
Foreign trade of Argentina
Encyclopedia
- This article is about the foreign trade of ArgentinaArgentinaArgentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
. See economy of ArgentinaEconomy of ArgentinaThis article provides an overview of the Economic history of Argentina.-Emergence into the world economy:Prior to the 1880s, Argentina was a relatively isolated backwater, dependent on the wool, leather and hide industry for both the greater part of its foreign exchange and the generation of...
for a more general overview.
Modern history
Agriculturally productive and thinly populated, Argentina recorded trade surpluses for most of the period between 1900 and 1948, including a cumulative US$1 billion during World War I and US$1.7 billion during World War II. Record taxes on grain exports imposed by the administration of Pres. Juan Domingo Perón and an increasing need for costly fuel and machinery helped result in a nearly-unbroken string of trade deficits between 1949 and 1962, however.
Arturo Frondizi
Arturo Frondizi Ercoli was the President of Argentina between May 1, 1958, and March 29, 1962, for the Intransigent Radical Civic Union.-Early life:Frondizi was born in Paso de los Libres, Corrientes Province...
encouraged foreign (as well as local) investment in energy and industry. Drawn to an economy that, at the time, provided Latin America's highest standard of living, investors responded and the country's trade position remained modestly positive throughout the 1963–79 era, while demand also grew.
Policies of "free trade
Free trade
Under a free trade policy, prices emerge from supply and demand, and are the sole determinant of resource allocation. 'Free' trade differs from other forms of trade policy where the allocation of goods and services among trading countries are determined by price strategies that may differ from...
" and financial deregulation pursued by Argentina's last dictatorship
National Reorganization Process
The National Reorganization Process was the name used by its leaders for the military government that ruled Argentina from 1976 to 1983. In Argentina it is often known simply as la última junta militar or la última dictadura , because several of them existed throughout its history.The Argentine...
led to a sudden, record deficit in 1980 and, by 1981, a mountain of bad debts and financial collapse. The climate of slack domestic demand that prevailed in Argentina throughout the 1980s resulted in a cumulative US$38 billion in surpluses from 1982 to 1991; this brought the economy little direct benefit, however, as much of this was deposited abroad during that era of interest payment burdens and financial instability.
In 1991, Economy Minister Domingo Cavallo
Domingo Cavallo
Domingo Felipe "Mingo" Cavallo is an Argentine economist and politician. He has a long history of public service and is known for implementing the Convertibilidad plan, which fixed the dollar-peso exchange rate at 1:1 between 1991 and 2001, which brought the Argentine inflation rate down from over...
created the Argentine Currency Board
Argentine Currency Board
The Argentine Currency Board pegged the Argentine peso to the U.S. dollar between 1991 and 2002 in an attempt to eliminate hyperinflation and stimulate economic growth. While it initially met with considerable success, the board's actions ultimately failed. In contrast of what most people think,...
, pegging the monetary value of the Argentine peso
Argentine peso
The peso is the currency of Argentina, identified by the symbol $ preceding the amount in the same way as many countries using dollar currencies. It is subdivided into 100 centavos. Its ISO 4217 code is ARS...
to the United States dollar by law. The fixed exchange rate
Fixed exchange rate
A fixed exchange rate, sometimes called a pegged exchange rate, is a type of exchange rate regime wherein a currency's value is matched to the value of another single currency or to a basket of other currencies, or to another measure of value, such as gold.A fixed exchange rate is usually used to...
(1 peso to the dollar) allowed for a macroeconomic stabilization. Taking advantage of this low exchange rate, on the lower tariffs on imports and on the reappearance of credit after the free trade
Free trade
Under a free trade policy, prices emerge from supply and demand, and are the sole determinant of resource allocation. 'Free' trade differs from other forms of trade policy where the allocation of goods and services among trading countries are determined by price strategies that may differ from...
liberalization measures taken by President Carlos Menem
Carlos Menem
Carlos Saúl Menem is an Argentine politician who was President of Argentina from 1989 to 1999. He is currently an Argentine National Senator for La Rioja Province.-Early life:...
's administration, Argentine firms and consumers tripled capital goods purchases from 1990 to 1994, while depressed auto sales rose by fivefold. The influx of imported machines and supplies helped the modernization of the country's industrial base; but it negatively impacted its trade balance, which accumulated US$22 billion in deficits from 1992 to 1999.
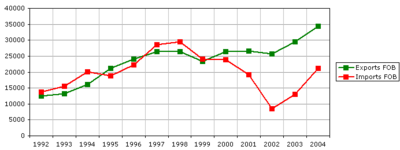
Relying on sizable foreign investment inflows to balance the current account, these did not suffice and the Argentine Central Bank was again forced to resort to borrowing to protect the peso's value against such pressure (mostly by floating bonds, then the most sought-after in the developing world). Recession helped lead to a US$1 billion surplus in 2000 and another US$6 billion in 2001; but it was too little, too late. Buffeted by generalized global instability, the international derivatives market massively shorted Argentine bonds in the second half of 2001 and on December 23, following a spate of unpopular crisis measures, the Argentine government declared a default on US$93 billion of its bonds, the largest sovereign debt default in history.
The effects of the 2001 crisis
Immediately after the collapse of the Argentine economy at the end of 2001 and the devaluationDevaluation
Devaluation is a reduction in the value of a currency with respect to those goods, services or other monetary units with which that currency can be exchanged....
of the peso in 2002, imports fell over half and Argentina's trade surplus soared to over US$16 billion, providing for the first current account surplus since 1990. As recovery ensued and the exchange rate stabilized around 3 pesos/dollar, exports (mainly soy, cereals and other agricultural products, as well as machinery and fuels) grew steadily.
Imports began recovering sharply in 2003, as the purchasing power
Purchasing power
Purchasing power is the number of goods/services that can be purchased with a unit of currency. For example, if you had taken one dollar to a store in the 1950s, you would have been able to buy a greater number of items than you would today, indicating that you would have had a greater purchasing...
of companies and individuals increased and, despite this, from 2003 to 2008, the nation's trade balance recorded a cumulative US$77 billion in surpluses.
Mercosur
MercosurMercosur
Mercosur or Mercosul is an economic and political agreement among Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Founded in 1991 by the Treaty of Asunción, which was later amended and updated by the 1994 Treaty of Ouro Preto. Its purpose is to promote free trade and the fluid movement of goods, people,...
, the customs union
Customs union
A customs union is a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff. The participant countries set up common external trade policy, but in some cases they use different import quotas...
that includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay
Paraguay
Paraguay , officially the Republic of Paraguay , is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. Paraguay lies on both banks of the Paraguay River, which runs through the center of the...
, and Uruguay
Uruguay
Uruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
, entered into force January 1, 1995. Chile and Bolivia joined the pact subsequently as associate members. Cooperation between Brazil and Argentina (historic competitors) is the key to Mercosur's integration process, which includes political and military elements in addition to a customs union. Brazil accounts for more than 70% of Mercosur GDP and Argentina about 27%. Intra-Mercosur trade rose dramatically from US$4 billion in 1991 to over US$23 billion in 1998. More than 90% of intra-Mercosur trade is duty-free, while the group's common external tariff
Common external tariff
When a group of countries form a customs union they must introduce a common external tariff. The same customs duties, import quotas, preferences or other non-tariff barriers to trade apply to all goods entering the area, regardless of which country within the area they are entering...
(CET) applies to more than 85% of imported goods. Remaining goods will be phased into the CET by 2006.
Brazil's higher level of industrialization and production capacity, as well as other economic asymmetries, have been a source of tension with Argentina. In recent years, Argentina's recovering industrial sector has pressured the government to obtain restrictions (especially quotas) on Mercosur's free trade regulations, in order to protect their growth from what they see as disloyal competition from their larger partner to the north. Exports to Brazil helped lessen the impact of the 2001–02 crisis on the industrial sector, somewhat, though Argentina's intra-Mercosur trade yielded it a cumulative US$15 billion deficit from 2004 to 2008.
United States
The United States traditionally records a modest trade surplus with Argentina and the record for this figure was logged in 1998, when it reaped a nearly US$3.7 billion surplus; these have been much smaller, since then. Fresh Argentine beefArgentine beef
Beef is a key component of traditional Argentine cuisine.-Current situation:Argentina has the world's second highest consumption rate of beef, at 55 kg a year per capita. In 2006, livestock farmers kept between 50 and 55 million head of cattle, mostly in the fertile pastures of the Pampas...
was exported to the U.S. market in 1997 for the first time in over 60 years, and in 1999 its export quota of 20,000 tons was filled. However, beef exports to the U.S. were suspended in August 2000 when Argentine cattle near the border with Paraguay (whose authorities refuse to vaccinate cattle against highly contagious hoof and mouth disease) were discovered to have anti-bodies for the infection. The quota was reinstated in early 2002 and has since averaged 28,000 tons.
Intellectual property issues
Argentina adheres to most treaties and international agreements on intellectual property. It is a member of the World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property Organization
The World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
and signed the Uruguay Round agreements in December 1993, including measures related to intellectual property. However, extension of adequate patent protection to pharmaceuticals has been a highly contentious bilateral issue.
In May 1997, the U.S. suspended 50% of Argentina's GSP benefits because of its allegedly unsatisfactory pharmaceutical patent law. In May 1999, The U.S. Government initiated consultations under World Trade Organization
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
procedures to address these inadequacies and expanded the consultations in May 2007
Exports and imports
- Last available data on exports are from 2007. Such qualitative data on imports are not immediately available. INDEC provides import estimates according to final use.
Argentine exports are mainly of the agricultural type, mostly processed goods. In all, exports of agricultural origin make up 54% of the total. Soybean
Soybean
The soybean or soya bean is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean which has numerous uses...
products (the beans themselves, feed, oils, etc.) account for 24.1% of total exports. Cereals (mostly wheat and maize) make up for 8.3%. Beef, for which Argentina is well-known, made up 3.3%.
Industrial manufactures, which twenty years ago were but 10% of exports, provided 31.1% of the total in 2007. Motor vehicles and parts constituted 9.6% of exports, chemicals and medicine, 5.3% and the siderurgical industry (mostly steel and aluminum), 5.1%.
Fuels and energy provided 12.2% of total exports. Petrochemical
Petrochemical
Petrochemicals are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn or sugar cane....
industries provide 7.2% of exports (mainly refined fuels). Petroleum and natural gas each accounted for 2.3%. Argentina's principal mineral export is copper, 2.7%.
Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
has, since the 1991 creation of the Mercosur
Mercosur
Mercosur or Mercosul is an economic and political agreement among Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Founded in 1991 by the Treaty of Asunción, which was later amended and updated by the 1994 Treaty of Ouro Preto. Its purpose is to promote free trade and the fluid movement of goods, people,...
common market, been Argentina's largest trading partner, though Brazil usually runs a trade surplus with Argentina (US$4.2 billion in 2007, a record). Brazil took 18.8% of Argentina's exports and provided it with 32.8% of its imports in 2007. Formerly Argentina's largest trading partner, the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
took 17.7% of exports and provided 16.6% of imports. The United States has enjoyed a trade surplus with Argentina for most of the last sixty years. In 2007, it took 8% of Argentine exports and provided 13.1% of imports, resulting in a US$1 billion surplus for the U.S.
Asian nations have also become significant trading partners with Argentina. Including the Middle East, they took 20.2% of exports and provided 19.6% of imports; China makes up about half of this. Because of the large trade surpluses Argentina has been running with Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
(mostly on account of growing fuel and energy needs), this neighboring nation has become very important to Argentine foreign trade; Argentina recorded a US$3.5 billion surplus with Chile in 2007, more than with any other trading partner.
In March 2006, after several unsuccessful attempts to contain rising beef prices in the internal market, the national government suspended all beef exports, with a few exceptions, for 180 days, a drastic measure intended to redirect up to 600,000 tonnes for internal consumption.
Argentina's merchandise imports and exports both reached historical highs in 2007. Imports grew 31% to US$44.7 billion and exports, 20%, to US$55.8 million. This resulted in a trade surplus of US$11.1 billion (the sixth straight year double-digit trade surpluses were recorded). The largest growth in exports was found in the agricultural raw materials sector (45%). Imports continued to be dominated by the need for industrial and information equipment, parts and supplies; together, they amounted to US$34 billion in 2007 (about three-fourths of the total). Motor vehicles and other consumer goods make up most of the rest.
A non-official source, Foreign Trade of Argentina, has compiled a list of principal definitive imported products for 2009, for 2008 and for 2007, as well as for export statistics, among which are the principal these are the main definitive exported products for 2009, for 2008 and for 2007.
EWLINE
|
EWLINE
|
Sources
- Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas y Censos (statistics available in Spanish and English)
- Lewis, Paul. The Crisis of Argentine Capitalism. University of North Carolina Press, 1990.





















.svg.png)





