blades, and especially the introduction of multi-spool engines with several different rotational speeds, led to the much higher pressure ratios common today. Modern civilian engines generally operate between 30 and 40:1. The three-spool Rolls-Royce Trent 900
Rolls-Royce Trent
Rolls-Royce Trent is the name given to a family of high bypass turbofan aircraft engines manufactured by Rolls-Royce plc. All are developments of the RB211 with thrust ratings of . Versions of the Trent are in service on the Airbus A330, A340, A380, Boeing 777, and 787, and variants are in...
used on the Airbus A380
Airbus A380
The Airbus A380 is a double-deck, wide-body, four-engine jet airliner manufactured by the European corporation Airbus, a subsidiary of EADS. It is the largest passenger airliner in the world. Due to its size, many airports had to modify and improve facilities to accommodate it...
, for instance, has a pressure ratio of about 39:1.
Advantages of high overall pressure ratios
A high overall pressure ratio permits a larger area ratio nozzle to be fitted on the jet engine. This means that more of the heat energy is converted to jet speed, and energetic efficiency improves. This is reflected in improvements in the engine's specific fuel consumptionSpecific fuel consumption
Thrust specific fuel consumption or sometimes simply specific fuel consumption, SFC, is an engineering term that is used to describe the fuel efficiency of an engine design with respect to thrust output...
.
Disadvantages of high overall pressure ratios
One of the primary limiting factors on pressure ratio in modern designs is that the air heats up as it is compressed. As the air travels through the compressor stages it can reach temperatures that pose a material failure risk for the compressor blades. This is especially true for the last compressor stage, and the inlet temperature to this stage, , is a common figure of merit
, is a common figure of meritFigure of merit
A figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
for engine designs. For civilian engines, the pressure ratio can be adjusted as the aircraft climbs, allowing it to offset some of the heat load through the lowered pressure and temperature of the high-altitude air. This is one of the many reasons airliners climb to high altitude as quickly as possible.
Military engines are often forced to work under conditions that maximize the heating load. For instance, the General Dynamics F-111
General Dynamics F-111
The General Dynamics F-111 "Aardvark" was a medium-range interdictor and tactical strike aircraft that also filled the roles of strategic bomber, reconnaissance, and electronic warfare in its various versions. Developed in the 1960s by General Dynamics, it first entered service in 1967 with the...
was required to operate at speeds of Mach 1.1 at sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
. As a side-effect of these wide operating conditions, and generally older technology in most cases, military engines typically have lower overall pressure ratios. The Pratt & Whitney TF30 used on the F-111 had a pressure ratio of about 20:1, while newer engines like the General Electric F110
General Electric F110
-External links:* - The F110 Engine Family* - F110-GE-100 Gallery* - F110* - General Electric F110...
and Pratt & Whitney F135
Pratt & Whitney F135
The Pratt & Whitney F135 is an afterburning turbofan developed for the F-35 Lightning II single-engine strike fighter. The F135 family has several distinct variants, including a conventional, forward thrust variant and a multi-cycle STOVL variant that includes a forward lift fan...
have improved this to about 30:1.
An additional issue is weight: a higher compression ratio implies a heavier engine, which in turn costs fuel to carry around. Thus, for a particular construction technology and set of flight plans an optimal overall pressure ratio can be determined.
Examples
| Engine | Overall pressure ratio | notes |
|---|---|---|
| General Electric CF6 | 30.5:1 | Boeing 747 Boeing 747 The Boeing 747 is a wide-body commercial airliner and cargo transport, often referred to by its original nickname, Jumbo Jet, or Queen of the Skies. It is among the world's most recognizable aircraft, and was the first wide-body ever produced... , A300 |
| General Electric F110 General Electric F110 -External links:* - The F110 Engine Family* - F110-GE-100 Gallery* - F110* - General Electric F110... |
30:1 | F-14, F-15 F-15 Eagle The McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle is a twin-engine, all-weather tactical fighter designed by McDonnell Douglas to gain and maintain air superiority in aerial combat. It is considered among the most successful modern fighters with over 100 aerial combat victories with no losses in dogfights... , F-16 |
| Pratt & Whitney TF30 | 20:1 | F-111 |
| Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 The Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 was a reheated turbojet which powered the supersonic airliner Concorde. Initially a joint project between Bristol Siddeley and Snecma based on Bristol's Olympus engine, Rolls-Royce Limited acquired Bristol making it a division of Rolls-Royce.Until Concorde's... |
15.5:1 | Concorde, Mach 2 engine |
The Concorde
Concorde
Aérospatiale-BAC Concorde was a turbojet-powered supersonic passenger airliner, a supersonic transport . It was a product of an Anglo-French government treaty, combining the manufacturing efforts of Aérospatiale and the British Aircraft Corporation...
's Olympus engines get additional compression from its supersonic inlet, yielding an effective overall pressure ratio of 80:1.
Differences from other similar terms
The term should not be confused with the more familiar term compression ratioCompression ratio
The 'compression ratio' of an internal-combustion engine or external combustion engine is a value that represents the ratio of the volume of its combustion chamber from its largest capacity to its smallest capacity...
applied to reciprocating engine
Reciprocating engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types...
s. Compression ratio is a ratio of volumes. In the case of the reciprocating engine, the maximum expansion of the charge is limited by the mechanical movement of the pistons (or rotor), and so the compression can be measured by simply comparing the volume of the cylinder with the piston at the top and bottom of its motion. The same is not true of the "open ended" gas turbine, where operational and structural issues are the limiting factors. Nevertheless the two terms are similar in that they both offer a quick way of determining overall efficiency relative to other engines of the same class.
The broadly equivalent measure of rocket engine
Rocket engine
A rocket engine, or simply "rocket", is a jet engineRocket Propulsion Elements; 7th edition- chapter 1 that uses only propellant mass for forming its high speed propulsive jet. Rocket engines are reaction engines and obtain thrust in accordance with Newton's third law...
efficiency is chamber pressure/exit pressure, and this ratio can be over 2000 for the Space Shuttle Main Engine
Space Shuttle main engine
The RS-25, otherwise known as the Space Shuttle Main Engine , is a reusable liquid-fuel rocket engine built by Pratt & Whitney Rocketdyne for the Space Shuttle, running on liquid hydrogen and oxygen. Each Space Shuttle was propelled by three SSMEs mated to one powerhead...
.
Compression ratio versus overall pressure ratio
For any given gas mix compression ratio and overall pressure ratio are interrelated as follows:| CR | 1:1 | 3:1 | 5:1 | 10:1 | 15:1 | 20:1 | 25:1 | 35:1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR | 1:1 | 4:1 | 10:1 | 22:1 | 40:1 | 56:1 | 75:1 | 110:1 |
The reason for this difference is that compression ratio
Compression ratio
The 'compression ratio' of an internal-combustion engine or external combustion engine is a value that represents the ratio of the volume of its combustion chamber from its largest capacity to its smallest capacity...
is defined via the volume reduction,
-
 ,
,
Pressure ratio is defined as the pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
increase
-
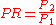 .
.
From the combined gas law
Combined gas law
The combined gas law is a gas law which combines Charles's law, Boyle's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. These laws each relate one thermodynamic variable to another mathematically while holding everything else constant. Charles's law states that volume and temperature are directly proportional to each...
we get:
-

Since T2 is much higher than T1 (compressing gases puts work into them, i.e. heats them up), CR is much lower than PR.
See also
- Brayton cycleBrayton cycleThe Brayton cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the workings of the gas turbine engine, basis of the airbreathing jet engine and others. It is named after George Brayton , the American engineer who developed it, although it was originally proposed and patented by Englishman John Barber...
- Carnot cycleCarnot cycleThe Carnot cycle is a theoretical thermodynamic cycle proposed by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot in 1824 and expanded by Benoit Paul Émile Clapeyron in the 1830s and 40s. It can be shown that it is the most efficient cycle for converting a given amount of thermal energy into work, or conversely,...
- Compression ratioCompression ratioThe 'compression ratio' of an internal-combustion engine or external combustion engine is a value that represents the ratio of the volume of its combustion chamber from its largest capacity to its smallest capacity...
- Engine pressure ratio (EPR)
- Brayton cycle

