
Data modeling
Encyclopedia
Data modeling in software engineering
is the process of creating a data model
for an information system
by applying formal data modeling techniques.
used to define and analyze data requirement
s needed to support the business process
es within the scope of corresponding information systems in organizations. Therefore, the process of data modeling involves professional data modelers working closely with business stakeholders, as well as potential users of the information system. There are three different types of data models produced while progressing from requirements to the actual database to be used for the information system. The data requirements are initially recorded as a conceptual data model
which is essentially a set of technology independent specifications about the data and is used to discuss initial requirements with the business stakeholders. The conceptual model is then translated into a logical data model
, which documents structures of the data that can be implemented in databases. To implement one conceptual data model may require multiple logical data models. The last step in data modeling is transforming the logical data model to a physical data model
that organizes the data into tables, and accounts for access, performance and storage details. Data modeling defines not just data elements, but their structures and relationships between them. Data modeling techniques and methodologies are used to model data in a standard, consistent, predictable manner in order to manage it as a resource. The use of data modeling standards is strongly recommended for all projects requiring a standard means of defining and analyzing data within an organization, e.g., using data modeling:
Data modeling may be performed during various types of projects and in multiple phases of projects. Data models are progressive; there is no such thing as the final data model for a business or application. Instead a data model should be considered a living document that will change in response to a changing business. The data models should ideally be stored in a repository so that they can be retrieved, expanded, and edited over time. Whitten (2004) determined two types of data modeling:
Data modeling is also used as a technique for detailing business requirement
s for specific database
s. It is sometimes called database modeling because a data model
is eventually implemented in a database.
s provide a structure for data
used within information system
s by providing specific definition and format. If a data model is used consistently across systems then compatibility of data can be achieved. If the same data structures are used to store and access data then different applications can share data seamlessly. The results of this are indicated in the diagram. However, systems and interfaces often cost more than they should, to build, operate, and maintain. They may also constrain the business rather than support it. This may occur when the quality of the data models implemented in systems and interfaces is poor.
described three kinds of data-model instance:
According to ANSI, this approach allows the three perspectives to be relatively independent of each other. Storage technology can change without affecting either the logical or the conceptual schema. The table/column structure can change without (necessarily) affecting the conceptual schema. In each case, of course, the structures must remain consistent across all schemas of the same data model.
, and ultimately results in database generation.
The process of designing a database involves producing the previously described three types of schemas - conceptual, logical, and physical. The database design documented in these schemas are converted through a Data Definition Language
, which can then be used to generate a database. A fully attributed data model contains detailed attributes (descriptions) for every entity within it. The term "database design" can describe many different parts of the design of an overall database system
. Principally, and most correctly, it can be thought of as the logical design of the base data structures used to store the data. In the relational model
these are the tables
and views
. In an object database
the entities and relationships map directly to object classes and named relationships. However, the term "database design" could also be used to apply to the overall process of designing, not just the base data structures, but also the forms and queries used as part of the overall database application within the Database Management System
or DBMS.
In the process, system interface
s account for 25% to 70% of the development and support costs of current systems. The primary reason for this cost is that these systems do not share a common data model. If data models are developed on a system by system basis, then not only is the same analysis repeated in overlapping areas, but further analysis must be performed to create the interfaces between them. Most systems within an organization contain the same basic data, redeveloped for a specific purpose. Therefore, an efficiently designed basic data model can minimize rework with minimal modifications for the purposes of different systems within the organization
s represent information areas of interest. While there are many ways to create data models, according to Len Silverston (1997) only two modeling methodologies stand out, top-down and bottom-up:
Sometimes models are created in a mixture of the two methods: by considering the data needs and structure of an application and by consistently referencing a subject-area model. Unfortunately, in many environments the distinction between a logical data model and a physical data model is blurred. In addition, some CASE
tools don’t make a distinction between logical and physical data model
s.
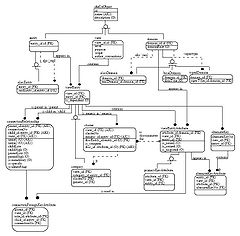 There are several notations for data modeling. The actual model is frequently called "Entity relationship model", because it depicts data in terms of the entities and relationships described in the data
There are several notations for data modeling. The actual model is frequently called "Entity relationship model", because it depicts data in terms of the entities and relationships described in the data
. An entity-relationship model (ERM) is an abstract conceptual representation of structured data. Entity-relationship modeling is a relational schema database model
ing method, used in software engineering
to produce a type of conceptual data model
(or semantic data model
) of a system, often a relational database
, and its requirements in a top-down fashion.
These models are being used in the first stage of information system
design during the requirements analysis
to describe information needs or the type of information
that is to be stored in a database
. The data model
ing technique can be used to describe any ontology
(i.e. an overview and classifications of used terms and their relationships) for a certain universe of discourse
i.e. area of interest.
Several techniques have been developed for the design of data models. While these methodologies guide data modelers in their work, two different people using the same methodology will often come up with very different results. Most notable are:
 Generic data model
Generic data model
s are generalizations of conventional data model
s. They define standardized general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type.
The definition of generic data model is similar to the definition of a natural language. For example, a generic data model may define relation types such as a 'classification relation', being a binary relation
between an individual thing and a kind of thing (a class) and a 'part-whole relation', being a binary relation between two things, one with the role of part, the other with the role of whole, regardless the kind of things that are related.
Given an extensible list of classes, this allows the classification of any individual thing and to specify part-whole relations for any individual object. By standardization of an extensible list of relation types, a generic data model enables the expression of an unlimited number of kinds of facts and will approach the capabilities of natural languages. Conventional data models, on the other hand, have a fixed and limited domain scope, because the instantiation (usage) of such a model only allows expressions of kinds of facts that are predefined in the model.
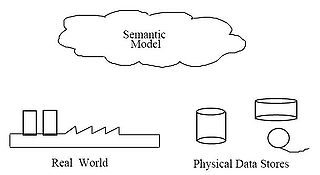 Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data model
Therefore, the need to define data from a conceptual view has led to the development of semantic data model
ing techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure the real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., are symbolically defined within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an abstraction
which defines how the stored symbols relate to the real world. Thus, the model must be a true representation of the real world.
A semantic data model can be used to serve many purposes, such as:.
The overall goal of semantic data models is to capture more meaning of data by integrating relational concepts with more powerful abstraction
concepts known from the Artificial Intelligence
field. The idea is to provide high level modeling primitives as integral part of a data model in order to facilitate the representation of real world situations.
Software engineering
Software Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
is the process of creating a data model
Data model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
for an information system
Information system
An information system - or application landscape - is any combination of information technology and people's activities that support operations, management, and decision making. In a very broad sense, the term information system is frequently used to refer to the interaction between people,...
by applying formal data modeling techniques.
Overview
Data modeling is a processSoftware development process
A software development process, also known as a software development life cycle , is a structure imposed on the development of a software product. Similar terms include software life cycle and software process. It is often considered a subset of systems development life cycle...
used to define and analyze data requirement
Requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s needed to support the business process
Business process
A business process or business method is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks that produce a specific service or product for a particular customer or customers...
es within the scope of corresponding information systems in organizations. Therefore, the process of data modeling involves professional data modelers working closely with business stakeholders, as well as potential users of the information system. There are three different types of data models produced while progressing from requirements to the actual database to be used for the information system. The data requirements are initially recorded as a conceptual data model
Conceptual schema
A conceptual schema or conceptual data model is a map of concepts and their relationships. This describes the semantics of an organization and represents a series of assertions about its nature...
which is essentially a set of technology independent specifications about the data and is used to discuss initial requirements with the business stakeholders. The conceptual model is then translated into a logical data model
Logical data model
A logical data model in systems engineering is a representation of an organization's data, organized in terms of entities and relationships and is independent of any particular data management technology.- Overview :...
, which documents structures of the data that can be implemented in databases. To implement one conceptual data model may require multiple logical data models. The last step in data modeling is transforming the logical data model to a physical data model
Physical data model
A physical data model is a representation of a data design which takes into account the facilities and constraints of a given database management system. In the lifecycle of a project it is typically derived from a logical data model, though it may be reverse-engineered from a given database...
that organizes the data into tables, and accounts for access, performance and storage details. Data modeling defines not just data elements, but their structures and relationships between them. Data modeling techniques and methodologies are used to model data in a standard, consistent, predictable manner in order to manage it as a resource. The use of data modeling standards is strongly recommended for all projects requiring a standard means of defining and analyzing data within an organization, e.g., using data modeling:
- to manage data as a resource;
- for the integration of information systems;
- for designing databases/data warehouses (aka data repositories)
Data modeling may be performed during various types of projects and in multiple phases of projects. Data models are progressive; there is no such thing as the final data model for a business or application. Instead a data model should be considered a living document that will change in response to a changing business. The data models should ideally be stored in a repository so that they can be retrieved, expanded, and edited over time. Whitten (2004) determined two types of data modeling:
- Strategic data modeling: This is part of the creation of an information systems strategy, which defines an overall vision and architecture for information systems is defined. Information engineeringInformation engineeringInformation engineering or information engineering methodology in software engineering is an approach to designing and developing information systems.-Overview:...
is a methodology that embraces this approach. - Data modeling during systems analysis: In systems analysisSystems analysisSystems analysis is the study of sets of interacting entities, including computer systems analysis. This field is closely related to requirements analysis or operations research...
logical data models are created as part of the development of new databases.
Data modeling is also used as a technique for detailing business requirement
Requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s for specific database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
s. It is sometimes called database modeling because a data model
Data model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
is eventually implemented in a database.
Data models
Data modelData model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
s provide a structure for data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
used within information system
Information system
An information system - or application landscape - is any combination of information technology and people's activities that support operations, management, and decision making. In a very broad sense, the term information system is frequently used to refer to the interaction between people,...
s by providing specific definition and format. If a data model is used consistently across systems then compatibility of data can be achieved. If the same data structures are used to store and access data then different applications can share data seamlessly. The results of this are indicated in the diagram. However, systems and interfaces often cost more than they should, to build, operate, and maintain. They may also constrain the business rather than support it. This may occur when the quality of the data models implemented in systems and interfaces is poor.
- Business rules, specific to how things are done in a particular place, are often fixed in the structure of a data model. This means that small changes in the way business is conducted lead to large changes in computer systems and interfaces. So, business rules need to be implemented in a flexible way that does not result in complicated dependencies, rather the data model should be flexible enough so that changes in the business can be implemented within the data model in a relatively quick and efficient way.
- Entity types are often not identified, or are identified incorrectly. This can lead to replication of data, data structure and functionality, together with the attendant costs of that duplication in development and maintenance.Therefore, data definitions should be made as explicit and easy to understand as possible to minimize misinterpretation and duplication.
- Data models for different systems are arbitrarily different. The result of this is that complex interfaces are required between systems that share data. These interfaces can account for between 25-70% of the cost of current systems. Required interfaces should be considered inherently while designing a data model, as a data model on its own would not be usable without interfaces within different systems.
- Data cannot be shared electronically with customers and suppliers, because the structure and meaning of data has not been standardised. To obtain optimal value from an implemented data model, it is very important to define standards that will ensure that data models will both meet business needs and be consistent.
Conceptual, logical and physical schemas
In 1975 ANSIAmerican National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international...
described three kinds of data-model instance:
- Conceptual schemaConceptual schemaA conceptual schema or conceptual data model is a map of concepts and their relationships. This describes the semantics of an organization and represents a series of assertions about its nature...
: describes the semantics of a domain (the scope of the model). For example, it may be a model of the interest area of an organization or of an industry. This consists of entity classes, representing kinds of things of significance in the domain, and relationships assertions about associations between pairs of entity classes. A conceptual schema specifies the kinds of facts or propositions that can be expressed using the model. In that sense, it defines the allowed expressions in an artificial "language" with a scope that is limited by the scope of the model. Simply described, a conceptual schema is the first step in organizing the data requirements.
- Logical schemaLogical schemaA Logical Schema is a data model of a specific problem domain expressed in terms of a particular data management technology. Without being specific to a particular database management product, it is in terms of either relational tables and columns, object-oriented classes, or XML tags...
: describes the structure of some domain of information. This consists of descriptions of (for example) tables, columns, object-oriented classes, and XML tags. The logical schema and conceptual schema are sometimes implemented as one and the same.
- Physical schemaPhysical schemaDescribes how data are to be represented and stored in secondary storage using a particular DBMS .Physical Schema is a term used in relation to data management....
: describes the physical means used to store data. This is concerned with partitions, CPUs, tablespaceTablespaceA tablespace is a storage location where the actual data underlying database objects can be kept. It provides a layer of abstraction between physical and logical data, and serves to allocate storage for all DBMS managed segments...
s, and the like.
According to ANSI, this approach allows the three perspectives to be relatively independent of each other. Storage technology can change without affecting either the logical or the conceptual schema. The table/column structure can change without (necessarily) affecting the conceptual schema. In each case, of course, the structures must remain consistent across all schemas of the same data model.
Data modeling process
In the context of business process integration (see figure), data modeling complements business process modelingBusiness process modeling
Business Process Modeling in systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current process may be analyzed and improved. BPM is typically performed by business analysts and managers who are seeking to improve process efficiency and quality...
, and ultimately results in database generation.
The process of designing a database involves producing the previously described three types of schemas - conceptual, logical, and physical. The database design documented in these schemas are converted through a Data Definition Language
Data Definition Language
A data definition language or data description language is a syntax similar to a computer programming language for defining data structures, especially database schemas.-History:...
, which can then be used to generate a database. A fully attributed data model contains detailed attributes (descriptions) for every entity within it. The term "database design" can describe many different parts of the design of an overall database system
Database system
A database system is a term that is typically used to encapsulate the constructs of a data model, database Management system and database....
. Principally, and most correctly, it can be thought of as the logical design of the base data structures used to store the data. In the relational model
Relational model
The relational model for database management is a database model based on first-order predicate logic, first formulated and proposed in 1969 by Edgar F...
these are the tables
Table (database)
In relational databases and flat file databases, a table is a set of data elements that is organized using a model of vertical columns and horizontal rows. A table has a specified number of columns, but can have any number of rows...
and views
View (database)
In database theory, a view consists of a stored query accessible as a virtual table in a relational database or a set of documents in a document-oriented database composed of the result set of a query or map and reduce functions...
. In an object database
Object database
An object database is a database management system in which information is represented in the form of objects as used in object-oriented programming...
the entities and relationships map directly to object classes and named relationships. However, the term "database design" could also be used to apply to the overall process of designing, not just the base data structures, but also the forms and queries used as part of the overall database application within the Database Management System
Database management system
A database management system is a software package with computer programs that control the creation, maintenance, and use of a database. It allows organizations to conveniently develop databases for various applications by database administrators and other specialists. A database is an integrated...
or DBMS.
In the process, system interface
Interface (computer science)
In the field of computer science, an interface is a tool and concept that refers to a point of interaction between components, and is applicable at the level of both hardware and software...
s account for 25% to 70% of the development and support costs of current systems. The primary reason for this cost is that these systems do not share a common data model. If data models are developed on a system by system basis, then not only is the same analysis repeated in overlapping areas, but further analysis must be performed to create the interfaces between them. Most systems within an organization contain the same basic data, redeveloped for a specific purpose. Therefore, an efficiently designed basic data model can minimize rework with minimal modifications for the purposes of different systems within the organization
Modeling methodologies
Data modelData model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
s represent information areas of interest. While there are many ways to create data models, according to Len Silverston (1997) only two modeling methodologies stand out, top-down and bottom-up:
- Bottom-up models are often the result of a reengineeringReengineeringReengineering can refer to:* Trouble shooting* Business process reengineering* Reengineering * Reengineering * User reengineering...
effort. They usually start with existing data structures forms, fields on application screens, or reports. These models are usually physical, application-specific, and incomplete from an enterprise perspectiveEnterprise architectureAn enterprise architecture is a rigorous description of the structure of an enterprise, which comprises enterprise components , the externally visible properties of those components, and the relationships between them...
. They may not promote data sharing, especially if they are built without reference to other parts of the organization. - Top-down logical data modelLogical data modelA logical data model in systems engineering is a representation of an organization's data, organized in terms of entities and relationships and is independent of any particular data management technology.- Overview :...
s, on the other hand, are created in an abstract way by getting information from people who know the subject area. A system may not implement all the entities in a logical model, but the model serves as a reference point or template.
Sometimes models are created in a mixture of the two methods: by considering the data needs and structure of an application and by consistently referencing a subject-area model. Unfortunately, in many environments the distinction between a logical data model and a physical data model is blurred. In addition, some CASE
Computer-aided software engineering
Computer-aided software engineering is the scientific application of a set of tools and methods to a software system which is meant to result in high-quality, defect-free, and maintainable software products...
tools don’t make a distinction between logical and physical data model
Physical data model
A physical data model is a representation of a data design which takes into account the facilities and constraints of a given database management system. In the lifecycle of a project it is typically derived from a logical data model, though it may be reverse-engineered from a given database...
s.
Entity relationship diagrams

Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
. An entity-relationship model (ERM) is an abstract conceptual representation of structured data. Entity-relationship modeling is a relational schema database model
Database model
A database model is the theoretical foundation of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized, and manipulated in a database system. It thereby defines the infrastructure offered by a particular database system...
ing method, used in software engineering
Software engineering
Software Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
to produce a type of conceptual data model
Conceptual schema
A conceptual schema or conceptual data model is a map of concepts and their relationships. This describes the semantics of an organization and represents a series of assertions about its nature...
(or semantic data model
Semantic data model
A semantic data model in software engineering has various meanings:# It is a conceptual data model in which semantic information is included. This means that the model describes the meaning of its instances...
) of a system, often a relational database
Relational database
A relational database is a database that conforms to relational model theory. The software used in a relational database is called a relational database management system . Colloquial use of the term "relational database" may refer to the RDBMS software, or the relational database itself...
, and its requirements in a top-down fashion.
These models are being used in the first stage of information system
Information system
An information system - or application landscape - is any combination of information technology and people's activities that support operations, management, and decision making. In a very broad sense, the term information system is frequently used to refer to the interaction between people,...
design during the requirements analysis
Requirements analysis
Requirements analysis in systems engineering and software engineering, encompasses those tasks that go into determining the needs or conditions to meet for a new or altered product, taking account of the possibly conflicting requirements of the various stakeholders, such as beneficiaries or users...
to describe information needs or the type of information
Information
Information in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
that is to be stored in a database
Database
A database is an organized collection of data for one or more purposes, usually in digital form. The data are typically organized to model relevant aspects of reality , in a way that supports processes requiring this information...
. The data model
Data model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
ing technique can be used to describe any ontology
Ontology (computer science)
In computer science and information science, an ontology formally represents knowledge as a set of concepts within a domain, and the relationships between those concepts. It can be used to reason about the entities within that domain and may be used to describe the domain.In theory, an ontology is...
(i.e. an overview and classifications of used terms and their relationships) for a certain universe of discourse
Domain of discourse
In the formal sciences, the domain of discourse, also called the universe of discourse , is the set of entities over which certain variables of interest in some formal treatment may range...
i.e. area of interest.
Several techniques have been developed for the design of data models. While these methodologies guide data modelers in their work, two different people using the same methodology will often come up with very different results. Most notable are:
- Bachman diagramBachman diagramBachman diagrams are diagrams which are used to design the data using a network or relational "logical" model, separating the data model from the way the data is stored in the system. The model is named after database pioneer Charles Bachman, and mostly used in computer software design...
s - Barker's NotationBarker's NotationBarker's notation refers to the ERD notation developed by Richard Barker, Ian Palmer, Harry Ellis et al. whilst working at the British consulting firm CACI around 1981. The notation was adopted by Barker when he joined Oracle and is effectively defined in his book Entity Relationship Modelling as...
- Chen's NotationEntity-relationship modelIn software engineering, an entity-relationship model is an abstract and conceptual representation of data. Entity-relationship modeling is a database modeling method, used to produce a type of conceptual schema or semantic data model of a system, often a relational database, and its requirements...
- Data Vault ModelingData Vault ModelingData Vault Modeling is a database modeling method that is designed to provide historical storage of data coming in from multiple operational systems. It is also a method of looking at historical data that, apart from the modeling aspect, deals with issues such as auditing, tracing of data, loading...
- Extended Backus–Naur formExtended Backus–Naur formIn computer science, Extended Backus–Naur Form is a family of metasyntax notations used for expressing context-free grammars: that is, a formal way to describe computer programming languages and other formal languages. They are extensions of the basic Backus–Naur Form metasyntax notation.The...
- IDEF1XIDEF1XIDEF1X is a data modeling language for the developing of semantic data models. IDEF1X is used to produce a graphical information model which represents the structure and semantics of information within an environment or system.IDEF1X permits the construction of semantic data models which may serve...
- Object-relational mappingObject-relational mappingObject-relational mapping in computer software is a programming technique for converting data between incompatible type systems in object-oriented programming languages. This creates, in effect, a "virtual object database" that can be used from within the programming language...
- Object Role ModelingObject role modelingObject Role Modeling is a method for conceptual modeling, and can be used as a tool for information and rules analysis, ontological analysis, and data modeling in the field of software engineering.- Overview :...
- Relational ModelRelational modelThe relational model for database management is a database model based on first-order predicate logic, first formulated and proposed in 1969 by Edgar F...
Generic data modeling

Generic data model
Generic data models are generalizations of conventional data models. They define standardised general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type.- Overview :...
s are generalizations of conventional data model
Data model
A data model in software engineering is an abstract model, that documents and organizes the business data for communication between team members and is used as a plan for developing applications, specifically how data is stored and accessed....
s. They define standardized general relation types, together with the kinds of things that may be related by such a relation type.
The definition of generic data model is similar to the definition of a natural language. For example, a generic data model may define relation types such as a 'classification relation', being a binary relation
Binary relation
In mathematics, a binary relation on a set A is a collection of ordered pairs of elements of A. In other words, it is a subset of the Cartesian product A2 = . More generally, a binary relation between two sets A and B is a subset of...
between an individual thing and a kind of thing (a class) and a 'part-whole relation', being a binary relation between two things, one with the role of part, the other with the role of whole, regardless the kind of things that are related.
Given an extensible list of classes, this allows the classification of any individual thing and to specify part-whole relations for any individual object. By standardization of an extensible list of relation types, a generic data model enables the expression of an unlimited number of kinds of facts and will approach the capabilities of natural languages. Conventional data models, on the other hand, have a fixed and limited domain scope, because the instantiation (usage) of such a model only allows expressions of kinds of facts that are predefined in the model.
Semantic data modeling
The logical data structure of a DBMS, whether hierarchical, network, or relational, cannot totally satisfy the requirements for a conceptual definition of data because it is limited in scope and biased toward the implementation strategy employed by the DBMS.
Semantic data model
A semantic data model in software engineering has various meanings:# It is a conceptual data model in which semantic information is included. This means that the model describes the meaning of its instances...
ing techniques. That is, techniques to define the meaning of data within the context of its interrelationships with other data. As illustrated in the figure the real world, in terms of resources, ideas, events, etc., are symbolically defined within physical data stores. A semantic data model is an abstraction
Abstraction (computer science)
In computer science, abstraction is the process by which data and programs are defined with a representation similar to its pictorial meaning as rooted in the more complex realm of human life and language with their higher need of summarization and categorization , while hiding away the...
which defines how the stored symbols relate to the real world. Thus, the model must be a true representation of the real world.
A semantic data model can be used to serve many purposes, such as:.
- planning of data resources
- building of shareable databases
- evaluation of vendor software
- integration of existing databases
The overall goal of semantic data models is to capture more meaning of data by integrating relational concepts with more powerful abstraction
Abstraction (computer science)
In computer science, abstraction is the process by which data and programs are defined with a representation similar to its pictorial meaning as rooted in the more complex realm of human life and language with their higher need of summarization and categorization , while hiding away the...
concepts known from the Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the intelligence of machines and the branch of computer science that aims to create it. AI textbooks define the field as "the study and design of intelligent agents" where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its...
field. The idea is to provide high level modeling primitives as integral part of a data model in order to facilitate the representation of real world situations.
See also
- Architectural pattern (computer science)Architectural pattern (computer science)An architectural pattern in software is a standard design in the field of software architecture. The concept of a software architectural pattern has a broader scope than the concept of a software design pattern...
- Comparison of data modeling toolsComparison of data modeling toolsThis article is a comparison of data modeling tools which are notable, including standalone, conventional data modeling tools and modeling tools supporting data modeling as part of a larger modeling environment.- General :- Features :- See also :...
- Data (computing)Data (computing)In computer science, data is information in a form suitable for use with a computer. Data is often distinguished from programs. A program is a sequence of instructions that detail a task for the computer to perform...
- Data dictionaryData dictionaryA data dictionary, or metadata repository, as defined in the IBM Dictionary of Computing, is a "centralized repository of information about data such as meaning, relationships to other data, origin, usage, and format." The term may have one of several closely related meanings pertaining to...
- Document modelingDocument modellingDocument Modelling looks at the inherent structure in documents. It looks not at the structure in formatting which is the classic realm of word-processing tools, but at the structure in content. Because document content is typically viewed as the ad hoc result of a creative process, the art of...
- Information ManagementInformation managementInformation management is the collection and management of information from one or more sources and the distribution of that information to one or more audiences. This sometimes involves those who have a stake in, or a right to that information...
- Informative modelingInformative ModellingInformative modelling is an interdisciplinary methodological approachlinking information technologies with architectural analysis and modelling....
- Three schema approachThree schema approachThe three-schema approach, or the Three Schema Concept, in software engineering is an approach to building information systems and systems information management from the 1970s...
- Zachman FrameworkZachman frameworkThe Zachman Framework is an Enterprise Architecture framework for enterprise architecture, which provides a formal and highly structured way of viewing and defining an enterprise...
Further reading
- J.H. ter Bekke (1991). Semantic Data Modeling in Relational Environments
- John Vincent Carlis, Joseph D. Maguire (2001). Mastering Data Modeling: A User-driven Approach.
- Alan Chmura, J. Mark Heumann (2005). Logical Data Modeling: What it is and how to Do it.
- Martin E. Modell (1992). Data Analysis, Data Modeling, and Classification.
- M. Papazoglou, Stefano Spaccapietra, Zahir Tari (2000). Advances in Object-oriented Data Modeling.
- G. Lawrence Sanders (1995). Data Modeling
- Graeme C. Simsion, Graham C. Witt (2005). Data Modeling Essentials
- Graeme Simsion (2007). Data Modeling: Theory and Practice.
- Chris Bradley, Donna Burbank, Steve Hoberman (2009). Data Modeling for the Business: A Handbook for Aligning the Business with IT using High-Level Data Models
External links
- Agile/Evolutionary Data Modeling
- Data Modelling Dictionary
- Data modeling articles
- Database Modelling in UML
- Data Modeling 101
- Semantic data modeling
- System Development, Methodologies and Modeling Notes on by Tony Drewry
- Request For Proposal - Information Management Metamodel (IMM) of the Object Management Group
- Data Modeling is NOT just for DBMS's Part 1 Chris Bradley
- Data Modeling is NOT just for DBMS's Part 2 Chris Bradley

