
Jitter
Encyclopedia
Jitter is the undesired deviation from true periodicity of an assumed periodic signal in electronics
and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source
. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency
of successive pulses, the signal amplitude
, or phase
of periodic signals. Jitter is a significant, and usually undesired, factor in the design of almost all communications links (e.g., USB, PCI-e, SATA
, OC-48). In clock recovery
applications it is called timing jitter.
Jitter can be quantified in the same terms as all time-varying signals, e.g., RMS
, or peak-to-peak displacement. Also like other time-varying signals, jitter can be expressed in terms of spectral density (frequency content).
Jitter period is the interval between two times of maximum effect (or minimum effect) of a signal characteristic that varies regularly with time. Jitter frequency, the more commonly quoted figure, is its inverse. ITU-T G.810 classifies jitter frequencies below 10 Hz as wander
and frequencies at or above 10 Hz as jitter.
Jitter may be caused by electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk with carriers of other signals. Jitter can cause a display monitor to flicker, affect the performance of processors in personal computers, introduce clicks or other undesired effects in audio signals, and loss of transmitted data between network devices. The amount of tolerable jitter depends on the affected application.
or a digital-to-analog converter
then the instantaneous signal error introduced will be proportional to the slew rate
of the desired signal and the absolute value of the clock error. Various effects can come about depending on the pattern of the jitter in relation to the signal. In some conditions, less than a nanosecond of jitter can reduce the effective bit resolution of a converter with a Nyquist frequency
of 22 kHz to 14 bits.
This is a consideration in high-frequency signal conversion, or where the clock signal is especially prone to interference.
However, for this use, the term is imprecise. The standards-based term is packet delay variation
(PDV). PDV is an important quality of service
factor in assessment of network performance.
from Compact Disc
s, seek jitter causes extracted audio samples
to be doubled-up or skipped entirely if the Compact Disc drive re-seeks. The problem occurs because the Red Book (audio CD standard)
does not require block-accurate addressing during seeking. As a result, the extraction process may restart a few samples early or late, resulting in doubled or omitted samples. These glitches often sound like tiny repeating clicks during playback. A successful approach to correction in software involves performing overlapping reads and fitting the data to find overlaps at the edges. Most extraction programs perform seek jitter correction. CD manufacturers avoid seek jitter by extracting the entire disc in one continuous read operation using special CD drive models at slower speeds so the drive does not re-seek.
A jitter meter is a testing instrument for measuring clock jitter values, and is used in manufacturing DVD
and CD-ROM
discs.
Due to additional sector level addressing added in the Yellow Book (CD standard)
, CD-ROM
data discs are not subject to seek jitter.
jitter, there are three commonly used metrics: absolute jitter, period jitter, and cycle to cycle jitter.
Absolute jitter is the absolute difference
in the position of a clock's edge from where it would ideally be.
Period jitter (aka cycle jitter) is the difference between any one clock period and the ideal clock period. Accordingly, it can be thought of as the discrete-time derivative of absolute jitter. Period jitter tends to be important in synchronous circuitry like digital state machines where the error-free operation of the circuitry is limited by the shortest possible clock period, and the performance of the circuitry is limited by the average clock period. Hence, synchronous circuitry benefits from minimizing period jitter, so that the shortest clock period approaches the average clock period.
Cycle-to-cycle jitter is the difference in length of any two adjacent clock periods. Accordingly, it can be thought of as the discrete-time derivative of period jitter. It can be important for some types of clock generation circuitry used in microprocessor
s and RAM
interfaces.
Since they have different generation mechanisms, different circuit effects, and different measurement methodology, it is useful to quantify them separately.
In telecommunications, the unit used for the above types of jitter is usually the Unit Interval (abbreviated UI) which quantifies the jitter in terms of a fraction of the ideal period of a bit. This unit is useful because it scales with clock frequency and thus allows relatively slow interconnects such as T1
to be compared to higher-speed internet backbone links such as OC-192. Absolute units such as picoseconds are more common in microprocessor applications. Units of degrees and radians are also used.
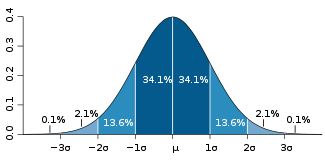 If jitter has a Gaussian distribution, it is usually quantified using the standard deviation
If jitter has a Gaussian distribution, it is usually quantified using the standard deviation
of this distribution (aka. RMS
). Often, jitter distribution is significantly non-Gaussian. This can occur if the jitter is caused by external sources such as power supply noise. In these cases, peak-to-peak measurements are more useful. Many efforts have been made to meaningfully quantify distributions that are neither Gaussian nor have meaningful peaks (which is the case in all real jitter). All have shortcomings but most tend to be good enough for the purposes of engineering work. Note that typically, the reference point for jitter is defined such that the mean
jitter is 0.
In networking
, in particular IP
networks
such as the Internet
, jitter can refer to the variation (statistical dispersion
) in the delay of the packets.
. The central limit theorem states that composite effect of many uncorrelated noise sources, regardless of the distributions, approaches a Gaussian distribution.
One of the main differences between random and deterministic jitter is that deterministic jitter is bounded and random jitter is unbounded.
is a type of clock
timing jitter or data signal jitter that is predictable and reproducible. The peak-to-peak value of this jitter is bounded, and the bounds can easily be observed and predicted. Determistic jitter can either be correlated to the data stream (data-dependent jitter) or uncorrelated to the data stream (bounded uncorrelated jitter). Examples of data-dependent jitter are duty-cycle dependent jitter (also known as duty-cycle distortion) and intersymbol interference
.
T = Dpeak-to-peak + 2× n×Rrms,
in which the value of n is based on the bit error rate (BER) required of the link.
A common bit error rate used in communication standards such as Ethernet
is 10−12.
s have serial bus architectures with eye openings of 160 picosecond
s or less. This is extremely small compared to parallel bus architectures with equivalent performance, which may have eye openings on the order of 1000 picosecond
s.
Testing of device performance for jitter tolerance often involves the injection of jitter into electronic components with specialized test equipment.
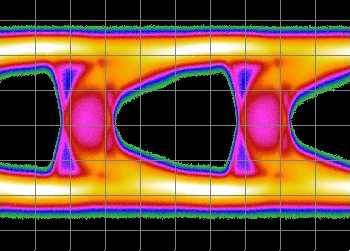
Jitter is measured and evaluated in various ways depending on the type of circuitry under test. For example, jitter in serial bus architectures is measured by means of eye diagrams, according to industry accepted standards. A less direct approach—in which analog waveforms are digitized and the resulting data stream analyzed—is employed when measuring pixel jitter in frame grabber
s. In all cases, the goal of jitter measurement is to verify that the jitter will not disrupt normal operation of the circuitry.
There are standards for jitter measurement in serial bus architectures. The standards cover jitter tolerance, jitter transfer function and jitter generation, with the required values for these attributes varying among different applications. Where applicable, compliant systems are required to conform to these standards.
s designed to reduce the level of jitter in a regular pulse signal. AJCs operate by re-timing the output pulses so they align more closely to an idealised pulse signal.
They are widely used in clock and data recovery circuits in digital communications, as well as for data sampling systems such as the analog-to-digital converter
and digital-to-analog converter
. Examples of anti-jitter circuits include phase-locked loop
and delay-locked loop
. Inside digital to analog converters jitter causes unwanted high-frequency distortions. In this case it can be suppressed with high fidelity clock signal usage.
s so that a continuous playout of audio (or video) transmitted over the network can be ensured. The maximum jitter that can be countered by a de-jitter buffer is equal to the buffering delay introduced before starting the play-out of the mediastream. In the context of packet-switched networks, the term packet delay variation
is often preferred over jitter.
Some systems use sophisticated delay-optimal de-jitter buffers that are capable of adapting the buffering delay to changing network jitter characteristics. These are known as adaptive de-jitter buffers and the adaptation logic is based on the jitter estimates computed from the arrival characteristics of the media packets. Adaptive de-jittering involves introducing discontinuities in the media play-out, which may appear offensive to the listener or viewer. Adaptive de-jittering is usually carried out for audio play-outs that feature a VAD
/DTX
encoded audio, that allows the lengths of the silence periods to be adjusted, thus minimizing the perceptual impact of the adaptation.
. A dejitterizer usually consists of an elastic buffer
in which the signal is temporarily stored and then retransmitted at a rate based on the average rate of the incoming signal. A dejitterizer is usually ineffective in dealing with low-frequency jitter, such as waiting-time jitter.
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
and telecommunications, often in relation to a reference clock source
Clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal is a particular type of signal that oscillates between a high and a low state and is utilized like a metronome to coordinate actions of circuits...
. Jitter may be observed in characteristics such as the frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
of successive pulses, the signal amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
, or phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
of periodic signals. Jitter is a significant, and usually undesired, factor in the design of almost all communications links (e.g., USB, PCI-e, SATA
Sata
Sata is a traditional dish from the Malaysian state of Terengganu, consisting of spiced fish meat wrapped in banana leaves and cooked on a grill.It is a type of Malaysian fish cake, or otak-otak...
, OC-48). In clock recovery
Clock recovery
Some digital data streams, especially high-speed serial data streams are sent without an accompanying clock signal. The receiver generates a clock from an approximate frequency reference, and then phase-aligns to the transitions in the data stream with a phase-locked loop...
applications it is called timing jitter.
Jitter can be quantified in the same terms as all time-varying signals, e.g., RMS
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
, or peak-to-peak displacement. Also like other time-varying signals, jitter can be expressed in terms of spectral density (frequency content).
Jitter period is the interval between two times of maximum effect (or minimum effect) of a signal characteristic that varies regularly with time. Jitter frequency, the more commonly quoted figure, is its inverse. ITU-T G.810 classifies jitter frequencies below 10 Hz as wander
Wander
In telecommunication, wander are long-term low-frequency random variations of the significant instants of a digital signal from their ideal positions. Phase variations with a frequency content above 10 Hertz are considered jitter, while those with a frequency below 10 Hz are referred to as wander....
and frequencies at or above 10 Hz as jitter.
Jitter may be caused by electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk with carriers of other signals. Jitter can cause a display monitor to flicker, affect the performance of processors in personal computers, introduce clicks or other undesired effects in audio signals, and loss of transmitted data between network devices. The amount of tolerable jitter depends on the affected application.

Sampling jitter
In conversion between digital and analog signals, the sampling frequency is normally assumed to be constant. Samples should be converted at regular intervals. If there is jitter present on the clock signal to the analog-to-digital converterAnalog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
or a digital-to-analog converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
then the instantaneous signal error introduced will be proportional to the slew rate
Slew rate
In electronics, the slew rate represents the maximum rate of change of a signal at any point in a circuit.Limitations in slew rate capability can give rise to non linear effects in electronic amplifiers...
of the desired signal and the absolute value of the clock error. Various effects can come about depending on the pattern of the jitter in relation to the signal. In some conditions, less than a nanosecond of jitter can reduce the effective bit resolution of a converter with a Nyquist frequency
Nyquist frequency
The Nyquist frequency, named after the Swedish-American engineer Harry Nyquist or the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, is half the sampling frequency of a discrete signal processing system...
of 22 kHz to 14 bits.
This is a consideration in high-frequency signal conversion, or where the clock signal is especially prone to interference.
Packet jitter in computer networks
In the context of computer networks, the term jitter is often used as a measure of the variability over time of the packet latency across a network. A network with constant latency has no variation (or jitter). Packet jitter is expressed as an average of the deviation from the network mean latency.However, for this use, the term is imprecise. The standards-based term is packet delay variation
Packet delay variation
In computer networking, packet delay variation is the difference in end-to-end delay between selected packets in a flow with any lost packets being ignored...
(PDV). PDV is an important quality of service
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
factor in assessment of network performance.
Compact disc seek jitter
In the context of digital audio extractionRipping
Ripping is the process of copying audio or video content to a hard disk, typically from removable media. The word is used to refer to all forms of media. Despite the name, neither the media nor the data is damaged after extraction....
from Compact Disc
Compact Disc
The Compact Disc is an optical disc used to store digital data. It was originally developed to store and playback sound recordings exclusively, but later expanded to encompass data storage , write-once audio and data storage , rewritable media , Video Compact Discs , Super Video Compact Discs ,...
s, seek jitter causes extracted audio samples
Sampling (signal processing)
In signal processing, sampling is the reduction of a continuous signal to a discrete signal. A common example is the conversion of a sound wave to a sequence of samples ....
to be doubled-up or skipped entirely if the Compact Disc drive re-seeks. The problem occurs because the Red Book (audio CD standard)
Red Book (audio CD standard)
Red Book is the standard for audio CDs . It is named after one of the Rainbow Books, a series of books that contain the technical specifications for all CD and CD-ROM formats.The first edition of the Red Book was released in 1980 by Philips and Sony; it was adopted by the Digital Audio Disc...
does not require block-accurate addressing during seeking. As a result, the extraction process may restart a few samples early or late, resulting in doubled or omitted samples. These glitches often sound like tiny repeating clicks during playback. A successful approach to correction in software involves performing overlapping reads and fitting the data to find overlaps at the edges. Most extraction programs perform seek jitter correction. CD manufacturers avoid seek jitter by extracting the entire disc in one continuous read operation using special CD drive models at slower speeds so the drive does not re-seek.
A jitter meter is a testing instrument for measuring clock jitter values, and is used in manufacturing DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
and CD-ROM
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
discs.
Due to additional sector level addressing added in the Yellow Book (CD standard)
Yellow Book (CD standard)
The Yellow Book is the standard that defines the format of CD-ROMs. The Yellow Book, created by Sony and Philips, was the first extension of the Red Book. It is named after one of a set of color-bound books that contain the technical specifications for all CD and CD-ROM formats.-External links:The...
, CD-ROM
CD-ROM
A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc that contains data accessible to, but not writable by, a computer for data storage and music playback. The 1985 “Yellow Book” standard developed by Sony and Philips adapted the format to hold any form of binary data....
data discs are not subject to seek jitter.
Phase jitter metrics
For clockClock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal is a particular type of signal that oscillates between a high and a low state and is utilized like a metronome to coordinate actions of circuits...
jitter, there are three commonly used metrics: absolute jitter, period jitter, and cycle to cycle jitter.
Absolute jitter is the absolute difference
Absolute difference
The absolute difference of two real numbers x, y is given by |x − y|, the absolute value of their difference. It describes the distance on the real line between the points corresponding to x and y...
in the position of a clock's edge from where it would ideally be.
Period jitter (aka cycle jitter) is the difference between any one clock period and the ideal clock period. Accordingly, it can be thought of as the discrete-time derivative of absolute jitter. Period jitter tends to be important in synchronous circuitry like digital state machines where the error-free operation of the circuitry is limited by the shortest possible clock period, and the performance of the circuitry is limited by the average clock period. Hence, synchronous circuitry benefits from minimizing period jitter, so that the shortest clock period approaches the average clock period.
Cycle-to-cycle jitter is the difference in length of any two adjacent clock periods. Accordingly, it can be thought of as the discrete-time derivative of period jitter. It can be important for some types of clock generation circuitry used in microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
s and RAM
Ram
-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
interfaces.
Since they have different generation mechanisms, different circuit effects, and different measurement methodology, it is useful to quantify them separately.
In telecommunications, the unit used for the above types of jitter is usually the Unit Interval (abbreviated UI) which quantifies the jitter in terms of a fraction of the ideal period of a bit. This unit is useful because it scales with clock frequency and thus allows relatively slow interconnects such as T1
Digital Signal 1
Digital signal 1 is a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs. DS1 is a widely used standard in telecommunications in North America and Japan to transmit voice and data between devices. E1 is used in place of T1 outside North America, Japan, and South Korea...
to be compared to higher-speed internet backbone links such as OC-192. Absolute units such as picoseconds are more common in microprocessor applications. Units of degrees and radians are also used.

Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
of this distribution (aka. RMS
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
). Often, jitter distribution is significantly non-Gaussian. This can occur if the jitter is caused by external sources such as power supply noise. In these cases, peak-to-peak measurements are more useful. Many efforts have been made to meaningfully quantify distributions that are neither Gaussian nor have meaningful peaks (which is the case in all real jitter). All have shortcomings but most tend to be good enough for the purposes of engineering work. Note that typically, the reference point for jitter is defined such that the mean
Arithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
jitter is 0.
In networking
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
, in particular IP
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
networks
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
such as the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
, jitter can refer to the variation (statistical dispersion
Statistical dispersion
In statistics, statistical dispersion is variability or spread in a variable or a probability distribution...
) in the delay of the packets.
Random jitter
Random Jitter, also called Gaussian jitter, is unpredictable electronic timing noise. Random jitter typically follows a Gaussian distribution or Normal distribution. It is believed to follow this pattern because most noise or jitter in a electrical circuit is caused by thermal noise, which has a Gaussian distribution. Another reason for random jitter to have a distribution like this is due to the central limit theoremCentral limit theorem
In probability theory, the central limit theorem states conditions under which the mean of a sufficiently large number of independent random variables, each with finite mean and variance, will be approximately normally distributed. The central limit theorem has a number of variants. In its common...
. The central limit theorem states that composite effect of many uncorrelated noise sources, regardless of the distributions, approaches a Gaussian distribution.
One of the main differences between random and deterministic jitter is that deterministic jitter is bounded and random jitter is unbounded.
Deterministic jitter
Deterministic jitterDeterministic jitter
Deterministic jitter is a type of jitter with a known non-Gaussian probability distribution. The other major class of jitter is non-deterministic, or random jitter.-Characteristics:...
is a type of clock
Clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal is a particular type of signal that oscillates between a high and a low state and is utilized like a metronome to coordinate actions of circuits...
timing jitter or data signal jitter that is predictable and reproducible. The peak-to-peak value of this jitter is bounded, and the bounds can easily be observed and predicted. Determistic jitter can either be correlated to the data stream (data-dependent jitter) or uncorrelated to the data stream (bounded uncorrelated jitter). Examples of data-dependent jitter are duty-cycle dependent jitter (also known as duty-cycle distortion) and intersymbol interference
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
.
| n | BER |
|---|---|
| 6.4 | 10−10 |
| 6.7 | 10−11 |
| 7 | 10−12 |
| 7.3 | 10−13 |
| 7.6 | 10−14 |
Total jitter
Total jitter (T) is the combination of random jitter (R) and deterministic jitter (D):T = Dpeak-to-peak + 2× n×Rrms,
in which the value of n is based on the bit error rate (BER) required of the link.
A common bit error rate used in communication standards such as Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
is 10−12.
Testing
Testing for jitter and its measurement is of growing importance to electronics engineers because of increased clock frequencies in digital electronic circuitry to achieve higher device performance. Higher clock frequencies have commensurately smaller eye openings, and thus impose tighter tolerances on jitter. For example, modern computer motherboardMotherboard
In personal computers, a motherboard is the central printed circuit board in many modern computers and holds many of the crucial components of the system, providing connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, or, on Apple...
s have serial bus architectures with eye openings of 160 picosecond
Picosecond
A picosecond is 10−12 of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to 31,700 years....
s or less. This is extremely small compared to parallel bus architectures with equivalent performance, which may have eye openings on the order of 1000 picosecond
Picosecond
A picosecond is 10−12 of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to 31,700 years....
s.
Testing of device performance for jitter tolerance often involves the injection of jitter into electronic components with specialized test equipment.
Jitter is measured and evaluated in various ways depending on the type of circuitry under test. For example, jitter in serial bus architectures is measured by means of eye diagrams, according to industry accepted standards. A less direct approach—in which analog waveforms are digitized and the resulting data stream analyzed—is employed when measuring pixel jitter in frame grabber
Frame grabber
A frame grabber is an electronic device that captures individual, digital still frames from an analog video signal or a digital video stream. It is usually employed as a component of a computer vision system, in which video frames are captured in digital form and then displayed, stored or...
s. In all cases, the goal of jitter measurement is to verify that the jitter will not disrupt normal operation of the circuitry.
There are standards for jitter measurement in serial bus architectures. The standards cover jitter tolerance, jitter transfer function and jitter generation, with the required values for these attributes varying among different applications. Where applicable, compliant systems are required to conform to these standards.
Anti-jitter circuits
Anti-jitter circuits (AJCs) are a class of electronic circuitElectronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow...
s designed to reduce the level of jitter in a regular pulse signal. AJCs operate by re-timing the output pulses so they align more closely to an idealised pulse signal.
They are widely used in clock and data recovery circuits in digital communications, as well as for data sampling systems such as the analog-to-digital converter
Analog-to-digital converter
An analog-to-digital converter is a device that converts a continuous quantity to a discrete time digital representation. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement...
and digital-to-analog converter
Digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter is a device that converts a digital code to an analog signal . An analog-to-digital converter performs the reverse operation...
. Examples of anti-jitter circuits include phase-locked loop
Phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input "reference" signal. It is an electronic circuit consisting of a variable frequency oscillator and a phase detector...
and delay-locked loop
Delay-locked loop
In electronics, a delay-locked loop is a digital circuit similar to a phase-locked loop , with the main difference being the absence of an internal voltage-controlled oscillator...
. Inside digital to analog converters jitter causes unwanted high-frequency distortions. In this case it can be suppressed with high fidelity clock signal usage.
Jitter buffers
Jitter buffers or de-jitter buffers are used to counter jitter introduced by queuing in packet switched networkPacket switching
Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data – regardless of content, type, or structure – into suitably sized blocks, called packets. Packet switching features delivery of variable-bit-rate data streams over a shared network...
s so that a continuous playout of audio (or video) transmitted over the network can be ensured. The maximum jitter that can be countered by a de-jitter buffer is equal to the buffering delay introduced before starting the play-out of the mediastream. In the context of packet-switched networks, the term packet delay variation
Packet delay variation
In computer networking, packet delay variation is the difference in end-to-end delay between selected packets in a flow with any lost packets being ignored...
is often preferred over jitter.
Some systems use sophisticated delay-optimal de-jitter buffers that are capable of adapting the buffering delay to changing network jitter characteristics. These are known as adaptive de-jitter buffers and the adaptation logic is based on the jitter estimates computed from the arrival characteristics of the media packets. Adaptive de-jittering involves introducing discontinuities in the media play-out, which may appear offensive to the listener or viewer. Adaptive de-jittering is usually carried out for audio play-outs that feature a VAD
Voice activity detection
Voice activity detection , also known as speech activity detection or speech detection, is a technique used in speech processing in which the presence or absence of human speech is detected.. The main uses of VAD are in speech coding and speech recognition...
/DTX
Discontinuous Transmission
Discontinuous transmission is a means by which a mobile telephone is temporarily shut off or muted while the phone lacks a voice input.-Misconception:...
encoded audio, that allows the lengths of the silence periods to be adjusted, thus minimizing the perceptual impact of the adaptation.
Dejitterizer
A dejitterizer is a device that reduces jitter in a digital signalDigital signal
A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal...
. A dejitterizer usually consists of an elastic buffer
Variable length buffer
In telecommunication, a variable length buffer is a buffer into which data may be entered at one rate and removed at another rate without changing the data sequence....
in which the signal is temporarily stored and then retransmitted at a rate based on the average rate of the incoming signal. A dejitterizer is usually ineffective in dealing with low-frequency jitter, such as waiting-time jitter.
Filtering
A filter can be designed to minimize the effect of sampling jitter. For more information, see the paper by S. Ahmed and T. Chen entitled, Minimizing the effects of sampling jitters in wireless sensors networks.See also
- Phase noisePhase noisePhase noise is the frequency domain representation of rapid, short-term, random fluctuations in the phase of a waveform, caused by time domain instabilities...
- Buffer (telecommunication)
- DitherDitherDither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images...
- Deterministic jitterDeterministic jitterDeterministic jitter is a type of jitter with a known non-Gaussian probability distribution. The other major class of jitter is non-deterministic, or random jitter.-Characteristics:...
- DriftDrift (telecommunication)In telecommunication, a drift is a comparatively long-term change in an attribute, value, or operational parameter of a system or equipment. The drift should be characterized, such as "diurnal frequency drift" and "output level drift." Drift is usually undesirable and unidirectional, but may be...
- Pulse (signal processing)Pulse (signal processing)In signal processing, the term pulse has the following meanings:#A rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value....
Further reading
- Wolaver, Dan H. 1991. Phase-Locked Loop Circuit Design, Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-662743-9, pages 211-237
- Trischitta, Patrick R. and Varma, Eve L. 1989. Jitter in Digital Transmission Systems, Artech ISBN 089006248X
External links
- Jitter in VoIP - Causes, solutions and recommended values
- Jitter Buffer
- [ftp://ftp.iol.unh.edu/pub/mplsServices/other/QoS_Testing_Methodology.pdf Definition of Jitter in a QoS Testing Methodology]
- An Introduction to Jitter in Communications Systems
- Jitter Specifications Made Easy A Heuristic Discussion of Fibre Channel and Gigabit Ethernet Methods
- Jitter in Packet Voice Networks
- Clock and data recovery/Introduction/Definition of (phase) jitter
- Zamek, Iliya. SOC-System Jitter Resonance and Its Impact on Common Approach to the PDN Impedance. Presented at International Test Conference 2008.
- Li, Mike P. Jitter and Signal Integrity Verification for Synchronous and Asynchronous I/Os at Multiple to 10 GHz/Gbps. Presented at International Test Conference 2008.
- Li, Mike P. A New Jitter Classification Method Based on Statistical, Physical, and Spectroscopic Mechanisms. Presented at DesignCon 2009.
- Liu, Hui, Hong Shi, Xiaohong Jiang, and Zhe Li. Pre-Driver PDN SSN, OPD, Data Encoding, and Their Impact on SSJ. Presented at Electronics Components and Technology Conference 2009.
- Phabrix SxE - Hand-held Tool for eye and jitter measurement and analysis
- Miki, Ohtani, and Kowalski Jitter Requirements (Causes, solutions and recommended values for digital audio)
- Igor Levin Terms and concepts involved with digital clocking related to Jitter issues in professional quality digital audio

