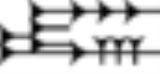
Lugal
Encyclopedia
Lugal is the Sumerian
cuneiform
sign for leader from the two signs, LÚ.GAL , and was one of several Sumer
ian titles that a ruler of a city-state could bear (alongside en
and ensi
, the exact difference being a subject of debate). The sign eventually became the predominant Sumerian term for a King
in general. In the Sumerian language
, lugal is used to mean an owner (e.g. of a boat or a field) or a head (of a unit such as a family).
sign LUGAL (Borger nr. 151, Unicode U+12217) serves as a determinative
in cuneiform texts (Sumerian
, Akkadian
and Hittite
), indicating that the following word is the name of a king. In Akkadian orthography, it may also be a syllabogram šàr, acrophonically based on the Akkadian for "king", šarrum.
, Uruk
and Ur
(as well as most of the rest of Sumer), although the various terms may have expressed different aspects of the Mesopotamian concept of kingship. A lugal at that time is assumed to have been "normally a young man of outstanding qualities from a rich landowning family." Thorkild Jacobsen
theorized that he was originally an (elected) war leader, as opposed to the (likewise elected) en, who dealt with internal issues. Among the earliest rulers whose inscriptions describe them as lugals are Enmebaragesi
and Mesilim
at Kish
, and Meskalamdug
, Mesannepada
and several of their successors at Ur
. At least from the Third Dynasty of Ur
onwards, only lugal was used to designate a contemporary sovereign in Sumerian.
, for addressing the kings or pharaohs, and elsewhere in speaking about the various kings. One common address, in the introduction
of many letters, from the vassal
s writing to the pharaoh
was to use: Šàr-ri, (for šarrum); they used Lugal + ri = Šàr-ri, (i.e. Pharaoh, or King of, Ancient Egypt). (Ri (cuneiform) is one of the more commonly used hieroglyphs, in many cases for the use of the "r" ).
Sumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
cuneiform
Cuneiform script
Cuneiform script )) is one of the earliest known forms of written expression. Emerging in Sumer around the 30th century BC, with predecessors reaching into the late 4th millennium , cuneiform writing began as a system of pictographs...
sign for leader from the two signs, LÚ.GAL , and was one of several Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
ian titles that a ruler of a city-state could bear (alongside en
EN (cuneiform)
EN is the Sumerian cuneiform for "lord" or "priest". Originally, it seems to have been used to designate a high priest or priestess of a Sumerian city-state's patron-deity - a position that entailed political power as well. It may also have been the original title of the ruler of Uruk...
and ensi
ENSI
ENSI is a Sumerian title designating the ruler or prince of a city state...
, the exact difference being a subject of debate). The sign eventually became the predominant Sumerian term for a King
King
- Centers of population :* King, Ontario, CanadaIn USA:* King, Indiana* King, North Carolina* King, Lincoln County, Wisconsin* King, Waupaca County, Wisconsin* King County, Washington- Moving-image works :Television:...
in general. In the Sumerian language
Sumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
, lugal is used to mean an owner (e.g. of a boat or a field) or a head (of a unit such as a family).
Cuneiform
The cuneiformCuneiform
Cuneiform can refer to:*Cuneiform script, an ancient writing system originating in Mesopotamia in the 4th millennium BC*Cuneiform , three bones in the human foot*Cuneiform Records, a music record label...
sign LUGAL (Borger nr. 151, Unicode U+12217) serves as a determinative
Determinative
A determinative, also known as a taxogram or semagram, is an ideogram used to mark semantic categories of words in logographic scripts which helps to disambiguate interpretation. They have no direct counterpart in spoken language, though they may derive historically from glyphs for real words, and...
in cuneiform texts (Sumerian
Sumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
, Akkadian
Akkadian language
Akkadian is an extinct Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia. The earliest attested Semitic language, it used the cuneiform writing system derived ultimately from ancient Sumerian, an unrelated language isolate...
and Hittite
Hittite language
Hittite is the extinct language once spoken by the Hittites, a people who created an empire centred on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia...
), indicating that the following word is the name of a king. In Akkadian orthography, it may also be a syllabogram šàr, acrophonically based on the Akkadian for "king", šarrum.
Lugal, ensi and en
There are different theories regarding the meaning of the title lugal in 3rd millenium Sumer. Some scholars believe that a ruler of an individual city-state was usually called ensi, and a ruler that headed a confederacy or larger dominion composed of several cities, perhaps even the whole of Sumer, was a lugal. The functions of such a lugal would include certain ceremonial and cultic activities, arbitration in border disputes, military defence against external enemies, and once the lugal has died, the eldest son must take over. Interestingly, the ensis of Lagash would sometimes refer to the city's patron deity, Ningirsu, as their lugal ("master"). All of the above is connected to the possibly priestly or sacral character of the titles ensi and especially en (the latter term continuing to designate priests in subsequent times). Other scholars consider ensi, en and lugal to have been merely three local designations for the sovereign, accepted respectively in the city-states of LagashLagash
Lagash is located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Ash Shatrah. Lagash was one of the oldest cities of the Ancient Near East...
, Uruk
Uruk
Uruk was an ancient city of Sumer and later Babylonia, situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates river, on the ancient dry former channel of the Euphrates River, some 30 km east of modern As-Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.Uruk gave its name to the Uruk...
and Ur
Ur
Ur was an important city-state in ancient Sumer located at the site of modern Tell el-Muqayyar in Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate...
(as well as most of the rest of Sumer), although the various terms may have expressed different aspects of the Mesopotamian concept of kingship. A lugal at that time is assumed to have been "normally a young man of outstanding qualities from a rich landowning family." Thorkild Jacobsen
Thorkild Jacobsen
Thorkild Jacobsen was a renowned historian specializing in Assyriology and Sumerian literature.He was one of the foremost scholars on the ancient Near East.-Biography:...
theorized that he was originally an (elected) war leader, as opposed to the (likewise elected) en, who dealt with internal issues. Among the earliest rulers whose inscriptions describe them as lugals are Enmebaragesi
Enmebaragesi
Enmebaragesi was a king of Kish, according to the Sumerian king list. The list states that he subdued Elam, reigned 900 years, and was captured single-handedly by Dumuzid "the fisherman" of Kuara, predecessor of Gilgamesh.He is the earliest ruler on the king list whose name is attested directly...
and Mesilim
Mesilim
Mesilim or Mesalim was lugal of the Sumerian city-state of Kish.Though his name is missing from the Sumerian king list, Mesilim is among the earliest historical figures recorded in archaeological documents. He was a monarch in the 3rd Dynasty of Kish, reigning some time in the "Early Dynastic...
at Kish
Kish (Sumer)
Kish is modern Tell al-Uhaymir , and was an ancient city of Sumer. Kish is located some 12 km east of Babylon, and 80 km south of Baghdad ....
, and Meskalamdug
Meskalamdug
Meskalamdug was an early ruler of Ur who does not appear in the Sumerian king list.His tomb, discovered by English archaeologist Sir Leonard Wooley in the Royal Cemetery of Ur in 1924, contained numerous gold artifacts including a golden helmet with an inscription of the king's name. His wife's...
, Mesannepada
Mesannepada
Mesannepada was the first king listed for the first dynasty of Ur on the Sumerian king list...
and several of their successors at Ur
Ur
Ur was an important city-state in ancient Sumer located at the site of modern Tell el-Muqayyar in Iraq's Dhi Qar Governorate...
. At least from the Third Dynasty of Ur
Third Dynasty of Ur
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also known as the Neo-Sumerian Empire or the Ur III Empire refers simultaneously to a 21st to 20th century BC Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state that some historians regard as a nascent empire...
onwards, only lugal was used to designate a contemporary sovereign in Sumerian.
Amarna letters Lugal
Lugal is used extensively in the Amarna lettersAmarna letters
The Amarna letters are an archive of correspondence on clay tablets, mostly diplomatic, between the Egyptian administration and its representatives in Canaan and Amurru during the New Kingdom...
, for addressing the kings or pharaohs, and elsewhere in speaking about the various kings. One common address, in the introduction
Salutation (greeting)
A salutation is a greeting used in a letter or other written communication, such as an email. Salutations can be formal or informal. The most common form of salutation in a letter is Dear followed by the recipient's given name or title...
of many letters, from the vassal
Vassal
A vassal or feudatory is a person who has entered into a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. The obligations often included military support and mutual protection, in exchange for certain privileges, usually including the grant of land held...
s writing to the pharaoh
Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Egyptian rulers of all periods. The title originates in the term "pr-aa" which means "great house" and describes the royal palace...
was to use: Šàr-ri, (for šarrum); they used Lugal + ri = Šàr-ri, (i.e. Pharaoh, or King of, Ancient Egypt). (Ri (cuneiform) is one of the more commonly used hieroglyphs, in many cases for the use of the "r" ).

