Iodoform
Encyclopedia
Iodoform is the organoiodine compound
with the formula
C
H
I
3. A pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, it has a penetrating odor (in older chemistry texts, the smell is sometimes referred to as the smell of hospitals) and, analogous to chloroform
, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant. It is sometimes also referred to as carbon triiodide (which is not strictly correct, as this compound also contains hydrogen
) or methyl triiodide (which is somewhat ambiguous as that name could also refer to the methylated triiodide
ion, CH3I3).
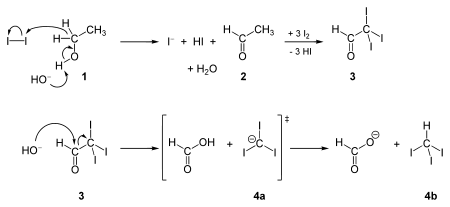
in 1834. It is synthesized in the haloform reaction
by the reaction of iodine and sodium hydroxide with any one of these four kinds of organic compounds: (i) a methyl ketone
: CH3COR, acetaldehyde
(CH3CHO), ethanol
(CH3CH2OH), and certain secondary alcohol
s (CH3CHROH, where R is an alkyl or aryl group).
The reaction of iodine and base with methyl ketones is so reliable, that the "iodoform test" (the appearance of a yellow precipitate) is used to probe the presence of a methyl ketone. This is also the case when testing for secondary alcohols (methyl alcohols).
Some reagents (e.g. Hydrogen iodide
) convert iodoform to diiodomethane
. Also conversion to carbon dioxide
is possible: Iodoform reacts with aqueous silver nitrate
to produce carbon monoxide
, which is oxidized by mixture of sulfuric acid
and iodine pentaoxide. When treated with powdered elemental silver the iodoform is reduced, producing acetylene
. Upon heating iodoform decomposes to produce diatomic iodine, hydrogen iodide gas, and carbon.
s. Adolf Hitler
's mother, Klara Hitler
, died of iodoform poisoning brought on by her treatment for breast cancer
. It is the active ingredient in many ear powders for dog
s and cat
s, to prevent infection and facilitate removal of ear hair, along with zinc oxide
and propanoic acid.
Organoiodine compound
Organoiodine compounds are organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–iodine bonds. They occur widely in organic chemistry, but are relatively rare in nature...
with the formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
I
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor....
3. A pale yellow, crystalline, volatile substance, it has a penetrating odor (in older chemistry texts, the smell is sometimes referred to as the smell of hospitals) and, analogous to chloroform
Chloroform
Chloroform is an organic compound with formula CHCl3. It is one of the four chloromethanes. The colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid is a trihalomethane, and is considered somewhat hazardous...
, sweetish taste. It is occasionally used as a disinfectant. It is sometimes also referred to as carbon triiodide (which is not strictly correct, as this compound also contains hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
) or methyl triiodide (which is somewhat ambiguous as that name could also refer to the methylated triiodide
Triiodide
In chemistry, triiodide can have several meanings. Triiodide primarily refers to the triiodide ion, I3−, a polyatomic anion composed of three iodine atoms. For some chemical compounds, triiodide indicates a salt of the named cation with the triiodide anion. Examples include sodium triiodide, ...
ion, CH3I3).
Synthesis and reactions
Iodoform was first prepared by Georges Serrulas in 1822 and its molecular formula was identified by Jean-Baptiste DumasJean-Baptiste Dumas
Jean Baptiste André Dumas was a French chemist, best known for his works on organic analysis and synthesis, as well as the determination of atomic weights and molecular weights by measuring vapor densities...
in 1834. It is synthesized in the haloform reaction
Haloform reaction
The haloform reaction is a chemical reaction where a haloform is produced by the exhaustive halogenation of a methyl ketone in the presence of a base. R may be , alkyl or aryl...
by the reaction of iodine and sodium hydroxide with any one of these four kinds of organic compounds: (i) a methyl ketone
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure RCR', where R and R' can be a variety of atoms and groups of atoms. It features a carbonyl group bonded to two other carbon atoms. Many ketones are known and many are of great importance in industry and in biology...
: CH3COR, acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO or MeCHO. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale industrially. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants as part...
(CH3CHO), ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
(CH3CH2OH), and certain secondary alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
s (CH3CHROH, where R is an alkyl or aryl group).
The reaction of iodine and base with methyl ketones is so reliable, that the "iodoform test" (the appearance of a yellow precipitate) is used to probe the presence of a methyl ketone. This is also the case when testing for secondary alcohols (methyl alcohols).
Some reagents (e.g. Hydrogen iodide
Hydrogen iodide
Hydrogen iodide is a diatomic molecule. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as iohydroic acid or hydroiodic acid, a strong acid. Gas and aqueous solution are interconvertible...
) convert iodoform to diiodomethane
Diiodomethane
Diiodomethane or methylene iodide, commonly abbreviated "MI", is a liquid organoiodine compound. It is insoluble in water, but soluble in ether and alcohol. It has a relatively high refractive index of 1.741, and a surface tension of 0.0508 N·m−1...
. Also conversion to carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
is possible: Iodoform reacts with aqueous silver nitrate
Silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . This compound is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides...
to produce carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
, which is oxidized by mixture of sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
and iodine pentaoxide. When treated with powdered elemental silver the iodoform is reduced, producing acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
. Upon heating iodoform decomposes to produce diatomic iodine, hydrogen iodide gas, and carbon.
Applications
The compound finds small scale use as a disinfectant. Around the beginning of the 20th century it was used in medicine as a healing and antiseptic dressing for wounds and sores, although this use is now superseded by superior antisepticAntiseptic
Antiseptics are antimicrobial substances that are applied to living tissue/skin to reduce the possibility of infection, sepsis, or putrefaction...
s. Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
's mother, Klara Hitler
Klara Hitler
Klara Hitler née Pölzl was an Austrian woman, the wife of Alois Hitler and the mother of Adolf Hitler.-Family background and marriage:...
, died of iodoform poisoning brought on by her treatment for breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
. It is the active ingredient in many ear powders for dog
Dog
The domestic dog is a domesticated form of the gray wolf, a member of the Canidae family of the order Carnivora. The term is used for both feral and pet varieties. The dog may have been the first animal to be domesticated, and has been the most widely kept working, hunting, and companion animal in...
s and cat
Cat
The cat , also known as the domestic cat or housecat to distinguish it from other felids and felines, is a small, usually furry, domesticated, carnivorous mammal that is valued by humans for its companionship and for its ability to hunt vermin and household pests...
s, to prevent infection and facilitate removal of ear hair, along with zinc oxide
Zinc oxide
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula ZnO. It is a white powder that is insoluble in water. The powder is widely used as an additive into numerous materials and products including plastics, ceramics, glass, cement, rubber , lubricants, paints, ointments, adhesives, sealants,...
and propanoic acid.