
Climate of the Philippines
Encyclopedia
Tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, also known as an equatorial climate, is a tropical climate usually found along the equator...
, tropical savanna
Tropical savanna climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a type of climate that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories "Aw" and '"As."...
or tropical monsoon
Tropical monsoon climate
Tropical monsoon climate, occasionally also known as a tropical wet climate or tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate in climate classification, is a relatively rare type of climate that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category "Am."Tropical monsoon climates have monthly...
, or humid subtropical
Humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a climate zone characterized by hot, humid summers and mild to cool winters...
(in higher-altitude areas) characterized by relatively high temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, oppressive humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
and plenty of rainfall. There are two seasons in the country, the wet season and the dry season, based upon the amount of rainfall. This is dependent as well on your location in the country as some areas experience rain all throughout the year (see Climate Types). Based on temperature, the seven warmest months of the year are from April to October; the winter monsoon
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
brings cooler air from November to March. May is the warmest month, and January, the coolest.
Weather in the Philippines is monitored and managed by the government agency known locally by its acronym, PAGASA or the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration is a Philippine national institution dedicated to provide flood and typhoon warnings, public weather forecasts and advisories, meteorological, astronomical, climatological, and other specialized information and...
.
Temperature
The average year-round temperature measured from all the weather stations in the Philippines, excepting Baguio CityBaguio City
The City of Baguio is a highly urbanized city in northern Luzon in the Philippines. Baguio City was established by Americans in 1900 at the site of an Ibaloi village known as Kafagway...
, is 26.6 °C (79.9 °F). Cooler days are usually felt in the month of January with temperature averaging at 25.5 °C (77.9 °F) and the warmest days, in the month of May with a mean of 28.3 °C (82.9 °F).
Elevation factors significantly in the variation of temperature in the Philippines. In Baguio City, with an elevation of 1,500 m (5,000 ft) above sea level, the mean average is 18.3 °C (64.9 °F) or cooler by about 4.3 °C (15 °F). In 1915, a one-year study was conducted by William H. Brown
William H. Brown
William H. Brown was a United States Navy sailor during the American Civil War and a recipient of America's highest military decoration—the Medal of Honor.-Biography:...
of the Philippine Journal of Science on top of Mount Banahaw
Mount Banahaw
Mount Banahaw is an active volcano on Luzon Island in the Republic of the Philippines. The three-peaked volcano complex is located between the provinces of Laguna and Quezon and is the tallest mountain in the CALABARZON region dominating the landscape for miles around.The mountain is considered by...
at 2,100 m. (6,900 ft) elevation. The mean temperature measured was 18.6 °C (65.5 °F), a difference of 10 °C (21.6 °F) from the lowland mean temperature.
In Manila and most of the lowland areas, temperatures rarely rise above 37 °C (98.6 °F). The highest temperature recorded in the country was 42.2 °C (108 °F) in Tuguegarao
Tuguegarao City
Tuguegarao City is the city capital of Cagayan, Philippines and the regional capital of Region 02 . Tuguegarao is the economic center of the Cagayan Valley Region; it is located on a peninsula in the Cagayan Valley. It is sheltered by the Sierra Madre Mountains in the East; Cordilleras in the...
Cagayan Valley
Cagayan Valley
Cagayan Valley is a region of the Philippines, also designated as Region II or Region 02. It is composed of five provinces, namely: Batanes, Cagayan, Isabela, Nueva Vizcaya, and Quirino...
on April 29,1912 and again on May 11, 1969. The absolute minimum temperature of 3 °C (37.4 °F) was recorded in January of 1903 in Baguio.
Rainfall
The summer monsoonMonsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
brings heavy rains to most of the archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
from May to October. Annual average rainfall ranges from as much as 5000 millimetres (196.9 in) in the mountainous east coast section of the country, to less than 1000 millimetres (39.4 in) in some of the sheltered valleys. Monsoon rains, although hard and drenching, are not normally associated with high winds and waves.
At least 30 percent of the annual rainfall in the northern Philippines can be traced to tropical cyclones, while the southern islands receiving less than 10 percent of their annual rainfall from tropical cyclones. The wettest known tropical cyclone to impact the archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
was the July 1911 cyclone
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
, which dropped over 1168 millimetres (46 in) of rainfall within a 24-hour period in Baguio City.
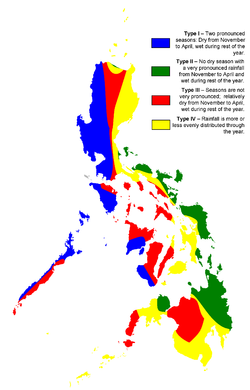
Climate types
There are four recognized climate types in the Philippines, and they are based on the distribution of rainfall (See the Philippine Climate Map). They are described as follows:- Type I. Two pronounced season: dry from November to April and wet during the rest of the year.
- Type II. No dry season with a pronounced rainfall from November to January.
- Type III. Seasons are not very pronounced, relatively dry from November to April, and wet during the rest of the year.
- Type IV. Rainfall is more or less evenly distributed throughout the year.
Type I: Metro Manila
Type II: Borongan
}}
Type III: Cebu City
Type IV: General Santos
Special: Baguio
Humidity
Relative humidityHumidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
is high in the Philippines. A high amount of moisture or vapor in the air makes hot temperatures feel hotter. This quantity of moisture is due to different factors - the extraordinary evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
from the seas that surrounds the country on all sides, to the different prevailing winds
Prevailing winds
Prevailing winds are winds that blow predominantly from a single general direction over a particular point on Earth's surface. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface. A region's prevailing and dominant winds...
in the different seasons of the year, and finally, to the abundant rains so common in a tropical country. The first may be considered as general causes of the great humidity, which is generally observed in all our islands throughout the year. The last two may influence the different degree of humidity for the different months of the year and for the different regions of the Archipelago.
In the cooler months, even though the rains are more abundant in the eastern part of the Philippines, owing to the prevailing northeasterly winds, the humidity is lesser than in the western part where a dry season prevails. From June to October, although the rains are quite general throughout the Archipelago, the rains are more abundant in the western part of the Philippines, which is more exposed to the prevailing westerly and southwesterly winds; hence the humidity of the air is greater there than in the eastern part of the Archipelago.
The most uncomfortable months are from March to May where temperature and humidity attain their maximum levels.
Typhoons

July
July is the seventh month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian Calendars and one of seven months with the length of 31 days. It is, on average, the warmest month in most of the Northern hemisphere and the coldest month in much of the Southern hemisphere...
through October
October
October is the tenth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian Calendars and one of seven months with a length of 31 days. The eighth month in the old Roman calendar, October retained its name after January and February were inserted into the calendar that had originally been created by the...
. These are especially hazardous for northern and eastern Luzon and the Bicol
Bicol Region
The Bicol Region or Bicolandia is one of the 17 regions of the Philippines. Its regional center is Legazpi City...
and Eastern Visayas
Eastern Visayas
Eastern Visayas is one of the two regions of the Philippines having no land border with another region, MIMAROPA being the other, and is designated as Region VIII...
regions, but Manila gets devastated periodically as well.
Bagyo is the local term to any tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
in the Philippine Islands. From the statistics gathered by PAGASA from 1948 to 2004, around an average of 20 storms and/or typhoons per year enter the PAR (Philippine Area of Responsibility) - the designated area assigned to PAGASA to monitor during weather disturbances. Those that made landfall or crossed the Philippines, the average was nine per year. In 1993, a record 19 typhoons made landfall in the country making it the most in one year. The least amount per year were 4 during the years 1955, 1958, 1992 and 1997.
Typhoons are categorized into four types according to its wind speed by the PAGASA
Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration is a Philippine national institution dedicated to provide flood and typhoon warnings, public weather forecasts and advisories, meteorological, astronomical, climatological, and other specialized information and...
. All tropical cyclones, regardless of strength, are named by PAGASA.
- Tropical Depressions have maximum sustained windMaximum sustained windThe maximum sustained winds associated with a tropical cyclone are a common indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, they are found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unlike gusts, the value of these winds are...
s of between 55 kilometres per hour (28.1 kn) and 64 kilometres per hour (32.7 kn) near its center. - Tropical Storms have maximum sustained winds of 65 kilometres per hour (33.2 kn) and 119 kilometres per hour (60.7 kn).
- Typhoons achieve maximum sustained winds of 120 kilometres per hour (61.2 kn) to 185 kilometres per hour (94.4 kn),
- Super typhoons having maximum winds exceeding 185 kilometres per hour (94.4 kn).
Deadliest storm
The deadliest typhoon to impact the Philippines was Typhoon Uring (Thelma)Tropical Storm Thelma
Tropical Storm Thelma was the deadliest tropical storm of the 1991 Pacific typhoon season, killing between 5,101 to 8,100 people as it crossed the Philippines.-Meteorological history:A tropical disturbance developed over the eastern Caroline Islands in late October...
in November, 1991, in which 5,080 lives were lost from its resultant flooding and over 1,200 went missing.
Strongest Typhoons
The highest wind velocity recorded for a typhoonTyphoons in the Philippines
Typhoons in the Philippines refer in general to tropical cyclones that enter the Philippine area of responsibility and affect the Philippines. Locally they are called bagyo...
that crossed the Philippines was recorded in Virac
Virac, Catanduanes
Virac is a 1st class municipality in the province of Catanduanes, Philippines. It is the capital municipality of the province and the third largest town with a land area of 188 km2...
on November 30, 2006 when Typhoon Reming (Durian)
Typhoon Durian
Typhoon Durian was an intense storm that wreaked havoc in the Philippines, causing massive loss of life when mudslides from the Mayon Volcano buried many villages...
had a peak gust of 320 km/h (198 mph).
Seasons
PAGASA divides the climate of the country into two seasonSeason
A season is a division of the year, marked by changes in weather, ecology, and hours of daylight.Seasons result from the yearly revolution of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's axis relative to the plane of revolution...
s, using rainfall and temperature as basis:
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall | ||||||||||||
| Temperature | ||||||||||||
- Blue: Rainy
- Yellow: Dry
- Cool: Green
- Hot: Red
Furthermore, the months where the dry and hot seasons are experienced are popularly known as the "summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
" season.
See also
- Climate
- List of wettest tropical cyclones in the Philippines
- Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services AdministrationPhilippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services AdministrationThe Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration is a Philippine national institution dedicated to provide flood and typhoon warnings, public weather forecasts and advisories, meteorological, astronomical, climatological, and other specialized information and...

