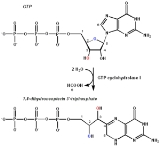
GTP cyclohydrolase I
Encyclopedia
GTP cyclohydrolase I is a member of the GTP cyclohydrolase family
of enzyme
s. GTPCH is part of the folate and biopterin
biosynthesis
pathway
s. It is responsible for the hydrolysis
of guanosine triphosphate
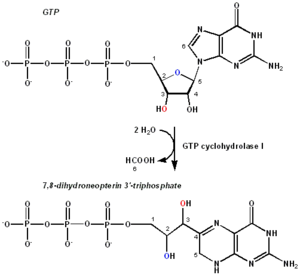
(GTP) to form 7,8-dihydroneopterin 3'-triphosphate (7,8-DHNP-3'-TP, 7,8-NH2-3'-TP).
GTPCH is encoded
by the gene
GCH1. The transcribed
protein
is the first and rate-limiting
enzyme in tetrahydrobiopterin
(THB, BH4) biosynthesis, catalyzing the conversion
of GTP into 7,8-DHNP-3'-TP. THB is an essential cofactor
required by the aromatic amino acid
hydroxylase (AAAH) and nitric oxide synthase
(NOS) enzymes in the biosynthesis of the monoamine neurotransmitter
s serotonin
(5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)), melatonin
, dopamine
, norepinephrine
(noradrenaline), and epinephrine
(adrenaline), and nitric oxide
(NO), respectively. Mutation
s in this gene are associated with malignant
phenylketonuria
(PKU) and hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA), as well as L-DOPA (Levodopa)-responsive dystonia
. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoform
s have been described; however, not all of the variants give rise to a functional enzyme.
Protein family
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily-related proteins, and is often nearly synonymous with gene family. The term protein family should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy....
of enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s. GTPCH is part of the folate and biopterin
Pterin
Pterin is a heterocyclic compound composed of a pteridine ring system, with a keto group and an amino group on positions 4 and 2 respectively...
biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
pathway
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
s. It is responsible for the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...
(GTP) to form 7,8-dihydroneopterin 3'-triphosphate (7,8-DHNP-3'-TP, 7,8-NH2-3'-TP).
GTPCH is encoded
Genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins by living cells....
by the gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
GCH1. The transcribed
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
is the first and rate-limiting
Rate-determining step
The rate-determining step is a chemistry term for the slowest step in a chemical reaction. The rate-determining step is often compared to the neck of a funnel; the rate at which water flows through the funnel is determined by the width of the neck, not by the speed at which water is poured in. In...
enzyme in tetrahydrobiopterin
Tetrahydrobiopterin
Tetrahydrobiopterin or sapropterin is a naturally occurring essential cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the degradation of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin , melatonin, dopamine, norepinephrine ,...
(THB, BH4) biosynthesis, catalyzing the conversion
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
of GTP into 7,8-DHNP-3'-TP. THB is an essential cofactor
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound that is bound to a protein and is required for the protein's biological activity. These proteins are commonly enzymes, and cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations....
required by the aromatic amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
hydroxylase (AAAH) and nitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthase
Nitric oxide synthases are a family of enzymes that catalyze the production of nitric oxide from L-arginine. NO is an important cellular signaling molecule, having a vital role in many biological processes...
(NOS) enzymes in the biosynthesis of the monoamine neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
s serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
(5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)), melatonin
Melatonin
Melatonin , also known chemically as N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, is a naturally occurring compound found in animals, plants, and microbes...
, dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
, norepinephrine
Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is the US name for noradrenaline , a catecholamine with multiple roles including as a hormone and a neurotransmitter...
(noradrenaline), and epinephrine
Epinephrine
Epinephrine is a hormone and a neurotransmitter. It increases heart rate, constricts blood vessels, dilates air passages and participates in the fight-or-flight response of the sympathetic nervous system. In chemical terms, adrenaline is one of a group of monoamines called the catecholamines...
(adrenaline), and nitric oxide
Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
(NO), respectively. Mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s in this gene are associated with malignant
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive metabolic genetic disorder characterized by a mutation in the gene for the hepatic enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase , rendering it nonfunctional. This enzyme is necessary to metabolize the amino acid phenylalanine to the amino acid tyrosine...
(PKU) and hyperphenylalaninemia (HPA), as well as L-DOPA (Levodopa)-responsive dystonia
Dystonia
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder, in which sustained muscle contractions cause twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. The disorder may be hereditary or caused by other factors such as birth-related or other physical trauma, infection, poisoning or reaction to...
. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoform
Protein isoform
A protein isoform is any of several different forms of the same protein. Different forms of a protein may be produced from related genes, or may arise from the same gene by alternative splicing. A large number of isoforms are caused by single-nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs, small genetic...
s have been described; however, not all of the variants give rise to a functional enzyme.

See also
- Guanosine triphosphateGuanosine triphosphateGuanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...
(GTP) - TetrahydrobiopterinTetrahydrobiopterinTetrahydrobiopterin or sapropterin is a naturally occurring essential cofactor of the three aromatic amino acid hydroxylase enzymes, used in the degradation of amino acid phenylalanine and in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin , melatonin, dopamine, norepinephrine ,...
(THB, BH4) - Vitamin B9 (folic acidFolic acidFolic acid and folate , as well as pteroyl-L-glutamic acid, pteroyl-L-glutamate, and pteroylmonoglutamic acid are forms of the water-soluble vitamin B9...
→ folate)

