
Mu Arae
Encyclopedia
Mu Arae often referred to by its designation in the Henry Draper catalogue
HD 160691, is a main sequence
G-type star
around 50 light-year
s away from Earth in the constellation
of Ara
. The star has a planetary system
with four known planets, three of them with masses comparable to that of Jupiter
. The system's innermost planet was the first "hot Neptune or super-Earth" to be discovered.
astrometric
satellite
, Mu Arae exhibits a parallax
of 64.47 milliarcsecond
s as the Earth moves around the Sun. When combined with the known distance from the Earth to the Sun, this means the star is located at a distance of 50.6 light years (15.51 parsec
s).The formula for converting parallax to distance is Seen from Earth it has an apparent magnitude
Seen from Earth it has an apparent magnitude
of +5.12 and is visible to the naked eye
.
analysis of the star reveals it is approximately 10% more massive than the Sun and significantly older, at around 6,340 million years. The radius of the star is 36% greater than that of the Sun and it is 90% more luminous. The star contains twice the abundance of iron
relative to hydrogen
of our Sun and is therefore described as metal-rich. Mu Arae is also more enriched than the Sun in the element helium
.
Mu Arae has a listed spectral type
of G3IV–V. The G3 part means the star is similar to our Sun (a G2V star). The star may be entering the subgiant stage of its evolution as it starts to run out of hydrogen
in its core. This is reflected in its uncertain luminosity class, between IV (the subgiants) and V (main sequence
dwarf star
stars like the Sun).
team, together with the planet orbiting Epsilon Reticuli
. The planet, designated Mu Arae b
, was thought to be in a highly eccentric orbit of around 743 days. The discovery was made by analysing variations in the star's radial velocity
(measured by observing the Doppler shift of the star's spectral line
s) as a result of being pulled around by the planet's gravity. Further observations revealed the presence of a second object in the system (now designated as Mu Arae e
), which was published in 2004. At the time, the parameters of this planet were poorly constrained and it was thought to be in an orbit of around 8.2 years with a high eccentricity. Later in 2004, a small inner planet designated Mu Arae c
was announced with a mass comparable to that of Uranus
in a 9-day orbit. This was the first of the class of planets known as "hot Neptune
s" to be discovered. The discovery was made by making high-precision radial velocity measurements with the High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher
(HARPS) spectrograph
.
In 2006, two teams, one led by Krzysztof Goździewski and the other by Francesco Pepe independently announced four-planet models for the radial velocity measurements of the star, with a new planet (Mu Arae d
) in a near-circular orbit lasting approximately 311 days. The new model gives revised parameters for the previously known planets, with lower eccentricity orbits than in the previous model and including a more robust characterization of the orbit of Mu Arae e. The discovery of the fourth planet made Mu Arae the second known four-planet extrasolar system, after 55 Cancri
.
, the core
of a gas giant which has had its outer layers stripped away by stellar radiation. Alternatively it may have formed in the inner regions of the Mu Arae system as a rocky "super-Earth". The inner gas giants "d" and "b" are located close to the 2:1 orbital resonance
which causes them to undergo strong interactions. The best-fit solution to the system is actually unstable: simulations suggest the system is destroyed after 78 million years, which is significantly shorter than the estimated age of the star system. More stable solutions, including ones in which the two planets are actually in the resonance (similar to the situation in the Gliese 876
system) can be found which give only a slightly worse fit to the data. Searches for circumstellar discs show no evidence for a debris disc similar to the Kuiper belt
around Mu Arae. If Mu Arae does have a Kuiper belt, it is too faint to be detected with current instruments.
The gas giant planet "b" is located in the liquid water habitable zone of Mu Arae. This would prevent an Earth-like planet from forming in the habitable zone, however large moons
of the gas giant could potentially support liquid water. On the other hand it is unclear whether such massive moons could actually form around a gas giant planet, thanks to an apparent scaling law between the mass of the planet and its satellite system. In addition, measurements of the star's ultraviolet
flux
suggest that any potentially habitable
planets or moons may not receive enough ultraviolet to trigger the formation of biomolecule
s. Planet "d" would receive a similar amount of ultraviolet to the Earth and thus lies in the ultraviolet habitable zone, however, it would be too hot for any moons to support surface liquid water.
starting from "b", in order of discovery. This system is used by the team led by Goździewski. On the other hand, the team led by Pepe have proposed a modification of the designation system, where the planets are designated in order of characterization. Since the parameters of the outermost planet were poorly constrained before the introduction of the 4-planet model of the system, this results in a different order of designations for the planets in the Mu Arae system. Both systems agree on the designation of the 640-day planet as "b". The old system designates the 9-day planet as "d", the 310-day planet as "e" and the outer planet as "c". Since the International Astronomical Union
has not defined an official system for designations of extrasolar planets, the issue of which convention is "correct" remains open, however subsequent scientific publications about this system appear to have adopted the Pepe et al. system, as has the system's entry in the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia
.
Henry Draper Catalogue
The Henry Draper Catalogue is an astronomical star catalogue published between 1918 and 1924, giving spectroscopic classifications for 225,300 stars; it was later expanded by the Henry Draper Extension , published between 1925 and 1936, which gave classifications for 46,850 more stars, and by the...
HD 160691, is a main sequence
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
G-type star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
around 50 light-year
Light-year
A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres...
s away from Earth in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
of Ara
Ara (constellation)
Ara is a southern constellation situated between Scorpius and Triangulum Australe. Its name is Latin for "altar". Ara was one of the 48 Greek constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical...
. The star has a planetary system
Planetary system
A planetary system consists of the various non-stellar objects orbiting a star such as planets, dwarf planets , asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and cosmic dust...
with four known planets, three of them with masses comparable to that of Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
. The system's innermost planet was the first "hot Neptune or super-Earth" to be discovered.
Distance and visibility
According to measurements made by the HipparcosHipparcos
Hipparcos was a scientific mission of the European Space Agency , launched in 1989 and operated between 1989 and 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky...
astrometric
Astrometry
Astrometry is the branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. The information obtained by astrometric measurements provides information on the kinematics and physical origin of our Solar System and our Galaxy, the Milky...
satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
, Mu Arae exhibits a parallax
Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight, and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. The term is derived from the Greek παράλλαξις , meaning "alteration"...
of 64.47 milliarcsecond
Minute of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute, or minute of angle , is a unit of angular measurement equal to one sixtieth of one degree. In turn, a second of arc or arcsecond is one sixtieth of one minute of arc....
s as the Earth moves around the Sun. When combined with the known distance from the Earth to the Sun, this means the star is located at a distance of 50.6 light years (15.51 parsec
Parsec
The parsec is a unit of length used in astronomy. It is about 3.26 light-years, or just under 31 trillion kilometres ....
s).The formula for converting parallax to distance is
 Seen from Earth it has an apparent magnitude
Seen from Earth it has an apparent magnitudeApparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of +5.12 and is visible to the naked eye
Naked eye
The naked eye is a figure of speech referring to human visual perception unaided by a magnifying or light-collecting optical device, such as a telescope or microscope. Vision corrected to normal acuity using corrective lenses is considered "naked"...
.
Stellar characteristics
AsteroseismicAsteroseismology
Asteroseismology also known as stellar seismology is the science that studies the internal structure of pulsating stars by the interpretation of their frequency spectra. Different oscillation modes penetrate to different depths inside the star...
analysis of the star reveals it is approximately 10% more massive than the Sun and significantly older, at around 6,340 million years. The radius of the star is 36% greater than that of the Sun and it is 90% more luminous. The star contains twice the abundance of iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
relative to hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
of our Sun and is therefore described as metal-rich. Mu Arae is also more enriched than the Sun in the element helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
.
Mu Arae has a listed spectral type
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
of G3IV–V. The G3 part means the star is similar to our Sun (a G2V star). The star may be entering the subgiant stage of its evolution as it starts to run out of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
in its core. This is reflected in its uncertain luminosity class, between IV (the subgiants) and V (main sequence
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
dwarf star
Dwarf star
The term dwarf star refers to a variety of distinct classes of stars.* Dwarf star alone generally refers to any main sequence star, a star of luminosity class V.** Red dwarfs are low-mass main sequence stars....
stars like the Sun).
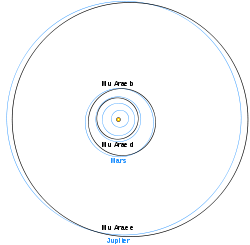
Planetary system

Discovery
In 2001, an extrasolar planet was announced by the Anglo-Australian Planet SearchAnglo-Australian Planet Search
The Anglo-Australian Planet Search or AAPS is a long-term astronomical survey started in 1998 and continuing to the present. It is being carried out on the 3.9m Anglo-Australian Telescope, AAT, of the Anglo-Australian Observatory in Australia. The purpose of this survey is to catalog planets around...
team, together with the planet orbiting Epsilon Reticuli
Epsilon Reticuli
Epsilon Reticuli is a binary system approximately 59 light-years away in the constellation of Reticulum. The primary star is an orange subgiant star, while the secondary star is a white dwarf star. The primary star should be easily visible without optical aid under dark skies in the southern...
. The planet, designated Mu Arae b
Mu Arae b
Mu Arae b is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star Mu Arae. At least one and a half times the mass of Jupiter, its orbital period is 643.25 days. This planet's discovery was announced on December 12, 2002 and was originally thought to be on a highly eccentric orbit...
, was thought to be in a highly eccentric orbit of around 743 days. The discovery was made by analysing variations in the star's radial velocity
Radial velocity
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the direction of the line of sight . In astronomy, radial velocity most commonly refers to the spectroscopic radial velocity...
(measured by observing the Doppler shift of the star's spectral line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
s) as a result of being pulled around by the planet's gravity. Further observations revealed the presence of a second object in the system (now designated as Mu Arae e
Mu Arae e
Mu Arae d is an extrasolar planet orbiting the star Mu Arae. The planet has a mass about half that of Jupiter and orbits at a distance of 0.921 AU from the star with a period of 310.55 days...
), which was published in 2004. At the time, the parameters of this planet were poorly constrained and it was thought to be in an orbit of around 8.2 years with a high eccentricity. Later in 2004, a small inner planet designated Mu Arae c
Mu Arae c
Mu Arae e is one of the four extrasolar planets orbiting the star Mu Arae. Its discovery was announced on June 13, 2002. Mu Arae e is a gas giant at least 1.8 times as massive as Jupiter. The planet orbits at Jupiter-like distance at 5.235 AU.-References:...
was announced with a mass comparable to that of Uranus
Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
in a 9-day orbit. This was the first of the class of planets known as "hot Neptune
Hot Neptune
A hot Neptune is an extrasolar planet in an orbit close to its star , with a mass similar to that of Uranus or Neptune. Recent observations have revealed a larger potential population of hot Neptunes than previously thought...
s" to be discovered. The discovery was made by making high-precision radial velocity measurements with the High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher
High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher
The High Accuracy Radial velocity Planet Searcher is a high-precision echelle spectrograph installed in 2002 on ESO's 3.6m telescope at La Silla Observatory in Chile. The first light was achieved in February 2003...
(HARPS) spectrograph
Spectrograph
A spectrograph is an instrument that separates an incoming wave into a frequency spectrum. There are several kinds of machines referred to as spectrographs, depending on the precise nature of the waves...
.
In 2006, two teams, one led by Krzysztof Goździewski and the other by Francesco Pepe independently announced four-planet models for the radial velocity measurements of the star, with a new planet (Mu Arae d
Mu Arae d
Mu Arae c, also known as HD 160691 c, is an extrasolar planet orbiting around Mu Arae. Its discovery was announced on August 25, 2004. At the time, its minimum mass was reported at just 14 times that of Earth, although later work established a value of 10.5 Earth masses. It orbits very close to Mu...
) in a near-circular orbit lasting approximately 311 days. The new model gives revised parameters for the previously known planets, with lower eccentricity orbits than in the previous model and including a more robust characterization of the orbit of Mu Arae e. The discovery of the fourth planet made Mu Arae the second known four-planet extrasolar system, after 55 Cancri
55 Cancri
55 Cancri , also cataloged Rho1 Cancri or abbreviated 55 Cnc, is a binary star approximately 41 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cancer...
.
System architecture and habitability
The Mu Arae system consists of an inner Uranus-mass planet in a tight 9-day orbit and three massive planets, probably gas giants, on wide, near-circular orbits, which contrasts with the high-eccentricity orbits typically observed for long-period extrasolar planets. The Uranus-mass planet may be a chthonian planetChthonian planet
A chthonian planet is a hypothetical class of celestial objects resulting from the stripping away of a gas giant's hydrogen and helium atmosphere and outer layers, which is called hydrodynamic escape. Such atmospheric stripping is a likely result of proximity to a star...
, the core
Planetary core
The planetary core consists of the innermost layer of a planet.The core may be composed of solid and liquid layers, while the cores of Mars and Venus are thought to be completely solid as they lack an internally generated magnetic field. In our solar system, core size can range from about 20% to...
of a gas giant which has had its outer layers stripped away by stellar radiation. Alternatively it may have formed in the inner regions of the Mu Arae system as a rocky "super-Earth". The inner gas giants "d" and "b" are located close to the 2:1 orbital resonance
Orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, an orbital resonance occurs when two orbiting bodies exert a regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually due to their orbital periods being related by a ratio of two small integers. Orbital resonances greatly enhance the mutual gravitational influence of...
which causes them to undergo strong interactions. The best-fit solution to the system is actually unstable: simulations suggest the system is destroyed after 78 million years, which is significantly shorter than the estimated age of the star system. More stable solutions, including ones in which the two planets are actually in the resonance (similar to the situation in the Gliese 876
Gliese 876
Gliese 876 is a red dwarf star approximately 15 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Aquarius. As of 2011, it has been confirmed that four extrasolar planets orbit the star...
system) can be found which give only a slightly worse fit to the data. Searches for circumstellar discs show no evidence for a debris disc similar to the Kuiper belt
Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt , sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt, is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, although it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive...
around Mu Arae. If Mu Arae does have a Kuiper belt, it is too faint to be detected with current instruments.
The gas giant planet "b" is located in the liquid water habitable zone of Mu Arae. This would prevent an Earth-like planet from forming in the habitable zone, however large moons
Natural satellite
A natural satellite or moon is a celestial body that orbits a planet or smaller body, which is called its primary. The two terms are used synonymously for non-artificial satellites of planets, of dwarf planets, and of minor planets....
of the gas giant could potentially support liquid water. On the other hand it is unclear whether such massive moons could actually form around a gas giant planet, thanks to an apparent scaling law between the mass of the planet and its satellite system. In addition, measurements of the star's ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
suggest that any potentially habitable
Planetary habitability
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia...
planets or moons may not receive enough ultraviolet to trigger the formation of biomolecule
Biomolecule
A biomolecule is any molecule that is produced by a living organism, including large polymeric molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and nucleic acids as well as small molecules such as primary metabolites, secondary metabolites, and natural products...
s. Planet "d" would receive a similar amount of ultraviolet to the Earth and thus lies in the ultraviolet habitable zone, however, it would be too hot for any moons to support surface liquid water.
Planet designations
The established convention for extrasolar planets is that the planets receive lower-case Roman lettersLatin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
starting from "b", in order of discovery. This system is used by the team led by Goździewski. On the other hand, the team led by Pepe have proposed a modification of the designation system, where the planets are designated in order of characterization. Since the parameters of the outermost planet were poorly constrained before the introduction of the 4-planet model of the system, this results in a different order of designations for the planets in the Mu Arae system. Both systems agree on the designation of the 640-day planet as "b". The old system designates the 9-day planet as "d", the 310-day planet as "e" and the outer planet as "c". Since the International Astronomical Union
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union IAU is a collection of professional astronomers, at the Ph.D. level and beyond, active in professional research and education in astronomy...
has not defined an official system for designations of extrasolar planets, the issue of which convention is "correct" remains open, however subsequent scientific publications about this system appear to have adopted the Pepe et al. system, as has the system's entry in the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia
Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia
The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopedia is an astronomy website, founded in Paris, France at the Meudon Observatory by Jean Schneider in February 1995, which maintains a database of all the currently known and candidate extrasolar planets, with individual "note" pages for each planet and a full list...
.
See also
- 55 Cancri55 Cancri55 Cancri , also cataloged Rho1 Cancri or abbreviated 55 Cnc, is a binary star approximately 41 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Cancer...
- Extrasolar planetExtrasolar planetAn extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars...
- List of extrasolar planets
- PSR 1257+12
External links
- GJ 691
- HR 6585
- Image Mu Arae
- Extrasolar Planet Interactions by Rory Barnes & Richard Greenberg, Lunar and Planetary Lab, University of Arizona

