
Language of the birds
Encyclopedia

Mythology
The term mythology can refer either to the study of myths, or to a body or collection of myths. As examples, comparative mythology is the study of connections between myths from different cultures, whereas Greek mythology is the body of myths from ancient Greece...
, medieval literature
Medieval literature
Medieval literature is a broad subject, encompassing essentially all written works available in Europe and beyond during the Middle Ages . The literature of this time was composed of religious writings as well as secular works...
and occultism, the language of the birds is postulated as a mystical, perfect divine language
Divine language
Divine language, the language of the gods, or, in monotheism, the language of God is the concept of a mystical or divine proto-language, which predates and supersedes human speech.-Abrahamic traditions:...
, green language, adamic language
Adamic language
The Adamic language is, according to certain sects within Abrahamic traditions, the language spoken by Adam and Eve in the Garden of Eden, i.e., either the language used by God to address Adam, or the language invented by Adam ....
, enochian language, angelic language
Angel
Angels are mythical beings often depicted as messengers of God in the Hebrew and Christian Bibles along with the Quran. The English word angel is derived from the Greek ἄγγελος, a translation of in the Hebrew Bible ; a similar term, ملائكة , is used in the Qur'an...
or a mythical
Mythical origins of language
There have been many accounts of the origin of language in the world's mythologies and other stories pertaining to the origin of language, the development of language and the reasons behind the diversity in languages today....
or magical language used by birds to communicate with the initiated.
History
In Indo-European religion, the behavior of birds has long been used for the purposes of divinationDivination
Divination is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic standardized process or ritual...
by augur
Augur
The augur was a priest and official in the classical world, especially ancient Rome and Etruria. His main role was to interpret the will of the gods by studying the flight of birds: whether they are flying in groups/alone, what noises they make as they fly, direction of flight and what kind of...
s. According to a suggestion by Walter Burkert
Walter Burkert
Walter Burkert is a German scholar of Greek mythology and cult.An emeritus professor of classics at the University of Zurich, Switzerland, he also has taught in the United Kingdom and the United States...
, these customs may have their roots in the Paleolithic
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic Age, Era or Period, is a prehistoric period of human history distinguished by the development of the most primitive stone tools discovered , and covers roughly 99% of human technological prehistory...
when, during the Ice Age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
, early humans looked for carrion
Carrion
Carrion refers to the carcass of a dead animal. Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters include vultures, hawks, eagles, hyenas, Virginia Opossum, Tasmanian Devils, coyotes, Komodo dragons, and burying beetles...
by observing scavenging birds.
There are also examples of contemporary bird-human communication and symbiosis
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is close and often long-term interaction between different biological species. In 1877 Bennett used the word symbiosis to describe the mutualistic relationship in lichens...
. In North America, ravens have been known to lead wolves (and native hunters) to prey they otherwise would be unable to consume. In Africa, the Greater Honeyguide
Greater Honeyguide
The Greater Honeyguide is a bird in the family Indicatoridae, paleotropical near passerine birds related to the woodpeckers. Its English and scientific names refer to its habit of guiding people to bee colonies....
is known to guide humans to beehives in the hope that the hive will be incapacitated and opened for them.
Dating to the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
, birdsong was the inspiration for some magic
Magic (paranormal)
Magic is the claimed art of manipulating aspects of reality either by supernatural means or through knowledge of occult laws unknown to science. It is in contrast to science, in that science does not accept anything not subject to either direct or indirect observation, and subject to logical...
al engineered language
Engineered language
Engineered languages are constructed languages devised to test or prove some hypotheses about how languages work or might work. There are at least three subcategories, philosophical languages , logical languages , and experimental languages...
s, in particular musical language
Musical language
Musical languages are languages based on musical sounds, either instead of or in addition to articulation. They can be categorized as constructed languages, and as whistled languages. Whistled languages are dependent on an underlying articulatory language, in actual use in various cultures as a...
s. Whistled language
Whistled language
Whistled languages use whistling to emulate speech and facilitate communication. A whistled language is a system of whistled communication which allows fluent whistlers to transmit and comprehend a potentially unlimited number of messages over long distances...
s based on spoken natural languages are also sometimes referred to as the language of the birds.
Norse mythology
In Norse mythologyNorse mythology
Norse mythology, a subset of Germanic mythology, is the overall term for the myths, legends and beliefs about supernatural beings of Norse pagans. It flourished prior to the Christianization of Scandinavia, during the Early Middle Ages, and passed into Nordic folklore, with some aspects surviving...
, the power to understand the language of the birds was a sign of great wisdom. The god Odin
Odin
Odin is a major god in Norse mythology and the ruler of Asgard. Homologous with the Anglo-Saxon "Wōden" and the Old High German "Wotan", the name is descended from Proto-Germanic "*Wodanaz" or "*Wōđanaz"....
had two ravens, called Hugin and Munin
Hugin and Munin
In Norse mythology, Huginn and Muninn are a pair of ravens that fly all over the world, Midgard, and bring the god Odin information...
, who flew around the world and told Odin what happened among mortal men.
The legendary king of Sweden Dag the Wise
Dag the Wise
Dag the Wise or Dagr Spaka was a mythological Swedish king of the House of Ynglings. He was the son of Dyggvi, the former king. According to legend, he could understand the speech of birds and had a sparrow that gathered news for him from many lands...
was so wise that he could understand what birds said. He had a tame house sparrow
House Sparrow
The House Sparrow is a bird of the sparrow family Passeridae, found in most parts of the world. One of about 25 species in the genus Passer, the House Sparrow occurs naturally in most of Europe, the Mediterranean region, and much of Asia...
which flew around and brought back news to him. Once, a farmer in Reidgotaland
Reidgotaland
Reidgotaland, Hreidgotaland or Hreiðgotaland was a land in Scandinavian sagas as well as in the pre-Viking English Widsith, which usually referred to the land of the Goths...
killed Dag's sparrow, which brought on a terrible retribution from the Swedes.
The ability could also be acquired by tasting dragon blood. According to the Poetic Edda
Poetic Edda
The Poetic Edda is a collection of Old Norse poems primarily preserved in the Icelandic mediaeval manuscript Codex Regius. Along with Snorri Sturluson's Prose Edda, the Poetic Edda is the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends, and from the early 19th century...
and the Völsunga saga
Volsunga saga
The Völsungasaga is a legendary saga, a late 13th century Icelandic prose rendition of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan . It is largely based on epic poetry...
, Sigurd
Sigurd
Sigurd is a legendary hero of Norse mythology, as well as the central character in the Völsunga saga. The earliest extant representations for his legend come in pictorial form from seven runestones in Sweden and most notably the Ramsund carving Sigurd (Old Norse: Sigurðr) is a legendary hero of...
accidentally tasted dragon blood while roasting the heart of Fafnir
Fafnir
In Norse mythology, Fáfnir or Frænir was a son of the dwarf king Hreidmar and brother of Regin and Ótr. In the Volsunga saga, Fáfnir was a dwarf gifted with a powerful arm and fearless soul. He guarded his father's house of glittering gold and flashing gems...
. This gave him the ability to understand the language of birds, and his life was saved as the birds were discussing Regin
Regin
Reginn, often Anglicized as Regin, in Norse mythology, was the son of Hreiðmarr and foster father of Sigurd. His brothers are Fafnir and Ótr. When Loki mistakenly kills Ótr, Hreiðmarr demands to be repaid with the amount of gold it takes to fill Ótr's skin and cover the outside. Loki takes this...
's plans to kill Sigurd. Through the same ability Áslaug
Aslaug
Aslaug, Aslög, Kraka, Kráka or Randalin, was a queen of Scandinavian mythology who appears in Snorri's Edda, the Völsunga saga and the saga of Ragnar Lodbrok.-The Legendary Aslaug:...
, Sigurd's daughter, found out the betrothment of her husband Ragnar Lodbrok
Ragnar Lodbrok
Ragnar Lodbrok was a Norse legendary hero from the Viking Age who was thoroughly reshaped in Old Norse poetry and legendary sagas.-Life as recorded in the sagas:...
, to another woman.
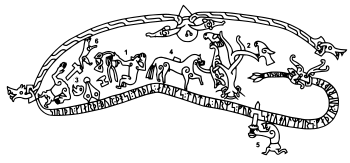
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
depicts how Sigurd
Sigurd
Sigurd is a legendary hero of Norse mythology, as well as the central character in the Völsunga saga. The earliest extant representations for his legend come in pictorial form from seven runestones in Sweden and most notably the Ramsund carving Sigurd (Old Norse: Sigurðr) is a legendary hero of...
learnt the language of birds, in the Poetic Edda
Poetic Edda
The Poetic Edda is a collection of Old Norse poems primarily preserved in the Icelandic mediaeval manuscript Codex Regius. Along with Snorri Sturluson's Prose Edda, the Poetic Edda is the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends, and from the early 19th century...
and the Völsunga saga
Volsunga saga
The Völsungasaga is a legendary saga, a late 13th century Icelandic prose rendition of the origin and decline of the Völsung clan . It is largely based on epic poetry...
.
- Sigurd is sitting naked in front of the fire preparing the dragon heart, from FafnirFafnirIn Norse mythology, Fáfnir or Frænir was a son of the dwarf king Hreidmar and brother of Regin and Ótr. In the Volsunga saga, Fáfnir was a dwarf gifted with a powerful arm and fearless soul. He guarded his father's house of glittering gold and flashing gems...
, for his foster-father ReginReginReginn, often Anglicized as Regin, in Norse mythology, was the son of Hreiðmarr and foster father of Sigurd. His brothers are Fafnir and Ótr. When Loki mistakenly kills Ótr, Hreiðmarr demands to be repaid with the amount of gold it takes to fill Ótr's skin and cover the outside. Loki takes this...
, who is FafnirFafnirIn Norse mythology, Fáfnir or Frænir was a son of the dwarf king Hreidmar and brother of Regin and Ótr. In the Volsunga saga, Fáfnir was a dwarf gifted with a powerful arm and fearless soul. He guarded his father's house of glittering gold and flashing gems...
's brother. The heart is not finished yet, and when Sigurd touches it, he burns himself and sticks his finger into his mouth. As he has tasted dragon blood, he starts to understand the birds' song. - The birds say that Regin will not keep his promise of reconciliation and will try to kill Sigurd, which causes Sigurd to cut off Regin's head.
- Regin is dead beside his own head, his smithing tools with which he reforged Sigurd's sword GramGram (mythology)In Norse mythology, Gram is the name of the sword that Sigurd used to kill the dragon Fafnir.It was forged by Wayland the Smith and originally belonged to his father, Sigmund, who received it in the hall of the Volsung after pulling it out of the tree Barnstokk into which Odin had stuck...
are scattered around him, and - Regin's horse is laden with the dragon's treasure.
- is the previous event when Sigurd killed Fafnir, and
- shows ÓtrÓtrIn Norse mythology, Ótr is a dwarf. He is the son of the king Hreidmar and the brother of Fafnir and Regin....
from the saga's beginning.
In an eddic poem
Poetic Edda
The Poetic Edda is a collection of Old Norse poems primarily preserved in the Icelandic mediaeval manuscript Codex Regius. Along with Snorri Sturluson's Prose Edda, the Poetic Edda is the most important extant source on Norse mythology and Germanic heroic legends, and from the early 19th century...
loosely connected with the Sigurd tradition which is named Helgakviða Hjörvarðssonar
Helgakviða Hjörvarðssonar
Helgakviða Hjörvarðssonar is a poem collected in the Poetic Edda, found in the Codex Regius manuscript where it follows Helgakviða Hundingsbana I and precedes Helgakviða Hundingsbana II...
, the reason why a man named Atli once had the ability is not explained. Atli's lord's son Helgi would marry what was presumably Sigurd's aunt, the Valkyrie
Valkyrie
In Norse mythology, a valkyrie is one of a host of female figures who decides who dies in battle. Selecting among half of those who die in battle , the valkyries bring their chosen to the afterlife hall of the slain, Valhalla, ruled over by the god Odin...
Sváfa
Sváfa
In Norse mythology, Sváfa or Sváva is a valkyrie and the daughter of king Eylimi. Consequently she was probably the maternal aunt of Sigurd, the dragon slayer, although this is not explicitly mentioned in Helgakviða Hjörvarðssonar where Sváfa's story appears.-Etymology:The etymology of the...
.
Greek mythology
According to Apollonius Rhodius, the figureheadFigurehead
A figurehead is a carved wooden decoration found at the prow of ships largely made between the 16th and 19th century.-History:Although earlier ships had often had some form of bow ornamentation A figurehead is a carved wooden decoration found at the prow of ships largely made between the 16th and...
of Jason
Jason
Jason was a late ancient Greek mythological hero from the late 10th Century BC, famous as the leader of the Argonauts and their quest for the Golden Fleece. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcus...
's ship, the Argo
Argo
In Greek mythology, the Argo was the ship on which Jason and the Argonauts sailed from Iolcos to retrieve the Golden Fleece. It was named after its builder, Argus.-Legend:...
, was built of oak
Oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus Quercus , of which about 600 species exist. "Oak" may also appear in the names of species in related genera, notably Lithocarpus...
from the sacred grove at Dodona
Dodona
Dodona in Epirus in northwestern Greece, was an oracle devoted to a Mother Goddess identified at other sites with Rhea or Gaia, but here called Dione, who was joined and partly supplanted in historical times by the Greek god Zeus.The shrine of Dodona was regarded as the oldest Hellenic oracle,...
and could speak the language of birds. Tiresias
Tiresias
In Greek mythology, Tiresias was a blind prophet of Thebes, famous for clairvoyance and for being transformed into a woman for seven years. He was the son of the shepherd Everes and the nymph Chariclo; Tiresias participated fully in seven generations at Thebes, beginning as advisor to Cadmus...
was also said to have been given the ability to understand the language of the birds by Athena
Athena
In Greek mythology, Athena, Athenê, or Athene , also referred to as Pallas Athena/Athene , is the goddess of wisdom, courage, inspiration, civilization, warfare, strength, strategy, the arts, crafts, justice, and skill. Minerva, Athena's Roman incarnation, embodies similar attributes. Athena is...
. The language of birds in Greek mythology
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
may be attained by magical means. Democritus
Democritus
Democritus was an Ancient Greek philosopher born in Abdera, Thrace, Greece. He was an influential pre-Socratic philosopher and pupil of Leucippus, who formulated an atomic theory for the cosmos....
, Anaximander
Anaximander
Anaximander was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus, a city of Ionia; Milet in modern Turkey. He belonged to the Milesian school and learned the teachings of his master Thales...
, Apollonius of Tyana
Apollonius of Tyana
Apollonius of Tyana was a Greek Neopythagorean philosopher from the town of Tyana in the Roman province of Cappadocia in Asia Minor. Little is certainly known about him...
, Melampus
Melampus
In Greek mythology, Melampus, or Melampous , was a legendary soothsayer and healer, originally of Pylos, who ruled at Argos. He was the introducer of the worship of Dionysus, according to Herodotus, who asserted that his powers as a seer were derived from the Egyptians and that he could understand...
and Aesopus were all said to have understood the birds.
Afro-Asiatic mythologies
In SufismSufism
Sufism or ' is defined by its adherents as the inner, mystical dimension of Islam. A practitioner of this tradition is generally known as a '...
, the language of birds is a mystical language of angels. The Conference of the Birds (mantiq at-tair) is a mystical poem of 4647 verses by the 12th century Persian
Persian literature
Persian literature spans two-and-a-half millennia, though much of the pre-Islamic material has been lost. Its sources have been within historical Persia including present-day Iran as well as regions of Central Asia where the Persian language has historically been the national language...
poet Farid al-Din Attar
In the Jerusalem Talmud
Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud, talmud meaning "instruction", "learning", , is a collection of Rabbinic notes on the 2nd-century Mishnah which was compiled in the Land of Israel during the 4th-5th century. The voluminous text is also known as the Palestinian Talmud or Talmud de-Eretz Yisrael...
(Louis Ginzberg
Louis Ginzberg
Rabbi Louis Ginzberg was a Talmudist and leading figure in the Conservative Movement of Judaism of the twentieth century. He was born on November 28, 1873, in Kovno, Lithuania; he died on November 11, 1953, in New York City.-Biographical background:...
, Legends of the Jews, 1909),
Solomon
Solomon
Solomon , according to the Book of Kings and the Book of Chronicles, a King of Israel and according to the Talmud one of the 48 prophets, is identified as the son of David, also called Jedidiah in 2 Samuel 12:25, and is described as the third king of the United Monarchy, and the final king before...
's proverbial wisdom was due to his being granted understanding of the language of birds by God.
In Egyptian Arabic, hieroglyphic
Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
writing is called "the alphabet of the birds". In Ancient Egyptian itself, the hieroglyphic form of writing was given the name medu-netjer ("words of the gods" or "divine language").
Folklore
The concept is also known from many folk tales (including Welsh, Russian, German, Estonian, Greek, Romany), where usually the protagonist is granted the gift of understanding the language of the birds either by some magical transformation, or as a boon by the king of birds. The birds then inform or warn the hero about some danger or hidden treasure.Alchemy
In KabbalahKabbalah
Kabbalah/Kabala is a discipline and school of thought concerned with the esoteric aspect of Rabbinic Judaism. It was systematized in 11th-13th century Hachmei Provence and Spain, and again after the Expulsion from Spain, in 16th century Ottoman Palestine...
, Renaissance
Renaissance magic
Renaissance humanism saw a resurgence in hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of ceremonial magic.The Renaissance and the Industrial Revolution, on the other hand, saw the rise of scientism, in such forms as the substitution of chemistry for alchemy, the dethronement of the Ptolemaic theory of...
magic
Magic (paranormal)
Magic is the claimed art of manipulating aspects of reality either by supernatural means or through knowledge of occult laws unknown to science. It is in contrast to science, in that science does not accept anything not subject to either direct or indirect observation, and subject to logical...
, and alchemy
Alchemy
Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base...
, the language of the birds was considered a secret and perfect language and the key to perfect knowledge, sometimes also called the langue verte, or green
Green
Green is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 520–570 nanometres. In the subtractive color system, it is not a primary color, but is created out of a mixture of yellow and blue, or yellow and cyan; it is considered...
language (Jean Julien Fulcanelli, Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim was a German magician, occult writer, theologian, astrologer, and alchemist.-Life:Agrippa was born in Cologne in 1486...
de occulta philosophia).
Literature and culture
Compare also the rather comical and satirical BirdsThe Birds (play)
The Birds is a comedy by the Ancient Greek playwright Aristophanes. It was performed in 414 BCE at the City Dionysia where it won second prize. It has been acclaimed by modern critics as a perfectly realized fantasy remarkable for its mimicry of birds and for the gaiety of its songs...
of Aristophanes
Aristophanes
Aristophanes , son of Philippus, of the deme Cydathenaus, was a comic playwright of ancient Athens. Eleven of his forty plays survive virtually complete...
and Parliament of Fowls
Parlement of Foules
The "Parlement of Foules" is a poem by Geoffrey Chaucer made up of approximately 700 lines. The poem is in the form of a dream vision in rhyme royal stanza and is interesting in that it is the first reference to the idea that St...
by Chaucer.
In medieval France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, the language of the birds (la langue des oiseaux) was a secret language of the Troubadour
Troubadour
A troubadour was a composer and performer of Old Occitan lyric poetry during the High Middle Ages . Since the word "troubadour" is etymologically masculine, a female troubadour is usually called a trobairitz....
s, connected with the Tarot
Tarot
The tarot |trionfi]] and later as tarocchi, tarock, and others) is a pack of cards , used from the mid-15th century in various parts of Europe to play a group of card games such as Italian tarocchini and French tarot...
, allegedly based on puns and symbolism drawn from homophony, e. g. an inn called au lion d'or "the Golden Lion" is allegedly "code" for au lit on dort "in the bed one sleeps" (note that this particular pun cannot be medieval, since final t was pronounced until Middle French, c.f. e.g. the 14th century loanword 'bonnet').
The artificial language zaum
Zaum
Zaum is a word used to describe the linguistic experiments in sound symbolism and language creation of Russian Futurist poets such as Velimir Khlebnikov and Aleksei Kruchenykh....
of Russian Futurism
Russian Futurism
Russian Futurism is the term used to denote a group of Russian poets and artists who adopted the principles of Filippo Marinetti's "Manifesto of Futurism"...
was described as "language of the birds" by Velimir Khlebnikov
Velimir Khlebnikov
Velimir Khlebnikov , pseudonym of Viktor Vladimirovich Khlebnikov , was a central part of the Russian Futurist movement, but his work and influence stretch far beyond it.Khlebnikov belonged to Hylaea,...
.
"The language of the birds" (Die Sprache der Vögel) is a 1991 German movie.
Jean Sibelius
Jean Sibelius
Jean Sibelius was a Finnish composer of the later Romantic period whose music played an important role in the formation of the Finnish national identity. His mastery of the orchestra has been described as "prodigious."...
composed a wedding march titled "The language of the birds" in 1911. The children's book author Rafe Martin has written "The Language of Birds" as an adaptation of a Russian folk tale; it was made into a children's opera by composer John Kennedy.
In her first book, Jonathan Strange & Mr Norrell
Jonathan Strange & Mr Norrell
Jonathan Strange & Mr Norrell is the 2004 first novel by British writer Susanna Clarke. An alternative history set in 19th-century England around the time of the Napoleonic Wars, it is based on the premise that magic once existed in England and has returned with two men: Gilbert Norrell and...
, Susanna Clarke
Susanna Clarke
Susanna Mary Clarke is a British author best known for her debut novel Jonathan Strange & Mr Norrell , a Hugo Award-winning alternate history. Clarke began Jonathan Strange in 1993 and worked on it during her spare time...
, in her faux footnotes, refers to a book called, "The Language of the Birds." It is among other things a reference to the fictional Raven King.
A Bird in Your Ear is a one act opera by British/American composer David Bruce based on the Russian folk tale, The Language of the Birds, with a libretto by Alasdair Middleton. It was commissioned by Bard College, NY and first performed there in March 2008. Further extracts were performed by New York City Opera in 2009.
See also
- Bird vocalization
- Confusion of tonguesConfusion of tonguesThe confusion of tongues is the initial fragmentation of human languages described in the Book of Genesis 11:1–9, as a result of the construction of the Tower of Babel....
- GlossolaliaGlossolaliaGlossolalia or speaking in tongues is the fluid vocalizing of speech-like syllables, often as part of religious practice. The significance of glossolalia has varied with time and place, with some considering it a part of a sacred language...
- Hebban olla vogalaHebban olla vogalaHebban olla vogala, sometimes spelt hebban olla uogala, are the first three words of a 12th century fragment of Old Dutch.The fragment was discovered in 1932 in the margin of a Latin manuscript that was made in the abbey of Rochester, Kent and that is kept in Oxford...
- Musical languageMusical languageMusical languages are languages based on musical sounds, either instead of or in addition to articulation. They can be categorized as constructed languages, and as whistled languages. Whistled languages are dependent on an underlying articulatory language, in actual use in various cultures as a...
External links
- Sacred Texts - Russian folk tales
- Jewish Heritage Online Magazine - Ellen Frankel
- Le Tarot
- The Society of Inner Light
- Belén Gache

