Angiotensin-converting enzyme
Encyclopedia
Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE), an exopeptidase
, is a circulating enzyme
that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin system
(RAS), which mediates extracellular
volume (i.e. that of the blood plasma
, lymph
and interstitial fluid
), and arterial vasoconstriction
. It is secreted by pulmonary and renal endothelial cells and catalyzes the conversion of decapeptide angiotensin I to octapeptide angiotensin II.
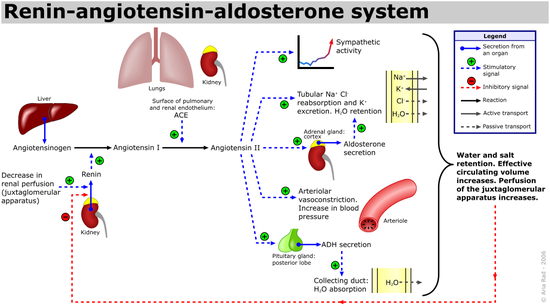 It has two primary functions:
It has two primary functions:
These two actions make ACE inhibition a goal in the treatment of conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, diabetic nephropathy
, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Inhibition of ACE (by ACE inhibitor
s) results in the decreased formation of angiotensin II and decreased metabolism of bradykinin
, leading to systematic dilation of the arteries and veins and a decrease in arterial blood pressure. In addition, inhibiting angiotension II formation diminishes angiotensin II-mediated aldosterone
secretion from the adrenal cortex
, leading to a decrease in water and sodium reabsorption and a reduction in extracellular
volume.
s. The somatic isozyme is expressed in many tissues, mainly in the lung, including vascular endothelial
cells, epithelial kidney
cells, and testicular
Leydig cell
s, whereas the germinal is expressed only in sperm
. Brain tissue has ACE enzyme which takes part in local RAAS
and converts Aβ42 (which aggregates into plaques) to Aβ40 (which is thought to be less toxic) forms of Beta amyloid. The latter is predominantly a function of N domain portion on the ACE enzyme. ACE inhibitors that cross the blood brain barrier and have preferentially select N terminal activity may therefore cause accumulation of Aβ42 and progression of dementia.
Exopeptidase
An exopeptidase is an enzyme produced in the pancreas that catalyses the removal of an amino acid from the end of a polypeptide chain. Exopeptidase cleaves the end of a polypeptide chain....
, is a circulating enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin system
Renin-angiotensin system
The renin-angiotensin system or the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure and water balance....
(RAS), which mediates extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
volume (i.e. that of the blood plasma
Blood plasma
Blood plasma is the straw-colored liquid component of blood in which the blood cells in whole blood are normally suspended. It makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is the intravascular fluid part of extracellular fluid...
, lymph
Lymph
Lymph is considered a part of the interstitial fluid, the fluid which lies in the interstices of all body tissues. Interstitial fluid becomes lymph when it enters a lymph capillary...
and interstitial fluid
Interstitial fluid
Interstitial fluid is a solution that bathes and surrounds the cells of multicellular animals. It is the main component of the extracellular fluid, which also includes plasma and transcellular fluid...
), and arterial vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of the blood vessels resulting from contraction of the muscular wall of the vessels, particularly the large arteries, small arterioles and veins. The process is the opposite of vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels. The process is particularly important in...
. It is secreted by pulmonary and renal endothelial cells and catalyzes the conversion of decapeptide angiotensin I to octapeptide angiotensin II.
Functions

- ACE catalyses the conversion of angiotensin IAngiotensinAngiotensin, a peptide hormone, causes blood vessels to constrict, and drives blood pressure up. It is part of the renin-angiotensin system, which is a major target for drugs that lower blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone, another hormone, from the adrenal cortex...
to angiotensin IIAngiotensinAngiotensin, a peptide hormone, causes blood vessels to constrict, and drives blood pressure up. It is part of the renin-angiotensin system, which is a major target for drugs that lower blood pressure. Angiotensin also stimulates the release of aldosterone, another hormone, from the adrenal cortex...
, a potent vasoconstrictor in a substrate concentration dependent manner. - ACE degrades bradykininBradykininBradykinin is a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate , and therefore causes blood pressure to lower. A class of drugs called ACE inhibitors, which are used to lower blood pressure, increase bradykinin further lowering blood pressure...
, a potent vasodilator, and other vasoactive peptides,
These two actions make ACE inhibition a goal in the treatment of conditions such as high blood pressure, heart failure, diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy , also known as Kimmelstiel-Wilson syndrome, or nodular diabetic glomerulosclerosis and intercapillary glomerulonephritis, is a progressive kidney disease caused by angiopathy of capillaries in the kidney glomeruli. It is characterized by nephrotic syndrome and diffuse...
, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Inhibition of ACE (by ACE inhibitor
ACE inhibitor
ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are a group of drugs used primarily for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure...
s) results in the decreased formation of angiotensin II and decreased metabolism of bradykinin
Bradykinin
Bradykinin is a peptide that causes blood vessels to dilate , and therefore causes blood pressure to lower. A class of drugs called ACE inhibitors, which are used to lower blood pressure, increase bradykinin further lowering blood pressure...
, leading to systematic dilation of the arteries and veins and a decrease in arterial blood pressure. In addition, inhibiting angiotension II formation diminishes angiotensin II-mediated aldosterone
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is a hormone that increases the reabsorption of sodium ions and water and the release of potassium in the collecting ducts and distal convoluted tubule of the kidneys' functional unit, the nephron. This increases blood volume and, therefore, increases blood pressure. Drugs that...
secretion from the adrenal cortex
Adrenal cortex
Situated along the perimeter of the adrenal gland, the adrenal cortex mediates the stress response through the production of mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids, including aldosterone and cortisol respectively. It is also a secondary site of androgen synthesis.-Layers:Notably, the reticularis in...
, leading to a decrease in water and sodium reabsorption and a reduction in extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
volume.
Genetics & C and N domains with important functional difference
The ACE gene, ACE, encodes 2 isozymeIsozyme
Isozymes are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. These enzymes usually display different kinetic parameters Isozymes (also known as isoenzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. These enzymes...
s. The somatic isozyme is expressed in many tissues, mainly in the lung, including vascular endothelial
Endothelium
The endothelium is the thin layer of cells that lines the interior surface of blood vessels, forming an interface between circulating blood in the lumen and the rest of the vessel wall. These cells are called endothelial cells. Endothelial cells line the entire circulatory system, from the heart...
cells, epithelial kidney
Kidney
The kidneys, organs with several functions, serve essential regulatory roles in most animals, including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system and also serve homeostatic functions such as the regulation of electrolytes, maintenance of acid–base balance, and...
cells, and testicular
Testicle
The testicle is the male gonad in animals. Like the ovaries to which they are homologous, testes are components of both the reproductive system and the endocrine system...
Leydig cell
Leydig cell
Leydig cells, also known as interstitial cells of Leydig, are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle. They produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone...
s, whereas the germinal is expressed only in sperm
Spermatozoon
A spermatozoon is a motile sperm cell, or moving form of the haploid cell that is the male gamete. A spermatozoon joins an ovum to form a zygote...
. Brain tissue has ACE enzyme which takes part in local RAAS
Raas
Raas may refer to:*Robot as a Service, Robot as a Service*Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, a hormone system that helps regulate long-term blood pressure and blood volume in the body...
and converts Aβ42 (which aggregates into plaques) to Aβ40 (which is thought to be less toxic) forms of Beta amyloid. The latter is predominantly a function of N domain portion on the ACE enzyme. ACE inhibitors that cross the blood brain barrier and have preferentially select N terminal activity may therefore cause accumulation of Aβ42 and progression of dementia.
See also
- Renin-angiotensin systemRenin-angiotensin systemThe renin-angiotensin system or the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure and water balance....
- ACE inhibitorACE inhibitorACE inhibitors or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are a group of drugs used primarily for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure...
s - Hypotensive transfusion reactionHypotensive transfusion reactionA Hypotensive transfusion reaction or HTR is a rare condition that presents with hypotension associated with administration of blood products. The hypotension quickly resolves when the transfusion is stopped....
- Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2)Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2Angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 is an exopeptidase that catalyses the conversion of angiotensin I to the nonapeptide angiotensin[1-9]., or the conversion of angiotensin II to angiotensin 1-7...

