
Colors of noise
Encyclopedia
While noise
is by definition derived from a random
signal
, it can have different characteristic statistical properties corresponding to different mappings from a source of randomness to the concrete noise. Spectral density
(power
distribution in the frequency spectrum
) is such a property, which can be used to distinguish different types of noise. This classification by spectral density is given "color" terminology, with different types named after different colors, and is common in different disciplines where noise is an important factor (like acoustics
, electrical engineering
, and physics
). However, different fields may use the terminology with different degrees of specificity.
is flat (β = 0), while flicker
or pink noise
has β = 1, and brown noise has β = 2.
Telecommunications Glossary defines white, pink, blue, and black.
The color names for these different types of sounds are derived from a loose analogy between the spectrum of frequencies of sound wave present in the sound (as shown in the blue diagrams) and the equivalent spectrum of light wave frequencies. That is, if the sound wave pattern of "blue noise" were translated into light waves, the resulting light would be blue, and so on.
is a signal
(or process), named by analogy to white light
, with a flat frequency spectrum
. In other words, the signal has equal power
in any band of a given bandwidth (power spectral density). For example, with a white noise audio signal, the range of frequencies between 40 Hz
and 60 Hz contains the same amount of sound power as the range between 4000 Hz and 4020 Hz has.
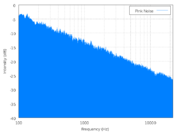 The frequency spectrum of pink noise
The frequency spectrum of pink noise
is linear in logarithmic space
; it has equal power in bands that are proportionally wide. This means that pink noise would have equal power in the frequency range from 40 to 60 Hz as in the band from 4000 to 6000 Hz. Since humans hear in such a proportional space, where a doubling of frequency (an octave) is perceived the same regardless of actual frequency (40–60 Hz is heard as the same interval and distance as 4000–6000 Hz), every octave contains the same amount of energy and thus pink noise is often used as a reference signal in audio engineering
. The power density
, compared with white noise, decreases by 3 dB
per octave
(density proportional to 1/f ). For this reason, pink noise is often called "1/f noise".
Since there are an infinite number of logarithmic bands at both the low frequency (DC) and high frequency ends of the spectrum, any finite energy spectrum must have less energy than pink noise at both ends. Pink noise is the only power-law spectral density that has this property: all steeper power-law spectra are finite if integrated to the high-frequency end, and all flatter power-law spectra are finite if integrated to the DC, low-frequency limit.
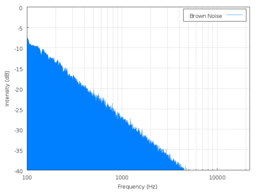 In fields that adopt precise definitions, the terminology "red noise", also called Brown noise or Brownian noise
In fields that adopt precise definitions, the terminology "red noise", also called Brown noise or Brownian noise
, will usually refer to a power density which decreases 6 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to 1/f 2) over a frequency range which does not include DC
(in a general sense, does not include a constant component, or value at zero frequency). In areas where terminology is used loosely, "red noise" may refer to any system where power density decreases with increasing frequency.
The first definition can be generated by an algorithm which simulates Brownian motion
or by integrating
white noise. "Brown" noise is not named for a power spectrum that suggests the color brown; rather, the name is a corruption of Brownian motion. "Red noise" describes the shape of the power spectrum, with pink being between red and white. Also known as "random walk" or "drunkard's walk" noise.
 Blue noise is also called azure noise. Blue noise's power density increases 3 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to f ) over a finite frequency range. In computer graphics, the term "blue noise" is sometimes used more loosely as any noise with minimal low frequency components and no concentrated spikes in energy. This can be good noise for dither
Blue noise is also called azure noise. Blue noise's power density increases 3 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to f ) over a finite frequency range. In computer graphics, the term "blue noise" is sometimes used more loosely as any noise with minimal low frequency components and no concentrated spikes in energy. This can be good noise for dither
ing. Retina
l cells are arranged in a blue-noise-like pattern which yields good visual resolution.
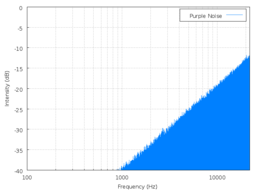 Violet noise is also called purple noise. Violet noise's power density increases 6 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to f 2) over a finite frequency range. It is also known as differentiated
Violet noise is also called purple noise. Violet noise's power density increases 6 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to f 2) over a finite frequency range. It is also known as differentiated
white noise, due to its being the result of the differentiation of a white noise signal.
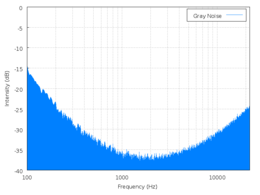 Grey noise
Grey noise
is random white noise subjected to a psychoacoustic equal loudness curve (such as an inverted A-weighting curve) over a given range of frequencies, giving the listener the perception that it is equally loud at all frequencies. This is in contrast to standard white noise which has equal strength over a linear scale of frequencies but is not perceived as being equally loud due to biases in the human equal-loudness contour
.
noise with a finite power spectrum with a finite number of small bands of zero energy dispersed throughout a continuous spectrum. These bands of zero energy are centered about the frequencies of music
al notes in whatever scale
is of interest. Since all in-tune musical notes are eliminated, the remaining spectrum could be said to consist of sour, citrus, or "orange" notes.
, the term noisy white has the following meanings:
, the term noisy black has the following meanings:
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
is by definition derived from a random
Randomness
Randomness has somewhat differing meanings as used in various fields. It also has common meanings which are connected to the notion of predictability of events....
signal
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
, it can have different characteristic statistical properties corresponding to different mappings from a source of randomness to the concrete noise. Spectral density
Spectral density
In statistical signal processing and physics, the spectral density, power spectral density , or energy spectral density , is a positive real function of a frequency variable associated with a stationary stochastic process, or a deterministic function of time, which has dimensions of power per hertz...
(power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
distribution in the frequency spectrum
Frequency spectrum
The frequency spectrum of a time-domain signal is a representation of that signal in the frequency domain. The frequency spectrum can be generated via a Fourier transform of the signal, and the resulting values are usually presented as amplitude and phase, both plotted versus frequency.Any signal...
) is such a property, which can be used to distinguish different types of noise. This classification by spectral density is given "color" terminology, with different types named after different colors, and is common in different disciplines where noise is an important factor (like acoustics
Acoustics
Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics...
, electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
, and physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
). However, different fields may use the terminology with different degrees of specificity.
Power-law noise
Many of these definitions assume a signal with components at all frequencies, with a power spectral density per unit of bandwidth proportional to 1/f β and hence they are examples of power-law noise. For instance, the spectral density of white noiseWhite noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
is flat (β = 0), while flicker
Flicker noise
Flicker noise is a type of electronic noise with a 1/ƒ, or pink power density spectrum. It is therefore often referred to as 1/ƒ noise or pink noise, though these terms have wider definitions...
or pink noise
Pink noise
Pink noise or 1/ƒ noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density is inversely proportional to the frequency. In pink noise, each octave carries an equal amount of noise power...
has β = 1, and brown noise has β = 2.
Technical definitions
Various noise models are employed in analysis, many of which fall under the above categories. AR noise or "autoregressive noise" is such a model, and generates simple examples of the above noise types, and more. The Federal Standard 1037CFederal Standard 1037C
Federal Standard 1037C, titled Telecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunication Terms is a United States Federal Standard, issued by the General Services Administration pursuant to the Federal Property and Administrative Services Act of 1949, as amended....
Telecommunications Glossary defines white, pink, blue, and black.
The color names for these different types of sounds are derived from a loose analogy between the spectrum of frequencies of sound wave present in the sound (as shown in the blue diagrams) and the equivalent spectrum of light wave frequencies. That is, if the sound wave pattern of "blue noise" were translated into light waves, the resulting light would be blue, and so on.
White noise
White noiseWhite noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
is a signal
Signal (electrical engineering)
In the fields of communications, signal processing, and in electrical engineering more generally, a signal is any time-varying or spatial-varying quantity....
(or process), named by analogy to white light
White Light
White Light may refer to:*Light with the color white*White Light , a 1980 novel by Rudy Rucke*White Light , 1971 album*White Light , 2010 album...
, with a flat frequency spectrum
Frequency spectrum
The frequency spectrum of a time-domain signal is a representation of that signal in the frequency domain. The frequency spectrum can be generated via a Fourier transform of the signal, and the resulting values are usually presented as amplitude and phase, both plotted versus frequency.Any signal...
. In other words, the signal has equal power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
in any band of a given bandwidth (power spectral density). For example, with a white noise audio signal, the range of frequencies between 40 Hz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
and 60 Hz contains the same amount of sound power as the range between 4000 Hz and 4020 Hz has.
Pink noise

Pink noise
Pink noise or 1/ƒ noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density is inversely proportional to the frequency. In pink noise, each octave carries an equal amount of noise power...
is linear in logarithmic space
Logarithmic scale
A logarithmic scale is a scale of measurement using the logarithm of a physical quantity instead of the quantity itself.A simple example is a chart whose vertical axis increments are labeled 1, 10, 100, 1000, instead of 1, 2, 3, 4...
; it has equal power in bands that are proportionally wide. This means that pink noise would have equal power in the frequency range from 40 to 60 Hz as in the band from 4000 to 6000 Hz. Since humans hear in such a proportional space, where a doubling of frequency (an octave) is perceived the same regardless of actual frequency (40–60 Hz is heard as the same interval and distance as 4000–6000 Hz), every octave contains the same amount of energy and thus pink noise is often used as a reference signal in audio engineering
Audio engineering
An audio engineer, also called audio technician, audio technologist or sound technician, is a specialist in a skilled trade that deals with the use of machinery and equipment for the recording, mixing and reproduction of sounds. The field draws on many artistic and vocational areas, including...
. The power density
Power density
Power density is the amount of power per unit volume....
, compared with white noise, decreases by 3 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
per octave
Octave
In music, an octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems"...
(density proportional to 1/f ). For this reason, pink noise is often called "1/f noise".
Since there are an infinite number of logarithmic bands at both the low frequency (DC) and high frequency ends of the spectrum, any finite energy spectrum must have less energy than pink noise at both ends. Pink noise is the only power-law spectral density that has this property: all steeper power-law spectra are finite if integrated to the high-frequency end, and all flatter power-law spectra are finite if integrated to the DC, low-frequency limit.
Brown(ian) noise

Brownian noise
In science, Brownian noise , also known as Brown noise or red noise, is the kind of signal noise produced by Brownian motion, hence its alternative name of random walk noise...
, will usually refer to a power density which decreases 6 dB per octave with increasing frequency (density proportional to 1/f 2) over a frequency range which does not include DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
(in a general sense, does not include a constant component, or value at zero frequency). In areas where terminology is used loosely, "red noise" may refer to any system where power density decreases with increasing frequency.
The first definition can be generated by an algorithm which simulates Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
or by integrating
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
white noise. "Brown" noise is not named for a power spectrum that suggests the color brown; rather, the name is a corruption of Brownian motion. "Red noise" describes the shape of the power spectrum, with pink being between red and white. Also known as "random walk" or "drunkard's walk" noise.
Blue noise

Dither
Dither is an intentionally applied form of noise used to randomize quantization error, preventing large-scale patterns such as color banding in images...
ing. Retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
l cells are arranged in a blue-noise-like pattern which yields good visual resolution.
Violet noise

Derivative
In calculus, a branch of mathematics, the derivative is a measure of how a function changes as its input changes. Loosely speaking, a derivative can be thought of as how much one quantity is changing in response to changes in some other quantity; for example, the derivative of the position of a...
white noise, due to its being the result of the differentiation of a white noise signal.
Grey noise

Grey noise
Grey noise is random noise subjected to a psychoacoustic equal loudness curve over a given range of frequencies, giving the listener the perception that it is equally loud at all frequencies....
is random white noise subjected to a psychoacoustic equal loudness curve (such as an inverted A-weighting curve) over a given range of frequencies, giving the listener the perception that it is equally loud at all frequencies. This is in contrast to standard white noise which has equal strength over a linear scale of frequencies but is not perceived as being equally loud due to biases in the human equal-loudness contour
Equal-loudness contour
An equal-loudness contour is a measure of sound pressure , over the frequency spectrum, for which a listener perceives a constant loudness when presented with pure steady tones. The unit of measurement for loudness levels is the phon, and is arrived at by reference to equal-loudness contours...
.
Red noise
- A synonym for Brownian noiseBrownian noiseIn science, Brownian noise , also known as Brown noise or red noise, is the kind of signal noise produced by Brownian motion, hence its alternative name of random walk noise...
, as above - A synonym for pink noisePink noisePink noise or 1/ƒ noise is a signal or process with a frequency spectrum such that the power spectral density is inversely proportional to the frequency. In pink noise, each octave carries an equal amount of noise power...
, as above
Orange noise
Orange noise is quasi-stationaryStationary process
In the mathematical sciences, a stationary process is a stochastic process whose joint probability distribution does not change when shifted in time or space...
noise with a finite power spectrum with a finite number of small bands of zero energy dispersed throughout a continuous spectrum. These bands of zero energy are centered about the frequencies of music
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
al notes in whatever scale
Musical scale
In music, a scale is a sequence of musical notes in ascending and descending order. Most commonly, especially in the context of the common practice period, the notes of a scale will belong to a single key, thus providing material for or being used to conveniently represent part or all of a musical...
is of interest. Since all in-tune musical notes are eliminated, the remaining spectrum could be said to consist of sour, citrus, or "orange" notes.
Green noise
- "Green noise is supposedly the background noise of the world. A really long term power spectrum averaged over several outdoor sites. Rather like pink noise with a hump added around 500 HzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
." - The mid-frequency component of white noise, used in halftoneHalftoneHalftone is the reprographic technique that simulates continuous tone imagery through the use of dots, varying either in size, in shape or in spacing...
dithering - Bounded Brownian noise
Black noise
Black noise is also called silent noise.- SilenceSilenceSilence is the relative or total lack of audible sound. By analogy, the word silence may also refer to any absence of communication, even in media other than speech....
- Noise with a 1/fβ spectrum, where β > 2 (Manfred Schroeder, "Fractals, chaosChaos theoryChaos theory is a field of study in mathematics, with applications in several disciplines including physics, economics, biology, and philosophy. Chaos theory studies the behavior of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions, an effect which is popularly referred to as the...
, power laws"). Used in modeling various environmental processes. - Noise that has a frequency spectrum of predominantly zero power level over all frequencies except for a few narrow bands or spikes. Note: An example of black noise in a facsimile transmission system is the spectrum that might be obtained when scanning a black area in which there are a few random white spots. Thus, in the time domain, a few random pulses occur while scanning.
- "The output of an active noise controlActive noise controlActive noise control is a method for reducing unwanted sound.- Explanation :...
system which cancels an existing noise, leaving the local environment noise free. The comic bookComic bookA comic book or comicbook is a magazine made up of comics, narrative artwork in the form of separate panels that represent individual scenes, often accompanied by dialog as well as including...
character Iron ManIron ManIron Man is a fictional character, a superhero in the . The character was created by writer-editor Stan Lee, developed by scripter Larry Lieber, and designed by artists Don Heck and Jack Kirby, first appearing in Tales of Suspense #39 .A billionaire playboy, industrialist and ingenious engineer,...
used to have a "black light beam" that could darken a room in this manner, and popular science fictionScience fictionScience fiction is a genre of fiction dealing with imaginary but more or less plausible content such as future settings, futuristic science and technology, space travel, aliens, and paranormal abilities...
has a tendency to portray active noise control in this light." The Batman BeyondBatman BeyondBatman Beyond is an American animated television series created by Warner Bros. Animation in collaboration with DC Comics as a continuation of the Batman legacy...
supervillian Shriek also had a weapon like this, which effectively blocked out all noise. - "As seen in the sales literature for an ultrasonic vermin repeller, black noise with a power density that is constant for a finite frequency range above 20 kHz. More accurately, ultrasonicUltrasoundUltrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
white noise. This black noise is like the so-called black lightBlack lightA black light, also referred to as a UV light, ultraviolet light, or Wood's lamp, is a lamp that emits ultraviolet radiation in the long-wave range, and little visible light...
with frequencies too high to be sensed, but still capable of affecting the environment." - Noise with a spectrum corresponding to the blackbody radiation (thermal noise).
Noisy white
In telecommunicationTelecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
, the term noisy white has the following meanings:
- In facsimileFaxFax , sometimes called telecopying, is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material , normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device...
or display systems, such as televisionTelevisionTelevision is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
, a nonuniformity in the white area of the image, i.e., document or picture, caused by the presence of noiseNoiseIn common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
in the received signal. - A signal or signal level that is supposed to represent a white area on the object, but has a noise content sufficient to cause the creation of noticeable black spots on the display surface or record mediumRecord mediumIn telecommunication, the term record medium has the following meanings:# The physical medium on which information is stored in recoverable form. For example, magnetic tape or disk....
.
Noisy black
In telecommunicationTelecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
, the term noisy black has the following meanings:
- In facsimileFaxFax , sometimes called telecopying, is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material , normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other output device...
or display systems, such as televisionTelevisionTelevision is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
, a nonuniformity in the black area of the image, i.e., document or picture, caused by the presence of noiseNoiseIn common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
in the received signal. - A signal or signal level that is supposed to represent a black area on the object, but has a noise content sufficient to cause the creation of noticeable white spots on the display surface or record mediumRecord mediumIn telecommunication, the term record medium has the following meanings:# The physical medium on which information is stored in recoverable form. For example, magnetic tape or disk....
.

