
Deoxygenation
Encyclopedia
Deoxygenation is a chemical reaction
involving the removal of molecular oxygen (O2) from a reaction mixture or solvent, or the removal of oxygen
atoms from a molecule.
Classic representatives of deoxygenation are:
A chemical reagent for the deoxygenation of many sulfur and nitrogen oxo
compounds is the trifluoroacetic anhydride
/ sodium iodide
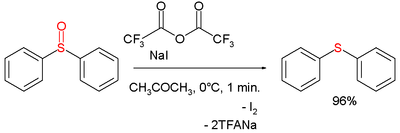
combination for example in the deoxygenation of the sulfoxide
diphenylsulfoxide to the sulfide
diphenylsulfide:
 The reaction mechanism
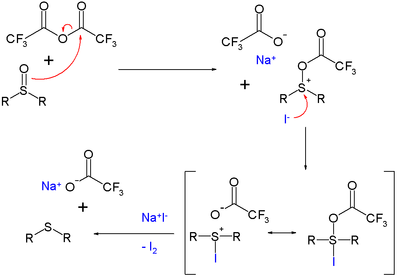
The reaction mechanism
is based on activation of the sulfoxide by a trifluoroacetyl group and oxidation of iodine. Iodine
is formed quantitatively in this reaction and therefore the reagent is used for the analytical detection of many oxo compounds.
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
involving the removal of molecular oxygen (O2) from a reaction mixture or solvent, or the removal of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
atoms from a molecule.
Classic representatives of deoxygenation are:
- the replacement of a hydroxylAlcoholIn chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
group by hydrogen (A-OH → A-H) in the Barton-McCombie deoxygenationBarton-McCombie deoxygenationThe Barton–McCombie deoxygenation is an organic reaction in which an hydroxy functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydride to give an alkyl group . It is named for the British chemists Sir Derek Harold Richard Barton and Stuart W. McCombie.This deoxygenation reaction is a...
or in the Markó-Lam deoxygenationMarkó-Lam deoxygenationThe Markó–Lam deoxygenation is an organic chemistry reaction where the hydroxy functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydrogen atom to give an alkyl group. The Markó-Lam reaction is a variant of the Bouveault–Blanc reduction and an alternative to the classical Barton–McCombie... - the replacement of an oxo group by two hydrogen atoms (A=O → A) in the Wolff-Kishner reductionWolff-Kishner reductionThe Wolff–Kishner reduction is a chemical reaction that fully reduces a ketone to an alkane.The method originally involved heating the hydrazine with sodium ethoxide in a sealed vessel at about 180 °C. Other bases have been found equally effective...
A chemical reagent for the deoxygenation of many sulfur and nitrogen oxo
Oxo
OXO was the first digital graphical computer game, a version of Tic-tac-toe.It is also the first puzzler game; As seen on Ginuess World Records 2010 Gamer's Edition.OXO Was first released in 1951, That makes it one of the oldest games standing....
compounds is the trifluoroacetic anhydride
Trifluoroacetic anhydride
Trifluoroacetic anhydride is the acid anhydride of trifluoroacetic acid. In particular, trifluoroacetic anhydride is the perfluorinated derivative of acetic anhydride. Like many acid anhydrides, it may be used to introduce the corresponding trifluoroacetyl group. The corresponding trifluoroacetyl...
/ sodium iodide
Sodium iodide
Sodium iodide is a white, crystalline salt with chemical formula NaI used in radiation detection, treatment of iodine deficiency, and as a reactant in the Finkelstein reaction.-Uses:Sodium iodide is commonly used to treat and prevent iodine deficiency....
combination for example in the deoxygenation of the sulfoxide
Sulfoxide
A sulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfinyl functional group attached to two carbon atoms. Sulfoxides can be considered as oxidized sulfides...
diphenylsulfoxide to the sulfide
Sulfide
A sulfide is an anion of sulfur in its lowest oxidation state of 2-. Sulfide is also a slightly archaic term for thioethers, a common type of organosulfur compound that are well known for their bad odors.- Properties :...
diphenylsulfide:

Reaction mechanism
In chemistry, a reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs.Although only the net chemical change is directly observable for most chemical reactions, experiments can often be designed that suggest the possible sequence of steps in...
is based on activation of the sulfoxide by a trifluoroacetyl group and oxidation of iodine. Iodine
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor....
is formed quantitatively in this reaction and therefore the reagent is used for the analytical detection of many oxo compounds.

See also
- Preparation of stable carbenes
- Hydrogen deoxygenation purifier

