
Direct digital synthesis
Encyclopedia

Frequency synthesizer
A frequency synthesizer is an electronic system for generating any of a range of frequencies from a single fixed timebase or oscillator. They are found in many modern devices, including radio receivers, mobile telephones, radiotelephones, walkie-talkies, CB radios, satellite receivers, GPS systems,...
used for creating arbitrary waveform
Waveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
s from a single, fixed-frequency reference clock. Applications of DDS include: signal generation
Signal generator
Signal generators, also known variously as function generators, RF and microwave signal generators, pitch generators, arbitrary waveform generators, digital pattern generators or frequency generators are electronic devices that generate repeating or non-repeating electronic signals...
, local oscillator
Local oscillator
A local oscillator is an electronic device used to generate a signal normally for the purpose of converting a signal of interest to a different frequency using a mixer. This process of frequency conversion, also referred to as heterodyning, produces the sum and difference frequencies of the...
s in communication systems, function generator
Function generator
A function generator is a piece of electronic test equipment or software used to generate different types of electrical waveforms over a wide range of frequencies. These waveforms can be either repetitive or single-shot, in which case some kind of triggering source is required...
s, mixers, modulators, sound synthesizers and as part of a digital phase-locked loop.
Overview
A basic Direct Digital Synthesizer consists of a frequency reference (often a crystalCrystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal of piezoelectric material to create an electrical signal with a very precise frequency...
or SAW
Surface acoustic wave
]A surface acoustic wave is an acoustic wave traveling along the surface of a material exhibiting elasticity, with an amplitude that typically decays exponentially with depth into the substrate.-Discovery:...
oscillator), a numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) and a digital-to-analog converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
(DAC) as shown in Figure 1.
The reference provides a stable time base for the system and determines the frequency accuracy of the DDS. It provides the clock to the NCO which produces at its output a discrete-time, quantized
Quantization (signal processing)
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set – such as rounding values to some unit of precision. A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by...
version of the desired output waveform (often a sinusoid) whose period is controlled by the digital word contained in the Frequency Control Register. The sampled, digital waveform is converted to an analog waveform by the DAC. The output reconstruction filter rejects the spectral replicas produced by the zero-order hold
Zero-order hold
The zero-order hold is a mathematical model of the practical signal reconstruction done by a conventional digital-to-analog converter . That is, it describes the effect of converting a discrete-time signal to a continuous-time signal by holding each sample value for one sample interval...
inherent in the analog conversion process.
Performance
A DDS has many advantages over its analog counterpart, the phase-locked loopPhase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
(PLL), including much better frequency agility, improved phase noise
Phase noise
Phase noise is the frequency domain representation of rapid, short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, caused by time domain instabilities...
, and precise control of the output phase across frequency switching transitions. Disadvantages include spurious due mainly to truncation effects in the NCO, crossing spurious resulting from high order (>1) Nyquist images, and a higher noise floor at large frequency offsets due mainly to the Digital-to-analog converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
.
Because a DDS is a sampled system
Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, after Harry Nyquist and Claude Shannon, is a fundamental result in the field of information theory, in particular telecommunications and signal processing. Sampling is the process of converting a signal into a numeric sequence...
, in addition to the desired waveform at output frequency Fout, Nyquist images
Nyquist frequency
The Nyquist frequency, named after the Swedish-American engineer Harry Nyquist or the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, is half the sampling frequency of a discrete signal processing system...
are also generated (the primary image is at Fclk-Fout, where Fclk is the reference clock frequency). In order to reject these undesired images, a DDS is generally used in conjunction with an analog reconstruction lowpass filter
Reconstruction filter
In a mixed-signal system , a reconstruction filter is used to construct a smooth analogue signal from a digital input, as in the case of a digital to analogue converter or other sampled data output device....
as shown in Figure 1.
Frequency agility
The output frequency of a DDS is determined by the value stored in the frequency control register (FCR) (see Fig.1), which in turn controls the NCO's phase accumulator step size. Because the NCO operates in the discrete-time domain, it changes frequency instantaneously at the clock edge coincident with a change in the value stored in the FCR. The DDS output frequency settling time is determined mainly by the phase response of the reconstruction filter. An ideal reconstruction filter with a linear phase response (meaning the output is simply a delayed version of the input signal) would allow instantaneous frequency response at its output because a linear system can not create frequencies not present at its input.Phase noise and jitter
The superior close-in phase noisePhase noise
Phase noise is the frequency domain representation of rapid, short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, caused by time domain instabilities...
performance of a DDS stems from the fact that it is a feed-forward system. In a traditional phase locked loop (PLL), the frequency divider in the feedback path acts to multiply the phase noise of the reference oscillator and, within the PLL loop bandwidth, impresses this excess noise onto the VCO output. A DDS on the other hand, reduces the reference clock phase noise by the ratio
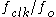 because its output is derived by fractional division of the clock. Reference clock jitter
because its output is derived by fractional division of the clock. Reference clock jitterJitter
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency of successive pulses, the signal amplitude, or phase of...
translates directly to the output, but this jitter is a smaller percentage of the output period (by the ratio above). Since the maximum output frequency is limited to
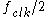 , the output phase noise at close-in offsets is always at least 6dB below the reference clock phase-noise.
, the output phase noise at close-in offsets is always at least 6dB below the reference clock phase-noise.At offsets far removed from the carrier, the phase-noise floor of a DDS is determined by the power sum of the DAC quantization
Quantization (signal processing)
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping a large set of input values to a smaller set – such as rounding values to some unit of precision. A device or algorithmic function that performs quantization is called a quantizer. The error introduced by...
noise floor and the reference clock phase noise floor.
See also
- Numerically controlled oscillator
- Digital-to-analog converterDigital-to-analog converterIn electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
- Reconstruction filterReconstruction filterIn a mixed-signal system , a reconstruction filter is used to construct a smooth analogue signal from a digital input, as in the case of a digital to analogue converter or other sampled data output device....
- Crystal oscillatorCrystal oscillatorA crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses the mechanical resonance of a vibrating crystal of piezoelectric material to create an electrical signal with a very precise frequency...
External links
- Tutorial on Digital Signal Synthesis (From Analog DevicesAnalog DevicesAnalog Devices, Inc. , known as ADI, is an American multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion and signal conditioning technology, headquartered in Norwood, Massachusetts...
) - Another thesis on high speed DDS (French)
- L. Cordesses, "Direct Digital Synthesis: A Tool for Periodic Wave Generation (Part 1)" IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, DSP Tips & Tricks column, pp. 50–54, Vol. 21, No. 4 July 2004.
- L. Cordesses, Direct Digital Synthesis: A Tool for Periodic Wave Generation (Part 2) IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, DSP Tips & Tricks column, pp. 110–117, Vol. 21, No. 5, Sep. 2004.

