
Nd:YAG laser
Encyclopedia
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
that is used as a lasing medium
Active laser medium
The active laser medium is the source of optical gain within a laser. The gain results from the stimulated emission of electronic or molecular transitions to a lower energy state from a higher energy state...
for solid-state laser
Solid-state laser
A solid-state laser is a laser that uses a gain medium that is a solid, rather than a liquid such as in dye lasers or a gas as in gas lasers. Semiconductor-based lasers are also in the solid state, but are generally considered as a separate class from solid-state lasers .-Solid-state...
s. The dopant
Dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace impurity element that is inserted into a substance in order to alter the electrical properties or the optical properties of the substance. In the case of crystalline substances, the atoms of the dopant very commonly take the place of elements that...
, triply ionized neodymium
Neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite...
, typically replaces yttrium
Yttrium
Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is...
in the crystal structure of the yttrium aluminium garnet
Yttrium aluminium garnet
Yttrium aluminium garnet is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group. It is also one of three phases of the yttria-aluminium composite, the other two being yttrium aluminium monoclinic and yttrium aluminium perovskite . YAG is commonly used as a host material in various solid-state...
(YAG), since they are of similar size. Generally the crystalline host is doped with around 1% neodymium by atomic percent.
Laser operation of Nd:YAG was first demonstrated by J. E. Geusic et al. at Bell Laboratories in 1964.
Technology
Nd:YAGYttrium aluminium garnet
Yttrium aluminium garnet is a synthetic crystalline material of the garnet group. It is also one of three phases of the yttria-aluminium composite, the other two being yttrium aluminium monoclinic and yttrium aluminium perovskite . YAG is commonly used as a host material in various solid-state...
lasers are optically pumped
Laser pumping
Laser pumping is the act of energy transfer from an external source into the gain medium of a laser. The energy is absorbed in the medium, producing excited states in its atoms. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in the ground state or a less-excited...
using a flashtube
Flashtube
A flashtube, also called a flashlamp, is an electric arc lamp designed to produce extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for very short durations. Flashtubes are made of a length of glass tubing with electrodes at either end and are filled with a gas that, when triggered, ionizes...
or laser diode
Laser diode
The laser diode is a laser where the active medium is a semiconductor similar to that found in a light-emitting diode. The most common type of laser diode is formed from a p-n junction and powered by injected electric current...
s. These are one of the most common types of laser, and are used for many different applications.
Nd:YAG lasers typically emit light with a wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of 1064 nm, in the infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
. However, there are also transitions near 940, 1120, 1320, and 1440 nm. Nd:YAG lasers operate in both pulsed and continuous mode. Pulsed Nd:YAG lasers are typically operated in the so called Q-switching
Q-switching
Q-switching, sometimes known as giant pulse formation, is a technique by which a laser can be made to produce a pulsed output beam. The technique allows the production of light pulses with extremely high peak power, much higher than would be produced by the same laser if it were operating in a...
mode: An optical switch is inserted in the laser cavity waiting for a maximum population inversion
Population inversion
In physics, specifically statistical mechanics, a population inversion occurs when a system exists in state with more members in an excited state than in lower energy states...
in the neodymium ions before it opens. Then the light wave can run through the cavity, depopulating the excited laser medium at maximum population inversion. In this Q-switched mode, output powers of 250 megawatts and pulse durations of 10 to 25 nanoseconds have been achieved. The high-intensity pulses may be efficiently frequency doubled
Second harmonic generation
An optical frequency multiplier is a nonlinear optical device, in which photons interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to form new photons with greater energy, and thus higher frequency...
to generate laser light at 532 nm, or higher harmonics at 355 and 266 nm.
Nd:YAG absorbs mostly in the bands between 730–760 nm and 790–820 nm. At low current densities
Current density
Current density is a measure of the density of flow of a conserved charge. Usually the charge is the electric charge, in which case the associated current density is the electric current per unit area of cross section, but the term current density can also be applied to other conserved...
krypton
Krypton
Krypton is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a member of Group 18 and Period 4 elements. A colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, krypton occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere, is isolated by fractionally distilling liquified air, and is often used with other...
flashlamps have higher output in those bands than do the more common xenon
Xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. The element name is pronounced or . A colorless, heavy, odorless noble gas, xenon occurs in the Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts...
lamps, which produce more light at around 900 nm. The former are therefore more efficient for pumping Nd:YAG lasers.
The amount of the neodymium dopant
Dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace impurity element that is inserted into a substance in order to alter the electrical properties or the optical properties of the substance. In the case of crystalline substances, the atoms of the dopant very commonly take the place of elements that...
in the material varies according to its use. For continuous wave
Continuous wave
A continuous wave or continuous waveform is an electromagnetic wave of constant amplitude and frequency; and in mathematical analysis, of infinite duration. Continuous wave is also the name given to an early method of radio transmission, in which a carrier wave is switched on and off...
output, the doping is significantly lower than for pulsed lasers. The lightly doped CW rods can be optically distinguished by being less colored, almost white, while higher-doped rods are pink-purplish.
Other common host materials for neodymium are: YLF (yttrium lithium fluoride
Yttrium lithium fluoride
Yttrium lithium fluoride is a birefringent crystal, typically doped with neodymium and used as again medium in solid-state lasers....
, 1047 and 1053 nm), YVO4 (yttrium orthovanadate
Yttrium orthovanadate
Yttrium orthovanadate is a transparent crystal. Undoped YVO4 is also used to make efficient high-power polarizing prisms similar to Glan–Taylor prisms.There are two principal applications for doped Yttrium orthovanadate:...
, 1064 nm), and glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
. A particular host material is chosen in order to obtain a desired combination of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties. Nd:YAG lasers and variants are pumped
Laser pumping
Laser pumping is the act of energy transfer from an external source into the gain medium of a laser. The energy is absorbed in the medium, producing excited states in its atoms. When the number of particles in one excited state exceeds the number of particles in the ground state or a less-excited...
either by flashtube
Flashtube
A flashtube, also called a flashlamp, is an electric arc lamp designed to produce extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for very short durations. Flashtubes are made of a length of glass tubing with electrodes at either end and are filled with a gas that, when triggered, ionizes...
s, continuous gas discharge lamps, or near-infrared laser diode
Laser diode
The laser diode is a laser where the active medium is a semiconductor similar to that found in a light-emitting diode. The most common type of laser diode is formed from a p-n junction and powered by injected electric current...
s (DPSS lasers). Prestabilized laser (PSL) types of Nd:YAG lasers have proved to be particularly useful in providing the main beams for gravitational wave
Gravitational wave
In physics, gravitational waves are theoretical ripples in the curvature of spacetime which propagates as a wave, traveling outward from the source. Predicted to exist by Albert Einstein in 1916 on the basis of his theory of general relativity, gravitational waves theoretically transport energy as...
interferometers such as LIGO
LIGO
LIGO, which stands for the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory, is a large-scale physics experiment aiming to directly detect gravitational waves. Cofounded in 1992 by Kip Thorne and Ronald Drever of Caltech and Rainer Weiss of MIT, LIGO is a joint project between scientists at MIT,...
, VIRGO
Virgo
-Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo...
, GEO600 and TAMA
Tama
-Religion:* Tama , part of the soul in the Japanese Shinto faith, roughly equivalent to ghost, spirit, or soul* Tama , a votive deposit or ex-voto used in the Eastern Orthodox Churches...
.
Medicine
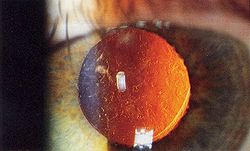
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology is the branch of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology and diseases of the eye. An ophthalmologist is a specialist in medical and surgical eye problems...
to correct posterior capsular opacification, a condition that may occur after cataract
Cataract
A cataract is a clouding that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope, varying in degree from slight to complete opacity and obstructing the passage of light...
surgery, and for peripheral iridotomy in patients with acute angle-closure glaucoma, where it has superseded surgical iridectomy
Iridectomy
An iridectomy, also known as a surgical iridectomy or corectomy, is the surgical removal of part of the iris. These procedures are most frequently performed in the treatment of closed-angle glaucoma and iris melanoma....
. Frequency-doubled
Second harmonic generation
An optical frequency multiplier is a nonlinear optical device, in which photons interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to form new photons with greater energy, and thus higher frequency...
Nd:YAG lasers (wavelength 532 nm) are used for pan-retinal photocoagulation in patients with diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is retinopathy caused by complications of diabetes mellitus, which can eventually lead to blindness....
.
In oncology
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with cancer...
, Nd:YAG lasers can be used to remove skin cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
s.
These lasers are also used extensively in the field of cosmetic medicine for laser hair removal
Laser hair removal
Laser hair removal was performed experimentally for about 20 years before it became commercially available in the mid 1990s. One of the first published articles describing laser hair removal was authored by the group at Massachusetts General Hospital in 1998...
and the treatment of minor vascular
Vascular
Vascular in zoology and medicine means "related to blood vessels", which are part of the circulatory system. An organ or tissue that is vascularized is heavily endowed with blood vessels and thus richly supplied with blood....
defects such as spider veins on the face and legs. Recently used for dissecting cellulitis, a rare skin disease usually occurring on the scalp.
Using hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is the inspection of the uterine cavity by endoscopy with access through the cervix. It allows for the diagnosis of intrauterine pathology and serves as a method for surgical intervention .-Method:...
the Nd:YAG laser has been used for removal of uterine septa
Uterine septum
A uterine septum is a form of a congenital malformation where the uterine cavity is partitioned by a longitudinal septum; the outside of the uterus has a normal typical shape...
within the inside of the uterus.
In podiatry
Podiatry
Podiatry is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and lower leg. The term podiatry came into use first in the early 20th century United States, where it now denotes a Doctor of Podiatric Medicine , a specialist who is qualified by their...
, the Nd:YAG laser is being used to treat onychomycosis
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis means fungal infection of the nail. It is the most common disease of the nails and constitutes about a half of all nail abnormalities....
, which is fungus infection of the toenail. The merits of laser treatment of these infections are not yet clear, and research is being done to establish effectiveness.
Manufacturing
Nd:YAG lasers are also used in manufacturing for engraving, etching, or marking a variety of metals and plastics. They are extensively used in manufacturing for cuttingLaser cutting
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to cut materials, and is typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, but is also starting to be used by schools, small businesses and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser, by computer, at the...
and welding steel, semiconductors
Wafer dicing
Wafer dicing is the process by which die are separated from a wafer of semiconductor following the processing of the wafer. The dicing process can be accomplished by scribing and breaking, by mechanical sawing or by laser cutting...
and various alloys. For automotive applications (cutting and welding steel) the power levels are typically 1–5 kW. Super alloy drilling (for gas turbine parts) typically uses pulsed Nd:YAG lasers (millisecond pulses, not Q-switched). Nd:YAG lasers are also employed to make subsurface markings in transparent materials such as glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
or acrylic glass
Acrylic glass
Poly is a transparent thermoplastic, often used as a light or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It is sometimes called acrylic glass. Chemically, it is the synthetic polymer of methyl methacrylate...
. Lasers of up to 400 W are used for selective laser melting of metals in additive layered manufacturing.
Fluid dynamics
Nd:YAG lasers can also be used for flow visualization techniques in fluid dynamics (for example particle image velocimetryParticle image velocimetry
Particle image velocimetry is an optical method of flow visualization used in education and research. It is used to obtain instantaneous velocity measurements and related properties in fluids...
or laser induced fluorescence).
Dentistry
Nd:YAG lasers are used for soft tissueSoft tissue
In anatomy, the term soft tissue refers to tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body, not being bone. Soft tissue includes tendons, ligaments, fascia, skin, fibrous tissues, fat, and synovial membranes , and muscles, nerves and blood vessels .It is sometimes...
surgeries
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
in the oral cavity, such as gingivectomy
Gingivectomy
A gingivectomy is a periodontal surgical procedure which includes the removal of gingival tissue in order to achieve a more aesthetic appearance and/or functional contour. The procedure is particularly useful if the gingival tissues have become enlarged, e.g. due to certain medications...
, periodontal sulcular debridement, LANAP, frenectomy
Frenectomy
A lingual frenectomy is a form of frenectomy associated with the tongue.The removal of the lingual frenulum under the tongue can be accomplished with either frenectomy or frenuloplasty. This is used to treat a tongue tied patient. It is rumored that, immediately after this minor oral surgery, the...
, biopsy
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
, and coagulation
Coagulation
Coagulation is a complex process by which blood forms clots. It is an important part of hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, wherein a damaged blood vessel wall is covered by a platelet and fibrin-containing clot to stop bleeding and begin repair of the damaged vessel...
of graft donor sites.
Military and defense

Laser designator
A laser designator is a laser light source which is used to designate a target. Laser designators provide targeting for laser guided bombs, missiles, or precision artillery munitions, such as the Paveway series of bombs, Lockheed-Martin's Hellfire, or the Copperhead round, respectively.When a...
s and laser rangefinders.
Cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS)
The Nd:YAG may be used in the application of cavity ring-down spectroscopy, which is used to measure the concentration of some light-absorbing substance.Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS)
A range of Nd:YAG lasers are used in analysis of elements in the periodic table. Though the application by itself is fairly new with respect to conventional methods such as XRF or ICP, it has proven to be less time consuming and a cheaper option to test element concentrations. A high-power Nd:YAG laser is focused onto the sample surface to produce plasmaPlasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
. Light from the plasma is captured by spectrometers and the characteristic spectra of each element can be identified, allowing concentrations of elements in the sample to be measured.
Laser pumping
Nd:YAG lasers, mainly via their second and third harmonics, are widely used to excite dye lasers either in the liquid or solid stateSolid state dye lasers
Solid state dye lasers were introduced in 1967 by Soffer and McFarland. In these solid state lasers, the gain medium is a laser dye-doped organic matrix such as poly , rather than a liquid solution of the dye...
. They are also used as pump sources for vibronically broadened solid-state lasers such as Cr4+:YAG or via the second harmonic for pumping Ti:sapphire laser
Ti-sapphire laser
Ti:sapphire lasers are tunable lasers which emit red and near-infrared light in the range from 650 to 1100 nanometers. These lasers are mainly used in scientific research because of their tunability and their ability to generate ultrashort pulses...
s.
Additional frequencies
For many applications, the infrared light is frequency-doubledNonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
or -tripled using nonlinear optical materials
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
such as lithium triborate
Lithium triborate
Lithium triborate LBO is a non-linear optics crystal. It has a wide transparency range, moderately high nonlinear coupling, high damage threshold and desirable chemical and mechanical properties. This crystal is often used for second harmonic generation of Nd:YAG lasers...
to obtain visible (532 nm, green) or ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
light. Cesium lithium borate
Cesium lithium borate
CsLiB6O10 is a non-linear crystal for ultraviolet applications and generates the 4th and 5th harmonics of the Nd:YAG fundamental laser wavelength .-Nonlinear optical properties of CLBO:...
generates the 4th and 5th harmonics of the Nd:YAG 1064 nm fundamental wavelength. A green laser pointer
Laser pointer
A laser pointer or laser pen is a small portable device with a power source and a laser emitting a very narrow coherent low-powered beam of visible light, intended to be used to highlight something of interest by illuminating it with a small bright spot of colored light...
is a frequency doubled Nd:YVO4
Neodymium doped yttrium orthovanadate
Neodymium-doped yttrium orthovanadate is a crystalline material formed by adding neodymium ions to yttrium orthovanadate. It is commonly used as an active laser medium for diode-pumped solid-state lasers. It comes as a transparent blue-tinted material...
DPSS laser. Nd:YAG can be also made to lase at its non-principal wavelength. The line at 946 nm is typically employed in "blue laser pointer" DPSS lasers, where it is doubled to 473 nm.
Properties of YAG crystal
- Formula: Y3Al5O12
- Molecular weight: 596.7
- Crystal structure: Cubic
- Hardness: 8–8.5 (Moh)
- Melting point: 1950 °C (3540 °F)
- Density: 4.55 g/cm3
Refractive index of Nd:YAG
| Wavelength (μm) | Index n (25°C) |
|---|---|
| 0.8 | 1.8245 |
| 0.9 | 1.8222 |
| 1.0 | 1.8197 |
| 1.2 | 1.8152 |
| 1.4 | 1.8121 |
Properties of Nd:YAG @ 25°C (with 1% Nd doping)
- Formula: Y2.97Nd0.03Al5O12
- Weight of Nd: 0.725%
- Atoms of Nd per unit volume: 1.38×1020 /cm3
- Charge state of Nd: 3+
- Emission wavelength: 1064 nm
- Transition: 4F3/2 → 4I11/2
- Duration of fluorescence: 230 μs
- Thermal conductivity: 0.14 W·cm−1·K−1
- Specific heat capacity: 0.59 J·g−1·K−1
- Thermal expansion: 6.9×10−6 K−1
- dn/dT: 7.3×10−6 K−1
- Young's modulus: 3.17×104 K·g/mm−2
- Poisson's ratio: 0.25
- Resistance to thermal shock: 790 W·m−1

