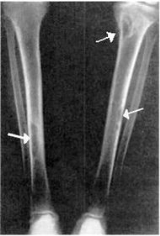
Osteitis fibrosa cystica
Encyclopedia
Osteitis fibrosa cystica (icon), abbreviated OFC, and also known as osteitis fibrosa, osteodystrophia fibrosa, not to be confused with Von Recklinghausen's
disease of bone ([neurofibromatosis type I]]). Osteitis Fbrosa Cystica is a skeletal disorder caused by a surplus of parathyroid hormone
from over-active parathyroid glands. This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclast
s, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption
. The over-activity of the parathyroid glands, or hyperparathyroidism
, can be triggered by parathyroid adenoma
, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma
, or renal osteodystrophy
.
Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium
, from the bone into the bloodstream. In addition to elevated blood calcium levels, over-activity of this process results in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue (peritrabecular
fibrosis
), and the formation of cyst
-like brown tumor
s in and around the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea
, appetite loss, and weight loss.
First described in the nineteenth century, OFC is currently detected through a combination of blood testing, X-rays, and tissue sampling
. Before 1950, around half of those diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism in the United States saw it progress to OFC, but with early identification techniques and improved treatment methods, instances of OFC in developed countries are increasingly rare. Where treatment is required, it normally involves addressing the underlying hyperparathyroidism before commencing long-term treatment for OFC—depending on its cause and severity, this can range from hydration and exercise to surgical intervention.
. Under the ICD-10
classification system, established by the World Health Organization
, OFC is listed under category E21.0, primary hyperparathyroidism.
s, and skeletal deformities such as bowing of the bones. The underlying hyperparathyroidism
may cause kidney stone
s, nausea
, constipation
, fatigue and weakness. X-ray
s may indicate thin bones, fractures, bowing, and cysts. Fractures are most commonly localized in the arms, legs, or spine.
The addition of weight loss, appetite loss
, vomiting, polyuria
, and polydipsia
to the aforementioned symptoms may indicate that OFC is the result of parathyroid carcinoma
. Parathyroid carcinoma, an uncommon cancer of the parathyroid glands, is generally indicated by serum calcium levels higher than usual, even in comparison to the high serum calcium levels that OFC generally presents with. Symptoms are also often more severe. Generally, the presence of a palpable neck mass is also indicative of the cancer, occurring in approximately 50% of sufferers, but virtually nonexistent in individuals with OFC with a different origin.
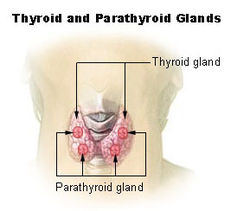 Osteitis fibrosa cystica is the result of unchecked hyperparathyroidism, or the overactivity of the parathyroid glands, which results in an overproduction of parathyroid hormone
Osteitis fibrosa cystica is the result of unchecked hyperparathyroidism, or the overactivity of the parathyroid glands, which results in an overproduction of parathyroid hormone
(PTH). PTH causes the release of calcium from the bones into the blood, and the reabsorption of calcium in the kidney. Thus, excess PTH in hyperparathyroidism causes elevated blood calcium levels, or hypercalcemia.
There are four major causes of primary hyperparathyroidism that result in OFC:
The vast majority of cases of hyperparathyroidism are the result of the random formation of benign, but metabolically active, parathyroid adenoma
swellings. These instances comprise approximately 80–85% of all documented cases of hyperparathyroidism.
Approximately 1 in 10 documented cases of hyperparathyroidism are a result of hereditary factors. Disorders such as familial hyperparathyroidism, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
(MEN Type 1) and hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome can, if left unchecked, result in OFC. MEN Type 1 is an autosomal dominant disorder and the most common hereditary form of hyperparathyroidism, affecting about 95% of genetic cases of OFC, and also tends to affect younger patients than other forms. Major mutations which can lead to hyperparathyroidism generally involve the parathyroid hormone receptor, G protein
s, or adenylate cyclase
. Certain genetic mutations have been linked to a higher rate of parathyroid carcinoma occurrence, specifically mutations to the gene HRPT2, which codes for the protein parafibromin.
Parathyroid carcinoma
(cancer
of the parathyroid gland
) is the rarest cause of OFC, accounting for about 0.5% of all cases of hyperparathyroidism. OFC onset by parathyroid carcinoma is difficult to diagnose.
OFC is a common presentation of renal osteodystrophy
, which is a term used to refer to the skeletal complications of end stage renal disease (ESRD). OFC occurs in approximately 50% of patients with ESRD. ESRD occurs when the kidneys fail to produce calcitriol
, a form of Vitamin D
, which assists in the absorption of calcium into the bones. When calcitriol levels decrease, parathyroid hormone levels increase, halting the storage of calcium, and instead triggering its removal from the bones.
calcium concentration in the blood. It activates the parathyroid-hormone related protein receptor located on osteoblast
s and osteocyte
s, both of which are responsible for the building and calcification
of bone. Abnormalities affecting the parathyroid glands cause a surplus of PTH, which, in turn, increases the activity and frequency of osteoblasts and osteocytes. Increased PTH levels trigger the release of stored calcium through the dissolution of old bone, as well as the conservation of serum calcium through a cessation in the production of new bone.
Generally, the first bones to be affected are the fingers, facial bones, ribs, and pelvis. Long bones, which are longer than they are wide, are also among the first affected. As the disease progresses, any bone may be affected.

(a condition in which the trachea shifts from its position at the midline of the neck), in conjunction with other known symptoms of OFC can point to a diagnosis of parathyroid carcinoma.
Blood tests on patients with OFC generally show high levels of calcium
(normal levels are considered to range between 8.5 and 10.2 mg/dL, parathyroid hormone
(levels generally above 250 pg/mL, as opposed to the "normal" upper-range value of 65 pg/mL), and alkaline phosphatase
(normal range is 20 to 140 IU
/L).
X-rays may also be used to diagnose the disease. Usually, these X-rays will show extremely thin bones, which are often bowed or fractured. However, such symptoms are also associated with other bone diseases, such as osteopenia
or osteoporosis
. Generally, the first bones to show symptoms via X-ray are the fingers. Furthermore, brown tumors, especially when manifested on facial bones, can be misdiagnosed as cancerous. Radiographs distinctly show bone resorption and X-rays of the skull may depict an image often described as "ground glass" or "salt and pepper". Dental X-rays
may also be abnormal.
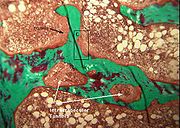 Cysts may be lined by osteoclast
Cysts may be lined by osteoclast
s and sometimes blood pigments, which lend to the notion of "brown tumors." Such cysts can be identified with nuclear imaging combined with specific tracers
, such as sestamibi
. Identification of muscular degeneration or lack of reflex can occur through clinical testing of deep tendon reflexes, or via photomotogram (an achilles tendon
reflex test).
Fine needle aspiration
(FNA) can be used to biopsy
bone lesions
, once found on an X-ray or other scan. Such tests can be vital in diagnosis and can also prevent unnecessary treatment and invasive surgery. Conversely, FNA biopsy of tumors of the parathyroid gland is not recommended for diagnosing parathyroid carcinoma and may in fact be harmful, as the needle can puncture the tumor, leading to dissemination and the possible spread of cancerous cells.
The brown tumors commonly associated with OFC display many of the same characteristics of osteoclasts. These cells are characteristically benign, feature a dense, granular cytoplasm
, and a nucleus that tends to be ovular in shape, enclosing comparatively fine chromatin
. Nucleoli also tend to be smaller than average.
, delivered intravenously. Studies have shown that in cases of OFC caused by either end-stage renal disease or primary hyperparathyoidism, this method is successful not only in treating underlying hyperparathyoidism, but also in causing the regression of brown tumors and other symptoms of OFC.
Bone transplants
have proven successful in filling the lesions caused by OFC. A report showed that in 8 out of 11 instances where cavities caused by OFC were filled with transplanted bone, the lesion healed and the transplanted bone blended rapidly and seamlessly with the original bone.
is common. This results from a combination of suppressed parathyroid glands due to prolonged hypercalcaemia
, as well as the need for calcium and phosphate in the mineralization
of new bone.
Thirty percent of patients with OFC caused by parathyroid carcinoma who undergo surgery see a local recurrence of symptoms. The post-surgical survival rate hovers around seven years, while patients who do not undergo surgery have a survival rate of around five years.
.
The hospitalization rate for hyperparathyroidism in the United States in 1999 was 8.0 out of 100,000. The disease has a definite tendency to affect younger individuals, typically appearing before the age of 40, with a study in 1922 reporting that 70% of cases display symptoms before the age of 20, and 85% before 35. Primary hyperparathyoidism, as well as OFC, is more common in Asiatic countries. Before treatment for hyperparathyroidism improved in the 1950s, half of those diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism saw it progress into OFC.
Rates of OFC increase alongside cases of unchecked primary hyperparathyroidism. In developing countries, such as India, rates of disease as well as case reports often mirror those published in past decades in the developed world.
The other 10% of cases are primarily caused by primary hyperplasia
, or an increase of the number of cells. Parathyroid carcinoma accounts for less than 1% of all cases, occurring most frequently in individuals around 50 years of age (in stark contrast to OFC as a result of primary hyperparathyroidism) and showing no gender preference. Approximately 95% of hyperparatyhroidism caused by genetic factors is attributed to MEN type 1. This mutation also tends to affect younger individuals.
 The condition was first described by Gerhard Engel in 1864 and Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen
The condition was first described by Gerhard Engel in 1864 and Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen
in 1890, though William Hunter
, who died in 1783, is credited with finding the first example of the disease. "von Recklinghausen's disease" (without the qualification "of bone") is a completely unrelated disorder, nowadays termed neurofibromatosis
. In 1884, Davies Colley delivered a presentation to the Pathological Society of London
that detailed the manifestation of hyperparathyroidism into a brown tumor of the mandible, as well as the histological makeup of the tumor.
The discovery and subsequent description of the parathyroid glands is credited to Ivar Sandstrom, though his publication, On a New Gland in Man and Several Mammals-Glandulae Parathyroideae, received little attention. Gustaf Retzius
and Eugene Gley
compounded his research, the latter credited with the discovery of the function of the parathyroid glands. This research cumulated in the first surgical removal of a parathyroid tumor by Felix Mandel in 1925. A 2.5 × 1.5-inch (64 × 38 mm) tumor was removed from the thyroid artery of a man suffering from advanced OFC. The patient's symptoms disappeared, only to return in approximately six years as a result of renal stones that were diagnosed only after the patient had died. In 1932, blood tests on a female patient suffering from renal stone-based OFC revealed extremely high blood calcium
levels. Fuller Albright diagnosed and treated the woman, who suffered from a large tumor of the neck as well as renal stones.
The first published literature to describe a brown tumor (which was linked to OFC) was published in 1953, though clinical reports from before 1953 do draw a correlation between the disease and tumors previous to the publication.
The advent of the multichannel autoanalyzer in the 1960s and 70s led to an increase in early diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism. This increase led to a sharp decline in the prolonged manifestation of the disease, leading to a drop in the number of cases of OFC due to the early detection of hyperparathyroidism. Before this invention, the diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism was generally prolonged until the emergence of severe manifestations, such as OFC.
Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen
Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen was a German pathologist who practiced medicine in Würzburg and Strassburg . Born in Gütersloh, Westphalia, he was the father of physiologist Heinrich von Recklinghausen ....
disease of bone ([neurofibromatosis type I]]). Osteitis Fbrosa Cystica is a skeletal disorder caused by a surplus of parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone , parathormone or parathyrin, is secreted by the chief cells of the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids...
from over-active parathyroid glands. This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclast
Osteoclast
An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue by removing its mineralized matrix and breaking up the organic bone . This process is known as bone resorption. Osteoclasts were discovered by Kolliker in 1873...
s, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption
Bone resorption
Bone resorption is the process by which osteoclasts break down bone and release the minerals, resulting in a transfer of calcium from bone fluid to the blood....
. The over-activity of the parathyroid glands, or hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is overactivity of the parathyroid glands resulting in excess production of parathyroid hormone . The parathyroid hormone regulates calcium and phosphate levels and helps to maintain these levels...
, can be triggered by parathyroid adenoma
Parathyroid adenoma
A parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland. It can cause hyperparathyroidism.CT scans or sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy can be used in detection.It can be associated with Cyclin D1 expression....
, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma is a rare cause of hypercalcemia. It forms in tissues of one or more of the parathyroid glands ....
, or renal osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy or chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder is a bone pathology, characterized by bone mineralization deficiency, that is a direct result of the electrolyte and endocrine derangements that accompany chronic kidney disease...
.
Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
, from the bone into the bloodstream. In addition to elevated blood calcium levels, over-activity of this process results in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue (peritrabecular
Trabecula
A trabecula is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod, generally having a mechanical function, and usually composed of dense collagenous tissue They can be composed of other materials; in the heart, for example, muscles such as trabeculae carneae...
fibrosis
Fibrosis
Fibrosis is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue in a reparative or reactive process. This is as opposed to formation of fibrous tissue as a normal constituent of an organ or tissue...
), and the formation of cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
-like brown tumor
Brown tumor
Brown tumors are tumors of bone that arise in settings of excess osteoclast activity, such as hyperparathyroidism, and consist of fibrous tissue, woven bone and supporting vasculature, but no matrix. They are radiolucent on x-ray...
s in and around the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, appetite loss, and weight loss.
First described in the nineteenth century, OFC is currently detected through a combination of blood testing, X-rays, and tissue sampling
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
. Before 1950, around half of those diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism in the United States saw it progress to OFC, but with early identification techniques and improved treatment methods, instances of OFC in developed countries are increasingly rare. Where treatment is required, it normally involves addressing the underlying hyperparathyroidism before commencing long-term treatment for OFC—depending on its cause and severity, this can range from hydration and exercise to surgical intervention.
Classification
Osteitis fibrosa cystica is defined as the classic skeletal manifestation of advanced hyperparathyroidismHyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is overactivity of the parathyroid glands resulting in excess production of parathyroid hormone . The parathyroid hormone regulates calcium and phosphate levels and helps to maintain these levels...
. Under the ICD-10
ICD-10
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision is a medical classification list for the coding of diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases, as maintained by the...
classification system, established by the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
, OFC is listed under category E21.0, primary hyperparathyroidism.
Signs and symptoms
The major symptoms of OFC are bone pain or tenderness, bone fractureBone fracture
A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a break in the continuity of the bone...
s, and skeletal deformities such as bowing of the bones. The underlying hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is overactivity of the parathyroid glands resulting in excess production of parathyroid hormone . The parathyroid hormone regulates calcium and phosphate levels and helps to maintain these levels...
may cause kidney stone
Kidney stone
A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine...
s, nausea
Nausea
Nausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
, constipation
Constipation
Constipation refers to bowel movements that are infrequent or hard to pass. Constipation is a common cause of painful defecation...
, fatigue and weakness. X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s may indicate thin bones, fractures, bowing, and cysts. Fractures are most commonly localized in the arms, legs, or spine.
The addition of weight loss, appetite loss
Anorexia (symptom)
Anorexia is the decreased sensation of appetite...
, vomiting, polyuria
Polyuria
Polyuria is a condition usually defined as excessive or abnormally large production or passage of urine . Frequent urination is sometimes included by definition, but is nonetheless usually an accompanying symptom...
, and polydipsia
Polydipsia
Polydipsia is a medical symptom in which the patient displays excessive thirst. The word derives from the Greek πολυδιψία, which is derived from πολύς + δίψα...
to the aforementioned symptoms may indicate that OFC is the result of parathyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma is a rare cause of hypercalcemia. It forms in tissues of one or more of the parathyroid glands ....
. Parathyroid carcinoma, an uncommon cancer of the parathyroid glands, is generally indicated by serum calcium levels higher than usual, even in comparison to the high serum calcium levels that OFC generally presents with. Symptoms are also often more severe. Generally, the presence of a palpable neck mass is also indicative of the cancer, occurring in approximately 50% of sufferers, but virtually nonexistent in individuals with OFC with a different origin.
Causes

Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone , parathormone or parathyrin, is secreted by the chief cells of the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids...
(PTH). PTH causes the release of calcium from the bones into the blood, and the reabsorption of calcium in the kidney. Thus, excess PTH in hyperparathyroidism causes elevated blood calcium levels, or hypercalcemia.
There are four major causes of primary hyperparathyroidism that result in OFC:
- Parathyroid Adenoma
The vast majority of cases of hyperparathyroidism are the result of the random formation of benign, but metabolically active, parathyroid adenoma
Parathyroid adenoma
A parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland. It can cause hyperparathyroidism.CT scans or sestamibi parathyroid scintigraphy can be used in detection.It can be associated with Cyclin D1 expression....
swellings. These instances comprise approximately 80–85% of all documented cases of hyperparathyroidism.
- Hereditary factors
Approximately 1 in 10 documented cases of hyperparathyroidism are a result of hereditary factors. Disorders such as familial hyperparathyroidism, multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 or Wermer's syndrome is part of a group of disorders that affect the endocrine system.-Explanation:...
(MEN Type 1) and hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome can, if left unchecked, result in OFC. MEN Type 1 is an autosomal dominant disorder and the most common hereditary form of hyperparathyroidism, affecting about 95% of genetic cases of OFC, and also tends to affect younger patients than other forms. Major mutations which can lead to hyperparathyroidism generally involve the parathyroid hormone receptor, G protein
G protein
G proteins are a family of proteins involved in transmitting chemical signals outside the cell, and causing changes inside the cell. They communicate signals from many hormones, neurotransmitters, and other signaling factors. G protein-coupled receptors are transmembrane receptors...
s, or adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase
Adenylate cyclase is part of the G protein signalling cascade, which transmits chemical signals from outside the cell across the membrane to the inside of the cell ....
. Certain genetic mutations have been linked to a higher rate of parathyroid carcinoma occurrence, specifically mutations to the gene HRPT2, which codes for the protein parafibromin.
- Parathyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma is a rare cause of hypercalcemia. It forms in tissues of one or more of the parathyroid glands ....
(cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
of the parathyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
The parathyroid glands are small endocrine glands in the neck that produce parathyroid hormone. Humans usually have four parathyroid glands, which are usually located on the rear surface of the thyroid gland, or, in rare cases, within the thyroid gland itself or in the chest...
) is the rarest cause of OFC, accounting for about 0.5% of all cases of hyperparathyroidism. OFC onset by parathyroid carcinoma is difficult to diagnose.
- Renal complications
OFC is a common presentation of renal osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy
Renal osteodystrophy or chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder is a bone pathology, characterized by bone mineralization deficiency, that is a direct result of the electrolyte and endocrine derangements that accompany chronic kidney disease...
, which is a term used to refer to the skeletal complications of end stage renal disease (ESRD). OFC occurs in approximately 50% of patients with ESRD. ESRD occurs when the kidneys fail to produce calcitriol
Calcitriol
Calcitriol , also called 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, is the hormonally active form of vitamin D with three hydroxyl groups...
, a form of Vitamin D
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids. In humans, vitamin D is unique both because it functions as a prohormone and because the body can synthesize it when sun exposure is adequate ....
, which assists in the absorption of calcium into the bones. When calcitriol levels decrease, parathyroid hormone levels increase, halting the storage of calcium, and instead triggering its removal from the bones.
Pathophysiology
The effects of OFC on bone are largely dependent on the duration of the disease and the level of parathyroid hormone (PTH) produced. PTH is responsible for maintaining a homeostaticHomeostasis
Homeostasis is the property of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable, constant condition of properties like temperature or pH...
calcium concentration in the blood. It activates the parathyroid-hormone related protein receptor located on osteoblast
Osteoblast
Osteoblasts are mononucleate cells that are responsible for bone formation; in essence, osteoblasts are specialized fibroblasts that in addition to fibroblastic products, express bone sialoprotein and osteocalcin.Osteoblasts produce a matrix of osteoid, which is composed mainly of Type I collagen...
s and osteocyte
Osteocyte
An osteocyte, a star-shaped cell, is the most abundant cell found in compact bone. Cells contain a nucleus and a thin ring of cytoplasm. When osteoblasts become trapped in the matrix they secrete, they become osteocytes...
s, both of which are responsible for the building and calcification
Calcification
Calcification is the process in which calcium salts build up in soft tissue, causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification.-Causes:...
of bone. Abnormalities affecting the parathyroid glands cause a surplus of PTH, which, in turn, increases the activity and frequency of osteoblasts and osteocytes. Increased PTH levels trigger the release of stored calcium through the dissolution of old bone, as well as the conservation of serum calcium through a cessation in the production of new bone.
Generally, the first bones to be affected are the fingers, facial bones, ribs, and pelvis. Long bones, which are longer than they are wide, are also among the first affected. As the disease progresses, any bone may be affected.

Diagnosis
OFC may be diagnosed using a variety of techniques. Muscles in patients afflicted with OFC can either appear unaffected or "bulked up." If muscular symptoms appear upon the onset of hyperparathyroidism, they are generally sluggish contraction and relaxation of the muscles. Deviation of the tracheaVertebrate trachea
In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
(a condition in which the trachea shifts from its position at the midline of the neck), in conjunction with other known symptoms of OFC can point to a diagnosis of parathyroid carcinoma.
Blood tests on patients with OFC generally show high levels of calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
(normal levels are considered to range between 8.5 and 10.2 mg/dL, parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone
Parathyroid hormone , parathormone or parathyrin, is secreted by the chief cells of the parathyroid glands as a polypeptide containing 84 amino acids...
(levels generally above 250 pg/mL, as opposed to the "normal" upper-range value of 65 pg/mL), and alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase is a hydrolase enzyme responsible for removing phosphate groups from many types of molecules, including nucleotides, proteins, and alkaloids. The process of removing the phosphate group is called dephosphorylation...
(normal range is 20 to 140 IU
International unit
In pharmacology, the International Unit is a unit of measurement for the amount of a substance, based on biological activity or effect. It is abbreviated as IU, as UI , or as IE...
/L).
X-rays may also be used to diagnose the disease. Usually, these X-rays will show extremely thin bones, which are often bowed or fractured. However, such symptoms are also associated with other bone diseases, such as osteopenia
Osteopenia
Osteopenia is a condition where bone mineral density is lower than normal. It is considered by many doctors to be a precursor to osteoporosis. However, not every person diagnosed with osteopenia will develop osteoporosis...
or osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
. Generally, the first bones to show symptoms via X-ray are the fingers. Furthermore, brown tumors, especially when manifested on facial bones, can be misdiagnosed as cancerous. Radiographs distinctly show bone resorption and X-rays of the skull may depict an image often described as "ground glass" or "salt and pepper". Dental X-rays
Dental radiography
Dental radiographs, commonly referred to as X-ray films, or informally, X-rays, are pictures of the teeth, bones, and surrounding soft tissues to screen for and help identify problems with the teeth, mouth, and jaw. X-ray pictures can show cavities, cancerous or benign masses, hidden dental...
may also be abnormal.

Osteoclast
An osteoclast is a type of bone cell that removes bone tissue by removing its mineralized matrix and breaking up the organic bone . This process is known as bone resorption. Osteoclasts were discovered by Kolliker in 1873...
s and sometimes blood pigments, which lend to the notion of "brown tumors." Such cysts can be identified with nuclear imaging combined with specific tracers
Radioactive tracer
A radioactive tracer, also called a radioactive label, is a substance containing a radioisotope that is used to measure the speed of chemical processes and to track the movement of a substance through a natural system such as a cell or tissue...
, such as sestamibi
Sestamibi
Technetium sestamibi is a pharmaceutical agent used in nuclear medicine imaging. The drug is a coordination complex of the radioisotope technetium-99m with the ligand methoxyisobutylisonitrile . The generic drug became available late September 2008...
. Identification of muscular degeneration or lack of reflex can occur through clinical testing of deep tendon reflexes, or via photomotogram (an achilles tendon
Achilles tendon
The Achilles tendon , also known as the calcaneal tendon or the tendo calcaneus, is a tendon of the posterior leg. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius and soleus muscles to the calcaneus bone.- Anatomy :The Achilles is the tendonous extension of 3 muscles in the lower leg:...
reflex test).
Fine needle aspiration
Needle aspiration biopsy
Needle aspiration biopsy , may refer to fine needle aspiration cytology , fine needle aspiration biopsy and fine needle aspiration , is a diagnostic procedure sometimes used to investigate superficial lumps or masses...
(FNA) can be used to biopsy
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
bone lesions
Lesion
A lesion is any abnormality in the tissue of an organism , usually caused by disease or trauma. Lesion is derived from the Latin word laesio which means injury.- Types :...
, once found on an X-ray or other scan. Such tests can be vital in diagnosis and can also prevent unnecessary treatment and invasive surgery. Conversely, FNA biopsy of tumors of the parathyroid gland is not recommended for diagnosing parathyroid carcinoma and may in fact be harmful, as the needle can puncture the tumor, leading to dissemination and the possible spread of cancerous cells.
The brown tumors commonly associated with OFC display many of the same characteristics of osteoclasts. These cells are characteristically benign, feature a dense, granular cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
, and a nucleus that tends to be ovular in shape, enclosing comparatively fine chromatin
Chromatin
Chromatin is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell. The primary functions of chromatin are; to package DNA into a smaller volume to fit in the cell, to strengthen the DNA to allow mitosis and meiosis and prevent DNA damage, and to control gene...
. Nucleoli also tend to be smaller than average.
Medical
Medical management of OFC consists of Vitamin D treatment, generally alfacalcidol or calcitriolCalcitriol
Calcitriol , also called 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, is the hormonally active form of vitamin D with three hydroxyl groups...
, delivered intravenously. Studies have shown that in cases of OFC caused by either end-stage renal disease or primary hyperparathyoidism, this method is successful not only in treating underlying hyperparathyoidism, but also in causing the regression of brown tumors and other symptoms of OFC.
Surgery
In especially severe cases of OFC, parathyroidectomy, or the full removal of the parathyroid glands, is the chosen route of treatment. Parathyroidectomy has been shown to result in the reversal of bone resorption and the complete regression of brown tumors. In situations where parathyroid carcinoma is present, surgery to remove the tumors has also led to the regression of hyperparathyroidism as well as the symptoms of OFC.Bone transplants
Bone grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly....
have proven successful in filling the lesions caused by OFC. A report showed that in 8 out of 11 instances where cavities caused by OFC were filled with transplanted bone, the lesion healed and the transplanted bone blended rapidly and seamlessly with the original bone.
Prognosis
Almost all who undergo parathyroidectomy experience increased bone density and repair of the skeleton within weeks. Additionally, patients with OFC who have undergone parathyroidectomy begin to show regression of brown tumors within six months. Following parathyroidectomy, hypocalcaemiaHypocalcaemia
In medicine, hypocalcaemia is the presence of low serum calcium levels in the blood, usually taken as less than 2.1 mmol/L or 9 mg/dl or an ionized calcium level of less than 1.1 mmol/L or 4.5 mg/dL. It is a type of electrolyte disturbance...
is common. This results from a combination of suppressed parathyroid glands due to prolonged hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia is an elevated calcium level in the blood. . It can be an asymptomatic laboratory finding, but because an elevated calcium level is often indicative of other diseases, a workup should be undertaken if it persists...
, as well as the need for calcium and phosphate in the mineralization
Ossification
Ossification is the process of laying down new bone material by cells called osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation...
of new bone.
Thirty percent of patients with OFC caused by parathyroid carcinoma who undergo surgery see a local recurrence of symptoms. The post-surgical survival rate hovers around seven years, while patients who do not undergo surgery have a survival rate of around five years.
Epidemiology
Osteitis fibrosa cystica has long been a rare disease. Today, it appears in only 2% of individuals diagnosed with primary hyperparathyroidism, which accounts for 90% of instances of the disease. Primary hyperparathyroidism is three times as common in individuals with diabetes mellitusDiabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes, is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced...
.
The hospitalization rate for hyperparathyroidism in the United States in 1999 was 8.0 out of 100,000. The disease has a definite tendency to affect younger individuals, typically appearing before the age of 40, with a study in 1922 reporting that 70% of cases display symptoms before the age of 20, and 85% before 35. Primary hyperparathyoidism, as well as OFC, is more common in Asiatic countries. Before treatment for hyperparathyroidism improved in the 1950s, half of those diagnosed with hyperparathyroidism saw it progress into OFC.
Rates of OFC increase alongside cases of unchecked primary hyperparathyroidism. In developing countries, such as India, rates of disease as well as case reports often mirror those published in past decades in the developed world.
The other 10% of cases are primarily caused by primary hyperplasia
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia means increase in number of cells/proliferation of cells. It may result in the gross enlargement of an organ and the term is sometimes mixed with benign neoplasia/ benign tumor....
, or an increase of the number of cells. Parathyroid carcinoma accounts for less than 1% of all cases, occurring most frequently in individuals around 50 years of age (in stark contrast to OFC as a result of primary hyperparathyroidism) and showing no gender preference. Approximately 95% of hyperparatyhroidism caused by genetic factors is attributed to MEN type 1. This mutation also tends to affect younger individuals.
History

Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen
Friedrich Daniel von Recklinghausen was a German pathologist who practiced medicine in Würzburg and Strassburg . Born in Gütersloh, Westphalia, he was the father of physiologist Heinrich von Recklinghausen ....
in 1890, though William Hunter
William Hunter (anatomist)
William Hunter FRS was a Scottish anatomist and physician. He was a leading teacher of anatomy, and the outstanding obstetrician of his day...
, who died in 1783, is credited with finding the first example of the disease. "von Recklinghausen's disease" (without the qualification "of bone") is a completely unrelated disorder, nowadays termed neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis is a genetically-inherited disorder in which the nerve tissue grows tumors that may be benign or may cause serious damage by compressing nerves and other tissues...
. In 1884, Davies Colley delivered a presentation to the Pathological Society of London
Pathological Society of London
The Pathological Society of London was founded in 1846 for the "cultivation and promotion of Pathology by the exhibition and description of specimens, drawings, microscopic preparations, casts or models of morbid parts." Its first meeting was held in February 1847...
that detailed the manifestation of hyperparathyroidism into a brown tumor of the mandible, as well as the histological makeup of the tumor.
The discovery and subsequent description of the parathyroid glands is credited to Ivar Sandstrom, though his publication, On a New Gland in Man and Several Mammals-Glandulae Parathyroideae, received little attention. Gustaf Retzius
Gustaf Retzius
Magnus Gustaf Retzius was a Swedish physician and anatomist who dedicated a large part of his life to researching the histology of the sense organs and nervous system.-Biography:...
and Eugene Gley
Eugène Gley
Marcel Eugène Émile Gley was a French physiologist and endocrinologist born in Épinal, Vosges.He studied physiology in Beaune and Nancy, and afterwards worked as assistant to Étienne-Jules Marey in Paris. Later he received the title of professeur agrégé, and in 1908 became a professor at the...
compounded his research, the latter credited with the discovery of the function of the parathyroid glands. This research cumulated in the first surgical removal of a parathyroid tumor by Felix Mandel in 1925. A 2.5 × 1.5-inch (64 × 38 mm) tumor was removed from the thyroid artery of a man suffering from advanced OFC. The patient's symptoms disappeared, only to return in approximately six years as a result of renal stones that were diagnosed only after the patient had died. In 1932, blood tests on a female patient suffering from renal stone-based OFC revealed extremely high blood calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
levels. Fuller Albright diagnosed and treated the woman, who suffered from a large tumor of the neck as well as renal stones.
The first published literature to describe a brown tumor (which was linked to OFC) was published in 1953, though clinical reports from before 1953 do draw a correlation between the disease and tumors previous to the publication.
The advent of the multichannel autoanalyzer in the 1960s and 70s led to an increase in early diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism. This increase led to a sharp decline in the prolonged manifestation of the disease, leading to a drop in the number of cases of OFC due to the early detection of hyperparathyroidism. Before this invention, the diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism was generally prolonged until the emergence of severe manifestations, such as OFC.

