
Rate
Encyclopedia
In mathematics
, a rate is a ratio
between two measurement
s, often with different units. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit time. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit time
, or per unit of length
or mass
or another quantity. The most common type of rate is "per unit time", such as speed
, heart rate
and flux
. Rates that have a non-time denominator include exchange rate
s, literacy rates and electric flux.
In describing the units of a rate, the word "per" is used to separate the units of the two measurements used to calculate the rate (for example a heart rate
is expressed "beats per minute"). A rate defined using two numbers of the same units
(such as tax rates) or counts (such as literacy rate) will result in a dimensionless quantity
, which can be expressed as a percentage
(for example, the global literacy rate in 1998 was 80%) or fraction
or as a multiple
.
Often "rate" is a synonym of rhythm
or frequency
, a count per second (i.e. Hertz
) e.g. radio frequencies or heart rate
or sample rate.
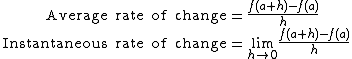
where f(x) is the function with respect to x over the interval from a to a+h. An instantaneous rate of change is equivalent to a derivative
.
An example to contrast the differences between the average and instantaneous definitions: the speed
of a car can be calculated:
In computing:
In finance:
Miscellaneous definitions:
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, a rate is a ratio
Ratio
In mathematics, a ratio is a relationship between two numbers of the same kind , usually expressed as "a to b" or a:b, sometimes expressed arithmetically as a dimensionless quotient of the two which explicitly indicates how many times the first number contains the second In mathematics, a ratio is...
between two measurement
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
s, often with different units. If the unit or quantity in respect of which something is changing is not specified, usually the rate is per unit time. However, a rate of change can be specified per unit time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
, or per unit of length
Length
In geometric measurements, length most commonly refers to the longest dimension of an object.In certain contexts, the term "length" is reserved for a certain dimension of an object along which the length is measured. For example it is possible to cut a length of a wire which is shorter than wire...
or mass
Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
or another quantity. The most common type of rate is "per unit time", such as speed
Speed
In kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity ; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as...
, heart rate
Heart rate
Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
and flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
. Rates that have a non-time denominator include exchange rate
Exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency...
s, literacy rates and electric flux.
In describing the units of a rate, the word "per" is used to separate the units of the two measurements used to calculate the rate (for example a heart rate
Heart rate
Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
is expressed "beats per minute"). A rate defined using two numbers of the same units
Units of measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention and/or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same physical quantity. Any other value of the physical quantity can be expressed as a simple multiple of the unit of...
(such as tax rates) or counts (such as literacy rate) will result in a dimensionless quantity
Dimensionless quantity
In dimensional analysis, a dimensionless quantity or quantity of dimension one is a quantity without an associated physical dimension. It is thus a "pure" number, and as such always has a dimension of 1. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and...
, which can be expressed as a percentage
Percentage
In mathematics, a percentage is a way of expressing a number as a fraction of 100 . It is often denoted using the percent sign, “%”, or the abbreviation “pct”. For example, 45% is equal to 45/100, or 0.45.Percentages are used to express how large/small one quantity is, relative to another quantity...
(for example, the global literacy rate in 1998 was 80%) or fraction
Fraction
In common usage a fraction is any part of a unit.Fraction may also mean:*Fraction , one of more equal parts of something, eg...
or as a multiple
Multiple
The word multiple can refer to:*Multiple , multiples of numbers*List of multiple discoveries, instances of scientists, working independently of each other, reaching similar findings...
.
Often "rate" is a synonym of rhythm
Rhythm
Rhythm may be generally defined as a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions." This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time may be applied to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or...
or frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, a count per second (i.e. Hertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
) e.g. radio frequencies or heart rate
Heart rate
Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
or sample rate.
Rate of change
A rate of change can be formally defined in two ways: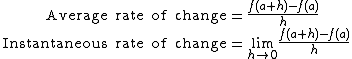
where f(x) is the function with respect to x over the interval from a to a+h. An instantaneous rate of change is equivalent to a derivative
Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
.
An example to contrast the differences between the average and instantaneous definitions: the speed
Speed
In kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity ; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as...
of a car can be calculated:
- An average rate can be calculated using the total distance travelled between a and b, divided by the travel time
- An instantaneous rate can be determined by viewing a speedometerSpeedometerA speedometer is a gauge that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a land vehicle. Now universally fitted to motor vehicles, they started to be available as options in the 1900s, and as standard equipment from about 1910 onwards. Speedometers for other vehicles have specific names...
.
Terms based on rates
In chemistry and physics:- SpeedSpeedIn kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity ; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as...
, being the distance covered per unit time, e.g. miles per hour and meters per second - AccelerationAccelerationIn physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
, the rate of change in speed, or the change in speed per unit time - Radioactive decayRadioactive decayRadioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles . The emission is spontaneous, in that the atom decays without any physical interaction with another particle from outside the atom...
, the amount of radioactive material in which one nucleus decays per second, measured in BecquerelBecquerelThe becquerel is the SI-derived unit of radioactivity. One Bq is defined as the activity of a quantity of radioactive material in which one nucleus decays per second. The Bq unit is therefore equivalent to an inverse second, s−1...
s - Reaction rateReaction rateThe reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place...
, the speed at which chemical reactions occur - Volumetric flow rateVolumetric flow rateThe volumetric flow rate in fluid dynamics and hydrometry, is the volume of fluid which passes through a given surface per unit time...
, the volume of fluid which passes through a given surface per unit time, e.g. cubic meters per second
In computing:
- Bit rateBit rateIn telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
, the number of bits that are conveyed or processed by a computer per unit of time - Symbol rateSymbol rateIn digital communications, symbol rate is the number of symbol changes made to the transmission medium per second using a digitally modulated signal or a line code. The Symbol rate is measured in baud or symbols/second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses/second...
, the number of symbol changes (signalling events) made to the transmission medium per second - Sampling rateSampling rateThe sampling rate, sample rate, or sampling frequency defines the number of samples per unit of time taken from a continuous signal to make a discrete signal. For time-domain signals, the unit for sampling rate is hertz , sometimes noted as Sa/s...
, the number of samples (signal measurements) per second
In finance:
- Interest rateInterest rateAn interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
, the price a borrower pays for the use of money they do not own, usually expressed as a percentage rate over the period of one year; see also for related rates - Exchange rateExchange rateIn finance, an exchange rate between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency...
, how much one currency is worth in terms of the other - Inflation rateInflation rateIn economics, the inflation rate is a measure of inflation, the rate of increase of a price index . It is the percentage rate of change in price level over time. The rate of decrease in the purchasing power of money is approximately equal.The inflation rate is used to calculate the real interest...
, a measure of inflation change per year - Rate of returnRate of returnIn finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
, the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested - Tax rate, the tax amount divided by the taxable income
Miscellaneous definitions:
- Rate of reinforcementRate of reinforcementIn behaviorism, rate of reinforcement is number of reinforcements per time, usually per minute. Symbol of this rate is usually Rf. Its first major exponent was B.F. Skinner . It is used in the Matching Law....
, number of reinforcements per time, usually per minute - Heart rateHeart rateHeart rate is the number of heartbeats per unit of time, typically expressed as beats per minute . Heart rate can vary as the body's need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide changes, such as during exercise or sleep....
, usually measured in beats per minute - Unemployment rate, a ratio between those in the labor force to those who are unemployed
- Birth rateBirth rateCrude birth rate is the nativity or childbirths per 1,000 people per year . Another word used interchangeably with "birth rate" is "natality". When the crude birth rate is subtracted from the crude death rate, it reveals the rate of natural increase...
and mortality rateMortality rateMortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
, the number of births or deaths scaled to the size of that population, per unit time - Literacy rate, the proportion of the population over age fifteen that can read and write

