
Lung
Encyclopedia

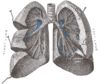
Respiration organ
Respiratory organs are used by most, or all, animals to exchange the gases necessary for their life function known as respiration...
in many air-breathing animals
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
, including most tetrapod
Tetrapod
Tetrapods are vertebrate animals having four limbs. Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are all tetrapods; even snakes and other limbless reptiles and amphibians are tetrapods by descent. The earliest tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian...
s, a few fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
and a few snail
Snail
Snail is a common name applied to most of the members of the molluscan class Gastropoda that have coiled shells in the adult stage. When the word is used in its most general sense, it includes sea snails, land snails and freshwater snails. The word snail without any qualifier is however more often...
s. In mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
. Their principal function is to transport oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
from the atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
from the bloodstream into the atmosphere. This exchange of gases is accomplished in the mosaic of specialized cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
that form millions of tiny, exceptionally thin-walled air sacs called alveoli.
To completely explain the anatomy of the lungs, it is necessary to discuss the passage of air through the mouth to the alveoli. Once air progresses through the mouth or nose, it travels through the oropharynx
Oropharynx
The Oropharynx reaches from the Uvula to the level of the hyoid bone.It opens anteriorly, through the isthmus faucium, into the mouth, while in its lateral wall, between the two palatine arches, is the palatine tonsil....
, nasopharynx
Nasopharynx
The nasopharynx is the uppermost part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate; it differs from the oral and laryngeal parts of the pharynx in that its cavity always remains patent .-Lateral:On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal ostium of the...
, the larynx
Larynx
The larynx , commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles and mammals involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. It manipulates pitch and volume...
, the trachea
Vertebrate trachea
In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
, and a progressively subdividing system of bronchi and bronchioles until it finally reaches the alveoli where the gas exchange of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
and oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
takes place.
The drawing and expulsion of air (ventilation
Ventilation (physiology)
In respiratory physiology, ventilation is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung. It is categorized under the following definitions:-Sample values:...
) is driven by muscular
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
action; in early tetrapod
Tetrapod
Tetrapods are vertebrate animals having four limbs. Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are all tetrapods; even snakes and other limbless reptiles and amphibians are tetrapods by descent. The earliest tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian...
s, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal
Pharynx
The human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately posterior to the mouth and nasal cavity, and anterior to the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx , the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx...
muscles via buccal pumping
Buccal pumping
Buccal pumping is a method of respiration in which the animal moves the floor of the mouth in a rhythmic manner that is externally apparent.This method has several stages. These will be described for an animal starting with lungs in a deflated state: First, the glottis is closed, and the...
, whereas in reptile
Reptile
Reptiles are members of a class of air-breathing, ectothermic vertebrates which are characterized by laying shelled eggs , and having skin covered in scales and/or scutes. They are tetrapods, either having four limbs or being descended from four-limbed ancestors...
s, bird
Bird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
s and mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s a more complicated musculoskeletal system
Musculoskeletal system
A musculoskeletal system is an organ system that gives animals the ability to move using the muscular and skeletal systems...
is used.
Medical terms related to the lung often begin with pulmo-, such as in the (adjectival form: pulmonary) or from the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
pulmonarius ("of the lungs"), or with pneumo- (from Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
πνεύμων "lung").
Mammalian lungs
The lungs of mammals have a spongy and soft texture and are honeycombed with epitheliumEpithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
, having a much larger surface area in total than the outer surface area of the lung itself. The lungs of humans
Human lung
The human lungs are the organs of respiration in humans. Humans have two lungs, with the left being divided into two lobes and the right into three lobes. Together, the lungs contain approximately of airways and 300 to 500 million alveoli, having a total surface area of about in...
are a typical example of this type of lung.
Breathing is largely driven by the muscular diaphragm at the bottom of the thorax. Contraction of the diaphragm pulls the bottom of the cavity in which the lung is enclosed downward, increasing volume and thus decreasing pressure, causing air to flow into the airways. Air enters through the oral and nasal cavities; it flows through the pharynx, then the larynx
Larynx
The larynx , commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles and mammals involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. It manipulates pitch and volume...
and into the trachea
Vertebrate trachea
In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
, which branches out into the main bronchi and then subsequent divisions. During normal breathing, expiration is passive and no muscles are contracted (the diaphragm relaxes). The rib cage
Rib cage
The rib cage is an arrangement of bones in the thorax of animals. It is formed by the vertebral column, ribs and sternum and encloses the heart and lungs....
itself is also able to expand and contract to some degree, through the action of other respiratory and accessory respiratory muscles. As a result, air is transported into or expelled out of the lungs. This type of lung is known as a bellows lung as it resembles a blacksmith's bellows
Bellows
A bellows is a device for delivering pressurized air in a controlled quantity to a controlled location.Basically, a bellows is a deformable container which has an outlet nozzle. When the volume of the bellows is decreased, the air escapes through the outlet...
.
Anatomy
In humans, the trachea divides into the two main bronchi that enter the roots of the lungs. The bronchi continue to divide within the lung, and after multiple divisions, give rise to bronchioles. The bronchial tree continues branching until it reaches the level of terminal bronchioles, which lead to alveolar sacs. Alveolar sacs are made up of clusters of alveoliPulmonary alveolus
An alveolus is an anatomical structure that has the form of a hollow cavity. Found in the lung parenchyma, the pulmonary alveoli are the dead ends of the respiratory tree, which outcrop from either alveolar sacs or alveolar ducts, which are both sites of gas exchange with the blood as well...
, like individual grapes within a bunch. The individual alveoli are tightly wrapped in blood vessels and it is here that gas exchange actually occurs. Deoxygenated blood from the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
is pumped through the pulmonary artery
Pulmonary artery
The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood....
to the lungs, where oxygen diffuses
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
into blood and is exchanged for carbon dioxide in the hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
of the erythrocytes
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
. The oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins to be pumped back into systemic circulation.
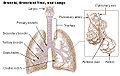
Human lungs are located in two cavities on either side of the heart. Though similar in appearance, the two are not identical. Both are separated into lobes
Lobe (anatomy)
In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension that can be determined without the use of a microscope This is in contrast to a lobule, which is a clear division only visible histologically....
by fissures, with three lobes on the right and two on the left. The lobes are further divided into segments and then into lobules, hexagonal divisions of the lungs that are the smallest subdivision visible to the naked eye. The connective tissue that divides lobules is often blackened in smokers. The medial border of the right lung is nearly vertical, while the left lung contains a cardiac notch. The cardiac notch is a concave impression molded to accommodate the shape of the heart.
Each lobe is surrounded by a pleural cavity
Pleural cavity
In human anatomy, the pleural cavity is the potential space between the two pleura of the lungs. The pleura is a serous membrane which folds back onto itself to form a two-layered, membrane structure. The thin space between the two pleural layers is known as the pleural cavity; it normally...
, which consists of two pleurae. The parietal pleura lies against the rib cage, and the visceral pleura lies on the surface of the lungs. In between the pleura is pleural fluid. The pleural cavity helps the lubricate the lungs, as well as providing surface tension to keep the lung surface in contact with the rib cage.
Lungs are to a certain extent 'overbuilt' and have a tremendous reserve volume as compared to the oxygen exchange requirements when at rest. Such excess capacity is one of the reasons that individuals can smoke for years without having a noticeable decrease in lung function while still or moving slowly; in situations like these only a small portion of the lungs are actually perfused with blood for gas exchange. Destruction of too many alveoli over time leads to the condition emphysema
Emphysema
Emphysema is a long-term, progressive disease of the lungs that primarily causes shortness of breath. In people with emphysema, the tissues necessary to support the physical shape and function of the lungs are destroyed. It is included in a group of diseases called chronic obstructive pulmonary...
, which is associated with extreme shortness of breath. As oxygen requirements increase due to exercise, a greater volume of the lungs is perfused, allowing the body to match its CO2
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
/O2
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
exchange requirements. Additionally, due to the excess capacity, it is possible for humans to live with only one lung, with the one compensating for the other's loss.
The environment of the lung is very moist, which makes it hospitable for bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
. Many respiratory illnesses are the result of bacterial or viral
Virus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
of the lungs. Inflammation of the lungs is known as pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
; inflammation of the pleura surrounding the lungs is known as pleurisy
Pleurisy
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleura, the lining of the pleural cavity surrounding the lungs. Among other things, infections are the most common cause of pleurisy....
.
Vital capacity
Vital capacity
Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inspiration. It is equal to the inspiratory reserve volume plus the tidal volume plus the expiratory reserve volume....
is the maximum volume of air that a person can exhale after maximum inhalation; it can be measured with a spirometer
Spirometer
A spirometer is an apparatus for measuring the volume of air inspired and expired by the lungs. It is a precision differential pressure transducer for the measurements of respiration flow rates. The spirometer records the amount of air and the rate of air that is breathed in and out over a...
. In combination with other physiological measurements, the vital capacity can help make a diagnosis of underlying lung disease.
The lung parenchyma
Parenchyma
Parenchyma is a term used to describe a bulk of a substance. It is used in different ways in animals and in plants.The term is New Latin, f. Greek παρέγχυμα - parenkhuma, "visceral flesh", f. παρεγχεῖν - parenkhein, "to pour in" f. para-, "beside" + en-, "in" + khein, "to pour"...
is strictly used to refer solely to alveolar
Pulmonary alveolus
An alveolus is an anatomical structure that has the form of a hollow cavity. Found in the lung parenchyma, the pulmonary alveoli are the dead ends of the respiratory tree, which outcrop from either alveolar sacs or alveolar ducts, which are both sites of gas exchange with the blood as well...
tissue with respiratory bronchiole
Respiratory bronchiole
The respiratory bronchioles are interrupted by alveoli which are thin walled evaginations. Alveolar ducts are distal continuations of the respiratory bronchioles.-External links:*...
s, alveolar duct
Alveolar duct
Alveolar ducts are the tiny end ducts of the branching airways that fill the lungs. Each lung holds approximately 1.5 to 2 million of them. The tubules divide into two or three alveolar sacs at the distal end. They are formed from the confluence openings of several alveoli...
s and terminal bronchiole
Terminal bronchiole
A terminal bronchiole is a bronchiole at the end of the conducting zone. At the transition into the respiratory zone, alveoli become present.The terminal bronchiole is the most distal segment of the conducting zone. Each of the terminal bronchioles divides to form respiratory bronchioles which...
s. However, it often includes any form of lung tissue, also including bronchioles, bronchi, blood vessel
Blood vessel
The blood vessels are the part of the circulatory system that transports blood throughout the body. There are three major types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the capillaries, which enable the actual exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and...
s and lung interstitium.
Non respiratory functions
In addition to their function in respiration, the lungs also:- Alter the pHPHIn chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
of blood by facilitating alterations in the partial pressure of carbon dioxideCarbon dioxideCarbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom... - Filter out small blood clotsThrombusA thrombus , or blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. It is achieved via the aggregation of platelets that form a platelet plug, and the activation of the humoral coagulation system...
formed in veinVeinIn the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
s - Filter out gas micro-bubbles occurring in the venousVeinIn the circulatory system, veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart...
blood stream such as those created after scuba divingScuba divingScuba diving is a form of underwater diving in which a diver uses a scuba set to breathe underwater....
during decompression. - Influence the concentration of some biologic substances and drugs used in medicine in blood
- Convert angiotensin IAngiotensinAngiotensin, a peptide hormone, causes blood vessels to constrict, and drives blood pressure up. It is part of the renin-angiotensin system, which is a major target for drugs that lower blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone, another hormone, from the adrenal cortex...
to angiotensin IIAngiotensinAngiotensin, a peptide hormone, causes blood vessels to constrict, and drives blood pressure up. It is part of the renin-angiotensin system, which is a major target for drugs that lower blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone, another hormone, from the adrenal cortex...
by the action of angiotensin-converting enzymeAngiotensin-converting enzymeAngiotensin I-converting enzyme , an exopeptidase, is a circulating enzyme that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin system , which mediates extracellular volume , and arterial vasoconstriction... - May serve as a layer of soft, shockShock (mechanics)A mechanical or physical shock is a sudden acceleration or deceleration caused, for example, by impact, drop, kick, earthquake, or explosion. Shock is a transient physical excitation....
-absorbent protection for the heart, which the lungs flank and nearly enclose. - Immunoglobulin-A is secreted in the bronchial secretion and protects against respiratory infections.
- Maintain sterility by producing mucusMucusIn vertebrates, mucus is a slippery secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. Mucous fluid is typically produced from mucous cells found in mucous glands. Mucous cells secrete products that are rich in glycoproteins and water. Mucous fluid may also originate from mixed glands, which...
containing antimicrobial compounds. Mucus contains glycoproteinGlycoproteinGlycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to polypeptide side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. In proteins that have segments extending...
s, e.g. mucinMucinMucins are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins produced by epithelial tissues in most metazoans. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most gel-like secretions, serving functions from lubrication to cell...
s, lactoferrinLactoferrinLactoferrin , also known as lactotransferrin , is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, such as milk, saliva, tears, and nasal secretions...
, lysozymeLysozymeLysozyme, also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase, are glycoside hydrolases, enzymes that damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between...
, lactoperoxidaseLactoperoxidaseLactoperoxidase is a peroxidase enzyme secreted from mammary, salivary, and other mucosal glands that functions as a natural antibacterial agent. Lactoperoxidase is a member of the heme peroxidase family of enzymes. In humans, lactoperoxidase is encoded by the LPO gene.Lactoperoxidase catalyzes...
. We find also on the epithelium Dual oxidase 2 proteins generating hydrogen peroxide, useful for hypothiocyaniteHypothiocyaniteHypothiocyanite is the anion [OSCN]- and the conjugate base of hypothiocyanous acid. It is an organic compound part of the thiocyanates as it contains the functional group SCN. It is formed when an oxygen is singly bonded to the thiocyanate group...
endogenous antimicrobial synthesis. Function not in place in cystic fibrosisCystic fibrosisCystic fibrosis is a recessive genetic disease affecting most critically the lungs, and also the pancreas, liver, and intestine...
patient lungs. - Ciliary escalator action is an important defence system against air-borne infection.The dust particles and bacteria in the inhaled air are caught in the mucous layer present at the mucosal surface of respiratory passages and are moved up towards pharynx by the rhythmic upward beating action of the cilia.
- Provide airflow for the creation of vocal sounds.
- Thermoregulation (panting)
Avian lungs
Avian lungs do not have alveoli as mammalian lungs do, they have Faveolar lungs. They contain millions of tiny passages known as para-bronchi, connected at both ends by the dorsobronchi. The airflow through the avian lung always travels in the same direction posterior to anterior. This is in contrast to the mammalian system, in which the direction of airflow in the lung is tidal, reversing between inhalation and exhalation. By utilizing a unidirectional flow of air, avian lungs are able to extract a greater concentration of oxygen from inhaled air. Birds are thus equipped to fly at altitudes at which mammals would succumb to hypoxiaHypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
. This also allows them to sustain a higher metabolic rate
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
than an equivalent weight mammal.
The lungs of birds are relatively small, but are connected to 8-9 air sacs that extend through much of the body, and are in turn connected to air spaces within the bones. The air sacs are smooth-walled, and do not themselves contribute much to respiration, but they do help to maintain the airflow through the lungs as air is forced through them by the movement of the ribs and flight muscles.
Because of the complexity of the system, misunderstanding is common and it is incorrectly believed that it takes two breathing cycles for air to pass entirely through a bird's respiratory system. Air is not stored in either the posterior or anterior sacs between respiration cycles, air moves continuously from the posterior to the anterior of the lungs throughout respiration. This type of lung construction is called a circulatory lung, as distinct from the bellows lung possessed by other animals.
Reptilian lungs
ReptilianReptile
Reptiles are members of a class of air-breathing, ectothermic vertebrates which are characterized by laying shelled eggs , and having skin covered in scales and/or scutes. They are tetrapods, either having four limbs or being descended from four-limbed ancestors...
lungs are typically ventilated by a combination of expansion and contraction of the ribs via axial muscles and buccal pumping. Crocodilians also rely on the hepatic piston method, in which the liver is pulled back by a muscle anchored to the pubic bone (part of the pelvis), which in turn pulls the bottom of the lungs backward, expanding them. Turtle
Turtle
Turtles are reptiles of the order Testudines , characterised by a special bony or cartilaginous shell developed from their ribs that acts as a shield...
s, which are unable to move their ribs, instead use their forelimbs and pectoral girdle to force air in and out of the lungs.
The lung of most reptiles has a single bronchus running down the centre, from which numerous branches reach out to individual pockets throughout the lungs. These pockets are similar to, but much larger and fewer in number than, mammalian alveoli, and give the lung a sponge-like texture. In tuatara
Tuatara
The tuatara is a reptile endemic to New Zealand which, though it resembles most lizards, is actually part of a distinct lineage, order Sphenodontia. The two species of tuatara are the only surviving members of its order, which flourished around 200 million years ago. Their most recent common...
s, snake
Snake
Snakes are elongate, legless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes that can be distinguished from legless lizards by their lack of eyelids and external ears. Like all squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales...
s, and some lizard
Lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with nearly 3800 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica as well as most oceanic island chains...
s, the lungs are simpler in structure, similar to that of typical amphibians.
Snakes and limbless lizards typically possess only the right lung as a major respiratory organ; the left lung is greatly reduced, or even absent. Amphisbaenians, however, have the opposite arrangement, with a major left lung, and a reduced or absent right lung.
Amphibian lungs
The lungs of most frogFrog
Frogs are amphibians in the order Anura , formerly referred to as Salientia . Most frogs are characterized by a short body, webbed digits , protruding eyes and the absence of a tail...
s and other amphibian
Amphibian
Amphibians , are a class of vertebrate animals including animals such as toads, frogs, caecilians, and salamanders. They are characterized as non-amniote ectothermic tetrapods...
s are simple balloon-like structures, with gas exchange limited to the outer surface area of the lung. This is not a very efficient arrangement, but amphibians have low metabolic demands and also frequently supplement their oxygen supply by diffusion across the moist outer skin of their bodies. Unlike mammals, which use a breathing system driven by negative pressure
Negative pressure
Negative pressure may refer to:*negative pressure as opposed to positive pressure*stretched liquid*vacuum*negative gauge pressure, a way of expressing pressure measurements below atmospheric pressure*suction*transpirational pull...
, amphibians employ positive pressure
Positive pressure
Positive pressure is a pressure within a system that is greater than the environment that surrounds that system. Consequently if there is any leak from the positively pressured system it will egress into the surrounding environment....
. The majority of salamander species are lungless salamander
Lungless salamander
The Plethodontidae, or Lungless salamanders, are a family of salamanders. Most species are native to the western hemisphere, from British Columbia to Brazil, although a few species are found in Sardinia, Europe south of the Alps, and South Korea...
s, which respirate through their skin and tissues lining their mouth. The only other known lungless tetrapod
Tetrapod
Tetrapods are vertebrate animals having four limbs. Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are all tetrapods; even snakes and other limbless reptiles and amphibians are tetrapods by descent. The earliest tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian...
s are also amphibians; the Bornean Flat-headed Frog
Bornean Flat-headed Frog
The Bornean Flat-headed Frog is a species of toad in the Bombinatoridae family. It is the second frog known to have no lungs....
(Barbourula kalimantanensis) and Atretochoana eiselti
Atretochoana eiselti
Atretochoana eiselti is a species of amphibian in the Caeciliidae family. It the sole species in its genus, Atretochoana. It is notable for having no lungs, one of only two lungless caecilians....
, a caecilian
Caecilian
The caecilians are an order of amphibians that superficially resemble earthworms or snakes. They mostly live hidden in the ground, making them the least familiar order of amphibians. All extant caecilians and their closest fossil relatives are grouped as the clade Apoda. They are mostly...
.
The lungs of amphibians typically have a few narrow septa
Septum
In anatomy, a septum is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones.-In human anatomy:...
of soft tissue around the outer walls, increasing the respiratory surface area and giving the lung a honey-comb appearance. In some salamanders even these are lacking, and the lung has a smooth wall. In caecilians, as in snakes, only the right lung attains any size or development.
Lungfish
The lungs of lungfish are similar to those of amphibians, with few, if any, internal septa. In PolypterusPolypterus
Polypterus is a genus of freshwater fish in the bichir family of order Polypteriformes. The type species is the Nile bichir . Fishes in this genus live in various areas in Africa...
and the Australian lungfish, there is only a single lung, albeit divided into two lobes in the former case. Other lungfish, however, have two lungs, which are located in the upper part of the body, with the connecting duct curving round and above the esophagus
Esophagus
The esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
. The blood supply also twists around the esophagus, suggesting that the lungs originally evolved in the ventral part of the body, as in other vertebrates.
Invertebrate lungs
Some invertebrateInvertebrate
An invertebrate is an animal without a backbone. The group includes 97% of all animal species – all animals except those in the chordate subphylum Vertebrata .Invertebrates form a paraphyletic group...
s have "lungs" that serve a similar respiratory purpose as, but are not evolutionarily related to, vertebrate lungs. Some arachnid
Arachnid
Arachnids are a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals in the subphylum Chelicerata. All arachnids have eight legs, although in some species the front pair may convert to a sensory function. The term is derived from the Greek words , meaning "spider".Almost all extant arachnids are terrestrial...
s have structures called "book lung
Book lung
A book lung is a type of respiration organ used for atmospheric gas exchange and is found in arachnids, such as scorpions and spiders. Each of these organs is found inside a ventral abdominal cavity and connects with the surroundings through a small opening. Book lungs are not related to the lungs...
s" used for atmospheric gas exchange. The Coconut crab
Coconut crab
The coconut crab, Birgus latro, is a species of terrestrial hermit crab, also known as the robber crab or palm thief. It is the largest land-living arthropod in the world, and is probably at the upper size limit of terrestrial animals with exoskeletons in today's atmosphere at a weight of up to...
uses structures called Branchiostegal lung
Branchiostegal lung
A branchiostegal lung is a respiration organ used by some air-breathing arthropods. It is one of the most significant adaptations of some crabs and hermit crabs such as the coconut crab to their terrestrial habitats....
s to breathe air and indeed will drown in water, hence it breathes on land and holds its breath underwater. The Pulmonata
Pulmonata
The Pulmonata, or "pulmonates", are an informal group of snails and slugs characterized by the ability to breathe air, by virtue of having a pallial lung instead of a gill, or gills...
are an order of snails and slugs that have developed "lungs".
Origins of the vertebrate lung
The lungs of today's terrestrial vertebrateVertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s and the gas bladder
Gas bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ that contributes to the ability of a fish to control its buoyancy, and thus to stay at the current water depth without having to waste energy in swimming...
s of today's fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
are believed to have evolved from simple sacs (outpocketings) of the esophagus
Esophagus
The esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
that allowed early fish to gulp air under oxygen-poor conditions. These outpocketings first arose in the bony fish
Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes , also called bony fish, are a taxonomic group of fish that have bony, as opposed to cartilaginous, skeletons. The vast majority of fish are osteichthyes, which is an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of over 29,000 species...
; in some of the ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii
The Actinopterygii or ray-finned fishes constitute a class or sub-class of the bony fishes.The ray-finned fishes are so called because they possess lepidotrichia or "fin rays", their fins being webs of skin supported by bony or horny spines , as opposed to the fleshy, lobed fins that characterize...
the sacs evolved into gas bladders, while in other ray-finned fish (such as the gar
Gar
In American English the name gar is strictly applied to members of the Lepisosteidae, a family including seven living species of fish in two genera that inhabit fresh, brackish, and occasionally marine, waters of eastern North America, Central America, and the Caribbean islands.-Etymology:In...
, bichir
Bichir
The bichirs are a family, Polypteridae, of archaic-looking ray-finned fishes, the sole family in the order Polypteriformes.All species occur in freshwater habitats in tropical Africa and the Nile River system, mainly swampy, shallow floodplains and estuaries.-Anatomy and appearance:Bichirs are...
and amia
Amia
Amia, AMIA, or AMiA can refer to:*American Medical Informatics Association*Bowfin, a fish genus*Anglican Mission in the Americas*Asociación Mutual Israelita Argentina, a Jewish community center located in Buenos Aires, Argentina...
) as well as the lobe-finned fish
Sarcopterygii
The Sarcopterygii or lobe-finned fishes – sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii constitute a clade of the bony fishes, though a strict classification would include the terrestrial vertebrates...
they evolved into lungs. The lobe-finned fish gave rise to the land-based tetrapod
Tetrapod
Tetrapods are vertebrate animals having four limbs. Amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals are all tetrapods; even snakes and other limbless reptiles and amphibians are tetrapods by descent. The earliest tetrapods evolved from the lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian...
s. Thus, the lungs of vertebrates are homologous
Homology (biology)
Homology forms the basis of organization for comparative biology. In 1843, Richard Owen defined homology as "the same organ in different animals under every variety of form and function". Organs as different as a bat's wing, a seal's flipper, a cat's paw and a human hand have a common underlying...
to the gas bladders of fish (but not to their gill
Gill
A gill is a respiratory organ found in many aquatic organisms that extracts dissolved oxygen from water, afterward excreting carbon dioxide. The gills of some species such as hermit crabs have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist...
s). This is reflected by the fact that the lungs of a fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
also develop from an outpocketing of the esophagus
Esophagus
The esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
and in the case of gas bladders, this connection to the gut
Gastrointestinal tract
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
continues to exist as the pneumatic duct in more "primitive" teleosts, and is lost in the higher orders. (This is an instance of correlation between ontogeny and phylogeny.) No known animals have both a gas bladder and lungs.
Further reading
- Lung Function Fundamentals. http://www.anaesthetist.com/icu/organs/lung/lungfx.htm
- Dr D.R. Johnson: Introductory anatomy, respiratory system
- Franlink Institute Online: The Respiratory System
- Lungs 'best in late afternoon'
- Chronic Respiratory Disease - leading research and articles on respiratory disease.
- Avian lungs and respiration

