Information design
Encyclopedia

From graphic design
Information design began as a subset of, or synonym for, graphic designGraphic design
Graphic design is a creative process – most often involving a client and a designer and usually completed in conjunction with producers of form – undertaken in order to convey a specific message to a targeted audience...
and is often taught as part of graphic design courses. One of the first uses of the term was by the London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
graphic design consultancy Pentagram
Pentagram (design studio)
Pentagram is a design studio that was founded in 1972 by Alan Fletcher, Theo Crosby, Colin Forbes, Kenneth Grange and Mervyn Kurlansky in Needham Road, West London, UK...
, who used the term in the 1970s to mean their graphic design, as distinct from product or other kinds of design. Since then, the term has come to be used specifically for graphic design for displaying information effectively, rather than just attractively or for artistic expression.
The term 'information design' emerged as a multidisciplinary area of study in the 1970s. Some graphic designers started to use the term, and it was consolidated with the publication of the Information Design Journal in 1979.
Proceedings of other multidisciplinary conferences include Easterby & Zwaga (1984) and Duffy & Waller (1985). Schriver (1997) has a good history of the emergence of information design.
During the 1980s, the role of graphic information design broadened to include responsibility for message content and language. This required more user-testing and research for those elements than is common in mainstream graphic design.
From statistics and technology
During the 1970s, Edward TufteEdward Tufte
Edward Rolf Tufte is an American statistician and professor emeritus of political science, statistics, and computer science at Yale University. He is noted for his writings on information design and as a pioneer in the field of data visualization....
developed a course on statistical graphics, which he further developed in joint seminars with John Tukey
John Tukey
John Wilder Tukey ForMemRS was an American statistician.- Biography :Tukey was born in New Bedford, Massachusetts in 1915, and obtained a B.A. in 1936 and M.Sc. in 1937, in chemistry, from Brown University, before moving to Princeton University where he received a Ph.D...
, a pioneer in the field of information design. The course materials became the foundation for his first book on information design, The Visual Display of Quantitative Information, which he self-published in 1982. The book was called striking, beautiful, and ground-breaking. It raised non-professionals' awareness of the issues and possibilities of presenting information.
The term information graphics
Information graphics
Information graphics or infographics are graphic visual representations of information, data or knowledge. These graphics present complex information quickly and clearly, such as in signs, maps, journalism, technical writing, and education...
tends to be used by those primarily concerned with diagramming and display of quantitative information.
Information designers with roots in professional writing
Professional writing
Professional writing involves the use of clear language to convey information in a way that is easily understood by the intended audience. Individuals who can use language well may be employed as full-time professional writers in a variety of communications-related occupations, such as journalist,...
sometimes refer to the field as 'document design', particularly in the USA.
In technical communication
Technical communication
Technical communication is a method of researching and creating information about technical processes or products directed to an audience through media. The information must be relevant to the intended audience. Technical communicators often work collaboratively to create products for various...
, information design refers to creating an information structure for a set of information aimed at specified audiences. It can be practiced on different scales.
- On a large scale, it implies choosing relevant content and dividing it into separate manuals by audience and purpose.
- On a medium scale, it means organizing the content in each manual and making sure that overviews, concepts, examples, references, and definitions are included and that topics follow an organizing principle.
- On a fine scale, it includes logical development of topics, emphasis on what's important, clear writing, navigational clues, and even page design, choice of font, and use of white space.
Similar skills are brought to bear in designing web sites, with additional constraints and functions that earn a designer the title information architect.
In computer science
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
and information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
, 'information design' is sometimes a rough synonym for (but is not necessarily the same discipline as) information architecture
Information Architecture
Information architecture is the art of expressing a model or concept of information used in activities that require explicit details of complex systems. Among these activities are library systems, Content Management Systems, web development, user interactions, database development, programming,...
, the design of information system
Information system
An information system - or application landscape - is any combination of information technology and people's activities that support operations, management, and decision making. In a very broad sense, the term information system is frequently used to refer to the interaction between people,...
s, database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
s, or data structure
Data structure
In computer science, a data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.Different kinds of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks...
s. This sense includes data modeling
Data modeling
Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying formal data modeling techniques.- Overview :...
and process analysis
Process analysis
A form of technical writing and expository writing "designed to convey to the reader how a change takes place through a series of stages" .While the traditional process analysis and a set of instructions are both organized chronologically, the reader of a process analysis is typically interested...
.
History
Information design is associated with the age of technology but it does have historical roots. Early instances of modern information design include these effective examples:- John SnowJohn Snow (physician)John Snow was an English physician and a leader in the adoption of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered to be one of the fathers of epidemiology, because of his work in tracing the source of a cholera outbreak in Soho, England, in 1854.-Early life and education:Snow was born 15 March...
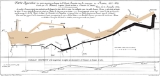
's spot maps, which pinpointed the source of a deadly cholera outbreak in 1850s London - Charles Joseph MinardCharles Joseph MinardCharles Joseph Minard was a French civil engineer noted for his inventions in the field of information graphics.- Biography :...
's 1861 diagram depicting Napoleon's Russian campaign of 1812 - Otto NeurathOtto NeurathOtto Neurath was an Austrian philosopher of science, sociologist, and political economist...
's International Picture LanguageIsotype (pictograms)Isotype is a method of showing social, technological, biological and historical connections in pictorial form...
of the 1930s - Florence NightingaleFlorence NightingaleFlorence Nightingale OM, RRC was a celebrated English nurse, writer and statistician. She came to prominence for her pioneering work in nursing during the Crimean War, where she tended to wounded soldiers. She was dubbed "The Lady with the Lamp" after her habit of making rounds at night...
's information graphic depicting army mortality rates
Audiences
Information designers may cater to very broad audiences: for example, public signs in airports are for everybody. Or they may cater to very specific ones: information products such as telephone bills may be personalized for individual customers using market segmentation and information managementInformation management
Information management is the collection and management of information from one or more sources and the distribution of that information to one or more audiences. This sometimes involves those who have a stake in, or a right to that information...
techniques and technologies similar to those used in direct marketing
Direct marketing
Direct marketing is a channel-agnostic form of advertising that allows businesses and nonprofits to communicate straight to the customer, with advertising techniques such as mobile messaging, email, interactive consumer websites, online display ads, fliers, catalog distribution, promotional...
.
Information design projects often seek to create or reinforce trust in users of design products. Examples of such products are medicine packaging inserts, operational instructions for industrial machinery, and information for emergencies. If it's important for the instructions to be carried out, readers must understand, trust, and be motivated by the products. In other words, the audience needs to rely on the information conveyed. The designers must get the message across in ways that reach the audience.
This gives information designers unusual power over their audiences compared to other designers, and "with great power comes great responsibility". The increased responsibility means information designers require accountability, and this is developed through user testing
Usability testing
Usability testing is a technique used in user-centered interaction design to evaluate a product by testing it on users. This can be seen as an irreplaceable usability practice, since it gives direct input on how real users use the system...
of design artifacts.
The power relationship between information designers and their clients is also different from that between graphic designers and their clients. Information designers seek to serve the interests of their clients' audiences as well as those of their clients, and they often advocate for the audience over the client.
Competencies
Information design draws on a wide range of competencies that are seldom possessed by a single person. For this reason, information designers tend to work on information products in teams that include specialists and other information designers.In the United States, the title of information designer is sometimes used by graphic designers who specialize in creating websites. The skill set of the information designer, as the title is applied more globally, is closer to that of the information architect
Information Architecture
Information architecture is the art of expressing a model or concept of information used in activities that require explicit details of complex systems. Among these activities are library systems, Content Management Systems, web development, user interactions, database development, programming,...
in the U.S.
This list is indicative rather than prescriptive or fully descriptive.
Research:
- Using, commissioning, co-ordinating and understanding research. All design involves research as an initial stage
- Information design research is likely to involve some or all of
- Business process investigation and analysis
- Qualitative and quantitative user research
- Reference to existing academic research (e.g., ergonomics, cognitive and perceptual psychology)
- Craft knowledge: what has been tried before
Transformation:
- Using words, diagrams, type, and sequencing to restructure messages so that they tell a story more effectively
Writing for clear communication:
- Writing or editing to make messages clear, unambiguous and understandable by their intended audience(s)
Graphic and typographic design:
- Designing the appearance of an information product so that users can find what they want and understand it when they get there
Information visualization:
- Creating graphic displays that turn data into lucid information
Prototyping:
- Making preliminary visualizations, models, and prototypes that facilitate discussion and useful testing
Testing:
- Understanding a range of techniques for testing prototypes and finished information products with their intended audiences. There is a wide range of techniques, which vary according to the medium used and the intended process and audience(s). Designers must select and manage suitable methods for each project.
Co-ordination:
- The ability to work well with a range of specialties and yet to act as 'professional amateur' in such teams, representing the user
Accessibility:
- Understanding what accessibility means for an intended audience
- The ability to assess risk realistically. Information design is actually all about accessibility in the wider sense.
Specification:
- Understanding chosen production media and processes
- The ability to specify to production specialists in a wide range of industries (print, video, software, web, product manufacturers) clearly and efficiently
Typical applications and contexts
Information design affects to a wide range of applications and document genres, including financial information, administrative documents such as forms, medical and pharmaceutical information, food and health information, user guides, technical manuals, travel information, and wayfinding information.Governments and regulatory authorities have legislated about a number of information design issues, such as the minimum size of font in financial small print, the labeling of ingredients in processed food, and the testing of medicine labeling. Examples of this are the Truth in Lending Act
Truth in Lending Act
The Truth in Lending Act of 1968 is United States federal law designed to promote the informed use of consumer credit, by requiring disclosures about its terms and cost to standardize the manner in which costs associated with borrowing are calculated and disclosed...
in the USA, which introduced the Schumer box (a concise summary of charges for people applying for a credit card), and the Guideline on the Readability of the Label and Package Leaflet of Medicinal Products for Human Use (European Commission September 1998).
See also
- CartographyCartographyCartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
- Content managementContent managementContent management, or CM, is the set of processes and technologies that support the collection, managing, and publishing of information in any form or medium. In recent times this information is typically referred to as content or, to be precise, digital content...
- EpidemiologyEpidemiologyEpidemiology is the study of health-event, health-characteristic, or health-determinant patterns in a population. It is the cornerstone method of public health research, and helps inform policy decisions and evidence-based medicine by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive...
- Graphic designGraphic designGraphic design is a creative process – most often involving a client and a designer and usually completed in conjunction with producers of form – undertaken in order to convey a specific message to a targeted audience...
- Information architectureInformation ArchitectureInformation architecture is the art of expressing a model or concept of information used in activities that require explicit details of complex systems. Among these activities are library systems, Content Management Systems, web development, user interactions, database development, programming,...
- Knowledge visualization
- New Epoch Notation Painting
- Plain languagePlain languagePlain language is clear, succinct writing designed to ensure the reader understands as quickly and completely as possible.Plain language strives to be easy to read, understand, and use. It avoids verbose, convoluted language and jargon...
- SignageSignageSignage is any kind of visual graphics created to display information to a particular audience. This is typically manifested in the form of wayfinding information in places such as streets or inside/outside of buildings.-History:...
- StatisticsStatisticsStatistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
- Technical communicationTechnical communicationTechnical communication is a method of researching and creating information about technical processes or products directed to an audience through media. The information must be relevant to the intended audience. Technical communicators often work collaboratively to create products for various...
- Technical illustrationTechnical illustrationTechnical Illustration is the use of illustration to visually communicate information of a technical nature. Technical illustrations can be components of technical drawings or diagrams...
- TypographyTypographyTypography is the art and technique of arranging type in order to make language visible. The arrangement of type involves the selection of typefaces, point size, line length, leading , adjusting the spaces between groups of letters and adjusting the space between pairs of letters...
- Visual literacyVisual literacyVisual literacy is the ability to interpret, negotiate, and make meaning from information presented in the form of an image. Visual literacy is based on the idea that pictures can be “read” and that meaning can be communicated through a process of reading....
- WayfindingWayfindingWayfinding encompasses all of the ways in which people and animals orient themselves in physical space and navigate from place to place.-Historical:...
- Web indexingWeb indexingWeb indexing includes back-of-book-style indexes to individual websites or an intranet, and the creation of keyword metadata to provide a more useful vocabulary for Internet or onsite search engines...
External links
- InformationDesign.org
- International Institute for Information Design
- Communication Research Institute of Australia: Information Design for the Information Age
- Information Design Journal
- UK Information Design Association
- Society for Technical Communication Information Design – Information Architecture (ID–IA) Special Interest Group (SIG)
- Visualizing Information for Advocacy: An Introduction to Information Design Booklet on information design for non-profit and non-governmental organizations.

