
Graphic display resolutions
Encyclopedia
The graphics display resolution describes the width and height dimensions of a display, such as a computer monitor, in pixels. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism
that is descriptive of its dimensions. A higher display resolution means that displayed content appears sharper and smaller (depending on the physical size of the display).
The gradual change of the favored aspect ratio of mass market display industry products, from 4:3, then to 16:10, and then to 16:9, has made many of the display resolutions listed in this article difficult to obtain in mass market products. The 4:3 aspect ratio generally reflects older products, especially the era of the cathode ray tube (CRT). The 16:10 aspect ratio had its largest use in the 1995-2010 period, and the 16:9 aspect ratio tends to reflect the newest (post 2010) mass market computer monitor, laptop, and entertainment products displays. In many cases the resolutions listed in the sections below may have a small market, may only be seen in specialized industrial or computer market products, or may not be available for sale.
The 4:3 aspect ratio was common in older television cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, which were not easily adaptable to a wider aspect ratio. When good quality alternate technologies (i.e., liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and plasma displays) became more available and less costly, around the year 2000, the common computer displays and entertainment products moved to a wider aspect ratio, first to the 16:10 ratio. The 16:10 ratio allowed some compromise between showing older 4:3 aspect ratio broadcast TV shows, but also allowing better viewing of widescreen movies. However, around the year 2005, entertainment industry displays (i.e., TV sets) gradually moved from 16:10 to the 16:9 aspect ratio, for further improvement of viewing widescreen movies. By about 2007, virtually all mass market entertainment displays were 16:9. In 2011, 1920x1080 was the favored resolution in the most heavily marketed entertainment market displays.
The computer display industry maintained the 16:10 aspect ratio longer than the entertainment industry, but in the 2005-2010 period, computers were increasingly marketed as dual use products, with uses in the traditional computer applications, but also as means of viewing entertainment content. In this time frame, almost all desktop, laptop, and display manufacturers gradually moved to promoting only 16:9 aspect ratio displays. By 2011 the 16:10 aspect ratio had virtually disappeared from the laptop display market. One artifact is that the highest available resolution in laptop displays moved downward in this time frame (i.e., the move from 1920x1200 laptop displays to 1920x1080 displays).
The acronym qqVGA may be used to distinguish quarter from quad, just like qVGA.
. This resolution is half of QVGA, which is itself a quarter of VGA, which is 640×480 pixels.
 The Quarter Video Graphics Array (also known as Quarter VGA, QVGA, or qVGA) is a popular term for a computer display with 320×240 display resolution
The Quarter Video Graphics Array (also known as Quarter VGA, QVGA, or qVGA) is a popular term for a computer display with 320×240 display resolution
. QVGA displays are most often used in mobile phone
s, personal digital assistant
s (PDA), and some handheld game console
s. Often the displays are in a “portrait
” orientation (i.e., taller than they are wide, as opposed to “landscape
”) and are referred to as 240×320.
The name comes from having a quarter of the 640×480 maximum resolution of the original IBM
VGA
display technology, which became a de facto industry standard in the late 1980s. QVGA is not a standard mode offered by the VGA BIOS
, even though VGA and compatible chipsets
support a QVGA-sized Mode X
. The term refers only to the display's resolution and thus the abbreviated term QVGA or Quarter VGA is more appropriate to use.
QVGA resolution is also used in digital video
recording equipment as a low-resolution mode requiring less data storage capacity than higher resolutions, typically in still digital camera
s with video recording capability, and some mobile phone
s. Each frame is an image of 320×240 pixels. QVGA video is typically recorded at 15 or 30 frames per second. QVGA mode describes the size of an image in pixels, commonly called the resolution; numerous video file formats support this resolution.
While QVGA is a lower resolution than VGA, at higher resolutions the "Q" prefix commonly means quad(ruple) or four times higher display resolution (e.g., QXGA is 4 times higher resolution than XGA). To distinguish quarter from quad, lowercase "q" is sometimes used for "quarter" and uppercase "Q" for "quad", by analogy with SI prefix
es like k/K and m/M, but this is not a consistent usage.
having the same height in pixels as QVGA, but wider. This definition is consistent with other 'wide' versions of computer displays.
Since QVGA is 320 pixels wide and 240 pixels high (aspect ratio of 4:3), the resolution of a WQVGA screen might be 384x240 (8:5 aspect ratio), 400x240 (5:3 - such as the Nintendo 3DS
screen or the maximum resolution in YouTube
at 240p), 428x240 (107:60 ratio), or 432x240 (9:5 ratio). As with WVGA, exact ratios of N:9 are not practical because of the way VGA controllers internally deal with pixels. For instance, when using graphical combinatorial operations on pixels, VGA controllers will use 1 bit per pixel. Since bits cannot be accessed individually but by chunks of 16 or an even higher power of 2, this limits the horizontal resolution to a 16-pixel granularity, i.e., the horizontal resolution must be divisible by 16. In the case of 16:9 ratio, with 240 pixels high, the horizontal resolution should be 240 / 9 x 16 = 426.66 which is not a multiple of 16. The closest is 432, which is where the '432' comes from.
WQVGA has also been used to describe displays that are not 240 pixels high, for example Sixteenth HD1080
displays which are 270 or 272 pixels high or displays like 480×272. This may be due to QVGA having the nearest screen height.
WQVGA resolutions are commonly used in touch screen mobile phones, such as 240×400, 240×432, and 240×480. For example, the Sony Ericsson Aino and the Samsung Instinct both have WQVGA screen resolutions - 240x432. Other devices such as the Apple iPod nano
also use a WQVGA screen, 240×376 pixels.
) screens have 480×320 pixels (3:2 aspect ratio), 480×360 pixels (4:3 aspect ratio), 480×272 (~16:9 aspect ratio) or 640×240 pixels (8:3 aspect ratio).
The former is used by a variety of PDA
devices, starting with the Sony CLIÉ
PEG-NR70 in 2002, and standalone PDAs by Palm
. The latter was used by a variety of handheld PC
devices. VGA resolution is 640×480.
Examples of devices that use HVGA include the Apple iPhone
3GS/3G/2G, BlackBerry Bold
9000, HTC Dream
, HTC Hero
, HTC Wildfire S
, LG GW620
Eve, MyTouch 3G Slide
, Nokia 6260 Slide
, Palm Pre
, Samsung M900 Moment, and Sony Ericsson Xperia X8
.
Texas Instruments
produces the DLP pico projector which supports HVGA resolution.
HVGA was the only resolution supported in the first versions of Google Android, up to release 1.5. Other higher and lower resolutions are now available starting on release 1.6, like the popular WVGA resolution on the Motorola Droid
or the QVGA resolution on the HTC Tattoo
.
Three dimensional computer graphics
common on television
throughout the 1980s
were mostly rendered at this resolution, causing objects to have jagged edges on the top and bottom when edges were not anti-aliased.
line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog
computer display standard
, the 15-pin D-subminiature
VGA connector
or the 640×480 resolution itself. While this resolution was superseded in the personal computer
market in the 1990s, it is becoming a popular resolution on mobile devices. VGA is still the universal fallback troubleshooting mode in the case of trouble with graphic device drivers in operating systems.
for Wide Video Graphics Array is any display resolution
with the same 480 pixel height as VGA but wider, such as 800×480, 848×480, 852x480, or 854×480. It is a common resolution among LCD projector
s and later portable and hand-held internet-enabled devices (such as MID and Netbook
s) as it is capable of rendering web sites designed for an 800 wide window in full page-width. Examples of hand-held internet devices, without phone capability, with this resolution include: ASUS Eee PC
700 series, Dell
XCD35
, Nokia
770, N800
, and N810
.
As of 2011, mobile phones with WVGA display resolution are becoming more common. A list of mobile phones with WVGA displays is available.
for Full Wide Video Graphics Array which refers to a display resolution of 854×480 pixels. 854×480 is approximately the 16:9 aspect ratio
of anamorphically
"un-squeezed" NTSC DVD widescreen video and considered a "safe" resolution that does not crop any of the image. It is called Full WVGA to distinguish it from other, narrower WVGA resolutions which require cropping 16:9 aspect ratio
high-definition video
(i.e. it is full width, albeit with considerable reduction in size
). The 854 pixel width is rounded up from . . Since a pixel must be a whole number, rounding up to 854 ensures inclusion of the entire image. Due to physical devices often being manufactured with pixel resolutions that are multiples of 16, the horizontal resolution of 854 may be implemented by the OS simply pretending the 10 edgemost columns, from a full physical width of 864, don't exist.
As of 2011, mobile phones with FWVGA display resolution are becoming more common. A list of mobile phones with FWVGA displays is available.
s.
Originally, it was an extension to the VGA
standard first released by IBM
in 1987. Unlike VGA—a purely IBM-defined standard—Super VGA was defined by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), an open consortium set up to promote interoperability and define standards. When used as a resolution specification, in contrast to VGA or XGA for example, the term SVGA normally refers to a resolution of 800 × 600 pixels.
s, netbooks, and tablet computer
s. The resolution is either 1024×576 or 1024×600 with screen sizes normally ranging from 7 to 10 inches. The aspect ratio is approximately 5:3 or 16:9. Some netbooks with 11.6 inch screens use 1366×768 (16:9 aspect ratio).
, but the official definition is broader than that. It was not a new and improved replacement for Super VGA, but rather became one particular subset of the broad range of capabilities covered under the "Super VGA" umbrella.
The initial version of XGA expanded upon IBM's VGA
, adding support for two resolutions:
Like its predecessor (the IBM 8514), XGA offered fixed function hardware acceleration
to offload processing of 2D drawing tasks. XGA and 8514 could offload line-draw, bitmap-copy (bitblt), and color-fill operations from the host CPU
. XGA's acceleration was faster than 8514's, and more comprehensive in that it supported more drawing primitives and XGA's 16 bits per pixel (65,536 color) display-mode.
XGA-2 added Truecolor mode for 640×480, high color mode and higher refresh rate
s for 1024×768, and improved accelerator performance. All XGA modes have a 4:3 aspect ratio
rounded to 8 pixels.
XGA should not be confused with EVGA
(Extended Video Graphics Array), a contemporaneous VESA
standard.
. WXGA is commonly used for low-end LCD TVs and LCD computer monitors for widescreen presentation.
When referring to televisions and other monitors intended for consumer entertainment use, WXGA is generally understood to refer to a resolution of 1366(1365.333)×768, with an aspect ratio of 16:9. In 2006 this was the most popular resolution for liquid crystal display television
s while XGA was for Plasma
TVs flat panel display
s.
When referring to laptop displays or monitors intended primarily as computer displays, WXGA is most commonly used to refer to a resolution of 1280×800 pixels with an aspect ratio of 16:10. This resolution is particularly popular for most laptops with a 14" or 15" screen. The exact resolution this refers to is somewhat variable, however, as the 1280xnnn resolutions were among the first widescreen resolutions commonly used, and term entered use (especially for laptop displays) before the broad standardization 16:10 for widescreen computer displays.
Overall, several resolutions have been labeled as WXGA. These are the most common resolutions given the label (in ascending order by total number of pixels):
1280×720 provides perfectly square pixels at an aspect ratio of 16:9, while the additional pixels in 1280×768 and 1280×800 must be ignored to give the 16:9 ratio without vertical stretching of the image. 1360×768 and 1366×768 come very close to 16:9, displaying exactly square pixels if 1360×765 pixels of the display are used.
Recent widespread availability of 1280×800 pixel resolution LCDs for laptop monitors can be considered an OS
driven evolution from the formerly popular 1024×768 screen size. In Microsoft Windows
operating system
specifically, the task bar when fit to the bottom of the screen occupies about 30 pixels, allowing a program window
sized 1024×768 pixels to fit on screen without obstruction(800-768=32). Operating the Windows Sidebar in Windows Vista
can use the remaining width of 256 pixels (1280-1024).
720p
is a related HDTV video display resolution measuring 1280×720 pixels.
1440×900 resolution displays have also been found labeled as WXGA; however, the correct label is actually WSXGA or WXGA+.
. XGA+ is often used on 17 inch desktop CRT
monitors. XGA+ is usually understood to refer to the 1152×864 resolution with an aspect ratio of 4:3. As widescreen LCD are getting increasingly popular, this resolution is decreasing in use, but it is the native resolution of some 17 inch 4:3 LCD displays.
Historically, the resolution relates to the earlier standard of 1152×900 pixels, which was adopted by Sun Microsystems
for the Sun-2
workstation
in the early 1980s. This resolution is close to the maximum practical which, using one byte
per pixel, can fit into a video memory or frame-buffer of one megabyte
. However, its aspect ratio is 3.84:3 (1.28:1). When Apple Computer
defined a standard resolution for 21-inch CRT monitors, intended for use as Two-Page Displays on the Macintosh II
computer, Apple selected instead 1152×864, which is the highest 4:3 resolution below one million pixels.
XGA+ is the next step after XGA (1024×768), although it's not approved by any standard organizations. The next step with an aspect ratio of 4:3 is 1280×960 ("SXGA-") or SXGA+ (1400×1050).
WSXGA and WXGA+ can be considered enhanced versions of WXGA with more pixels, or as widescreen variants of SXGA. The aspect ratios of each are 16:10 (widescreen
).
WXGA+ (1440×900) resolution is common in 19" widescreen desktop monitors (a very small number of such monitors uses WSXGA+), and is also optional, although less common, in laptop
LCDs, in sizes ranging from 12.1" to 17".
resolution of 1280×1024 pixels. This display resolution
is the "next step" above the XGA resolution that IBM
developed in 1990.
The 1280×1024 resolution is not the standard 4:3 aspect ratio
, but 5:4 (1.25:1 instead of 1.333:1). A standard 4:3 monitor using this resolution will have rectangular rather than square pixels, meaning that unless the software compensates for this the picture will be distorted, causing circles to appear elliptical. There is a less common 1280×960 resolution sometimes unofficially called "SXGA-" (to avoid confusion with the "standard" SXGA) that preserves the common 4:3 aspect ratio.
SXGA is the most common native resolution of 17" and 19" LCD
monitors. An LCD monitor with SXGA native resolution will typically have a physical 5:4 aspect ratio, preserving a 1:1 pixel aspect ratio
.
Apple Computer
referred to displays with this resolution as "two-page displays", because they could be used to display two A4 pages
side-by-side at a resolution of 72 dots per inch
. Sony
manufactured a 17" CRT
monitor with a 5:4 aspect ratio designed for this resolution. It was sold under the Apple brand name.
SXGA is also a popular resolution for cell phone cameras, such as the Motorola Razr and most Samsung and LG phones. Although being taken over by newer UXGA (2.0 megapixel) cameras, the 1.3 megapixel was the most common around 2007.
Any CRT that can run 1280×1024 can also run 1280×960, which has the standard 4:3 ratio. Displaying any 4:3 resolution on a 5:4 monitor, like a TFT with a native resolution of 1280×1024, will look stretched. But on a TFT, displaying any other resolution than the native one is not a good idea anyway, as the image needs to be interpolated to fit in the fixed grid display (and some TFT displays do not allow a user to disable this and use a letterbox format).
The 1280×1024 resolution became popular because at 24-bit color it fit well into 4 megabyte
s of video RAM. At the time, memory was extremely expensive. Using 1280×1024 at 24-bit color depth
allowed using 3.75 MiB
of video RAM, fitting nicely with VRAM
chip sizes which were available at the time (4 MiB).
. An SXGA+ display is commonly used on 14 inch or 15 inch laptop
LCD screens with a resolution
of 1400×1050 pixels. An SXGA+ display is used on a few 12 inch laptop screens such as the ThinkPad
X60 & X61 (both only as tablet) as well as the Toshiba
Portégé M200 and M400, but these are far less common. Dell offered a 14.1" SXGA+ screen on the many of the Dell Latitude "C" series laptops, such as the C640 and the C810. Sony also used SXGA+ in their Z1 series, but no longer produce them as wide screen has become more predominant.
There is a widescreen
version of SXGA+ called WSXGA+ with a resolution of 1680×1050. This is a common native resolution of 19-22 inch wide-aspect LCD monitors, and is also available on many laptops.
It is the next common step in resolution after SXGA, although it is not approved by any organization. The most common resolution immediately above is called UXGA (sometimes also known as UGA) which has 1600×1200 pixels.
In desktop LCDs, SXGA+ is used on some low-end 20" monitors, whereas most of the 20" LCDs use UXGA (standard screen ratio), or WSXGA+ (widescreen ratio).
. A WSXGA+ display is commonly used on Widescreen 20", 21", and popular 22" LCD monitors from numerous manufacturers (and a very small number of 19" widescreen monitors), as well as widescreen 15.4" and 17" laptop
LCD screens like the Thinkpad
T61 and the Apple 15" MacBook Pro
. The resolution
is 1680×1050 pixels (1,764,000 pixels) and has a 16:10 aspect ratio
.
WSXGA+ is the widescreen version of SXGA+, but it is not approved by any organization. The next highest resolution (for widescreen) after it is WUXGA, which is 1920×1200 pixels.
resolution
of 1600×1200 pixels (totaling 1,920,000 pixels), which is exactly four times the default resolution
of SVGA (800×600) (totaling 480,000 pixels). Dell Computer refers to the same resolution of 1,920,000 pixels as UGA. It is generally considered to be the next step above SXGA (1280×960 or 1280×1024), but some resolutions (such as the unnamed 1366×1024 and SXGA+ at 1400×1050) fit between the two.
UXGA has been the native resolution of many fullscreen monitors of 15" or more, including laptop LCDs such as the ones in ThinkPad
A21p, A31p, T42p, and T43p; Dell Inspiron 8000/8100/8200; Panasonic Toughbook CF-51; and the original Alienware Area 51m. However, in more recent times, UXGA is not used in laptops at all but rather in desktop UXGA monitors that have been made in sizes of 20" and 21.3". Some 14" laptop LCDs with UXGA have also existed, but these were very rare.
There are two different widescreen
cousins of UXGA, one called UWXGA with 1600×768 (750) and one called WUXGA with 1920×1200 resolution.
Ultra eXtended Graphics Array and is a display resolution
of 1920×1200 pixels (2,304,000 pixels) with a 16:10 screen aspect ratio
.
It is a wide version of UXGA, and can be used for viewing high-definition television
(HDTV) content, which uses a 16:9 aspect ratio and a 1920x1080 resolution.
The 16:10 aspect ratio (as opposed to the 16:9 used in widescreen televisions) was chosen because this aspect ratio is appropriate for displaying two full pages of text side by side.
WUXGA resolution is equivalent to 2.3 megapixels. An 8-bit RGB WUXGA image has an uncompressed size of around 6.6 MiB
. This was the highest resolution that was ever commonly available in the computer display industry, but its use had been almost completely ended by 2010 as the computer industry moved to the 16:9 aspect ratio (i.e., 1920x1080 is the highest resolution available from most laptop and computer monitor manufacturers). This resolution is currently available in a few high-end LCD
television
s and computer monitors, the latter of which are typically in the size range of approximately 23"–28" for desktop monitors, but has become almost completely unavailable on notebook monitors. A small number of 22" WUXGA desktop monitors exist (i.e., Lenovo L220x and Samsung T220P). WUXGA use predates the introduction of LCDs of that resolution. Most QXGA displays support 1920×1200 and widescreen CRTs
such as the Sony GDM-FW900 and Hewlett Packard A7217A do as well.
The next lower resolution (for widescreen) before it is WSXGA+, which is 1680×1050 pixels (1,764,000 pixels, or 30.61% fewer than the WUXGA); the next higher resolution widescreen is an unnamed 2304×1440 resolution (supported by the above GDM-FW900 & A7217A) and then the more common WQXGA, which has 2560×1600 pixels (4,096,000 pixels, or 77.78% more than WUXGA).
There are two wider formats called UWXGA 1600×768 (25:12) and UW-UXGA that has 2560×1080 pixels, a 2.37:1 or 21⅓:9 or 64:27 aspect ratio, sometimes erroneously labeled 21:9.
The QXGA, or Quad eXtended Graphics Array, display standard is a resolution standard in display technology. Their high pixel counts and heavy display hardware requirements mean that there are currently few CRT
and LCD
monitors that have pixel counts at these levels. These terms are currently reserved for the highest-end consumer computer display
hardware for those buying LCDs.
WQXGA is often found in 30" displays like the Dell 3008WFP and the Apple Cinema Display
. As of 2010, there are few WQXGA displays in the consumer marketplace, but their price is higher than most displays used by graphic professionals, and their refresh speed is not close to that used in current consumer displays. It is unlikely that WQXGA, or next-generation HXGA, displays will be commonplace before 2015. It should also be noted, however, that many standard 21"/22" CRT monitors can be used at the QXGA resolution. Some of the highest-end 19" CRTs also support this resolution.
In 2010 WQXGA made its debut in a handful of home theater projectors targeted at the Contant Height Screen application market. Both Digital Projection Inc and projectiondesign released models based on a Texas Instrument DLP chip with a native WQXGA resolution, alleviating the need for an anamorphic lens to achieve 1:2.35 image projection.
of 2048×1152 pixels with a 16:9
aspect ratio
. A few LCD QWXGA monitors are available with 23 and 27 inch displays, such as the Acer B233HU (23") and B273HU (27"), the Dell
SP2309W, and the Samsung
2343BWX.
of 2048×1536 pixels with a 4:3 aspect ratio
. The name comes from it having four times as many pixels as an XGA display. As of 2007, this is the highest non-experimental and non-widescreen resolution, and the number of monitors that can display images at this resolution are somewhat limited, especially among LCDs. The number of CRT monitors offering this resolution has actually dropped off, as CRT makers such as NEC
and Sony
have stopped offering their higher end models. Examples of LCDs with this resolution are the IBM
T210 and the Eizo
G33 and R31 screens, but in CRT monitors this resolution is much more common; some examples include the ViewSonic
G225fB, NEC
FP2141SB or Mitsubishi
DP2070SB, Iiyama
Vision Master Pro 514, and Dell
and HP P1230. Of these monitors, none is still in production. A related display size is WQXGA, which is a wide screen version. CRTs offer a way to achieve QXGA cheaply. Models like the Mitsubishi Diamond Pro 2045U and IBM ThinkVision C220P retailed for around 200 USD, and even higher performance ones like the ViewSonic PerfectFlat P220fB remained under 500 USD. As recently as last year, many off-lease P1230s could be found on eBay for under 150 USD. The LCDs with WQXGA or QXGA resolution typically cost 4 to 5 times more for the same resolution. IDTech manufactured a 15" QXGA IPS panel. NEC had sold laptops with QXGA screens in 2002-2005 for Japanese market.
of 2560×1600 pixels with a 16:10 aspect ratio
. The name comes from it being a wide version of QXGA and having four times as many pixels as an WXGA (1280×800) display.
Before 2007, devices that could display this resolution were very rare, but many manufacturers have since come out with a 27"–30" model that is capable of WQXGA, albeit at a much higher price than lower resolution monitors of the same size. Several mainstream WQXGA monitors are available with 30 inch displays, such as the Apple Cinema Display
, the Dell UltraSharp 3007WFP-HC
, Dell UltraSharp 3008WFP and Dell UltraSharp 3011, the Hewlett-Packard
LP3065, the Gateway
XHD3000, and the Samsung
305T. Specialist manufacturers like Eizo
, Planar Systems
, Barco
(LC-3001), and possibly others offer similar models.
One feature which is currently unique to the 30" WQXGA monitors is the ability to function as the centerpiece and main display of a three-monitor array of complementary aspect ratios, with two UXGA (1600×1200) 20" monitors turned vertically on either side. The resolutions are equal, and the size of the 1600 resolution edges (if the manufacturer is honest) is within a tenth of an inch (16" vs. 15.89999"), presenting a "picture window view" without the extreme lateral dimensions, small central panel, asymmetry, resolution differences, or dimensional difference of other three-monitor combinations. The resulting 4960×1600 composite image has a 3.1:1 aspect ratio.
Of course, this also means one UXGA 20" monitor in portrait orientation can also be flanked by two 30" WQXGA monitors for a 6320×1600 composite image with a 11.85:3 (79:20, 3.95:1) aspect ratio.
. Grayscale monitors with a 2560×2048 resolution, primarily for medical use, are available from Planar Systems
(Dome E5), Eizo
(Radiforce G51), Barco
(Nio 5,MP), WIDE
(IF2105MP), IDTech (IAQS80F) and possibly others.
A similar resolution of 2560×1920 (4:3) was supported by a small number of CRT displays via VGA such as the Viewsonic P225f when paired with the right graphics card.
supports 3280×2048 (approx. 16:10).
In June 2001, WQUXGA was introduced in the IBM T220 LCD monitor
using a LCD panel built by IDTech. LCD displays that support WQUXGA resolution include: IBM T220, IBM T221 (models DG1, DG3, DG4, DG5), Iiyama
AQU5611DTBK, ViewSonic
VP2290, ADTX MD22292B and IDTech MD22292 (models B0, B1, B2, B5, C0, C2). IDTech was the original equipment manufacturer which sold these monitors to ADTX, IBM
, Iiyama
, and ViewSonic
.
Most display cards with a DVI connector are capable of supporting the 3840×2400 resolution. However, the maximum refresh rate will be limited by the number of DVI links which are connected to the monitor. 1, 2, or 4 DVI connectors are used to drive the monitor using various tile configurations. Only the IBM T221-DG5 and IDTech MD22292B5 support the use of dual-link DVI ports through an external converter box.
Many systems using these monitors use at least 2 DVI connectors to send video to the monitor. These DVI connectors can be from the same graphics card, different graphics cards, or even different computers. Motion across the tile boundary(ies) can show tearing if the DVI links are not synchronized. The display panel can be updated at a speed between 0 Hz and 41 Hz (48 Hz for the IBM T221-DG5, and IDTech MD22292B5). The refresh rate of the video signal can be higher than 41 Hz (or 48 Hz) but the monitor will not update the display any faster if graphics card(s) do so.
There was one series of WQUXGA displays in the consumer marketplace, but it was discontinued in Q2 of 2005. That series of displays had prices which were well above even the higher end displays used by graphic professionals. In addition, the lower refresh rates, 41 Hz and 48 Hz, made them less attractive for many applications.
As of January 2007, none of the WQUXGA monitors (IBM, ViewSonic, Iiyama, ADTX) are in production anymore. Toshiba announced its intention to market a new WQUXGA 22" monitor in November 2007. However, it has not done so to date. Neither Toshiba nor public speculation on the Internet has provided any new information since the November 2007 press release.
WQUXGA is the maximum resolution supported by DisplayPort
1.2, though actually displaying such a resolution on a device with DisplayPort 1.2 is dependent on the graphics system in much the same way devices with VGA connectors do not necessarily maximize that standard's highest possible resolution.
The HXGA display standard and its derivatives are a standard in display technology. Their high pixel counts and heavy display hardware requirements mean that there is currently no monitor
that singly displays at these levels. These terms are currently reserved for digital camera
hardware. An example can be found in HIPerSpace of a case where multiple WQXGA displays must be stacked to exceed HXGA or WHXGA resolution.
[adecatuple] Extended Graphics Array is a display standard that can support a resolution of 4096×3072 pixels (or 3200 pixels) with a 4:3 aspect ratio. The name comes from it having sixteen (hexadecatuple) times as many pixels as an XGA display. As of 2011, there are no displays that can render images at such high resolution but several digital cameras can record such images. A related display size is WHXGA, which is a wide screen version.
[adecatuple] Extended Graphics Array is a display standard that can support a resolution of roughly 5120×3200 pixels with a 16:10 aspect ratio. The name comes from it being a wide version of HXGA, which has sixteen (hexadecatuple) times as many pixels as an XGA display. As of 2011, there are no displays that can render images at such high resolution but several digital cameras can record such images. It would require four WQXGA devices to display at this resolution. A resolution of 5120×3072 should, in theory, also qualify as WHXGA, if such a display were to be made.
[adecatuple] Super Extended Graphics Array, is a display standard that can support a resolution of roughly 5120×4096 pixels with a 5:4 aspect ratio. The name comes from it having sixteen (hexadecatuple) times as many pixels as an SXGA display.
As of January 2007, there is no display with a maximum resolution 5120×4096. If this display were to exist, it would have a maximum resolution 10 times that of the 1080 ATSC HDTV video standard.
[adecatuple] Super Extended Graphics Array, is a display standard that can support a resolution up to 6400 x 4096 pixels, assuming a 1.56:1 aspect ratio. The name comes from it having sixteen (hexadecatuple) times as many pixels as an WSXGA display.
[adecatuple] Ultra Extended Graphics Array, is a display standard that can support a resolution of roughly 6400×4800 pixels with a 4:3 aspect ratio. The name comes from it having sixteen (hexadecatuple) times as many pixels as an UXGA display.
[adecatuple] Ultra Extended Graphics Array, is a display standard that can support a resolution up to 7680×4800 pixels, assuming a 16:10 aspect ratio. The name comes from it having sixteen (hexadecatuple) times as many pixels as a WUXGA display. A WHUXGA image consists of 36,864,000 pixels (approximately 37 megapixels).
A monitor of 7680×4320 would also qualify as a WHUXGA display. UHDTV video requires a display of similar resolution (7680×4320) for properly displaying UHDTV content, which is 16 times the pixel count of the 1080 ATSC HDTV video standard.
frame and one quarter of a 720p
frame. 2x2 nHD frames will form one 720p frame and 3x3 nHD frames will form one 1080p frame.
One drawback of this resolution is that the vertical resolution is not an even multiple of 16 which is a common macroblock
size for video codec
s. Video frames encoded with 16x16 pixel macroblocks would be padded to 640x368 and the added pixels would be cropped away at playback. The same is true for qHD and 1080p but the relative amount of padding is more for lower resolutions such as nHD.
To avoid storing padding data some people prefer to encode video at 624x352. When such video streams are either encoded from HD frames or played back on HD displays in full screen mode (either 720p or 1080p) they are scaled by non-integer scale factors. True nHD frames on the other hand has integer scale factors.
frame, in a 16:9 aspect ratio
.
This resolution became popular for high-end smartphone displays in early 2011. Mobile phones including the HTC Sensation
, Motorola Droid RAZR and Motorola Atrix 4G
have displays with the qHD resolution.
. It is four times the pixel resolution of the 720p
HDTV video standard, hence the name. Their high pixel counts and heavy display hardware requirements mean that there are currently few LCD
monitors that have pixel counts at these levels. It is a resolution found in some displays, such as the Dell UltraSharp U2711, NEC MultiSync PA271W, and the 27" iMac
.
In autumn 2006, Chi Mei Optoelectronics
(CMO) announced a 47" 1440 LCD panel to be released in Q2 2007; the panel was planned to finally debut at FPD International 2008 in a form on autostereoscopic
3D display
.
display resolution of 3840×2160 pixels arranged in a 16:9 aspect ratio
. It is four times the resolution of the 1080p
HDTV video standard, hence the name (Quad meaning 4).
In early 2008, Samsung revealed a proof-of-concept 82-inch LCD TV set capable of this resolution and LG has demonstrated an 84-inch display.
Eyevis produces a 56" LCD named EYELCD 56 QHD HD while Toshiba
makes the P56QHD, Mitsubishi Electric
the 56P-QF60LCU, and Sony
the SRM-L560, all which can deliver a resolution of 3840×2160. Landmark also has produced a 56" QFHD monitor, the M5600.
CMI has built a 27.84" 158 PPI QFHD IPS panel for medical displays since November 2010.
Acronym and initialism
Acronyms and initialisms are abbreviations formed from the initial components in a phrase or a word. These components may be individual letters or parts of words . There is no universal agreement on the precise definition of the various terms , nor on written usage...
that is descriptive of its dimensions. A higher display resolution means that displayed content appears sharper and smaller (depending on the physical size of the display).
Aspect ratio and its impact on the available resolution

The gradual change of the favored aspect ratio of mass market display industry products, from 4:3, then to 16:10, and then to 16:9, has made many of the display resolutions listed in this article difficult to obtain in mass market products. The 4:3 aspect ratio generally reflects older products, especially the era of the cathode ray tube (CRT). The 16:10 aspect ratio had its largest use in the 1995-2010 period, and the 16:9 aspect ratio tends to reflect the newest (post 2010) mass market computer monitor, laptop, and entertainment products displays. In many cases the resolutions listed in the sections below may have a small market, may only be seen in specialized industrial or computer market products, or may not be available for sale.
The 4:3 aspect ratio was common in older television cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, which were not easily adaptable to a wider aspect ratio. When good quality alternate technologies (i.e., liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and plasma displays) became more available and less costly, around the year 2000, the common computer displays and entertainment products moved to a wider aspect ratio, first to the 16:10 ratio. The 16:10 ratio allowed some compromise between showing older 4:3 aspect ratio broadcast TV shows, but also allowing better viewing of widescreen movies. However, around the year 2005, entertainment industry displays (i.e., TV sets) gradually moved from 16:10 to the 16:9 aspect ratio, for further improvement of viewing widescreen movies. By about 2007, virtually all mass market entertainment displays were 16:9. In 2011, 1920x1080 was the favored resolution in the most heavily marketed entertainment market displays.
The computer display industry maintained the 16:10 aspect ratio longer than the entertainment industry, but in the 2005-2010 period, computers were increasingly marketed as dual use products, with uses in the traditional computer applications, but also as means of viewing entertainment content. In this time frame, almost all desktop, laptop, and display manufacturers gradually moved to promoting only 16:9 aspect ratio displays. By 2011 the 16:10 aspect ratio had virtually disappeared from the laptop display market. One artifact is that the highest available resolution in laptop displays moved downward in this time frame (i.e., the move from 1920x1200 laptop displays to 1920x1080 displays).
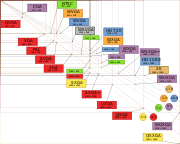
Video graphics array
| Name | x (px) | y (px) | x:y | x*y (Mpx) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QQVGA | 160 | 120 | 4:3 | 0.019 |
| HQVGA | 240 | 160 | 3:2 | 0.038 |
| QVGA | 320 | 240 | 4:3 | 0.077 |
| WQVGA | 400 | 240 | 5:3 | 0.096 |
| HVGA | 480 | 320 | 3:2 | 0.154 |
| VGA | 640 | 480 | 4:3 | 0.307 |
| WVGA | 800 | 480 | 5:3 | 0.384 |
| FWVGA | ~854 | 480 | 16:9 | 0.410 |
| SVGA | 800 | 600 | 4:3 | 0.480 |
| WSVGA | 1024 | 576 | 16:9 | 0.590 |
| WSVGA | 1024 | 600 | 17:10 | 0.614 |
QQVGA (160×120)
Quarter-QVGA (QQVGA or qqVGA) denotes a resolution of 160×120 or 120×160 pixels, usually used in displays of handheld devices. The term Quarter-QVGA signifies a resolution of one fourth the number of pixels in a QVGA display (half the number of vertical and half the number of horizontal pixels) which itself has one fourth the number of pixels in a VGA display.The acronym qqVGA may be used to distinguish quarter from quad, just like qVGA.
HQVGA (240×160)
Half-QVGA denotes a display screen resolution of 240×160 or 160×240 pixels, as seen on the Game Boy AdvanceGame Boy Advance
The is a 32-bit handheld video game console developed, manufactured, and marketed by Nintendo. It is the successor to the Game Boy Color. It was released in Japan on March 21, 2001; in North America on June 11, 2001; in Australia and Europe on June 22, 2001; and in the People's Republic of China...
. This resolution is half of QVGA, which is itself a quarter of VGA, which is 640×480 pixels.
QVGA (320×240)

Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
. QVGA displays are most often used in mobile phone
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
s, personal digital assistant
Personal digital assistant
A personal digital assistant , also known as a palmtop computer, or personal data assistant, is a mobile device that functions as a personal information manager. Current PDAs often have the ability to connect to the Internet...
s (PDA), and some handheld game console
Handheld game console
A handheld game console is a lightweight, portable electronic device with a built-in screen, game controls and speakers. Handheld game consoles are run on machines of small size allowing people to carry them and play them at any time or place...
s. Often the displays are in a “portrait
Portrait
thumb|250px|right|Portrait of [[Thomas Jefferson]] by [[Rembrandt Peale]], 1805. [[New-York Historical Society]].A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face and its expression is predominant. The intent is to display the likeness,...
” orientation (i.e., taller than they are wide, as opposed to “landscape
Landscape
Landscape comprises the visible features of an area of land, including the physical elements of landforms such as mountains, hills, water bodies such as rivers, lakes, ponds and the sea, living elements of land cover including indigenous vegetation, human elements including different forms of...
”) and are referred to as 240×320.
The name comes from having a quarter of the 640×480 maximum resolution of the original IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
display technology, which became a de facto industry standard in the late 1980s. QVGA is not a standard mode offered by the VGA BIOS
Video BIOS
Video BIOS is the BIOS of a graphics card in a computer.Much the way the system BIOS provides a set of functions that are used by software programs to access the system hardware, the video BIOS provides a set of video-related functions that are used by programs to access the video hardware...
, even though VGA and compatible chipsets
Graphics processing unit
A graphics processing unit or GPU is a specialized circuit designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory in such a way so as to accelerate the building of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display...
support a QVGA-sized Mode X
Mode X
Mode X is an alternative video graphics display mode of the IBM VGA graphics hardware that was popularized by Michael Abrash, first published in July 1991 in Dr...
. The term refers only to the display's resolution and thus the abbreviated term QVGA or Quarter VGA is more appropriate to use.
QVGA resolution is also used in digital video
Digital video
Digital video is a type of digital recording system that works by using a digital rather than an analog video signal.The terms camera, video camera, and camcorder are used interchangeably in this article.- History :...
recording equipment as a low-resolution mode requiring less data storage capacity than higher resolutions, typically in still digital camera
Digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that takes video or still photographs, or both, digitally by recording images via an electronic image sensor. It is the main device used in the field of digital photography...
s with video recording capability, and some mobile phone
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
s. Each frame is an image of 320×240 pixels. QVGA video is typically recorded at 15 or 30 frames per second. QVGA mode describes the size of an image in pixels, commonly called the resolution; numerous video file formats support this resolution.
While QVGA is a lower resolution than VGA, at higher resolutions the "Q" prefix commonly means quad(ruple) or four times higher display resolution (e.g., QXGA is 4 times higher resolution than XGA). To distinguish quarter from quad, lowercase "q" is sometimes used for "quarter" and uppercase "Q" for "quad", by analogy with SI prefix
SI prefix
The International System of Units specifies a set of unit prefixes known as SI prefixes or metric prefixes. An SI prefix is a name that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a decadic multiple or fraction of the unit. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to the unit symbol...
es like k/K and m/M, but this is not a consistent usage.
WQVGA (400×240)
Wide QVGA or WQVGA is any display resolutionDisplay resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
having the same height in pixels as QVGA, but wider. This definition is consistent with other 'wide' versions of computer displays.
Since QVGA is 320 pixels wide and 240 pixels high (aspect ratio of 4:3), the resolution of a WQVGA screen might be 384x240 (8:5 aspect ratio), 400x240 (5:3 - such as the Nintendo 3DS
Nintendo 3DS
The is a portable game console produced by Nintendo. The autostereoscopic device is able to project stereoscopic 3D effects without the use of 3D glasses or any additional accessories. The Nintendo 3DS features backward compatibility with Nintendo DS series software, including Nintendo DSi software...
screen or the maximum resolution in YouTube
YouTube
YouTube is a video-sharing website, created by three former PayPal employees in February 2005, on which users can upload, view and share videos....
at 240p), 428x240 (107:60 ratio), or 432x240 (9:5 ratio). As with WVGA, exact ratios of N:9 are not practical because of the way VGA controllers internally deal with pixels. For instance, when using graphical combinatorial operations on pixels, VGA controllers will use 1 bit per pixel. Since bits cannot be accessed individually but by chunks of 16 or an even higher power of 2, this limits the horizontal resolution to a 16-pixel granularity, i.e., the horizontal resolution must be divisible by 16. In the case of 16:9 ratio, with 240 pixels high, the horizontal resolution should be 240 / 9 x 16 = 426.66 which is not a multiple of 16. The closest is 432, which is where the '432' comes from.
WQVGA has also been used to describe displays that are not 240 pixels high, for example Sixteenth HD1080
Sixteenth HD1080
Sixteenth HD1080 is a display resolution that is the same aspect ratio and one 16th the area of 1080 line high-definition TV resolution.HD1080 is 1920×1080 pixels, so dividing the resolution by 4 in each axis gives 480×270 pixels...
displays which are 270 or 272 pixels high or displays like 480×272. This may be due to QVGA having the nearest screen height.
WQVGA resolutions are commonly used in touch screen mobile phones, such as 240×400, 240×432, and 240×480. For example, the Sony Ericsson Aino and the Samsung Instinct both have WQVGA screen resolutions - 240x432. Other devices such as the Apple iPod nano
IPod nano
iPod Nano is a digital media player designed and marketed by Apple Inc.. The first generation of iPod Nano was introduced on September 7, 2005 as a replacement for iPod Mini. It uses flash memory for storage. iPod Nano has gone through six models, or generations, since its introduction...
also use a WQVGA screen, 240×376 pixels.
HVGA (480×320)
HVGA (Half-size VGAVideo Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
) screens have 480×320 pixels (3:2 aspect ratio), 480×360 pixels (4:3 aspect ratio), 480×272 (~16:9 aspect ratio) or 640×240 pixels (8:3 aspect ratio).
The former is used by a variety of PDA
PDA
A PDA is most commonly a Personal digital assistant, also known as a Personal data assistant, a mobile electronic device.PDA may also refer to:In science, medicine and technology:...
devices, starting with the Sony CLIÉ
CLIÉ
The Sony CLIÉ was a series of personal digital assistants running the Palm Operating System developed and marketed by Sony from 2000 to 2005. The devices introduced many new features to the PDA market, such as a jog-wheel interface, high-resolution displays, and Sony technologies like Memory Stick...
PEG-NR70 in 2002, and standalone PDAs by Palm
Palm, Inc.
Palm, Inc., was a smartphone manufacturer headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, that was responsible for products such as the Pre and Pixi as well as the Treo and Centro smartphones. Previous product lines include the PalmPilot, Palm III, Palm V, Palm VII, Zire and Tungsten. While their older...
. The latter was used by a variety of handheld PC
Handheld PC
A Handheld PC, or H/PC for short, is a term for a computer built around a form factor which is smaller than any standard laptop computer. It is sometimes referred to as a Palmtop. The first handheld device compatible with desktop IBM personal computers of the time was the Atari Portfolio of 1989...
devices. VGA resolution is 640×480.
Examples of devices that use HVGA include the Apple iPhone
IPhone
The iPhone is a line of Internet and multimedia-enabled smartphones marketed by Apple Inc. The first iPhone was unveiled by Steve Jobs, then CEO of Apple, on January 9, 2007, and released on June 29, 2007...
3GS/3G/2G, BlackBerry Bold
BlackBerry Bold
The BlackBerry Bold 9000 is a line of smartphones developed by Research in Motion. The family includes the 9000 , the 9700 , the 9650 and 9780, both of which were released in 2010, 9788 released in 2011 and the 9900/9930, the first touchscreen Bold, released in August 2011...
9000, HTC Dream
HTC Dream
The HTC Dream is an Internet-enabled smartphone with an operating system designed by Google and hardware designed by HTC...
, HTC Hero
HTC Hero
The HTC Hero is the third phone manufactured by the HTC Corporation for the Android platform, as part of the A series...
, HTC Wildfire S
HTC Wildfire S
The HTC Wildfire S is a smartphone developed by the HTC Corporation. The model was announced on 15 February 2011 at the Mobile World Congress and released in Europe three months later. It is powered by a 600 MHz Qualcomm processor and runs the Android operating system, version 2.3.3...
, LG GW620
LG GW620
The LG GW620 Eve, also known as the LG InTouch Max, is a smartphone manufactured by LG Electronics. It is the first smartphone from LG that runs the Android operating system....
Eve, MyTouch 3G Slide
MyTouch 3G Slide
The T-Mobile myTouch 3G Slide is a smartphone designed and manufactured by HTC and is sold exclusively by T-Mobile USA. HTC's name for the device during development was "Espresso"...
, Nokia 6260 Slide
Nokia 6260 Slide
- Features :Among its key features are integrated A-GPS with included maps, WLAN, VoIP, a 5.0 megapixel camera with LED flash, WebKit Open Source Browser, Flash Lite 3.0, Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR and MIDP Java 2.1 with additional Java APIs.- Specification sheet :...
, Palm Pre
Palm Pre
The Palm Pre is a multimedia smartphone designed and marketed by Palm with a multi-touch screen and a sliding keyboard. The smartphone was the first to use Palm's Linux based mobile operating system, webOS...
, Samsung M900 Moment, and Sony Ericsson Xperia X8
Sony Ericsson Xperia X8
The Sony Ericsson Xperia X8 is a mid-range 3G Android smart phone developed by Sony Ericsson in the Xperia series in released in Q4 2010. It is sold in many countries worldwide, including the United States on AT&T Mobility and low-end pay-monthly contracts in the UK...
.
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Inc. , widely known as TI, is an American company based in Dallas, Texas, United States, which develops and commercializes semiconductor and computer technology...
produces the DLP pico projector which supports HVGA resolution.
HVGA was the only resolution supported in the first versions of Google Android, up to release 1.5. Other higher and lower resolutions are now available starting on release 1.6, like the popular WVGA resolution on the Motorola Droid
Motorola Droid
The Motorola Droid is an Internet and multimedia enabled smartphone designed by Motorola, which runs Google's Android operating system. The Droid had been publicized under the codenames Sholes and Tao and the model number A855...
or the QVGA resolution on the HTC Tattoo
HTC Tattoo
The HTC Tattoo is a phone manufactured by the HTC Corporation for the Android platform. It is the second phone to feature the HTC Sense interface. The phone was announced on 8 September 2009....
.
Three dimensional computer graphics
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering 2D images...
common on television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
throughout the 1980s
1980s
File:1980s decade montage.png|thumb|400px|From left, clockwise: The first Space Shuttle, Columbia, lifted off in 1981; American President Ronald Reagan and Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev eased tensions between the two superpowers, leading to the end of the Cold War; The Fall of the Berlin Wall in...
were mostly rendered at this resolution, causing objects to have jagged edges on the top and bottom when edges were not anti-aliased.
VGA (640×480)
Video Graphics Array (VGA) refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2IBM Personal System/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 was IBM's third generation of personal computers. The PS/2 line, released to the public in 1987, was created by IBM in an attempt to recapture control of the PC market by introducing an advanced proprietary architecture...
line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog
Analogue electronics
Analogue electronics are electronic systems with a continuously variable signal, in contrast to digital electronics where signals usually take only two different levels. The term "analogue" describes the proportional relationship between a signal and a voltage or current that represents the signal...
computer display standard
Computer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
, the 15-pin D-subminiature
D-subminiature
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smaller connectors used on computer systems....
VGA connector
VGA connector
A Video Graphics Array connector is a three-row 15-pin DE-15 connector. The 15-pin VGA connector is found on many video cards, computer monitors, and some high definition television sets...
or the 640×480 resolution itself. While this resolution was superseded in the personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
market in the 1990s, it is becoming a popular resolution on mobile devices. VGA is still the universal fallback troubleshooting mode in the case of trouble with graphic device drivers in operating systems.
WVGA (800×480)
Wide VGA or WVGA an abbreviationAbbreviation
An abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase. Usually, but not always, it consists of a letter or group of letters taken from the word or phrase...
for Wide Video Graphics Array is any display resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
with the same 480 pixel height as VGA but wider, such as 800×480, 848×480, 852x480, or 854×480. It is a common resolution among LCD projector
LCD projector
An LCD projector is a type of video projector for displaying video, images or computer data on a screen or other flat surface. It is a modern equivalent of the slide projector or overhead projector...
s and later portable and hand-held internet-enabled devices (such as MID and Netbook
Netbook
Netbooks are a category of small, lightweight, legacy-free, and inexpensive laptop computers.At their inception in late 2007 as smaller notebooks optimized for low weight and low cost — netbooks omitted certain features , featured smaller screens and keyboards, and offered reduced computing...
s) as it is capable of rendering web sites designed for an 800 wide window in full page-width. Examples of hand-held internet devices, without phone capability, with this resolution include: ASUS Eee PC
ASUS Eee PC
The Asus Eee PC is a subnotebook/netbook computer line from ASUSTeK Computer Incorporated, and a part of the Asus Eee product family. At the time of its introduction in late 2007, it was noted for its combination of a light weight, Linux operating system, solid-state drive , and relatively low cost...
700 series, Dell
Dell
Dell, Inc. is an American multinational information technology corporation based in 1 Dell Way, Round Rock, Texas, United States, that develops, sells and supports computers and related products and services. Bearing the name of its founder, Michael Dell, the company is one of the largest...
XCD35
ZTE Blade
The ZTE Blade , is a phone manufactured by China's ZTE Corporation for the Android platform...
, Nokia
Nokia
Nokia Corporation is a Finnish multinational communications corporation that is headquartered in Keilaniemi, Espoo, a city neighbouring Finland's capital Helsinki...
770, N800
Nokia N800
The Nokia N800 Internet tablet is a wireless Internet appliance from Nokia, originally announced at the Las Vegas CES 2007 Summit in January 2007. N800 allows the user to browse the Internet and communicate using Wi-Fi networks or with mobile phone via Bluetooth. The N800 was developed as the...
, and N810
Nokia N810
The Nokia N810 Internet tablet is an Internet appliance from Nokia, announced on 17 October, 2007 at the Web 2.0 Summit in San Francisco. Despite Nokia's strong association with cellular products, the N810 is not a phone, but instead allows the user to browse the Internet and communicate using...
.
As of 2011, mobile phones with WVGA display resolution are becoming more common. A list of mobile phones with WVGA displays is available.
FWVGA (854×480)
FWVGA is an abbreviationAbbreviation
An abbreviation is a shortened form of a word or phrase. Usually, but not always, it consists of a letter or group of letters taken from the word or phrase...
for Full Wide Video Graphics Array which refers to a display resolution of 854×480 pixels. 854×480 is approximately the 16:9 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
of anamorphically
Anamorphic widescreen
Anamorphic widescreen, when applied to DVD manufacture, is a video process that horizontally squeezes a widescreen image so that it can be stored in a standard 4:3 aspect ratio DVD image frame. Compatible playback equipment can then re-expand the horizontal dimension to show the original widescreen...
"un-squeezed" NTSC DVD widescreen video and considered a "safe" resolution that does not crop any of the image. It is called Full WVGA to distinguish it from other, narrower WVGA resolutions which require cropping 16:9 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
high-definition video
High-definition video
High-definition video or HD video refers to any video system of higher resolution than standard-definition video, and most commonly involves display resolutions of 1,280×720 pixels or 1,920×1,080 pixels...
(i.e. it is full width, albeit with considerable reduction in size
Image scaling
In computer graphics, image scaling is the process of resizing a digital image. Scaling is a non-trivial process that involves a trade-off between efficiency, smoothness and sharpness. As the size of an image is increased, so the pixels which comprise the image become increasingly visible, making...
). The 854 pixel width is rounded up from . . Since a pixel must be a whole number, rounding up to 854 ensures inclusion of the entire image. Due to physical devices often being manufactured with pixel resolutions that are multiples of 16, the horizontal resolution of 854 may be implemented by the OS simply pretending the 10 edgemost columns, from a full physical width of 864, don't exist.
As of 2011, mobile phones with FWVGA display resolution are becoming more common. A list of mobile phones with FWVGA displays is available.
SVGA (800×600)
Super Video Graphics Array or Ultra Video Graphics Array, almost always abbreviated to Super VGA, Ultra VGA or just SVGA or UVGA is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standardComputer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
s.
Originally, it was an extension to the VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
standard first released by IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
in 1987. Unlike VGA—a purely IBM-defined standard—Super VGA was defined by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), an open consortium set up to promote interoperability and define standards. When used as a resolution specification, in contrast to VGA or XGA for example, the term SVGA normally refers to a resolution of 800 × 600 pixels.
WSVGA (1024×576/600)
The Wide version of SVGA is known as WSVGA, featured on Ultra-Mobile PCUltra-Mobile PC
An ultra-mobile PC is a small form factor version of a pen computer, a class of laptop whose specifications were launched by Microsoft and Intel in spring 2006. Sony had already made a first attempt in this direction in 2004 with its Vaio U series, which was however only sold in Asia...
s, netbooks, and tablet computer
Tablet computer
A tablet computer, or simply tablet, is a complete mobile computer, larger than a mobile phone or personal digital assistant, integrated into a flat touch screen and primarily operated by touching the screen...
s. The resolution is either 1024×576 or 1024×600 with screen sizes normally ranging from 7 to 10 inches. The aspect ratio is approximately 5:3 or 16:9. Some netbooks with 11.6 inch screens use 1366×768 (16:9 aspect ratio).
Extended graphics array
| Name | x (px) | y (px) | x:y | x*y (Mpx) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XGA | 1024 | 768 | 4:3 | 0.786 |
| WXGA | 1280 | 720 | 16:9 | 0.922 |
| WXGA | 1280 | 768 | 5:3 | 0.983 |
| WXGA | 1280 | 800 | 8:5 | 1.024 |
| WXGA | 1360 | 768 | ~16:9 | 1.044 |
| WXGA | 1366 | 768 | ~16:9 | 1.049 |
| XGA+ | 1152 | 864 | 4:3 | 0.995 |
| WXGA+ | 1440 | 900 | 8:5 | 1.296 |
| SXGA | 1280 | 1024 | 5:4 | 1.310 |
| SXGA+ | 1400 | 1050 | 4:3 | 1.470 |
| WSXGA+ | 1680 | 1050 | 8:5 | 1.764 |
| UXGA | 1600 | 1200 | 4:3 | 1.920 |
| WUXGA | 1920 | 1200 | 8:5 | 2.304 |
XGA (1024×768)
XGA, the Extended Graphics Array, is an IBM display standard introduced in 1990. Today, it is the most common appellation of the 1024×768 pixels display resolutionDisplay resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
, but the official definition is broader than that. It was not a new and improved replacement for Super VGA, but rather became one particular subset of the broad range of capabilities covered under the "Super VGA" umbrella.
The initial version of XGA expanded upon IBM's VGA
Video Graphics Array
Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution...
, adding support for two resolutions:
- 800×600 pixels with high color (16 bits per pixel; i.e.. 65,536 colors).
- 1024×768 pixels with a palettePalette (computing)In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,...
of 256 colors (8 bits per pixel)
Like its predecessor (the IBM 8514), XGA offered fixed function hardware acceleration
Hardware acceleration
In computing, Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware to perform some function faster than is possible in software running on the general-purpose CPU...
to offload processing of 2D drawing tasks. XGA and 8514 could offload line-draw, bitmap-copy (bitblt), and color-fill operations from the host CPU
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
. XGA's acceleration was faster than 8514's, and more comprehensive in that it supported more drawing primitives and XGA's 16 bits per pixel (65,536 color) display-mode.
XGA-2 added Truecolor mode for 640×480, high color mode and higher refresh rate
Refresh rate
The refresh rate is the number of times in a second that a display hardware draws the data...
s for 1024×768, and improved accelerator performance. All XGA modes have a 4:3 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
rounded to 8 pixels.
XGA should not be confused with EVGA
Extended Video Graphics Array
Extended Video Graphics Array is a standard created by VESA in 1991 denoting a non-interlaced resolution of 1024x768 at a maximum of 70Hz refresh rate. EVGA is similar to the IBM XGA standard.- External links :...
(Extended Video Graphics Array), a contemporaneous VESA
VESA
VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
standard.
WXGA (1280×768)
Wide eXtended Graphics Array (Wide XGA or WXGA) is a set of non standard resolutions derived from the XGA display standard by widening it to a wide screen aspect ratioAspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
. WXGA is commonly used for low-end LCD TVs and LCD computer monitors for widescreen presentation.
When referring to televisions and other monitors intended for consumer entertainment use, WXGA is generally understood to refer to a resolution of 1366(1365.333)×768, with an aspect ratio of 16:9. In 2006 this was the most popular resolution for liquid crystal display television
Liquid crystal display television
Liquid-crystal display televisions are television sets that use LCD display technology to produce images. LCD televisions are thinner and lighter than cathode ray tube of similar display size, and are available in much larger sizes...
s while XGA was for Plasma
Plasma display
A plasma display panel is a type of flat panel display common to large TV displays or larger. They are called "plasma" displays because the technology utilizes small cells containing electrically charged ionized gases, or what are in essence chambers more commonly known as fluorescent...
TVs flat panel display
Flat panel display
Flat panel displays encompass a growing number of electronic visual display technologies. They are far lighter and thinner than traditional television sets and video displays that use cathode ray tubes , and are usually less than thick...
s.
When referring to laptop displays or monitors intended primarily as computer displays, WXGA is most commonly used to refer to a resolution of 1280×800 pixels with an aspect ratio of 16:10. This resolution is particularly popular for most laptops with a 14" or 15" screen. The exact resolution this refers to is somewhat variable, however, as the 1280xnnn resolutions were among the first widescreen resolutions commonly used, and term entered use (especially for laptop displays) before the broad standardization 16:10 for widescreen computer displays.
Overall, several resolutions have been labeled as WXGA. These are the most common resolutions given the label (in ascending order by total number of pixels):
- 1280×720
- 1280×768
- 1280×800
- 1360×768
- 1366×768
1280×720 provides perfectly square pixels at an aspect ratio of 16:9, while the additional pixels in 1280×768 and 1280×800 must be ignored to give the 16:9 ratio without vertical stretching of the image. 1360×768 and 1366×768 come very close to 16:9, displaying exactly square pixels if 1360×765 pixels of the display are used.
Recent widespread availability of 1280×800 pixel resolution LCDs for laptop monitors can be considered an OS
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
driven evolution from the formerly popular 1024×768 screen size. In Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
specifically, the task bar when fit to the bottom of the screen occupies about 30 pixels, allowing a program window
Window (computing)
In computing, a window is a visual area containing some kind of user interface. It usually has a rectangular shape that can overlap with the area of other windows...
sized 1024×768 pixels to fit on screen without obstruction(800-768=32). Operating the Windows Sidebar in Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
can use the remaining width of 256 pixels (1280-1024).
720p
720p
720p is the shorthand name for 1280x720, a category of High-definition television video modes having a resolution of 1080 or 720p and a progressive scan...
is a related HDTV video display resolution measuring 1280×720 pixels.
1440×900 resolution displays have also been found labeled as WXGA; however, the correct label is actually WSXGA or WXGA+.
XGA+ (1152×864)
XGA+ stands for eXtended Graphics Array Plus and is a computer display standardComputer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
. XGA+ is often used on 17 inch desktop CRT
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
monitors. XGA+ is usually understood to refer to the 1152×864 resolution with an aspect ratio of 4:3. As widescreen LCD are getting increasingly popular, this resolution is decreasing in use, but it is the native resolution of some 17 inch 4:3 LCD displays.
Historically, the resolution relates to the earlier standard of 1152×900 pixels, which was adopted by Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. was a company that sold :computers, computer components, :computer software, and :information technology services. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982...
for the Sun-2
Sun-2
The Sun-2 series of UNIX workstations and servers was launched by Sun Microsystems in November 1983. As the name suggests, the Sun-2 represented the second generation of Sun systems, superseding the original Sun-1 series...
workstation
Workstation
A workstation is a high-end microcomputer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems...
in the early 1980s. This resolution is close to the maximum practical which, using one byte
Byte
The byte is a unit of digital information in computing and telecommunications that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, a byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the basic addressable element in many computer...
per pixel, can fit into a video memory or frame-buffer of one megabyte
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
. However, its aspect ratio is 3.84:3 (1.28:1). When Apple Computer
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs and markets consumer electronics, computer software, and personal computers. The company's best-known hardware products include the Macintosh line of computers, the iPod, the iPhone and the iPad...
defined a standard resolution for 21-inch CRT monitors, intended for use as Two-Page Displays on the Macintosh II
Macintosh II
The Apple Macintosh II was the first personal computer model of the Macintosh II series in the Apple Macintosh line and the first Macintosh to support a color display.- History :...
computer, Apple selected instead 1152×864, which is the highest 4:3 resolution below one million pixels.
XGA+ is the next step after XGA (1024×768), although it's not approved by any standard organizations. The next step with an aspect ratio of 4:3 is 1280×960 ("SXGA-") or SXGA+ (1400×1050).
WXGA+ (1440×900)
WXGA+ and WSXGA are non-standard terms referring to computer display resolutions. Usually they refer to a resolution of 1440×900, but occasionally manufacturers use other terms to refer to this resolution (for example, http://www.renesas.com/fmwk.jsp?cnt=press_release20050912.htm&fp=/company_info/news_and_events/press_releases). The Standard Panels Working Group refers to the 1440×900 resolution as WXGA(II).WSXGA and WXGA+ can be considered enhanced versions of WXGA with more pixels, or as widescreen variants of SXGA. The aspect ratios of each are 16:10 (widescreen
Widescreen
Widescreen images are a variety of aspect ratios used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than the standard 1.37:1 Academy aspect ratio provided by 35mm film....
).
WXGA+ (1440×900) resolution is common in 19" widescreen desktop monitors (a very small number of such monitors uses WSXGA+), and is also optional, although less common, in laptop
Laptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
LCDs, in sizes ranging from 12.1" to 17".
SXGA (1280×1024)
SXGA is an acronym for Super eXtended Graphics Array referring to a standard monitorComputer display
A monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
resolution of 1280×1024 pixels. This display resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
is the "next step" above the XGA resolution that IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
developed in 1990.
The 1280×1024 resolution is not the standard 4:3 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
, but 5:4 (1.25:1 instead of 1.333:1). A standard 4:3 monitor using this resolution will have rectangular rather than square pixels, meaning that unless the software compensates for this the picture will be distorted, causing circles to appear elliptical. There is a less common 1280×960 resolution sometimes unofficially called "SXGA-" (to avoid confusion with the "standard" SXGA) that preserves the common 4:3 aspect ratio.
SXGA is the most common native resolution of 17" and 19" LCD
Liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
monitors. An LCD monitor with SXGA native resolution will typically have a physical 5:4 aspect ratio, preserving a 1:1 pixel aspect ratio
Pixel aspect ratio
Pixel aspect ratio is a mathematical ratio that describes how the width of a pixel in a digital image compares to the height of that pixel....
.
Apple Computer
Apple Computer
Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs and markets consumer electronics, computer software, and personal computers. The company's best-known hardware products include the Macintosh line of computers, the iPod, the iPhone and the iPad...
referred to displays with this resolution as "two-page displays", because they could be used to display two A4 pages
Paper size
Many paper size standards conventions have existed at different times and in different countries. Today there is one widespread international ISO standard and a localised standard used in North America . The paper sizes affect writing paper, stationery, cards, and some printed documents...
side-by-side at a resolution of 72 dots per inch
Dots per inch
Dots per inch is a measure of spatial printing or video dot density, in particular the number of individual dots that can be placed in a line within the span of 1 inch . The DPI value tends to correlate with image resolution, but is related only indirectly.- DPI measurement in monitor...
. Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
manufactured a 17" CRT
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
monitor with a 5:4 aspect ratio designed for this resolution. It was sold under the Apple brand name.
SXGA is also a popular resolution for cell phone cameras, such as the Motorola Razr and most Samsung and LG phones. Although being taken over by newer UXGA (2.0 megapixel) cameras, the 1.3 megapixel was the most common around 2007.
Any CRT that can run 1280×1024 can also run 1280×960, which has the standard 4:3 ratio. Displaying any 4:3 resolution on a 5:4 monitor, like a TFT with a native resolution of 1280×1024, will look stretched. But on a TFT, displaying any other resolution than the native one is not a good idea anyway, as the image needs to be interpolated to fit in the fixed grid display (and some TFT displays do not allow a user to disable this and use a letterbox format).
The 1280×1024 resolution became popular because at 24-bit color it fit well into 4 megabyte
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
s of video RAM. At the time, memory was extremely expensive. Using 1280×1024 at 24-bit color depth
Color depth
In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
allowed using 3.75 MiB
Binary prefix
In computing, a binary prefix is a specifier or mnemonic that is prepended to the units of digital information, the bit and the byte, to indicate multiplication by a power of 2...
of video RAM, fitting nicely with VRAM
VRAM
Video RAM, or VRAM, is a dual-ported variant of dynamic RAM , which was once commonly used to store the framebuffer in some graphics adapters....
chip sizes which were available at the time (4 MiB).
- 1280 px × 1024 px = 1,310,720 px
- 1,310,720 px × 8 bit/px = 10,485,760 bit
- 10,485,760 bit ÷ 8 bit/byte = 1,310,720 byte ÷ 1,0242 byte/MiB = 1.25 MiB
- 1,310,720 px × 24 bit/px = 31,457,280 bit
- 31,457,280 bit ÷ 8 bit/byte = 3,932,160 byte ÷ 1,0242 byte/MiB = 3.75 MiB
SXGA+ (1400×1050)
SXGA+ stands for Super eXtended Graphics Array Plus and is a computer display standardComputer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
. An SXGA+ display is commonly used on 14 inch or 15 inch laptop
Laptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
LCD screens with a resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
of 1400×1050 pixels. An SXGA+ display is used on a few 12 inch laptop screens such as the ThinkPad
ThinkPad
ThinkPad is line of laptop computers originally sold by IBM but now produced by Lenovo. They are known for their boxy black design, which was modeled after a traditional Japanese lunchbox...
X60 & X61 (both only as tablet) as well as the Toshiba
Toshiba
is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and...
Portégé M200 and M400, but these are far less common. Dell offered a 14.1" SXGA+ screen on the many of the Dell Latitude "C" series laptops, such as the C640 and the C810. Sony also used SXGA+ in their Z1 series, but no longer produce them as wide screen has become more predominant.
There is a widescreen
Widescreen
Widescreen images are a variety of aspect ratios used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than the standard 1.37:1 Academy aspect ratio provided by 35mm film....
version of SXGA+ called WSXGA+ with a resolution of 1680×1050. This is a common native resolution of 19-22 inch wide-aspect LCD monitors, and is also available on many laptops.
It is the next common step in resolution after SXGA, although it is not approved by any organization. The most common resolution immediately above is called UXGA (sometimes also known as UGA) which has 1600×1200 pixels.
In desktop LCDs, SXGA+ is used on some low-end 20" monitors, whereas most of the 20" LCDs use UXGA (standard screen ratio), or WSXGA+ (widescreen ratio).
WSXGA+ (1680×1050)
WSXGA+ stands for Widescreen Super eXtended Graphics Array Plus and is a computer display standardComputer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
. A WSXGA+ display is commonly used on Widescreen 20", 21", and popular 22" LCD monitors from numerous manufacturers (and a very small number of 19" widescreen monitors), as well as widescreen 15.4" and 17" laptop
Laptop
A laptop, also called a notebook, is a personal computer for mobile use. A laptop integrates most of the typical components of a desktop computer, including a display, a keyboard, a pointing device and speakers into a single unit...
LCD screens like the Thinkpad
ThinkPad
ThinkPad is line of laptop computers originally sold by IBM but now produced by Lenovo. They are known for their boxy black design, which was modeled after a traditional Japanese lunchbox...
T61 and the Apple 15" MacBook Pro
MacBook Pro
The MacBook Pro is a line of Macintosh portable computers introduced in January 2006 by Apple. It replaced the PowerBook G4 and was the second model, after the iMac, to be announced in the Apple–Intel transition...
. The resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
is 1680×1050 pixels (1,764,000 pixels) and has a 16:10 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
.
WSXGA+ is the widescreen version of SXGA+, but it is not approved by any organization. The next highest resolution (for widescreen) after it is WUXGA, which is 1920×1200 pixels.
UXGA (1600×1200)
UXGA is an abbreviation for Ultra eXtended Graphics Array referring to a standard monitorComputer display
A monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
of 1600×1200 pixels (totaling 1,920,000 pixels), which is exactly four times the default resolution
Image resolution
Image resolution is an umbrella term that describes the detail an image holds. The term applies to raster digital images, film images, and other types of images. Higher resolution means more image detail....
of SVGA (800×600) (totaling 480,000 pixels). Dell Computer refers to the same resolution of 1,920,000 pixels as UGA. It is generally considered to be the next step above SXGA (1280×960 or 1280×1024), but some resolutions (such as the unnamed 1366×1024 and SXGA+ at 1400×1050) fit between the two.
UXGA has been the native resolution of many fullscreen monitors of 15" or more, including laptop LCDs such as the ones in ThinkPad
ThinkPad
ThinkPad is line of laptop computers originally sold by IBM but now produced by Lenovo. They are known for their boxy black design, which was modeled after a traditional Japanese lunchbox...
A21p, A31p, T42p, and T43p; Dell Inspiron 8000/8100/8200; Panasonic Toughbook CF-51; and the original Alienware Area 51m. However, in more recent times, UXGA is not used in laptops at all but rather in desktop UXGA monitors that have been made in sizes of 20" and 21.3". Some 14" laptop LCDs with UXGA have also existed, but these were very rare.
There are two different widescreen
Widescreen
Widescreen images are a variety of aspect ratios used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than the standard 1.37:1 Academy aspect ratio provided by 35mm film....
cousins of UXGA, one called UWXGA with 1600×768 (750) and one called WUXGA with 1920×1200 resolution.
WUXGA (1920×1200)
WUXGA stands for WidescreenWidescreen
Widescreen images are a variety of aspect ratios used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ratio greater than the standard 1.37:1 Academy aspect ratio provided by 35mm film....
Ultra eXtended Graphics Array and is a display resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
of 1920×1200 pixels (2,304,000 pixels) with a 16:10 screen aspect ratio
Aspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
.
It is a wide version of UXGA, and can be used for viewing high-definition television
High-definition television
High-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
(HDTV) content, which uses a 16:9 aspect ratio and a 1920x1080 resolution.
The 16:10 aspect ratio (as opposed to the 16:9 used in widescreen televisions) was chosen because this aspect ratio is appropriate for displaying two full pages of text side by side.
WUXGA resolution is equivalent to 2.3 megapixels. An 8-bit RGB WUXGA image has an uncompressed size of around 6.6 MiB
Mebibyte
The mebibyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. The binary prefix mebi means 220, therefore 1 mebibyte is . The unit symbol for the mebibyte is MiB. The unit was established by the International Electrotechnical Commission in 2000 and has been accepted for use by all major...
. This was the highest resolution that was ever commonly available in the computer display industry, but its use had been almost completely ended by 2010 as the computer industry moved to the 16:9 aspect ratio (i.e., 1920x1080 is the highest resolution available from most laptop and computer monitor manufacturers). This resolution is currently available in a few high-end LCD
Liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
s and computer monitors, the latter of which are typically in the size range of approximately 23"–28" for desktop monitors, but has become almost completely unavailable on notebook monitors. A small number of 22" WUXGA desktop monitors exist (i.e., Lenovo L220x and Samsung T220P). WUXGA use predates the introduction of LCDs of that resolution. Most QXGA displays support 1920×1200 and widescreen CRTs
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
such as the Sony GDM-FW900 and Hewlett Packard A7217A do as well.
The next lower resolution (for widescreen) before it is WSXGA+, which is 1680×1050 pixels (1,764,000 pixels, or 30.61% fewer than the WUXGA); the next higher resolution widescreen is an unnamed 2304×1440 resolution (supported by the above GDM-FW900 & A7217A) and then the more common WQXGA, which has 2560×1600 pixels (4,096,000 pixels, or 77.78% more than WUXGA).
There are two wider formats called UWXGA 1600×768 (25:12) and UW-UXGA that has 2560×1080 pixels, a 2.37:1 or 21⅓:9 or 64:27 aspect ratio, sometimes erroneously labeled 21:9.
Quad-extended graphics array
| Name | x (px) | y (px) | x:y | x*y (Mpx) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QWXGA | 2048 | 1152 | 16:9 | 2.359 |
| QXGA | 2048 | 1536 | 4:3 | 3.145 |
| WQXGA | 2560 | 1600 | 8:5 | 4.096 |
| QSXGA | 2560 | 2048 | 5:4 | 5.242 |
| WQSXGA | 3200 | 2048 | 25:16 | 6.553 |
| QUXGA | 3200 | 2400 | 4:3 | 7.680 |
| WQUXGA | 3840 | 2400 | 8:5 | 9.216 |
The QXGA, or Quad eXtended Graphics Array, display standard is a resolution standard in display technology. Their high pixel counts and heavy display hardware requirements mean that there are currently few CRT
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
and LCD
Liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
monitors that have pixel counts at these levels. These terms are currently reserved for the highest-end consumer computer display
Computer display
A monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
hardware for those buying LCDs.
WQXGA is often found in 30" displays like the Dell 3008WFP and the Apple Cinema Display
Apple Cinema Display
The Apple Cinema Display was a line of flat panel computer monitors introduced in September 1999 by Apple Inc. It was initially sold alongside the older line of Studio Displays, but eventually replaced them. In July 2011, Apple replaced it with the Apple Thunderbolt Display...
. As of 2010, there are few WQXGA displays in the consumer marketplace, but their price is higher than most displays used by graphic professionals, and their refresh speed is not close to that used in current consumer displays. It is unlikely that WQXGA, or next-generation HXGA, displays will be commonplace before 2015. It should also be noted, however, that many standard 21"/22" CRT monitors can be used at the QXGA resolution. Some of the highest-end 19" CRTs also support this resolution.
In 2010 WQXGA made its debut in a handful of home theater projectors targeted at the Contant Height Screen application market. Both Digital Projection Inc and projectiondesign released models based on a Texas Instrument DLP chip with a native WQXGA resolution, alleviating the need for an anamorphic lens to achieve 1:2.35 image projection.
QWXGA (2048×1152)
QWXGA (Quad Wide eXtended Graphics Array) is a display resolutionDisplay resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
of 2048×1152 pixels with a 16:9
16:9
16:9 is an aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9. Since 2009, it has become the most common aspect ratio for sold televisions and computer monitors and is also the international standard format of HDTV, Full HD, non-HD digital television and analog widescreen television ...
aspect ratio
Aspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
. A few LCD QWXGA monitors are available with 23 and 27 inch displays, such as the Acer B233HU (23") and B273HU (27"), the Dell
Dell
Dell, Inc. is an American multinational information technology corporation based in 1 Dell Way, Round Rock, Texas, United States, that develops, sells and supports computers and related products and services. Bearing the name of its founder, Michael Dell, the company is one of the largest...
SP2309W, and the Samsung
Samsung
The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
2343BWX.
QXGA (2048×1536)
QXGA (Quad eXtended Graphics Array) is a display resolutionDisplay resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
of 2048×1536 pixels with a 4:3 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
. The name comes from it having four times as many pixels as an XGA display. As of 2007, this is the highest non-experimental and non-widescreen resolution, and the number of monitors that can display images at this resolution are somewhat limited, especially among LCDs. The number of CRT monitors offering this resolution has actually dropped off, as CRT makers such as NEC
NEC
, a Japanese multinational IT company, has its headquarters in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. NEC, part of the Sumitomo Group, provides information technology and network solutions to business enterprises, communications services providers and government....
and Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
have stopped offering their higher end models. Examples of LCDs with this resolution are the IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
T210 and the Eizo
Eizo
, or EIZO, is a manufacturer of high-end computer displays. A Japanese corporation, it was founded in March 1968 but did not adopt its current name until 1999 when Nanao Corporation and Eizo merged...
G33 and R31 screens, but in CRT monitors this resolution is much more common; some examples include the ViewSonic
ViewSonic
ViewSonic Corporation is a manufacturer and provider of visual technology, specifically CRT monitors, liquid crystal displays, projectors, plasma displays, HDTV technology, and mobile products, including Mini and All-in-One PCs and wireless monitors....
G225fB, NEC
NEC
, a Japanese multinational IT company, has its headquarters in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. NEC, part of the Sumitomo Group, provides information technology and network solutions to business enterprises, communications services providers and government....
FP2141SB or Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi
The Mitsubishi Group , Mitsubishi Group of Companies, or Mitsubishi Companies is a Japanese multinational conglomerate company that consists of a range of autonomous businesses which share the Mitsubishi brand, trademark and legacy...
DP2070SB, Iiyama
Iiyama (company)
is a manufacturer of high end computer monitors, medical monitors and televisions, named after the city Iiyama in Nagano, Japan. The company was founded in 1973....
Vision Master Pro 514, and Dell
Dell
Dell, Inc. is an American multinational information technology corporation based in 1 Dell Way, Round Rock, Texas, United States, that develops, sells and supports computers and related products and services. Bearing the name of its founder, Michael Dell, the company is one of the largest...
and HP P1230. Of these monitors, none is still in production. A related display size is WQXGA, which is a wide screen version. CRTs offer a way to achieve QXGA cheaply. Models like the Mitsubishi Diamond Pro 2045U and IBM ThinkVision C220P retailed for around 200 USD, and even higher performance ones like the ViewSonic PerfectFlat P220fB remained under 500 USD. As recently as last year, many off-lease P1230s could be found on eBay for under 150 USD. The LCDs with WQXGA or QXGA resolution typically cost 4 to 5 times more for the same resolution. IDTech manufactured a 15" QXGA IPS panel. NEC had sold laptops with QXGA screens in 2002-2005 for Japanese market.
WQXGA (2560×1600)
WQXGA (Wide Quad eXtended Graphics Array) is a display resolutionDisplay resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
of 2560×1600 pixels with a 16:10 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
. The name comes from it being a wide version of QXGA and having four times as many pixels as an WXGA (1280×800) display.
Before 2007, devices that could display this resolution were very rare, but many manufacturers have since come out with a 27"–30" model that is capable of WQXGA, albeit at a much higher price than lower resolution monitors of the same size. Several mainstream WQXGA monitors are available with 30 inch displays, such as the Apple Cinema Display
Apple Cinema Display
The Apple Cinema Display was a line of flat panel computer monitors introduced in September 1999 by Apple Inc. It was initially sold alongside the older line of Studio Displays, but eventually replaced them. In July 2011, Apple replaced it with the Apple Thunderbolt Display...
, the Dell UltraSharp 3007WFP-HC
Dell monitors
Dell sells LCD-based computer monitors. Dell bundles monitors with its desktop computers as package deals, as well as selling them separately through their online store and some other retailers...
, Dell UltraSharp 3008WFP and Dell UltraSharp 3011, the Hewlett-Packard
Hewlett-Packard
Hewlett-Packard Company or HP is an American multinational information technology corporation headquartered in Palo Alto, California, USA that provides products, technologies, softwares, solutions and services to consumers, small- and medium-sized businesses and large enterprises, including...
LP3065, the Gateway
Gateway, Inc.
Gateway Computer Corporation, is a computer hardware company headquartered in Irvine, California, USA which develops, manufactures, supports, and markets a wide range of personal computers, computer monitors, servers, and computer accessories...
XHD3000, and the Samsung
Samsung
The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
305T. Specialist manufacturers like Eizo
Eizo
, or EIZO, is a manufacturer of high-end computer displays. A Japanese corporation, it was founded in March 1968 but did not adopt its current name until 1999 when Nanao Corporation and Eizo merged...
, Planar Systems
Planar Systems
Planar Systems, Inc. is a U.S. digital display manufacturing corporation based in Hillsboro, Oregon. Founded in 1983 as a spin-off from Tektronix, it was the first U.S. manufacturer of electroluminescent digital displays. Planar also makes a variety of other specialty displays. The company, with...
, Barco
Barco
Barco N.V. is a display hardware manufacturer specialising in video projectors, LCD projectors, DLP projectors, LCoS projectors, LED displays, video walls, flat panel displays, automated luminaires, digital lighting and lighting controls....
(LC-3001), and possibly others offer similar models.
One feature which is currently unique to the 30" WQXGA monitors is the ability to function as the centerpiece and main display of a three-monitor array of complementary aspect ratios, with two UXGA (1600×1200) 20" monitors turned vertically on either side. The resolutions are equal, and the size of the 1600 resolution edges (if the manufacturer is honest) is within a tenth of an inch (16" vs. 15.89999"), presenting a "picture window view" without the extreme lateral dimensions, small central panel, asymmetry, resolution differences, or dimensional difference of other three-monitor combinations. The resulting 4960×1600 composite image has a 3.1:1 aspect ratio.
Of course, this also means one UXGA 20" monitor in portrait orientation can also be flanked by two 30" WQXGA monitors for a 6320×1600 composite image with a 11.85:3 (79:20, 3.95:1) aspect ratio.
QSXGA (2560×2048)
QSXGA (Quad Super eXtended Graphics Array) is a display resolution of 2560×2048 pixels with a 5:4 aspect ratioAspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
. Grayscale monitors with a 2560×2048 resolution, primarily for medical use, are available from Planar Systems
Planar Systems
Planar Systems, Inc. is a U.S. digital display manufacturing corporation based in Hillsboro, Oregon. Founded in 1983 as a spin-off from Tektronix, it was the first U.S. manufacturer of electroluminescent digital displays. Planar also makes a variety of other specialty displays. The company, with...
(Dome E5), Eizo
Eizo
, or EIZO, is a manufacturer of high-end computer displays. A Japanese corporation, it was founded in March 1968 but did not adopt its current name until 1999 when Nanao Corporation and Eizo merged...
(Radiforce G51), Barco
Barco
Barco N.V. is a display hardware manufacturer specialising in video projectors, LCD projectors, DLP projectors, LCoS projectors, LED displays, video walls, flat panel displays, automated luminaires, digital lighting and lighting controls....
(Nio 5,MP), WIDE
Wide-angle Infinity Display Equipment
Wide-angle Infinity Display Equipment , the proprietary name for a cross-cockpit collimated display wide-angle display system invented by the UK Rediffusion company at their factory at Crawley, near Gatwick, UK, now part of Thales UK. The general design is now in common use in most Full flight...
(IF2105MP), IDTech (IAQS80F) and possibly others.
A similar resolution of 2560×1920 (4:3) was supported by a small number of CRT displays via VGA such as the Viewsonic P225f when paired with the right graphics card.
WQSXGA (3200×2048)
WQSXGA (Wide Quad Super eXtended Graphics Array) describes a display standard that can support a resolution up to 3200×2048 pixels, assuming a 1.56:1 (25:16) aspect ratio. As of July 2008, the Coronis Fusion 6MP DL by BarcoBarco
Barco N.V. is a display hardware manufacturer specialising in video projectors, LCD projectors, DLP projectors, LCoS projectors, LED displays, video walls, flat panel displays, automated luminaires, digital lighting and lighting controls....
supports 3280×2048 (approx. 16:10).
QUXGA (3200×2400)
QUXGA (Quad Ultra Extended Graphics Array) describes a display standard that can support a resolution up to 3200×2400 pixels, assuming a 4:3 aspect ratio.WQUXGA (3840×2400)
WQUXGA (Wide Quad Ultra eXtended Graphics Array) describes a display standard that supports a resolution of 3840×2400 pixels, which provides a 16:10 aspect ratio. This resolution is exactly four times 1920×1200 (in pixels).In June 2001, WQUXGA was introduced in the IBM T220 LCD monitor
Computer display
A monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
using a LCD panel built by IDTech. LCD displays that support WQUXGA resolution include: IBM T220, IBM T221 (models DG1, DG3, DG4, DG5), Iiyama
Iiyama (company)
is a manufacturer of high end computer monitors, medical monitors and televisions, named after the city Iiyama in Nagano, Japan. The company was founded in 1973....
AQU5611DTBK, ViewSonic
ViewSonic
ViewSonic Corporation is a manufacturer and provider of visual technology, specifically CRT monitors, liquid crystal displays, projectors, plasma displays, HDTV technology, and mobile products, including Mini and All-in-One PCs and wireless monitors....
VP2290, ADTX MD22292B and IDTech MD22292 (models B0, B1, B2, B5, C0, C2). IDTech was the original equipment manufacturer which sold these monitors to ADTX, IBM
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
, Iiyama
Iiyama (company)
is a manufacturer of high end computer monitors, medical monitors and televisions, named after the city Iiyama in Nagano, Japan. The company was founded in 1973....
, and ViewSonic
ViewSonic
ViewSonic Corporation is a manufacturer and provider of visual technology, specifically CRT monitors, liquid crystal displays, projectors, plasma displays, HDTV technology, and mobile products, including Mini and All-in-One PCs and wireless monitors....
.
Most display cards with a DVI connector are capable of supporting the 3840×2400 resolution. However, the maximum refresh rate will be limited by the number of DVI links which are connected to the monitor. 1, 2, or 4 DVI connectors are used to drive the monitor using various tile configurations. Only the IBM T221-DG5 and IDTech MD22292B5 support the use of dual-link DVI ports through an external converter box.
Many systems using these monitors use at least 2 DVI connectors to send video to the monitor. These DVI connectors can be from the same graphics card, different graphics cards, or even different computers. Motion across the tile boundary(ies) can show tearing if the DVI links are not synchronized. The display panel can be updated at a speed between 0 Hz and 41 Hz (48 Hz for the IBM T221-DG5, and IDTech MD22292B5). The refresh rate of the video signal can be higher than 41 Hz (or 48 Hz) but the monitor will not update the display any faster if graphics card(s) do so.
There was one series of WQUXGA displays in the consumer marketplace, but it was discontinued in Q2 of 2005. That series of displays had prices which were well above even the higher end displays used by graphic professionals. In addition, the lower refresh rates, 41 Hz and 48 Hz, made them less attractive for many applications.
As of January 2007, none of the WQUXGA monitors (IBM, ViewSonic, Iiyama, ADTX) are in production anymore. Toshiba announced its intention to market a new WQUXGA 22" monitor in November 2007. However, it has not done so to date. Neither Toshiba nor public speculation on the Internet has provided any new information since the November 2007 press release.
WQUXGA is the maximum resolution supported by DisplayPort
DisplayPort
DisplayPort is a digital display interface standard produced by the Video Electronics Standards Association . The specification defines a royalty-free digital interconnect for audio and video. The interface is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device such as a computer monitor...
1.2, though actually displaying such a resolution on a device with DisplayPort 1.2 is dependent on the graphics system in much the same way devices with VGA connectors do not necessarily maximize that standard's highest possible resolution.
Hyper-extended graphics array
| Name | x (px) | y (px) | x:y | x*y (Mpx) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HXGA | 4096 | 3072 | 4:3 | 12.582 |
| WHXGA | 5120 | 3200 | 8:5 | 16.384 |
| HSXGA | 5120 | 4096 | 5:4 | 20.971 |
| WHSXGA | 6400 | 4096 | 25:16 | 26.214 |
| HUXGA | 6400 | 4800 | 4:3 | 30.720 |
| WHUXGA | 7680 | 4800 | 8:5 | 36,864 |
The HXGA display standard and its derivatives are a standard in display technology. Their high pixel counts and heavy display hardware requirements mean that there is currently no monitor
Computer display
A monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
that singly displays at these levels. These terms are currently reserved for digital camera
Digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that takes video or still photographs, or both, digitally by recording images via an electronic image sensor. It is the main device used in the field of digital photography...
hardware. An example can be found in HIPerSpace of a case where multiple WQXGA displays must be stacked to exceed HXGA or WHXGA resolution.
HXGA (4096×3072)
HXGA an abbreviation for HexWHXGA (5120×3200)
WHXGA an abbreviation for Wide HexHSXGA (5120×4096)
HSXGA, an abbreviation for HexAs of January 2007, there is no display with a maximum resolution 5120×4096. If this display were to exist, it would have a maximum resolution 10 times that of the 1080 ATSC HDTV video standard.
WHSXGA (6400×4096)
WHSXGA, an abbreviation for Wide HexHUXGA (6400×4800)
HUXGA, an abbreviation for HexWHUXGA (7680×4800)
WHUXGA an abbreviation for Wide HexA monitor of 7680×4320 would also qualify as a WHUXGA display. UHDTV video requires a display of similar resolution (7680×4320) for properly displaying UHDTV content, which is 16 times the pixel count of the 1080 ATSC HDTV video standard.
High Definition Television
| Name | x (px) | y (px) | x:y | x*y (Mpx) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nHD | 640 | 360 | 16:9 | 0.230 |
| qHD | 960 | 540 | 16:9 | 0.518 |
| HD | 1280 | 720 | 16:9 | 0.921 |
| FHD | 1920 | 1080 | 16:9 | 2.073 |
| QHD | 2560 | 1440 | 16:9 | 3.686 |
| QFHD | 3840 | 2160 | 16:9 | 8.294 |
nHD (640×360)
nHD is a display resolution of 640×360 pixels which is exactly one ninth of a full HD 1080p1080p
1080p is the shorthand identification for a set of HDTV high-definition video modes that are characterized by 1080 horizontal lines of resolution and progressive scan, meaning the image is not interlaced as is the case with the 1080i display standard....
frame and one quarter of a 720p
720p
720p is the shorthand name for 1280x720, a category of High-definition television video modes having a resolution of 1080 or 720p and a progressive scan...
frame. 2x2 nHD frames will form one 720p frame and 3x3 nHD frames will form one 1080p frame.
One drawback of this resolution is that the vertical resolution is not an even multiple of 16 which is a common macroblock
Macroblock
Macroblock is an image compression component and technique based on discrete cosine transform used on still images and video frames. Macroblocks are usually composed of two or more blocks of pixels. In the JPEG standard macroblocks are called MCU blocks....
size for video codec
Video codec
A video codec is a device or software that enables video compression and/or decompression for digital video. The compression usually employs lossy data compression. Historically, video was stored as an analog signal on magnetic tape...
s. Video frames encoded with 16x16 pixel macroblocks would be padded to 640x368 and the added pixels would be cropped away at playback. The same is true for qHD and 1080p but the relative amount of padding is more for lower resolutions such as nHD.
To avoid storing padding data some people prefer to encode video at 624x352. When such video streams are either encoded from HD frames or played back on HD displays in full screen mode (either 720p or 1080p) they are scaled by non-integer scale factors. True nHD frames on the other hand has integer scale factors.
qHD (960×540)
qHD is a display resolution of 960×540 pixels which is exactly one quarter of a full HD 1080p1080p
1080p is the shorthand identification for a set of HDTV high-definition video modes that are characterized by 1080 horizontal lines of resolution and progressive scan, meaning the image is not interlaced as is the case with the 1080i display standard....
frame, in a 16:9 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
.
This resolution became popular for high-end smartphone displays in early 2011. Mobile phones including the HTC Sensation
HTC Sensation
The HTC Sensation is a smartphone designed and manufactured by HTC Corporation that runs the Android 2.3 Gingerbread software stack. Officially announced by HTC on April 12, 2011, the HTC Sensation was launched by Vodafone in key European markets including the UK on May 19, 2011 and by T-Mobile in...
, Motorola Droid RAZR and Motorola Atrix 4G
Motorola Atrix 4G
The Motorola Atrix 4G is a high-end Android-based smartphone by Motorola, introduced in CES 2011 on January 5, 2011. It was made available in the first quarter of 2011. It was introduced along with three other products, Motorola Xoom, Motorola Droid Bionic, and Motorola Cliq 2. It uses an NVIDIA...
have displays with the qHD resolution.
WQHD (2560×1440)
The QHD or WQHD, or Wide Quad High Definition, display standard is a resolution of 2560×1440 pixels in a 16:9 aspect ratioAspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
. It is four times the pixel resolution of the 720p
720p
720p is the shorthand name for 1280x720, a category of High-definition television video modes having a resolution of 1080 or 720p and a progressive scan...
HDTV video standard, hence the name. Their high pixel counts and heavy display hardware requirements mean that there are currently few LCD
Liquid crystal display
A liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
monitors that have pixel counts at these levels. It is a resolution found in some displays, such as the Dell UltraSharp U2711, NEC MultiSync PA271W, and the 27" iMac
IMac
The iMac is a range of all-in-one Macintosh desktop computers built by Apple. It has been the primary part of Apple's consumer desktop offerings since its introduction in 1998, and has evolved through five distinct forms....
.
In autumn 2006, Chi Mei Optoelectronics
Chi Mei
Chi Mei Corporation is a plastics producer in Taiwan. It is the largest maker of ABS resin in the world, producing about 1 million tons of ABS annually as of 1999. It has factories in Tainan and Zhenjiang...
(CMO) announced a 47" 1440 LCD panel to be released in Q2 2007; the panel was planned to finally debut at FPD International 2008 in a form on autostereoscopic
Autostereoscopy
Autostereoscopy is any method of displaying stereoscopic images without the use of special headgear or glasses on the part of the viewer. Because headgear is not required, it is also called "glasses-free 3D" or "glassesless 3D"...
3D display
3D display
A 3D display is any display device capable of conveying a stereoscopic perception of 3-D depth to the viewer. The basic requirement is to present offset images that are displayed separately to the left and right eye. Both of these 2-D offset images are then combined in the brain to give the...
.
QFHD (3840×2160)
QFHD (Quad Full High Definition) is a non-standardComputer display standard
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio, display resolution, color depth, and refresh rate.This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.-History:...
display resolution of 3840×2160 pixels arranged in a 16:9 aspect ratio
Aspect ratio (image)
The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this...
. It is four times the resolution of the 1080p
1080p
1080p is the shorthand identification for a set of HDTV high-definition video modes that are characterized by 1080 horizontal lines of resolution and progressive scan, meaning the image is not interlaced as is the case with the 1080i display standard....
HDTV video standard, hence the name (Quad meaning 4).
In early 2008, Samsung revealed a proof-of-concept 82-inch LCD TV set capable of this resolution and LG has demonstrated an 84-inch display.
Eyevis produces a 56" LCD named EYELCD 56 QHD HD while Toshiba
Toshiba
is a multinational electronics and electrical equipment corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is a diversified manufacturer and marketer of electrical products, spanning information & communications equipment and systems, Internet-based solutions and services, electronic components and...
makes the P56QHD, Mitsubishi Electric
Mitsubishi Electric
is a multinational electronics and information technology company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. It is one of the core companies of the Mitsubishi Group....
the 56P-QF60LCU, and Sony
Sony
, commonly referred to as Sony, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan and the world's fifth largest media conglomerate measured by revenues....
the SRM-L560, all which can deliver a resolution of 3840×2160. Landmark also has produced a 56" QFHD monitor, the M5600.
CMI has built a 27.84" 158 PPI QFHD IPS panel for medical displays since November 2010.
See also
- Display resolutionDisplay resolutionThe display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
- VGA
- 720p720p720p is the shorthand name for 1280x720, a category of High-definition television video modes having a resolution of 1080 or 720p and a progressive scan...
- 1080p1080p1080p is the shorthand identification for a set of HDTV high-definition video modes that are characterized by 1080 horizontal lines of resolution and progressive scan, meaning the image is not interlaced as is the case with the 1080i display standard....
- 4K resolution4K resolution4K is an emerging standard for resolution in digital film and computer graphics. The name comes from its approximately 4,000 pixels of horizontal resolution. The fact that it describes the horizontal resolution is contrary to the standard resolutions 720p and 1080p, which represent the number of...
- Mode 13hMode 13hMode 13h is the IBM VGA BIOS mode number for a specific standard 256 color mode on IBM's VGA graphics hardware. It features a resolution of 320×200 pixels and was used extensively in computer games and art/animation software of the late 1980s and early- to mid-1990s...
and Mode XMode XMode X is an alternative video graphics display mode of the IBM VGA graphics hardware that was popularized by Michael Abrash, first published in July 1991 in Dr...
, video modes in VGA (including VGA-compatible and successors to VGA, such as VESAVESAVESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
) hardware with a resolution profile similar to QVGA

