
Kleihauer-Betke test
Encyclopedia
The Kleihauer-Betke test, Kleihauer-Betke ("KB") stain or Kleihauer test, is a blood test
used to measure the amount of fetal hemoglobin
transferred from a fetus
to a mother's bloodstream. It is usually performed on Rhesus-negative
mothers to determine the required dose of Rho(D) immune globulin
(RhIg) to inhibit formation of Rh antibodies
in the mother and prevent Rh disease
in future Rh-positive children.
. A standard blood smear is prepared from the mother's blood
, and exposed to an acid bath. This removes adult hemoglobin
, but not fetal hemoglobin, from the red blood cells. Subsequent staining makes fetal cells (containing fetal hemoglobin) appear rose-pink in color, while adult red blood cells are only seen as 'ghosts'. 2000 cells are counted under the microscope
and a percentage of fetal to maternal cells is calculated.
In those with positive tests, follow up testing at a postpartum check should be done to rule out the possibility of a false positive. This could be caused by a process in the mother which causes persistent elevation of fetal hemoglobin, e.g. sickle cell trait
.
Comparison with other more expensive or technologically advanced methods such as flow cytometry
has shown that the KB stain, like the more advanced methods, is sensitive in its detection of FMH. Background counting errors can result in estimates of as much as 5 ml
fetal blood loss when there actually is no such blood loss, but standard methods available in most laboratories
admit an extremely low probability of the return of a false positive when more severe FMH has taken place.
, the percent of total fetal blood volume lost should be calculated, making appropriate adjustments based on the following known relationships:
These constraint
s can then be applied to yield the formula
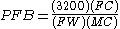
where
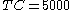 total red blood cells are observed,
total red blood cells are observed, 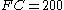 of which are found to be fetal red blood cells. Suppose further that the stillbirth weight of the fetus under consideration is
of which are found to be fetal red blood cells. Suppose further that the stillbirth weight of the fetus under consideration is 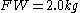 . Then we would conclude that the total percentage of fetal blood lost is approximately
. Then we would conclude that the total percentage of fetal blood lost is approximately
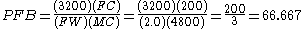
to five significant digits. We would hence conclude that the fetus under consideration lost 66.667% (two thirds) of its blood via FMH. Generally, stillbirth is highly probable for any value of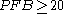 , particularly if the fetus abruptly loses this much blood; in this example, we would hence be likely to suspect FMH as the cause of the stillbirth. It is important to note, however, that such a diagnosis
, particularly if the fetus abruptly loses this much blood; in this example, we would hence be likely to suspect FMH as the cause of the stillbirth. It is important to note, however, that such a diagnosis
is still not completely conclusive; fetuses losing large quantities of blood over long periods of time are able to compensate for this slower blood loss; since the KB stain tells us nothing with regard to the level of acuity of FMH. This means that it is not possible to entirely correlate a positive KB stain and high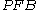 with a stillbirth, though in many cases, given other information, such as known hereditary complication
with a stillbirth, though in many cases, given other information, such as known hereditary complication
s of pregnancy
, extremely high positive correlation coefficients
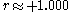 between FMH and stillbirth have been observed.
between FMH and stillbirth have been observed.
s have the same life expectancy
in the maternal bloodstream, it is possible to obtain informative results from a KB stain for a fair period of time after a stillbirth. However, if the mother and fetus are ABO
incompatible, it is more crucial to quickly perform the KB stain following a stillbirth, as the fetal red blood cells will be eliminated from the maternal bloodstream very quickly, causing the KB stain to underestimate the degree of FMH, if any.
Lots of concern has been raised in the literature concerning false positives when sampling is done after delivery. In general this is not a problem. Delivery does result in higher frequency of detection of micro-hemorrhages but this should not confound interpretation of FMH as a possible cause of stillbirth. It is not necessary to draw the sample before induction, onset of labor, delivery, placental delivery etc. despite what some published literature purports. However, if caesarean section is to be used, failure to draw the sample prior to that will result in a 2% false positive rate.
Finally, anything which causes persistence of fetal hemoglobin in maternal blood cells will make interpretation much trickier. Certain hemoglobinopathies
, the most common of which is sickle cell trait, do this. Overall, somewhere around 1-3% of the time this could result in false interpretation.
Blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a needle, or via fingerprick....
used to measure the amount of fetal hemoglobin
Fetal hemoglobin
Fetal hemoglobin, or foetal haemoglobin, is the main oxygen transport protein in the fetus during the last seven months of development in the uterus and in the newborn until roughly 6 months old...
transferred from a fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
to a mother's bloodstream. It is usually performed on Rhesus-negative
Rhesus blood group system
The Rh blood group system is one of thirty current human blood group systems. Clinically, it is the most important blood group system after ABO. At Present, the Rh blood group system consists of 50 defined blood-group antigens, among which the 5 antigens D, C, c, E, and e are the most important...
mothers to determine the required dose of Rho(D) immune globulin
Rho(D) Immune Globulin
Rho Immune Globulin is a medicine given by intramuscular injection that is used to prevent the immunological condition known as Rhesus disease...
(RhIg) to inhibit formation of Rh antibodies
Antibody
An antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
in the mother and prevent Rh disease
Rh disease
Rh disease is one of the causes of hemolytic disease of the newborn...
in future Rh-positive children.
Test details
The KB test is the standard method of quantitating fetal-maternal hemorrhage (FMH). It takes advantage of the differential resistance of fetal hemoglobin to acidAcid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
. A standard blood smear is prepared from the mother's blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
, and exposed to an acid bath. This removes adult hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
, but not fetal hemoglobin, from the red blood cells. Subsequent staining makes fetal cells (containing fetal hemoglobin) appear rose-pink in color, while adult red blood cells are only seen as 'ghosts'. 2000 cells are counted under the microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
and a percentage of fetal to maternal cells is calculated.
In those with positive tests, follow up testing at a postpartum check should be done to rule out the possibility of a false positive. This could be caused by a process in the mother which causes persistent elevation of fetal hemoglobin, e.g. sickle cell trait
Sickle cell trait
Sickle cell trait describes a condition in which a person has one abnormal allele of the hemoglobin beta gene , but does not display the severe symptoms of sickle cell disease that occur in a person who has two copies of that allele...
.
Comparison with other more expensive or technologically advanced methods such as flow cytometry
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique for counting and examining microscopic particles, such as cells and chromosomes, by suspending them in a stream of fluid and passing them by an electronic detection apparatus. It allows simultaneous multiparametric analysis of the physical and/or chemical...
has shown that the KB stain, like the more advanced methods, is sensitive in its detection of FMH. Background counting errors can result in estimates of as much as 5 ml
Litre
pic|200px|right|thumb|One litre is equivalent to this cubeEach side is 10 cm1 litre water = 1 kilogram water The litre is a metric system unit of volume equal to 1 cubic decimetre , to 1,000 cubic centimetres , and to 1/1,000 cubic metre...
fetal blood loss when there actually is no such blood loss, but standard methods available in most laboratories
Laboratory
A laboratory is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories...
admit an extremely low probability of the return of a false positive when more severe FMH has taken place.
Fetal-maternal hemorrhage severity estimation
To determine if a positive test for FMH should be considered as the likely cause of fetal deathDeath
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
, the percent of total fetal blood volume lost should be calculated, making appropriate adjustments based on the following known relationships:
-
- the size of a fetal red blood cell is 1.22 times that of an adult red blood cell;
- the KB stain is known to have a meanMeanIn statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
success rate of 92% in detecting fetal red blood cells; - in a woman at or near term in her pregnancy, the mean volume of maternal red blood cells is approximately 1800 ml;
- the mean fetal hematocritHematocritThe hematocrit or packed cell volume or erythrocyte volume fraction is the percentage of the concentration of red blood cells in blood. It is normally about 45% for men and 40% for women...
is 50%; and - at stillbirthStillbirthA stillbirth occurs when a fetus has died in the uterus. The Australian definition specifies that fetal death is termed a stillbirth after 20 weeks gestation or the fetus weighs more than . Once the fetus has died the mother still has contractions and remains undelivered. The term is often used in...
, the mean fetal blood volume is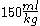
These constraint
Constraint (mathematics)
In mathematics, a constraint is a condition that a solution to an optimization problem must satisfy. There are two types of constraints: equality constraints and inequality constraints...
s can then be applied to yield the formula
Formula
In mathematics, a formula is an entity constructed using the symbols and formation rules of a given logical language....
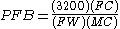
where
-
-
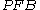 is the percentage of fetal blood lost;
is the percentage of fetal blood lost; -
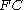 is the observed number of fetal red blood cells;
is the observed number of fetal red blood cells; -
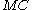 is the observed number of maternal red blood cells (N.B. we have that
is the observed number of maternal red blood cells (N.B. we have that 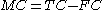 , where
, where 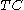 is the total observed number of red blood cells, both maternal and fetal);
is the total observed number of red blood cells, both maternal and fetal); -
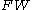 is the stillbirth weight of the fetus in kilograms.
is the stillbirth weight of the fetus in kilograms.
-
Stillbirth resolution
Suppose that a KB stain is performed and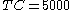 total red blood cells are observed,
total red blood cells are observed, 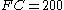 of which are found to be fetal red blood cells. Suppose further that the stillbirth weight of the fetus under consideration is
of which are found to be fetal red blood cells. Suppose further that the stillbirth weight of the fetus under consideration is 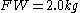 . Then we would conclude that the total percentage of fetal blood lost is approximately
. Then we would conclude that the total percentage of fetal blood lost is approximately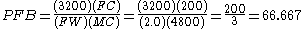
to five significant digits. We would hence conclude that the fetus under consideration lost 66.667% (two thirds) of its blood via FMH. Generally, stillbirth is highly probable for any value of
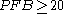 , particularly if the fetus abruptly loses this much blood; in this example, we would hence be likely to suspect FMH as the cause of the stillbirth. It is important to note, however, that such a diagnosis
, particularly if the fetus abruptly loses this much blood; in this example, we would hence be likely to suspect FMH as the cause of the stillbirth. It is important to note, however, that such a diagnosisDiagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of anything. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines with variations in the use of logics, analytics, and experience to determine the cause and effect relationships...
is still not completely conclusive; fetuses losing large quantities of blood over long periods of time are able to compensate for this slower blood loss; since the KB stain tells us nothing with regard to the level of acuity of FMH. This means that it is not possible to entirely correlate a positive KB stain and high
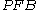 with a stillbirth, though in many cases, given other information, such as known hereditary complication
with a stillbirth, though in many cases, given other information, such as known hereditary complicationComplication (medicine)
Complication, in medicine, is an unfavorable evolution of a disease, a health condition or a medical treatment. The disease can become worse in its severity or show a higher number of signs, symptoms or new pathological changes, become widespread throughout the body or affect other organ systems. A...
s of pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
, extremely high positive correlation coefficients
Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient is a measure of the correlation between two variables X and Y, giving a value between +1 and −1 inclusive...
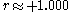 between FMH and stillbirth have been observed.
between FMH and stillbirth have been observed.Fetal red blood cell detection problems
Since fetal and maternal blood cellBlood cell
A blood cell, also called a hematocyte, is a cell normally found in blood. In mammals, these fall into three general categories:* red blood cells — Erythrocytes* white blood cells — Leukocytes* platelets — Thrombocytes...
s have the same life expectancy
Life expectancy
Life expectancy is the expected number of years of life remaining at a given age. It is denoted by ex, which means the average number of subsequent years of life for someone now aged x, according to a particular mortality experience...
in the maternal bloodstream, it is possible to obtain informative results from a KB stain for a fair period of time after a stillbirth. However, if the mother and fetus are ABO
Blood type
A blood type is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells . These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system...
incompatible, it is more crucial to quickly perform the KB stain following a stillbirth, as the fetal red blood cells will be eliminated from the maternal bloodstream very quickly, causing the KB stain to underestimate the degree of FMH, if any.
Lots of concern has been raised in the literature concerning false positives when sampling is done after delivery. In general this is not a problem. Delivery does result in higher frequency of detection of micro-hemorrhages but this should not confound interpretation of FMH as a possible cause of stillbirth. It is not necessary to draw the sample before induction, onset of labor, delivery, placental delivery etc. despite what some published literature purports. However, if caesarean section is to be used, failure to draw the sample prior to that will result in a 2% false positive rate.
Finally, anything which causes persistence of fetal hemoglobin in maternal blood cells will make interpretation much trickier. Certain hemoglobinopathies
Hemoglobinopathy
Hemoglobinopathy is a kind of genetic defect that results in abnormal structure of one of the globin chains of the hemoglobin molecule. Hemoglobinopathies are inherited single-gene disorders; in most cases, they are inherited as autosomal co-dominant traits. Common hemoglobinopathies include...
, the most common of which is sickle cell trait, do this. Overall, somewhere around 1-3% of the time this could result in false interpretation.

