
Defocus aberration
Encyclopedia

In optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, defocus is the aberration
Aberration in optical systems
Aberrations are departures of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. It occurs when light from one point of an object after transmission through the system does not converge...
in which an image is simply out of focus
Focus (optics)
In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by...
. This aberration is familiar to anyone who has used a camera, videocamera, microscope, telescope, or binoculars. Optically, defocus refers to a translation
Translation (physics)
In physics, translation is movement that changes the position of an object, as opposed to rotation. For example, according to Whittaker:...
along the optical axis
Optical axis
An optical axis is a line along which there is some degree of rotational symmetry in an optical system such as a camera lens or microscope.The optical axis is an imaginary line that defines the path along which light propagates through the system...
away from the plane or surface of best focus. In general, defocus reduces the sharpness and contrast
Contrast (vision)
Contrast is the difference in visual properties that makes an object distinguishable from other objects and the background. In visual perception of the real world, contrast is determined by the difference in the color and brightness of the object and other objects within the same field of view...
of the image
Image
An image is an artifact, for example a two-dimensional picture, that has a similar appearance to some subject—usually a physical object or a person.-Characteristics:...
. What should be sharp, high-contrast edges in a scene become gradual transitions. Fine detail in the scene is blurred or even becomes invisible. Nearly all image-forming optical devices incorporate some form of focus adjustment to minimize defocus and maximize image quality.
The degree of image blurring for a given amount of focus shift depends inversely on the lens f-number
F-number
In optics, the f-number of an optical system expresses the diameter of the entrance pupil in terms of the focal length of the lens; in simpler terms, the f-number is the focal length divided by the "effective" aperture diameter...
. Low f-numbers, such as to 2.8, are very sensitive to defocus and have very shallow depths of focus
Depth of focus
Depth of focus is a lens optics concept that measures the tolerance of placement of the image plane in relation to the lens...
. High f-numbers, in the 16 to 32 range, are highly tolerant of defocus, and consequently have large depths of focus. The limiting case in f-number is the pinhole camera
Pinhole camera
A pinhole camera is a simple camera without a lens and with a single small aperture – effectively a light-proof box with a small hole in one side. Light from a scene passes through this single point and projects an inverted image on the opposite side of the box...
, operating at perhaps 100 to 1000, in which case all objects are in focus almost regardless of their distance from the pinhole aperture
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,...
. The penalty for achieving this extreme depth of focus is very dim illumination at the imaging film
Photographic film
Photographic film is a sheet of plastic coated with an emulsion containing light-sensitive silver halide salts with variable crystal sizes that determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film...
or sensor
Image sensor
An image sensor is a device that converts an optical image into an electronic signal. It is used mostly in digital cameras and other imaging devices...
, limited resolution due to diffraction
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word "diffraction" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1665...
, and very long exposure time, which introduces the potential for image degradation due to motion blur
Motion blur
Motion blur is the apparent streaking of rapidly moving objects in a still image or a sequence of images such as a movie or animation. It results when the image being recorded changes during the recording of a single frame, either due to rapid movement or long exposure.- Photography :When a camera...
.
The amount of allowable defocus is related to the resolution
Optical resolution
Optical resolution describes the ability of an imaging system to resolve detail in the object that is being imaged.An imaging system may have many individual components including a lens and recording and display components...
of the imaging medium. A lower-resolution imaging chip or film is more tolerant of defocus and other aberrations. To take full advantage of a higher resolution medium, defocus and other aberrations must be minimized.
Defocus is modeled in Zernike polynomial format as
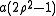 , where
, where  is the defocus coefficient in wavelength
is the defocus coefficient in wavelengthWavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
s of light. This corresponds to the parabola
Parabola
In mathematics, the parabola is a conic section, the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to a generating straight line of that surface...
-shaped optical path difference between two spherical wavefront
Wavefront
In physics, a wavefront is the locus of points having the same phase. Since infrared, optical, x-ray and gamma-ray frequencies are so high, the temporal component of electromagnetic waves is usually ignored at these wavelengths, and it is only the phase of the spatial oscillation that is described...
s that are tangent
Tangent
In geometry, the tangent line to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. More precisely, a straight line is said to be a tangent of a curve at a point on the curve if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope where f...
at their vertices and have different radii of curvature
Radius of curvature (optics)
Radius of curvature has specific meaning and sign convention in optical design. A spherical lens or mirror surface has a center of curvature located in either along or decentered from the system local optical axis. The vertex of the lens surface is located on the local optical axis...
.
For some applications, such as phase contrast electron microscopy, defocused images can contain useful information. Multiple images recorded with various values of defocus can be used to examine how the intensity of a the electron wave varies in three dimensional space, and from this information the phase of the wave can be inferred. This is the basis of non-interferometric phase retrieval
Phase retrieval
Phase retrieval concerns the solution to the phase problem. Given a complex signal F, of amplitude |F|, and phase \phi:phase retrieval consists in finding the phase that for a measured amplitude satisfies a set of constraints....
. Examples of phase retrieval algorithms that utilise defocused images include the Gerchberg-Saxton algorithm and various methods based on the transport of intensity equation.

