
Mental rotation
Encyclopedia
Mental image
A mental image is an experience that, on most occasions, significantly resembles the experience of perceiving some object, event, or scene, but occurs when the relevant object, event, or scene is not actually present to the senses...
of two-dimensional
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a space or object is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus a line has a dimension of one because only one coordinate is needed to specify a point on it...
and three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
objects.
Introduction
Mental rotation is somewhat localized to the right cerebral hemisphereCerebral hemisphere
A cerebral hemisphere is one of the two regions of the eutherian brain that are delineated by the median plane, . The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter called the cerebral cortex that is...
. It is thought to take place largely in the same areas as perception
Perception
Perception is the process of attaining awareness or understanding of the environment by organizing and interpreting sensory information. All perception involves signals in the nervous system, which in turn result from physical stimulation of the sense organs...
. It is associated with the rate
Rate
In mathematics, a rate is a ratio between two measurements, often with different units. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit time. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit time, or per unit of length or mass or...
of spatial processing and intelligence (Johnson 1990, Jones 1982, Hertzog 1991).
Mental rotation can be separated into the following cognitive
Cognition
In science, cognition refers to mental processes. These processes include attention, remembering, producing and understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Cognition is studied in various disciplines such as psychology, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science...
stages (Johnson 1990):
- Create a mental image of an object
- Rotate the object mentally until a comparisonComparisonComparison may refer to:-Language:* Comparison , a feature of many languages* Degree of comparison, an English language grammatical feature* Mass comparison, a test for the relatedness of languages-Mathematics:...
can be made - Make the comparison
- Decide if the objects are the same or not
- Report the decision
How mental rotation ability is assessed
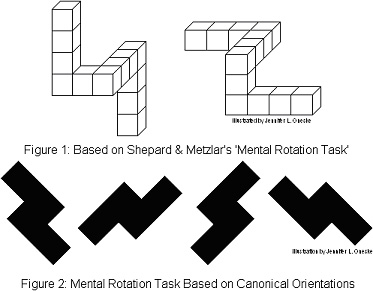
In a mental rotation test, the subject is asked to compare two 3DThree-dimensional space
Three-dimensional space is a geometric 3-parameters model of the physical universe in which we live. These three dimensions are commonly called length, width, and depth , although any three directions can be chosen, provided that they do not lie in the same plane.In physics and mathematics, a...
objects (or letters
Letter (alphabet)
A letter is a grapheme in an alphabetic system of writing, such as the Greek alphabet and its descendants. Letters compose phonemes and each phoneme represents a phone in the spoken form of the language....
) and state if they are the same image
Image
An image is an artifact, for example a two-dimensional picture, that has a similar appearance to some subject—usually a physical object or a person.-Characteristics:...
or if they are mirror image
Mirror image
A mirror image is a reflected duplication of an object that appears identical but reversed. As an optical effect it results from reflection off of substances such as a mirror or water. It is also a concept in geometry and can be used as a conceptualization process for 3-D structures...
s (enantiomorphs
Chirality (mathematics)
In geometry, a figure is chiral if it is not identical to its mirror image, or, more precisely, if it cannot be mapped to its mirror image by rotations and translations alone. For example, a right shoe is different from a left shoe, and clockwise is different from counterclockwise.A chiral object...
). Commonly, the test will have pairs of images each rotated a specific amount of degrees
Degree (angle)
A degree , usually denoted by ° , is a measurement of plane angle, representing 1⁄360 of a full rotation; one degree is equivalent to π/180 radians...
(eg. 0º, 60º, 120º or 180º). Some pairs will be the same image rotated, and others will be mirrored. The subject will be shown a set number of the pairs. The subject will be judged on how accurately and rapidly
Rate
In mathematics, a rate is a ratio between two measurements, often with different units. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit time. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit time, or per unit of length or mass or...
they can distinguish between the mirrored and non-mirrored pairs.
Notable research
Roger ShepardRoger Shepard
Roger Newland Shepard is a cognitive scientist and author of Toward a Universal Law of Generalization for Psychological Science. He is seen as a father of research on spatial relations....
and Jacqueline Metzler (1971) originally discovered this phenomenon
Phenomenon
A phenomenon , plural phenomena, is any observable occurrence. Phenomena are often, but not always, understood as 'appearances' or 'experiences'...
. Their research
Research
Research can be defined as the scientific search for knowledge, or as any systematic investigation, to establish novel facts, solve new or existing problems, prove new ideas, or develop new theories, usually using a scientific method...
showed that the reaction time for participants to decide if the pair of items matched or not was linearly proportional
Proportionality (mathematics)
In mathematics, two variable quantities are proportional if one of them is always the product of the other and a constant quantity, called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. In other words, are proportional if the ratio \tfrac yx is constant. We also say that one...
to the angle
Angle
In geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle.Angles are usually presumed to be in a Euclidean plane with the circle taken for standard with regard to direction. In fact, an angle is frequently viewed as a measure of an circular arc...
of rotation from the original position. That is, the more an object has been rotated from the original, the longer it takes an individual to determine if the 2 images are of the same object or enantiomorphs (Sternberg 247). Shortly afterwards, Robert Sekuler and David Nash (1972) demonstrated that a pair of mental transformations, size scaling and rotation, could be carried out in parallel.
In further research, Shepard and Cooper (1982) have proposed the concept
Concept
The word concept is used in ordinary language as well as in almost all academic disciplines. Particularly in philosophy, psychology and cognitive sciences the term is much used and much discussed. WordNet defines concept: "conception, construct ". However, the meaning of the term concept is much...
of a "Mental Imagery" facility, which is responsible for the ability to mentally rotate visual forms. Additionally, it has been found it does not matter on which axis an object is rotated, but rather the degree to which it is rotated that has the most significant effect on response time. So rotations within the depth plane
Plane (mathematics)
In mathematics, a plane is a flat, two-dimensional surface. A plane is the two dimensional analogue of a point , a line and a space...
(i.e., 2D rotations) and rotations in depth (3D rotations) behave similarly. Thus, the matching requires more time as the amount of depth rotation increases, just as for within the depth plane.
In subsequent research, it has been found that response times increase for degraded stimuli
Stimulation
Stimulation is the action of various agents on nerves, muscles, or a sensory end organ, by which activity is evoked; especially, the nervous impulse produced by various agents on nerves, or a sensory end organ, by which the part connected with the nerve is thrown into a state of activity.The word...
and can decrease when participants are allowed to practice
Practice (learning method)
Practice is the act of rehearsing a behavior over and over, or engaging in an activity again and again, for the purpose of improving or mastering it, as in the phrase "practice makes perfect". Sports teams practice to prepare for actual games. Playing a musical instrument well takes a lot of...
mentally rotating imagery (Sternberg 247). This research has been instrumental in showing how people use mental representations
Representations
Representations is an interdisciplinary journal in the humanities published quarterly by the University of California Press. The journals was established in 1983 and is the founding publication of the New Historicism movement of the 1980s. It covers topics including literary, historical, and...
to navigate their environments.
Also, males tend to be slightly faster in mental rotation tasks than females. The ability to rotate mentally (measured in terms of decline in response time) peaks in young adult-hood, and declines thereafter.
Recent breakthroughs in nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance is a physical phenomenon in which magnetic nuclei in a magnetic field absorb and re-emit electromagnetic radiation...
have allowed psychologists to discover what parts of the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
correspond to the use of this mental imagery function. Using Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI is a type of specialized MRI scan used to measure the hemodynamic response related to neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals. It is one of the most recently developed forms of neuroimaging...
, psychologists have shown that when participants are performing mental rotation tasks, there is activation in Brodmann's areas 7A and 7B, the middle frontal gyrus
Gyrus
A gyrus is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci .-Notable gyri:* Superior frontal gyrus, lat. gyrus frontalis superior* Middle frontal gyrus, lat. gyrus frontalis medius...
, extra-striate cortex, the hand somastosensory cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
, and frontal cortex (Cohen et al.).
Other recent research has centered on whether there might be multiple neural systems for the rotation of mental imagery. Parsons (1987) found that when participants were presented with line drawings of hands rather than Shepard and Metzler-like 3D blocks showed embodiment
Embodiment
Embodied or embodiment may refer to:in psychology and philosophy,*Embodied cognition , a position in cognitive science and the philosophy of mind emphasizing the role that the body plays in shaping the mind...
effects in which participants were slower to rotate hand stimuli in directions that were incompatible with the way human wrist and arm joints move. This finding suggested that the rotation of mental imagery was underlain by multiple neural systems: that is, (at least) a motoric/tactile one as well as a visual one. In a similar vein Amorim, Isableu and Jarraya (2006) have found that adding a cylindric "head" to Shepard and Metzler line drawings of 3D objects can create facilitation and inhibition effects as compared to standard Metzler-like stimuli, further suggesting that these neural systems rely on embodied cognition.
Studies of the development of mental rotation have revealed the emergence of this ability in male infants by 5 months of age (Moore & Johnson, 2008).

