
Computer display standard
Encyclopedia
Computer display standards are often a combination of aspect ratio
, display resolution
, color depth
, and refresh rate
.
This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.
. They are often a combination of aspect ratio
(specified as width-to-height ratio), display resolution
(specified as the width and height in pixel
s), color depth
(measured in bit
s per pixel), and refresh rate
(expressed in hertz
). Associated with the screen resolution and refresh rate is a display adapter. Earlier display adapters were simple frame-buffers, but later display standards also specified a more extensive set of display functions and software controlled interface.
Beyond display modes, the VESA
industry organization has defined several standards related to power management
and device identification, while ergonomics standards are set by the TCO
.
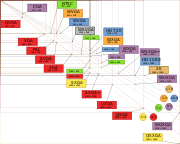
group has co-ordinated the efforts of several leading video display adapter manufacturers. Video standards associated with IBM-PC-descended personal computers are shown in the diagram and table below.
Quarter (Q or q)
Wide (W)
Quad(ruple) (Q)
Hex(adecatuple) (H)
Ultra (U)
eXtended (X)
These prefixes are also often combined, as in WQXGA or WHUXGA.
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
, display resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
, color depth
Color depth
In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
, and refresh rate
Refresh rate
The refresh rate is the number of times in a second that a display hardware draws the data...
.
This article describes the different display standards for computer displays.
History
Various computer display standards or display modes have been used in the history of the personal computerPersonal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
. They are often a combination of aspect ratio
Aspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
(specified as width-to-height ratio), display resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
(specified as the width and height in pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
s), color depth
Color depth
In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used...
(measured in bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s per pixel), and refresh rate
Refresh rate
The refresh rate is the number of times in a second that a display hardware draws the data...
(expressed in hertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
). Associated with the screen resolution and refresh rate is a display adapter. Earlier display adapters were simple frame-buffers, but later display standards also specified a more extensive set of display functions and software controlled interface.
Beyond display modes, the VESA
VESA
VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
industry organization has defined several standards related to power management
Power management
Power management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power state when inactive. In computing this is known as PC power management and is built...
and device identification, while ergonomics standards are set by the TCO
TCO Certification
TCO Certification is a series of product certifications for office equipment . It is set by TCO Development, owned by the Swedish Confederation of Professional Employees, TCO . The certifications are named after years...
.
Standards
A number of common resolutions have been used with computers descended from the original IBM PC. Some of these are now supported by other families of personal computers. These are de-facto standards, usually originated by one manufacturer and reverse-engineered by others, though the VESAVESA
VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays...
group has co-ordinated the efforts of several leading video display adapter manufacturers. Video standards associated with IBM-PC-descended personal computers are shown in the diagram and table below.

| Video standard | Full name | Description | Display resolution Display resolution The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection... (pixel Pixel In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled.... s) |
Aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... |
Color depth Color depth In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used... (2^bpp colors) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unnamed | unnamed | Various Apple Inc., Atari Atari Atari is a corporate and brand name owned by several entities since its inception in 1972. It is currently owned by Atari Interactive, a wholly owned subsidiary of the French publisher Atari, SA . The original Atari, Inc. was founded in 1972 by Nolan Bushnell and Ted Dabney. It was a pioneer in... , Commodore PCs introduced from 1977 to 1982. They used TVs for their displays and typically included a 32×40 wide border in the overscan region of the television, with a usable space of only 320×200 or 160×200 or 80×200 (approximately). They used the non-interlaced (NI) mode to provide a stable image. The non-interlaced designation was dropped after all monitors were manufactured this way. |
352×240 NI (approximately) | 4:3 | 8 or 16 colors typical. |
| unnamed | unnamed | Commodore Amiga, Atari ST Atari ST The Atari ST is a home/personal computer that was released by Atari Corporation in 1985 and commercially available from that summer into the early 1990s. The "ST" officially stands for "Sixteen/Thirty-two", which referred to the Motorola 68000's 16-bit external bus and 32-bit internals... and others. They used NTSC NTSC NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as... or PAL PAL PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system... -compliant RGB component displays or televisions. The interlaced (I) mode produced visible flickering. |
704×480 I (approximately) | 4:3 | 16 for ST or 4096 for Amiga (~256,000 for Amiga 4000 Amiga 4000 The Commodore Amiga 4000, or A4000, is the successor of the A2000 and A3000 computers. There are two models, the A4000/040 released in October 1992 with a Motorola 68040 CPU, and the A4000/030 released in April 1993 with a Motorola 68EC030.... ). |
| MDA Monochrome Display Adapter The Monochrome Display Adapter introduced in 1981 was IBM's standard video display card and computer display standard for the PC. The MDA did not have any pixel-addressable graphics modes... |
Monochrome Display Adapter | The original standard on IBM PC IBM PC The IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, is the original version and progenitor of the IBM PC compatible hardware platform. It is IBM model number 5150, and was introduced on August 12, 1981... s and IBM PC XTs with 4 KB Kilobyte The kilobyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information. Although the prefix kilo- means 1000, the term kilobyte and symbol KB have historically been used to refer to either 1024 bytes or 1000 bytes, dependent upon context, in the fields of computer science and information... video RAM. Introduced in 1981 by IBM. Supports text mode Text mode Text mode is a kind of computer display mode in which the content of the screen is internally represented in terms of characters rather than individual pixels. Typically, the screen consists of a uniform rectangular grid of character cells, each of which contains one of the characters of a... only. |
720×350 (text) | 72:35 | 1 bpp Color depth In computer graphics, color depth or bit depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel in a bitmapped image or video frame buffer. This concept is also known as bits per pixel , particularly when specified along with the number of bits used... |
| CGA Color Graphics Adapter The Color Graphics Adapter , originally also called the Color/Graphics Adapter or IBM Color/Graphics Monitor Adapter, introduced in 1981, was IBM's first color graphics card, and the first color computer display standard for the IBM PC.... |
Color Graphics Adapter | Introduced in 1981 by IBM, as the first color display standard for the IBM PC IBM PC The IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, is the original version and progenitor of the IBM PC compatible hardware platform. It is IBM model number 5150, and was introduced on August 12, 1981... . The standard CGA graphics cards were equipped with 16 KB video RAM. |
640×200 (128k) 320×200 (64k) 160×200 (32k) |
16:5 16:10 4:5 |
1 bpp 2 bpp 4 bpp |
| Hercules Hercules Graphics Card The Hercules Graphics Card was a computer graphics controller made by Hercules Computer Technology, Inc. which, through its popularity, became a widely supported display standard. It was common on IBM PC compatibles connected to a monochrome monitor . It supported one high resolution text mode and... |
A monochrome display capable of sharp text and graphics for its time of introduction. Very popular with the Lotus 1-2-3 Lotus 1-2-3 Lotus 1-2-3 is a spreadsheet program from Lotus Software . It was the IBM PC's first "killer application"; its huge popularity in the mid-1980s contributed significantly to the success of the IBM PC in the corporate environment.-Beginnings:... spreadsheet, which was one of the PC's first killer apps Killer application A killer application , in the jargon of marketing teams, has been used to refer to any computer program that is so necessary or desirable that it proves the core value of some larger technology, such as computer hardware, gaming console, software, or an operating system... . Introduced in 1982. |
720×348 (250.5k) | 60:29 | 1 bpp | |
| EGA Enhanced Graphics Adapter The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a... |
Enhanced Graphics Adapter | Introduced in 1984 by IBM. A resolution of 640×350 pixels of 16 different colors (4 bits per pixel, or bpp), selectable from a 64-color palette Palette (computing) In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,... (2 bits per each of red-green-blue). |
640×350 (224k) | 64:35 | 4 bpp |
| Professional Graphics Controller Professional Graphics Controller Professional Graphics Controller was a graphics card manufactured by IBM for the PC. It consisted of three interconnected PCBs, and contained its own processor and memory.... |
With on-board 2D and 3D acceleration introduced in 1984 for the 8-bit PC-bus, intended for CAD applications, a triple-board display adapter with built-in processor, and displaying video with a 60 Hz frame rate. | 640×480 (307k) | 4:3 | 8 bpp | |
| MCGA Multicolor Graphics Adapter The Multi-Color Graphics Array was a video subsystem built into the motherboard of the IBM PS/2 Model 30, introduced on April 2, 1987, and Model 25, introduced later on August 11; no standalone MCGA cards were ever made... |
Multicolor Graphics Adapter | Introduced by IBM on ISA Industry Standard Architecture Industry Standard Architecture is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088 microprocessor's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT's Intel 80286 processor... -based PS/2 IBM Personal System/2 The Personal System/2 or PS/2 was IBM's third generation of personal computers. The PS/2 line, released to the public in 1987, was created by IBM in an attempt to recapture control of the PC market by introducing an advanced proprietary architecture... models in 1987, with reduced cost compared to VGA. MCGA had a 320×200 256 color (from a 262,144 color palette Palette (computing) In computer graphics, a palette is either a given, finite set of colors for the management of digital images , or a small on-screen graphical element for choosing from a limited set of choices, not necessarily colors .Depending on the context In computer graphics, a palette is either a given,... ) mode, and a 640×480 mode only in monochrome due to 64k video memory, compared to the 256k memory of VGA. |
320×200 (64k) 640×480 (307k) |
16:10 4:3 |
8 bpp 1 bpp |
| VGA Video Graphics Array Video Graphics Array refers specifically to the display hardware first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, but through its widespread adoption has also come to mean either an analog computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector or the 640×480 resolution... |
Video Graphics Array | Introduced on MCA Micro Channel architecture Micro Channel Architecture was a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers through the mid 1990s.- Background :... -based PS/2 models in 1987. VGA is actually a set of different resolutions, but is most commonly used today to refer to 640×480 pixel displays with 16 colors (4 bits per pixel) and a 4:3 aspect ratio. Other display modes are also defined as VGA, such as 320×200 at 256 colors (8 bits per pixel) and a text mode with 720×400 pixels. VGA displays and adapters are generally capable of Mode X Mode X Mode X is an alternative video graphics display mode of the IBM VGA graphics hardware that was popularized by Michael Abrash, first published in July 1991 in Dr... graphics, an undocumented mode to allow increased non-standard resolutions. |
640×480 (307k) 640×350 (224k) 320×200 (64k) 720×400 (text) |
4:3 64:35 16:10 9:5 |
4 bpp 4 bpp 4/8 bpp 4 bpp |
| 8514 8514 (display standard) IBM 8514 is an IBM graphics computer display standard supporting a display resolution of 1024×768 pixels with 256 colors at 43.5 Hz , or 640×480 at 60 Hz... |
Precursor to XGA and released shortly after VGA in 1987. 8514/A cards displayed interlaced video at 43.5 Hz. | 1024×768 (786k) | 4:3 | 8 bpp | |
| SVGA Super Video Graphics Array Super Video Graphics Array or Ultra Video Graphics Array, almost always abbreviated to Super VGA, Ultra VGA or just SVGA or UVGA is a broad term that covers a wide range of computer display standards.... |
Super Video Graphics Array | A video display standard created by VESA VESA VESA is an international standards body for computer graphics founded in 1989 by NEC Home Electronics and eight other video display adapter manufacturers.VESA's initial goal was to produce a standard for 800×600 SVGA resolution video displays... for IBM PC compatible personal computers. Introduced in 1989. |
800×600 (480k) | 4:3 | 4 bpp |
| XGA | Extended Graphics Array | An IBM display standard introduced in 1990. XGA-2 added 1024×768 support for high color and higher refresh rates, improved performance, and support for 1360 (1365,333)×1024 in 16 colors (4 bits per pixel).[2] (+support 1056×400 [14h] Text Mode). | 1024×768 (786k) 640×480 (307k) |
4:3 4:3 |
8 bpp 16 bpp |
| XGA+ | Extended Graphics Array Plus | Although not an official name, this term is now used to refer to 1152×864, which is the largest 4:3 array yielding under one million pixels. Variants of this were used by Apple Computer (at 1152×870) and Sun Microsystems (at 1152×900) for 21 inches (533.4 mm) CRT displays. | 1152×864 (995k) 640×480 (307k) |
4:3 4:3 |
8 bpp 16 bpp |
| QVGA | Quarter Video Graphics Array | 320×240 (75k) | 4:3 | ||
| WQVGA | Wide Quarter Video Graphics Array | 480×272 (127.5k) | 16:9 | ||
| HQVGA | Half Quarter Video Graphics Array | 240×160 (38k) | 3:2 | ||
| QQVGA | Quarter QVGA | 160×120 (19k) | 4:3 | ||
| unnamed | unnamed | A common size for LCDs manufactured for small consumer electronics and mobile phones, typically in a 1.7" to 1.9" diagonal size. This LCD is often used in the portrait (128×160) orientation. The unusual 5:4 aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... makes the display slightly different from the QQVGA dimensions. |
160×128 (20k) | 5:4 | |
| HD | High Definition (720p) | This display aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... is among the most common in recent notebook computers and desktop monitors. |
1366x768 (1049k) | 16:9 (683:384) |
32bpp |
| WXGA | Widescreen Extended Graphics Array | A version of the XGA format. This display aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... is becoming popular in some recent notebook computers. |
1280×720 (922k) 1280×800 (1024k) |
16:9 or 16:10 | 32 bpp |
| HD+ | High Definition Plus (900p) | This display aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... is becoming popular in recent notebook computers and desktop widescreens. |
1600×900 (1440k) | 16:9 | 32 bpp |
| SXGA | Super Extended Graphics Array | A widely used de facto De facto De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or... 32 bit Truecolor standard, with an unusual aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... of 5:4 (1.25:1) instead of the more common 4:3 (1.33:1), which means that 4:3 pictures and video will appear letterboxed on the narrower 5:4 screens. This is generally the physical aspect ratio & native resolution of standard 17" and 19" LCD monitors.
|
1280×1024 (1310k) | 5:4 | 32 bpp |
| SXGA+ | Super Extended Graphics Array PLUS | Used on 14 inches (355.6 mm) and 15 inches (381 mm) notebook LCD screens and a few smaller screens. | 1400×1050 (1470k) | 4:3 | 32 bpp |
| WXGA+, or WXGA, (or WSXGA) |
Widescreen Extended Graphics Array PLUS | A version of the WXGA format. This display aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... is becoming popular in some recent notebook computers, and is the native resolution for many 19" widescreen LCD monitors. |
1440×900 (1296k) | 16:10 | 32 bpp |
| UXGA | Ultra Extended Graphics Array | A de facto De facto De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or... Truecolor standard. This is the native resolution for many 20" LCD monitors. |
1600×1200 (1920k) | 4:3 | 32 bpp |
| WSXGA+ | Widescreen Super Extended Graphics Array Plus | A version of the WXGA format. This is the native resolution for many 22" widescreen LCD monitors. | 1680×1050 (1764k) | 16:10 | 32 bpp |
| Full-HD (1080p) 1080p 1080p is the shorthand identification for a set of HDTV high-definition video modes that are characterized by 1080 horizontal lines of resolution and progressive scan, meaning the image is not interlaced as is the case with the 1080i display standard.... |
Full High Definition | This display aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... is the native resolution for many 24" widescreen LCD monitors. It is also that of any 1080p or 1080i HDTV. |
1920×1080 (2073k) | 16:9 | 32 bpp |
| WUXGA | Widescreen Ultra Extended Graphics Array | A version of the UXGA format. This display aspect ratio Aspect ratio (image) The aspect ratio of an image is the ratio of the width of the image to its height, expressed as two numbers separated by a colon. That is, for an x:y aspect ratio, no matter how big or small the image is, if the width is divided into x units of equal length and the height is measured using this... is becoming popular in high end 15" and 17" widescreen notebook computers, such as Apple's 17" MacBook Pro. This is the native resolution for many 23"-27" widescreen LCD monitors. |
1920×1200 (2304k) | 16:10 | 32 bpp |
| 2K Digital cinema Digital cinema refers to the use of digital technology to distribute and project motion pictures. A movie can be distributed via hard drives, optical disks or satellite and projected using a digital projector instead of a conventional film projector... |
DLP Cinema Technology | Digital Film Projection | 2048×1080 (2212k) | ≈19:10 | 48 bpp (at 24 frame/s) |
| QXGA | Quad Extended Graphics Array | This is the highest resolution that generally can be displayed on analog computer monitors (most CRTs). | 2048×1536 (3146k) | 4:3 | 32 bpp |
| QWXGA | Quad Wide Extended Graphics Array | Samsung have taken the wraps off of the company’s first QWXGA resolution 23 inches (584.2 mm) LCD monitor 2342BWX | 2048×1152 (2359k) | 16:9 | |
| WQHD | Wide Quad High Definition | This is the native resolution for many 27" widescreen LCD monitors. | 2560×1440 (3686.4k) | 16:9 | 32 bpp |
| WQXGA | Widescreen Quad Extended Graphics Array | A version of the XGA format. This is the native resolution for many 30" widescreen LCD monitors. | 2560×1600 (4096k) | 16:10 | 32 bpp |
| QSXGA | Quad Super Extended Graphics Array | 2560×2048 (5243k) | 5:4 | 32 bpp | |
| WQSXGA | Wide Quad Super Extended Graphics Array | 3200×2048 (6554k) | 25:16 | 32 bpp | |
| QUXGA | Quad Ultra Extended Graphics Array | 3200×2400 (7680k) | 4:3 | 32 bpp | |
| WQUXGA | Wide Quad Ultra Extended Graphics Array | The IBM T220/T221 LCD monitors supported this resolution, but they are no longer available. | 3840×2400 (9216k) | 16:10 | 32 bpp |
| 4K Digital cinema Digital cinema refers to the use of digital technology to distribute and project motion pictures. A movie can be distributed via hard drives, optical disks or satellite and projected using a digital projector instead of a conventional film projector... |
DLP Cinema Technology | Digital Film Projection | 4096×1716 (7029k) | 2.39 | 48 bpp (at 24 frame/s) |
| HXGA | Hex[adecatuple] Extended Graphics Array | 4096×3072 (12583k) | 4:3 | 32 bpp | |
| WHXGA | Wide Hex[adecatuple] Extended Graphics Array | 5120×3200 (16384k) | 16:10 | 32 bpp | |
| HSXGA | Hex[adecatuple] Super Extended Graphics Array | 5120×4096 (20972k) | 5:4 | 32 bpp | |
| WHSXGA | Wide Hex[adecatuple] Super Extended Graphics Array | 6400×4096 (26214k) | 25:16 | 32 bpp | |
| HUXGA | Hex[adecatuple] Ultra Extended Graphics Array | 6400×4800 (30720k) | 4:3 | 32 bpp | |
| Ultra High Definition Television | Ultra High Definition Television | 7680×4320 (33177k) | 16:9 | 32 bpp | |
| WHUXGA | Wide Hex[adecatuple] Ultra Extended Graphics Array | 7680×4800 (36864k) | 16:10 | 32 bpp |
Display resolution prefixes
Although the common standard prefixes super and ultra do not indicate specific modifiers to base standard resolutions, several others do:Quarter (Q or q)
- A quarter of the base resolution. E.g. QVGA, a term for a 320×240 resolution, half the width and height of VGA, hence the quarter total resolution. The "Q" prefix usually indicates "Quad" (4 times as many, not 1/4 times as many) in higher resolutions, and sometimes "q" is used instead of "Q" to specify quarter (by analogy with SI prefixSI prefixThe International System of Units specifies a set of unit prefixes known as SI prefixes or metric prefixes. An SI prefix is a name that precedes a basic unit of measure to indicate a decadic multiple or fraction of the unit. Each prefix has a unique symbol that is prepended to the unit symbol...
es like k/K, m/M), but this usage is not consistent.
Wide (W)
- The base resolution increased by increasing the width and keeping the height constant, for square or near-square pixels on a widescreen display, usually with an aspect ratio of either 16:9 or 16:10.
Quad(ruple) (Q)
- Four times as many pixels compared to the base resolution, i.e. twice the horizontal and vertical resolution respectively.
Hex(adecatuple) (H)
- Sixteen times as many pixels compared to the base resolution, i.e. four times the horizontal and vertical resolutions respectively.
Ultra (U)
eXtended (X)
These prefixes are also often combined, as in WQXGA or WHUXGA.
Other resolutions
There are also some other 4:3 ratio resolutions such as 1400×1050 SXGA+ and unnamed ones like 1152×864 (sometimes referred to as XGA+).See also
- Visual display unit
- Display resolutionDisplay resolutionThe display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
; this also lists the display resolutions of standard and HD televisions, which are sometimes used as computer monitors. - Graphic display resolutionsGraphic display resolutionsThe graphics display resolution describes the width and height dimensions of a display, such as a computer monitor, in pixels. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions...
- List of common resolutions
- List of display interfaces
- List of video connectors
- List of displays by pixel density
External links
- Calculate and compare display sizes, resolutions, and source material
- Display the resolution and color bit depth of your current monitor
- Calculate screen dimensions according to format and diagonal
- Standard resolutions used for computer graphics equipment, TV and video applications and mobile devices.

