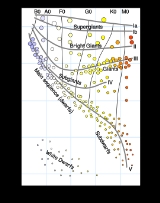
Stellar classification
Overview
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, stellar classification is a classification of star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s based on their spectral
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
characteristics. The spectral class of a star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
is a designated class of a star describing the ionization
Ionization
Ionization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
of its chromosphere
Chromosphere
The chromosphere is a thin layer of the Sun's atmosphere just above the photosphere, roughly 2,000 kilometers deep....
, what atomic excitations
Excited state
Excitation is an elevation in energy level above an arbitrary baseline energy state. In physics there is a specific technical definition for energy level which is often associated with an atom being excited to an excited state....
are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure of the temperature in this chromosphere. Light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
from the star is analyzed by splitting it up by a diffraction grating
Diffraction grating
In optics, a diffraction grating is an optical component with a periodic structure, which splits and diffracts light into several beams travelling in different directions. The directions of these beams depend on the spacing of the grating and the wavelength of the light so that the grating acts as...
, subdividing the incoming photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s into a spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
exhibiting a rainbow of colors interspersed by absorption lines
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
, each line indicating a certain ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
of a certain chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
.
Discussions

