
Goodness factor
Encyclopedia
Goodness factor is a metric developed by Eric Laithwaite
to determine the 'goodness' of an electric motor
. Using it he was able to develop efficient magnetic levitation
induction motor
s.

where
From this he showed that the most efficient motors are likely to be relatively large. However, the equation only directly relates to non-permanent magnet motors.
Laithwaite showed that for a simple induction motor this gave:
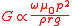
where p is the pole pitch arc length
, ρr is the surface resistivity
of the rotor
and g is the air gap.
Eric Laithwaite
Eric Roberts Laithwaite was a British electrical engineer, known as the "Father of Maglev" for his development of the linear induction motor and maglev rail system.- Biography :...
to determine the 'goodness' of an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
. Using it he was able to develop efficient magnetic levitation
Magnetic levitation
Magnetic levitation, maglev, or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is suspended with no support other than magnetic fields...
induction motor
Induction motor
An induction or asynchronous motor is a type of AC motor where power is supplied to the rotor by means of electromagnetic induction. These motors are widely used in industrial drives, particularly polyphase induction motors, because they are robust and have no brushes...
s.

where
- G is the goodness factor (factors above 1 are likely to be efficient)
- Am, Ae are the cross sectionCross section (geometry)In geometry, a cross-section is the intersection of a figure in 2-dimensional space with a line, or of a body in 3-dimensional space with a plane, etc...
s of the magnetic and electric circuit - lm, le are the lengths of the magnetic and electric circuits
- μ is the permeabilityPermeability (electromagnetism)In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
of the core - ω is the angular frequencyAngular frequencyIn physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
the motor is driven at
From this he showed that the most efficient motors are likely to be relatively large. However, the equation only directly relates to non-permanent magnet motors.
Laithwaite showed that for a simple induction motor this gave:
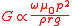
where p is the pole pitch arc length
Arc length
Determining the length of an irregular arc segment is also called rectification of a curve. Historically, many methods were used for specific curves...
, ρr is the surface resistivity
Resistivity
Electrical resistivity is a measure of how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows the movement of electric charge. The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm metre...
of the rotor
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is the non-stationary part of a rotary electric motor, electric generator or alternator, which rotates because the wires and magnetic field of the motor are arranged so that a torque is developed about the rotor's axis. In some designs, the rotor can act to serve as the motor's armature,...
and g is the air gap.

